Namrata
Diunggah oleh
K Pra Shant0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan11 halamanICT in natural disaster mangement
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniICT in natural disaster mangement
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan11 halamanNamrata
Diunggah oleh
K Pra ShantICT in natural disaster mangement
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 11
Namrata Nikam ( 07305082)
Under Guidance of
Prof. Krithi and Prof.Desai
Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
The most frequent natural hazards include geological risks
(earthquakes, tsunami, landslides and volcanoes)
floods, cyclones and droughts and other hazards such as
epidemics and insect infestations.
It can cause massive destruction to the lives and livelihoods
of large population and hence, to the national economies.
eg. The death-toll of the tsunami that occurred in the Indian
Ocean in December 2004 has risen to more than 300,000
people.
It is experienced that the least developed and developing
countries are impacted more severely by large scale natural
disasters.
The Asia-Pacific is among the most disaster prone regions
in the world
Number of Disasters by Origin: Regional Distribution,
19952004
Taking measures to reduce
the losses brought by
natural disasters has been
a major challenge for the
world in achieving its
development goals.
ICT can be as crucial as
Food & Shelter in any
disaster It can save lives
thro timely & accurate
Information
avoiding a disaster even at the eleventh hour.
activity that reduces the chance of a hazard
turning into disaster
actions that seek to avoid future risks as
a result of a disaster
plans made to save lives or property, and
help the response and rescue service operations
actions taken to save lives
includes actions that assist a community to
return to a sense of normality after a disaster
Radio and Television
Telephone
SMS
Cell Broadcasting
Satellite Radio
Internet
Channels Used for Disaster Warning
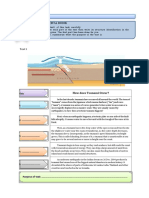
Using a GIS, it is possible to pinpoint hazard trends and
start to evaluate the consequences of potential
emergencies or disasters.
When hazards are viewed with other map data, such as
buildings, residential areas, rivers and waterways, streets,
pipelines, power lines, storage facilities, forests, etc.,
disaster management officials can formulate mitigation,
preparedness, response and possible recovery needs.
Missing Person Registry: Helping Families Find Each
Other
Organization Registry & Volunteer coordination :
Coordinating All Aid Groups and Helping Them to Operate
Effectively As One
Camps Registry: Capturing the Location of All Temporary
Camps and Shelters
Request Management System: Effectively Utilization
Inventory Management: Keeps track of inventories at a
high enough granularity to account for the chaotic transfer
of goods and aid.
Thank You
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NikecaseDokumen13 halamanNikecaseecoditaBelum ada peringkat
- Applications of RS & GIS in Disaster ManagementDokumen11 halamanApplications of RS & GIS in Disaster ManagementVinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Management PlanDokumen14 halamanDisaster Management PlanShailesh Mehta100% (1)
- NATURAL HAZARDS By: EDWARD BRYANTDokumen330 halamanNATURAL HAZARDS By: EDWARD BRYANTTarun SamaBelum ada peringkat
- ETE ReportDokumen16 halamanETE ReportSakshi TalwadeBelum ada peringkat
- SENSEDokumen33 halamanSENSECristine Gersary AguantaBelum ada peringkat
- Early Warning System ConceptDokumen8 halamanEarly Warning System Conceptmadhavi76952Belum ada peringkat
- Disaster Management Project FinalDokumen17 halamanDisaster Management Project FinalShashank Srikanth67% (3)
- ICT in Disaster Management in BangladeshDokumen70 halamanICT in Disaster Management in BangladeshAntonio Rogers100% (1)
- Abstract Legal LanguageDokumen1 halamanAbstract Legal LanguageHidayath UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Disaster Prevention: StructureDokumen21 halamanUnit 5 Disaster Prevention: StructureKapil Yadav100% (1)
- Disaster Management in India Past, Present and FutureDokumen25 halamanDisaster Management in India Past, Present and FutureKirti Kumar KasatBelum ada peringkat
- NSTP 10 Global WarmingDokumen35 halamanNSTP 10 Global WarmingH GnzlsBelum ada peringkat
- From Science To Safety - VinceDokumen16 halamanFrom Science To Safety - VincekelvingreyesBelum ada peringkat
- Risk AssessmentDokumen12 halamanRisk AssessmentBenjamin SimwingaBelum ada peringkat
- Final ESc 00Dokumen10 halamanFinal ESc 00ShivrahBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Management: Mahendra ChoudharyDokumen43 halamanDisaster Management: Mahendra ChoudharyROHIT SAGARBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Prevention and MitigationDokumen37 halamanDisaster Prevention and MitigationGladys Joyce FaustinoBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Risk MamnagementDokumen4 halamanDisaster Risk MamnagementBiYa ɱɥğȟålBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Disaster ManagementDokumen6 halamanImportance of Disaster Managementsikanderhayat007Belum ada peringkat
