Blood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of Bubbles
Diunggah oleh
MabesDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of Bubbles
Diunggah oleh
MabesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Transfusion
Purpose
to restore or replace blood volume
to increase oxygen carrying capacity of
blood
to combat infections if decreased WBCs
to prevent bleeding if platelets decreased
Nursing Management
1. Verify Doctors order
2. Check if client gave consent
3. Obtain
blood from blood bank if IV access is
available
maintained with normal saline
return to blood bank when infusions n/a
blood may not be returned to bank in 20
mins
do not keep blood inside nursing
refrigerator
4. Properly refrigerated
Platelets 5 days
RBCs 5 7 days, 250cc
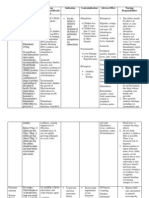
5. Proper blood typing and cross-matching
ABO
Blood
Group
Compatible Incompatible
A A, O B, AB
B B, O A, AB
AB A, B, AB, O none
O O only A, B, AB
O universal donor
AB universal recipient
85% of population is Rh+
6. Aseptically assemble all materials needed
BT set with filter to prevent
administration of blood clots and other
particulates
PNSS to prevent hemolysis
gauge 18 19 large bore needle to
prevent hemolysis and allows easy flow
of blood
7. Practice Strict Asepsis
8. Instruct another RN to re-validate the ff
Name of client (verify ID band)
Blood components
Blood typing and cross matching
Rh factor
Serial number
expiration date
Screening test
VDRL for STDs
HBsAg for HepB
Malarial Smear for malaria
9. Check blood for presence of bubbles,
cloudiness, sediments, and dark color may
indicate contamination
10. Never warm blood products! ROOM TEMP
ONLY!
warming only done if you have
dewarming device
warming only done during emergency
situations if massive blood loss
massive transfusion
11. Transfusion should be completed in 4 hours
because blood exposed at room temp more
than 2 hours causes blood deterioration
12. Start infusion slowly. Regulate at KVO (10-
15gtts/min) at 100cc/hr to prevent
circulatory overload. Remain at the bedside
for 15 30 minutes. Adverse reactions
usually occur during the first 15 20 minutes.
13. Monitor V/S before, during, and after
transfusion. Altered V/S indicates adverse
reaction
14. Avoid mixing or administering drug at BT line
to prevent hemolysis
15. Administer PNSS before, during, or after BT.
Never administer IV fluids with dextrose =
hemolysis
16. Observe for potential complications and
Notify Physician
Protocol for Suspected reaction
Stop infusion immediately
Start IV line! Keep IV line open with PNSS
(0.9% Normal Saline).
IV access must be needed for administration of
emergency drugs
Notify Physician
Monitor V/S every 5 minutes
Obtain urine specimen and have it tested for
Hgb to indicate RBC hemolysis.
Save blood transfusion set and labels.
Send unused blood and BT set to the blood
bank
Administer antihistamine, diuretics,
bronchodilators as ordered.
