A Model For Estimating CO2 in Aq Alkanolamines
Diunggah oleh
bltzkrigJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A Model For Estimating CO2 in Aq Alkanolamines
Diunggah oleh
bltzkrigHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A Model for Estimating CO
2
in Aqueous
Alkanolamines
J ostein Gabrielsen, Michael L. Michelsen, Georgios Kontogeorgis, Erling H. Stenby
IVC-SEP, Department of Chemical Engineering, The Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby
To beableto develop moreefficient processes for theseparation of acid gases fromfluegases, thermodynamic modelling of thevapour liquid phaseequilibriumis thefirst step. Most thermodynamic models used
to represent thevapour-liquid equilibriaof CO
2
in an aqueous solution of alkanolamines arevery complex and requirealargeamount of adjustableparameters. This is dueto thefact that thealkanolamines are
weak electrolytes and chemical reactions between alkanolamineand CO
2
occur in theliquid phase. Another problemconcerning therepresentation of thevapour-liquid equilibriais that theexperimental data
existing arenot always plentiful and reliable. Thereis alargescatter particularly at low partial pressures and loadings. In this work avery simplemodel has been developed for representing theVLE of aqueous
alkanolaminesolutions.
References:
[1] J ou, F.-Y.; Mather, A. E.; Otto, F. D. TheSolubility of CO
2
in a30Mass Percent MonoethanolamineSolution. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1995, 73, 140.
[2] Lawson, J . D.; Garst, A. W.; Gas SweeteningData: EquilibriumSolubility of HydrogenSulfideand Carbon Dioxidein Aqueous Monoethanolamineand Aqueous DiethanolamineSolutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 1976, 21, 20.
[3] Lal, D.; Otto, F. D.; Mather, A. E. TheSolubility of H2S and CO2 in aDiethanolamineSolution at Low Partial Pressures. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1985, 63, 681.
[4] Sidi-Boumedine, R.; Horstmann, S.; Fischer, K.; Provost, E.; Frst. W.; Gmehling, J . Experimental determination of carbon dioxidesolubility datain aqueous alkanolaminesolutions. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 218, 85.
[5] Park S.H., LeeK.B., Hyun J .C., KimS.H., Corellationand prediction of thesolubility of Carbon Dioxidein Aqueous Alkanolamineand Mixed AlkanolamineSolutions, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2002, 41, 1658.
[6] Bishnoi S., RochelleG.T., Absorption of carbondioxideinto aqueous piperazine: reaction kinetics, mass transfer and solubility, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2000, 55, 5531-5543
[7] Liu H.-B., ZhangC.-F., XuG.-W., A Study on EquilibriumSolubility for Carbon Dioxidein Metyldiethanolamine-Piperazine-Water Solution, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1999, 38, 4032-4036
Figure 1 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with
experimental data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over an
aqueous 30 wt % MEA solution, experimental data from [1]
Figure 2 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with experimental
data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over an aqueous 25 wt % DEA
solution, experimental data from [2] and [3].
Figure 3 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with
experimental data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over an
aqueous 46.88 wt % MDEA solution, experimental data from [4].
Figure 4 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with
experimental data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over an
aqueous 30 wt % solution of AMP, experimental data from [5].
Figure 5 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with experimental
data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over an aqueous 5.17 wt % solution of
Piperazine, experimental data from [6].
Figure 6 Comparison of model correlation results (solid lines) with
experimental data for CO
2
equilibrium partial pressures over a
blended aqueous solution of 0.35 M Piperazine and 3.15 M MDEA,
experimental data from [7].
2 3
2H O H O OH
+
+
2 2 3 3
2 CO H O H O HCO
+
+ +
2
3 2 3 3
HCO H O H O CO
+
+ +
2 2 3
' ' RR NH H O H O RR NH
+ +
+ +
2 3
' ' RR NCOO H O RR NH HCO
+ +
( )
2 2
' ' 2 ' . RR NH RR NCOO RR NH CO aq
+
+ +
( )
3 2 2
. RH HCO R CO aq H O
+
+ + +
2
2
2
0
2
2
,
'
2
CO
CO
moleCO amine
loading a initial concentrationof amine
moleamine amine+H O
K combined Henry s lawand equilibriumconstant for partial pressure
of CO over the solution
X molefractionof chemicallybound CO inthe s
= = = =
=
=
( )
olution
T temperature Kelvin =
[ ] ( )
0 2 0
' 1 2 , ' ' RR NH a R RNH RR NCOO a
+
= = =
( ) ( )
2 2 2
0
2
0
1 2
CO CO CO
a
p K X
a
[ ] ( )
0 3 0
1 , R a RH HCO a
+
= = =
( )
2 2 2
0
0
1
CO CO CO
a
p K X
a
2
0 0
ln
CO
B
K A Ca D a
T
= + + +
Thechemical equilibriumtakingplacein theliquid phasewhen CO
2
is
absorbed in aqueous MEA or DEA is described by the following
reactions:
But many simplifications may becarried out, given certain conditions
(loadingbetween 0.02 and 0.48), and the absorption can bedescribed
by onechemical equilibriumreaction:
2 3
2H O H O OH
+
+
2 2 3 3
2 CO H O H O HCO
+
+ +
2
3 2 3 3
HCO H O H O CO
+
+ +
2 3
RH H O H O R
+ +
+ +
Thechemical equilibriumtakingplacein theliquid phasewhen CO
2
is
absorbed in aqueous MDEA or AMP is described by the following
reactions:
But many simplifications may be carried out, given certain conditions
(loading between 0.02 and 0.8 or 0.98), and the absorption can be
described by one chemical equilibrium reaction (it is also used for
Piperazine:
Then defining K
CO2
as a combined Henrys Law and chemical
equilibriumconstant and using the following the partial pressure of
CO
2
over thesolution can beexpressed
Then defining K
CO2
as a combined Henrys Law and chemical
equilibriumconstant and using the following the partial pressure of
CO
2
over thesolution can beexpressed
MEA and DEA
AMP, MDEA, and Piperazine Common Definitions Used in the Model
Thecombined chemical equilibriumand Henrys Law constant is then
fit to experimental VLE data using four adjustable parameters (all
parameters arenot needed for all alkanolamines):
A and B represent the standard temperature dependence of the
chemical equilibriumconstant. The parameters C and D which are
dependent on the total loading is included to approximate an ionic
strength dependence. FurthermoretheB parameter is directly related
theheat of absorption of CO
2
through theGibbs-Helmholtz equation.
Model
Results
Alkanolamines
OH
N
H
H
MEA
Monoethanolamine
HO
N
OH
H
DEA
diethanolamine
OH
N
HO
CH
3
MDEA
Methyldiethanolamine
Piperazine
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Agitadores April06Dokumen8 halamanAgitadores April06Karem Jeanette Saenz BernalBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Stnar34 MetanfetaminasDokumen88 halamanStnar34 Metanfetaminashildana pachecoBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion Basics - An Introduction, 3rd EditionDokumen35 halamanCorrosion Basics - An Introduction, 3rd EditioncarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Tech Compendium Final PDFDokumen380 halamanTech Compendium Final PDFEni SumarsihBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro Cracker Q&ADokumen138 halamanHydro Cracker Q&ADeepesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Develop strong safety instincts to guide preliminary design decisionsDokumen11 halamanDevelop strong safety instincts to guide preliminary design decisionsrudy_423522658Belum ada peringkat
- MC Kee - Thermosiphon Reboileres A ReviewDokumen7 halamanMC Kee - Thermosiphon Reboileres A Reviewbltzkrig100% (1)
- 01 Teaching Front End Engineering Design FEEDDokumen13 halaman01 Teaching Front End Engineering Design FEEDJoshua Johnson100% (4)
- Nash Liquid Ring Vacuum PumpsDokumen6 halamanNash Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumpsbltzkrig100% (2)
- Ethylene Production PDFDokumen2 halamanEthylene Production PDFGinaBelum ada peringkat
- Sloley - Properly Design Thermosyphon ReboilersDokumen14 halamanSloley - Properly Design Thermosyphon Reboilersbltzkrig100% (4)
- Aspen Plus Workshop For Reaction EngineeringDokumen44 halamanAspen Plus Workshop For Reaction EngineeringkotiBelum ada peringkat
- Methanol TechnologyDokumen8 halamanMethanol TechnologybltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Chickering (1981) - Thesis - Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butane Over Mixed Metal Oxide CatalystsDokumen145 halamanChickering (1981) - Thesis - Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butane Over Mixed Metal Oxide CatalystsbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Back PainDokumen3 halamanUpper Back PainbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Benford and Wassermann (1939a) - Mechanism of Addition To Double Bonds VI - Kinetics of Gaseous AssociationsDokumen6 halamanBenford and Wassermann (1939a) - Mechanism of Addition To Double Bonds VI - Kinetics of Gaseous AssociationsbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Experience Big Bear Lake's White Sandy Beach & Lifeguarded LagoonDokumen1 halamanExperience Big Bear Lake's White Sandy Beach & Lifeguarded LagoonbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Zhang Et Al 2011Dokumen11 halamanZhang Et Al 2011bltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits Highlights BrochureDokumen6 halamanBenefits Highlights BrochurebltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Aminov - Efficacy of Reactor Vessels For Natural CircDokumen6 halamanAminov - Efficacy of Reactor Vessels For Natural CircbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Darshan PatwardhanDokumen3 halamanDarshan PatwardhanbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Process Development ProcedureDokumen4 halamanProcess Development ProcedurebltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Kim - CFD Analysis of Calandria CANDU-6Dokumen10 halamanKim - CFD Analysis of Calandria CANDU-6bltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- WCC01 DownstreamDokumen12 halamanWCC01 DownstreambltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- The Polymer Primer - 1Dokumen70 halamanThe Polymer Primer - 1bltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Kinetics in G-L Reaction Systems - An OverviewDokumen22 halamanDetermination of Kinetics in G-L Reaction Systems - An OverviewbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Resin PricesDokumen3 halamanResin PricesbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Impeller Guide: Choose the Right Mixer for Your Cell LineDokumen4 halamanImpeller Guide: Choose the Right Mixer for Your Cell LinenemfodendoBelum ada peringkat
- Bhargava - Wet Oxidation and Catalytic Wet OxidationDokumen38 halamanBhargava - Wet Oxidation and Catalytic Wet OxidationbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Future Prospects For Production of Methanol and Hydrogen From BiomassDokumen82 halamanFuture Prospects For Production of Methanol and Hydrogen From Biomassbltzkrig100% (1)