Make relevant documentation
Complications of BT
Complications Manifestations
Pyrogenic
most common
Flushing
Fever
Muscle pain
Chills
Anaphylactic Urticaria
Rash, Hives
Pruritus
Wheezes
Shock
Hemolytic
infusion of
incompatible blood
products
Low back pain 1
st
sign,
response of kidney
Fever
Chills
Flushing
Pain
Circulatory Overload Rales or Crackles
Moist Cough
Dyspnea
Distended Neck vein
Hyperthermia
Elevated BP
Sepsis components
contaminated by
bacteria
Chills
High Fever
Vomiting
Hypertension
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- University of San Carlos College of NursingDokumen1 halamanUniversity of San Carlos College of NursingfabaquitaBelum ada peringkat
- Nurse in The National and Global Health Care Delivery SystemDokumen9 halamanNurse in The National and Global Health Care Delivery Systemczeremar chanBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Transfusion LectureDokumen8 halamanBlood Transfusion LectureCamille Cirineo Arensol100% (2)
- PSYCHE Mental Health Concepts N2018 Ans KeyDokumen5 halamanPSYCHE Mental Health Concepts N2018 Ans KeyJo Hn Vengz100% (1)
- Learning Feedback DiaryDokumen10 halamanLearning Feedback DiaryLoids IgnacioBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Informatics Timeline (CENIZA BSN 3E)Dokumen1 halamanNursing Informatics Timeline (CENIZA BSN 3E)FATIMA IVAN S. CENIZABelum ada peringkat
- Plan of ActivitiesDokumen3 halamanPlan of ActivitiesLiiza G-GsprBelum ada peringkat
- AILYNDokumen98 halamanAILYNArvin EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- General Objective: College of NursingDokumen3 halamanGeneral Objective: College of NursingRaan Lade KilemBelum ada peringkat
- CHNDokumen11 halamanCHNAngelina Janiya NicoleBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDokumen7 halamanVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreBelum ada peringkat
- Internship ReflectionDokumen1 halamanInternship Reflectionapi-373242779Belum ada peringkat
- KardexDokumen2 halamanKardexKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Process RecordingDokumen5 halamanNursing Process RecordingErl Joy Montaño CañeteBelum ada peringkat
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDokumen52 halamanHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- Tpo Eo Poa LFDDokumen4 halamanTpo Eo Poa LFDEzra Miguel DarundayBelum ada peringkat
- PRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDDokumen8 halamanPRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDAloha ItsmeBelum ada peringkat
- Chn-Herbal MedicineDokumen5 halamanChn-Herbal MedicineBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciBelum ada peringkat
- ROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedDokumen53 halamanROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study Final PortraitDokumen11 halamanCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaBelum ada peringkat
- Charting TahbsoDokumen1 halamanCharting TahbsoVanessa VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Sop and Competencies For NG InsertionDokumen4 halamanSop and Competencies For NG InsertionReza ShinodaBelum ada peringkat
- Doctors Order LoveDokumen4 halamanDoctors Order LoveAubrey Unique EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study Case PresentationDokumen5 halamanDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ManagementDokumen19 halamanNursing ManagementAjie ZamBelum ada peringkat
- The Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingDokumen1 halamanThe Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingMelissa Briggs100% (1)
- Discharge Plan Post SeizureDokumen2 halamanDischarge Plan Post SeizureVecky TolentinoBelum ada peringkat
- AldazideDokumen2 halamanAldazideianecunarBelum ada peringkat
- Rinciples and Practice of The HospiceDokumen1 halamanRinciples and Practice of The HospiceCake ManBelum ada peringkat
- Example of Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study OrthoDokumen4 halamanDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Nursing Associations in The PhilippinesDokumen18 halamanNursing Associations in The PhilippinesGumama AmeiyrhaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationDokumen3 halamanNursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationJahseh WolfeBelum ada peringkat
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDokumen16 halamanAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzBelum ada peringkat
- SchedDokumen1 halamanSchedEdrick ValentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Care of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceDokumen7 halamanCare of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceIvy VillalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Plan of ActivitiesDokumen3 halamanPlan of ActivitiesLiiza G-GsprBelum ada peringkat
- List of Professional Organization and Associations of Nurses in The PhilippinesDokumen1 halamanList of Professional Organization and Associations of Nurses in The PhilippinesTrixie Adaley Xen Heirencia50% (2)
- Week 2 NCM 107Dokumen21 halamanWeek 2 NCM 107raise concern100% (1)
- Discharge PlanDokumen4 halamanDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDokumen2 halamanNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Dokumen2 halamanDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoBelum ada peringkat
- Kardex: Mental Status: Activities: Diet: Tubes: Special InfoDokumen3 halamanKardex: Mental Status: Activities: Diet: Tubes: Special InfoJanelle Cabida SupnadBelum ada peringkat
- Cellulitis Discharge PlanDokumen1 halamanCellulitis Discharge PlanJuvy Rose Tinga YeeBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Nurse Performance in Medical WardDokumen6 halamanFactors Affecting Nurse Performance in Medical Wardifa pannyaBelum ada peringkat
- MNAP Military Nursing in The Philippines May Be Said To Have Existed As Early As 1896 When The Legendary Tandang Sora Took Care of The Sick and WoundedDokumen4 halamanMNAP Military Nursing in The Philippines May Be Said To Have Existed As Early As 1896 When The Legendary Tandang Sora Took Care of The Sick and WoundedarjeighBelum ada peringkat
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDokumen3 halamanHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaBelum ada peringkat
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentDokumen1 halamanSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentVanetBelum ada peringkat
- HTP FinalDokumen3 halamanHTP Finalאורזלין לנזוןBelum ada peringkat
- Case Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CDokumen4 halamanCase Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonBelum ada peringkat
- Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen1 halamanAsessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChelsea Mae Bagalay GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokumen2 halamanGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan ADokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattBelum ada peringkat
- PNSSDokumen2 halamanPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 22Dokumen8 halamanDisaster Nursing SAS Session 22ZiaBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Nursing Informatics in Philippine Healthcare Delivery SystemDokumen18 halamanImportance of Nursing Informatics in Philippine Healthcare Delivery SystemRain MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDokumen1 halamanDischarge Plan For AppendectomyMyra AtuleBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NDokumen9 halamanNCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NJay VillasotoBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Requirement OB WardDokumen12 halamanWeekly Requirement OB WardXerxes DejitoBelum ada peringkat
- DuphalacDokumen2 halamanDuphalacianecunarBelum ada peringkat
- Asepsis and InfectionDokumen6 halamanAsepsis and InfectionMabes100% (1)
- Commonly Asked Emergency DrugsDokumen17 halamanCommonly Asked Emergency DrugsrianneBelum ada peringkat
- Prof Ad BON and NursesDokumen7 halamanProf Ad BON and NursesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- PositioningDokumen3 halamanPositioningMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Therapeutic Diet NutritionistDokumen3 halamanTherapeutic Diet NutritionistMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Bowel Diversion: Parameter Colostomy IleostomyDokumen1 halamanBowel Diversion: Parameter Colostomy IleostomyMabesBelum ada peringkat
- CHN GapuzDokumen23 halamanCHN GapuzMabes100% (1)
- Mabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDokumen15 halamanMabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Triage PrinciplesDokumen2 halamanTriage PrinciplesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Decubitus Ulcer / Pressure SoresDokumen1 halamanDecubitus Ulcer / Pressure SoresMabesBelum ada peringkat
- All Nursing TheoriesDokumen26 halamanAll Nursing TheoriesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Enema Administration: Size of Rectal TubeDokumen3 halamanEnema Administration: Size of Rectal TubeMabesBelum ada peringkat
- PainDokumen3 halamanPainMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Parenteral Therapy:: Intravenous Therapy (IVT) or VenipunctureDokumen3 halamanParenteral Therapy:: Intravenous Therapy (IVT) or VenipunctureMabes100% (1)
- Basic or InstrumentsDokumen21 halamanBasic or InstrumentsMabes100% (1)
- Suture and NeedlesDokumen5 halamanSuture and NeedlesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Taste and SmellDokumen1 halamanTaste and SmellMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Dokumen249 halamanRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesBelum ada peringkat