- FE Chem Apr 2009Dokumen6 halamanFE Chem Apr 2009hotdog0Belum ada peringkat
- Buld Robust Reactor ModelsDokumen16 halamanBuld Robust Reactor ModelsAmgad_SBelum ada peringkat
- Herzog (2002) - Carbon Sequestration by Mineral CarbonationDokumen11 halamanHerzog (2002) - Carbon Sequestration by Mineral CarbonationbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Drain Tech Valve Box SizesDokumen5 halamanDrain Tech Valve Box SizesbltzkrigBelum ada peringkat
- Artocarpus LakoochaDokumen16 halamanArtocarpus LakoochaMoney ManBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemical Chloride Extraction Impact on ConcreteDokumen10 halamanElectrochemical Chloride Extraction Impact on ConcreteLeonardo Medina RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study Polymer Flooding Viscosity LevelsDokumen9 halamanComparative Study Polymer Flooding Viscosity Levelsasad nadeemBelum ada peringkat
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan: Chennai RegionDokumen281 halamanKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan: Chennai RegionAshray EapurBelum ada peringkat
- Iodium Pada Telur AsinDokumen6 halamanIodium Pada Telur AsinBayu WaeBelum ada peringkat
- Water From The Surrounding Solution Due To Osmosis. The Process of Osmosis CausesDokumen1 halamanWater From The Surrounding Solution Due To Osmosis. The Process of Osmosis CausesMatthew BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Kuraray Technical Brochure - EnglishDokumen28 halamanKuraray Technical Brochure - EnglishrbucholzBelum ada peringkat
- Merran A. Daniel - Polyurethane Binder Systems For Polymer Bonded ExplosivesDokumen34 halamanMerran A. Daniel - Polyurethane Binder Systems For Polymer Bonded ExplosivesYamveaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 11Dokumen3 halamanUnit 11Bharath GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- The Determination of Specific Sulfur Compounds by Capillary Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectionDokumen12 halamanThe Determination of Specific Sulfur Compounds by Capillary Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectionnhanBelum ada peringkat
- Tribology International: Rongping Yun, Peter Filip, Yafei LuDokumen10 halamanTribology International: Rongping Yun, Peter Filip, Yafei LuRajiv Gandhi Rajiv GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- 18 Ni (250) MaragingDokumen68 halaman18 Ni (250) MaragingsunsirBelum ada peringkat
- Scheme of Salt AnalysisDokumen8 halamanScheme of Salt AnalysisAz Ahmed100% (1)
- Removing Chloroprene from 1,2-Dichloroethane by Heat TreatmentDokumen7 halamanRemoving Chloroprene from 1,2-Dichloroethane by Heat TreatmentsundharBelum ada peringkat
- SDS University, UttarakhandDokumen9 halamanSDS University, UttarakhandHemanginee DasBelum ada peringkat
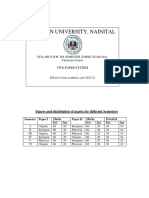
- B. Sc. Semester (Two Paper System) 2022-23Dokumen24 halamanB. Sc. Semester (Two Paper System) 2022-23yash.azad2005Belum ada peringkat
- SI BiodieselDokumen6 halamanSI BiodieselwidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDokumen274 halamanChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRohith KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry: CHAPTER 24-Practice Exercise Dr. PahlavanDokumen3 halamanOrganic Chemistry: CHAPTER 24-Practice Exercise Dr. Pahlavandelin21Belum ada peringkat
- Admixtures For Concrete, Mortar and Grout Ð Test Methods: Part 10. Determination of Water Soluble Chloride ContentDokumen10 halamanAdmixtures For Concrete, Mortar and Grout Ð Test Methods: Part 10. Determination of Water Soluble Chloride ContentRed FolderBelum ada peringkat
- Molisch TestDokumen5 halamanMolisch TestApril Kaye AbucejoBelum ada peringkat
- 13 PolimerDokumen54 halaman13 PolimerJhonsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Questions Answers: 8. Oil of Vitriol IsDokumen5 halamanChemistry Questions Answers: 8. Oil of Vitriol IsToyinBelum ada peringkat
- Chlorine Residual Testing Lab ExplainedDokumen7 halamanChlorine Residual Testing Lab ExplainedWaleed EmaraBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Characterization of Cefixime by Using IR, HPLC and Gas ChromatographyDokumen10 halamanAnalysis and Characterization of Cefixime by Using IR, HPLC and Gas ChromatographyFallahBelum ada peringkat