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDokumen5 halamanFat Soluble VitaminsMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen11 halamanNervous SystemMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Nursing TheoriesDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To Nursing TheoriesMabes100% (2)
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookDokumen17 halamanNutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookMabes100% (2)
- Factors That Affect Eating and NurtritureDokumen3 halamanFactors That Affect Eating and NurtritureMabesBelum ada peringkat
- The Concepts of Man and His Basic NeedsDokumen5 halamanThe Concepts of Man and His Basic NeedsMabes94% (16)
- Water Soluble VitaminsDokumen6 halamanWater Soluble VitaminsMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Nutritional Recommendation For Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen5 halamanNutritional Recommendation For Cardiovascular DiseaseMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Therapeutic DietsDokumen3 halamanBasic Therapeutic DietsMabes100% (1)
- All Nursing TheoriesDokumen26 halamanAll Nursing TheoriesMabesBelum ada peringkat
- Tammy, 2011. Drug Interaction PDFDokumen14 halamanTammy, 2011. Drug Interaction PDFdyahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan On Electroconvulsive TherapyDokumen13 halamanLesson Plan On Electroconvulsive Therapysimranjeet kaurBelum ada peringkat
- Dialysis Products Catalog PDFDokumen52 halamanDialysis Products Catalog PDFAFRIANSYAHBelum ada peringkat
- CholesteatomaDokumen44 halamanCholesteatomavna297Belum ada peringkat
- Balut Bidai: (Luthfi Fauzy Asriyanto)Dokumen63 halamanBalut Bidai: (Luthfi Fauzy Asriyanto)DiahNiatiBelum ada peringkat
- Cavite City Accomplishement Garantisadong Pambata DateDokumen60 halamanCavite City Accomplishement Garantisadong Pambata DateMike Ace MonzonBelum ada peringkat
- GP Factsheet - Steroids and The EyeDokumen6 halamanGP Factsheet - Steroids and The EyeBima RizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Rajnish Wattas ArticleDokumen8 halamanProf. Rajnish Wattas ArticleSurya EduBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer Cachexia FromDokumen5 halamanCancer Cachexia FromLanna HarumiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Design Manual - Municipal Wastewater DisinfectionDokumen264 halamanDesign Manual - Municipal Wastewater DisinfectionPillaca Ugarte Ulises RansesBelum ada peringkat
- TrandolaprilDokumen28 halamanTrandolaprilYeyenJaejoongBelum ada peringkat
- Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate InjectionDokumen10 halamanDexamethasone Sodium Phosphate InjectionRobiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- MEDIWAYSDokumen79 halamanMEDIWAYSRaj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Emergency Medicine Pharmacist ServicesDokumen15 halamanGuidelines Emergency Medicine Pharmacist ServicesMárcio BatistaBelum ada peringkat
- Med-Fit 3: Instruction Manual Betriebsanleitung Manuel D'instructionDokumen52 halamanMed-Fit 3: Instruction Manual Betriebsanleitung Manuel D'instructionCarlos ParraBelum ada peringkat
- 17-10 eJDD FinalDokumen116 halaman17-10 eJDD FinalMohamed GamalBelum ada peringkat
- NBME 13 Review 2Dokumen29 halamanNBME 13 Review 2MedStudent76Belum ada peringkat
- By Sweta Kumari Summer Project-II Submitted ToDokumen22 halamanBy Sweta Kumari Summer Project-II Submitted ToSudarshanKumar0% (1)
- Wound Care DescriptionDokumen4 halamanWound Care DescriptionRodriguez, Joyce Ann G.Belum ada peringkat
- Oral Preparations: Erdosteine ZertinDokumen4 halamanOral Preparations: Erdosteine ZertinmagreaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 ATN Lameire2013Dokumen10 halaman3 ATN Lameire2013angela_karenina_1Belum ada peringkat
- Dengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDokumen3 halamanDengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDr.SagindarBelum ada peringkat
- Extraordinary Published by Authority No. 1235, Cuttack Saturday, June 29, 2013/ ASADHA 8, 1935 Law DepartmentDokumen9 halamanExtraordinary Published by Authority No. 1235, Cuttack Saturday, June 29, 2013/ ASADHA 8, 1935 Law DepartmentVikash GoelBelum ada peringkat
- Wastewater Disposal.Dokumen266 halamanWastewater Disposal.FarazBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing Deep Vein ThrombosisDokumen8 halamanPreventing Deep Vein ThrombosisOncology NurseBelum ada peringkat
- Palaska 2014Dokumen10 halamanPalaska 2014Marco TeixeiraBelum ada peringkat
- Post Op Management Following Surgery For Rectal ProlapseDokumen2 halamanPost Op Management Following Surgery For Rectal ProlapseChris NewallBelum ada peringkat
- Interesting Case FinalDokumen33 halamanInteresting Case Finalazenith dumlaoBelum ada peringkat
- Research PaperDokumen12 halamanResearch PaperKiran Niazi100% (1)