- Rationale For Disaster Prevention and Loss ControlDokumen6 halamanRationale For Disaster Prevention and Loss ControlDarrell Gines Malto50% (2)
- DisasterDokumen3 halamanDisasterBhumika MistryBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 2 Types of DisasterDokumen52 halamanUnit - 2 Types of Disasterfree fireBelum ada peringkat
- Iisf 2015 Iitd PDFDokumen5 halamanIisf 2015 Iitd PDFShivam PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster ManagementDokumen41 halamanDisaster ManagementYuvarajBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Disasters & Their ManagementDokumen56 halamanNatural Disasters & Their Managementsumit bhujbalBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster ManagementDokumen27 halamanDisaster ManagementDebipriya MistryBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Management For Social & Economic Development: Midlands State UniversityDokumen24 halamanDisaster Management For Social & Economic Development: Midlands State UniversityTariro MwanzaBelum ada peringkat
- 20ME5A0104Dokumen15 halaman20ME5A0104Jeevan babu BandelaBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokumen36 halamanNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentPrijeesh Naduvalath100% (1)
- Group Four PresentationDokumen13 halamanGroup Four Presentationlaizerjobeth100% (1)
- Hazards, Risks, Disasters and VulnerabilityDokumen3 halamanHazards, Risks, Disasters and VulnerabilityTolly BeBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster: EtymologyDokumen5 halamanDisaster: EtymologyAbhinab MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Guidebook On Technologies For Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation ISRO Satyabrata SahuDokumen102 halamanGuidebook On Technologies For Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation ISRO Satyabrata SahuS.Alec KnowleBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 13Dokumen14 halamanLec 13Amit KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- 3 NDMA VinodDokumen22 halaman3 NDMA VinodAchyuth NandamBelum ada peringkat
- 3 NDMA VinodDokumen22 halaman3 NDMA VinodShruti GaurBelum ada peringkat
- 18ceo03 DMM Unit IV Two Marks Part BDokumen4 halaman18ceo03 DMM Unit IV Two Marks Part B19ECR021 Deepak.SBelum ada peringkat
- Bantay Baha 2020Dokumen28 halamanBantay Baha 2020Junard Dominguez100% (1)
- Assignment 4: Framework For Crisis Preparedness Planning: Four Required Areas For Developing A Learning ProcessDokumen9 halamanAssignment 4: Framework For Crisis Preparedness Planning: Four Required Areas For Developing A Learning ProcessElsa kBelum ada peringkat
- DM ProficiencyDokumen7 halamanDM Proficiency2021cs49yaBelum ada peringkat
- Rationale For Disaster Prevention and Loss ControlDokumen20 halamanRationale For Disaster Prevention and Loss ControlJohn Brix Balisteros100% (5)
- ExamNotes - Disaster Management Keypoints From ARC ReportDokumen36 halamanExamNotes - Disaster Management Keypoints From ARC ReportRamakadrama100% (1)
- Module-I EHS 403: Disaster Management: Department of Civil EngineeringDokumen70 halamanModule-I EHS 403: Disaster Management: Department of Civil Engineering121710201031 SAMBHANGI PRANAV RITHVIKBelum ada peringkat
- Group-Work - Disaster - ManagementDokumen35 halamanGroup-Work - Disaster - Managementntambik21Belum ada peringkat
- Sayli SM Sem 2Dokumen22 halamanSayli SM Sem 2SayliKadveBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2212420919310398 MainDokumen34 halaman1 s2.0 S2212420919310398 MainFish FriedBelum ada peringkat
- Decision Aid Models and Systems For Humanitarian Logistics. A SurveyDokumen29 halamanDecision Aid Models and Systems For Humanitarian Logistics. A Surveymichael17ph2003Belum ada peringkat
- Research Paper Outline On Natural DisastersDokumen6 halamanResearch Paper Outline On Natural Disastersmtxziixgf100% (1)
- DRRR Lesson 2Dokumen17 halamanDRRR Lesson 2wendell john medianaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To DisasterDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To Disasterkalibrice3Belum ada peringkat
- DP - PM Unit - 4.2Dokumen71 halamanDP - PM Unit - 4.2pooja.amanchiBelum ada peringkat
- NDMA Measures Now and ThenDokumen5 halamanNDMA Measures Now and Thentooba IshfaqBelum ada peringkat
- DISASTER ManagementDokumen12 halamanDISASTER Managementwajid ahmad0% (1)
- UserDokumen5 halamanUserRaam Sai BharadwajBelum ada peringkat
- GIS Flood HazardDokumen12 halamanGIS Flood HazardOon KooBelum ada peringkat
- 4 ChagutahDokumen14 halaman4 ChagutahKhalid BahauddinBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal Draft21Dokumen18 halamanProposal Draft21Gashahun kasayeBelum ada peringkat
- Earth and Atmospheric Disaster Management Natural and Man-madeDari EverandEarth and Atmospheric Disaster Management Natural and Man-madeBelum ada peringkat
- Policy Note - Understanding Risk in an Evolving WorldDari EverandPolicy Note - Understanding Risk in an Evolving WorldBelum ada peringkat
- Humanitarian and Relief Logistics: Research Issues, Case Studies and Future TrendsDari EverandHumanitarian and Relief Logistics: Research Issues, Case Studies and Future TrendsBelum ada peringkat
- PFC Apdrp IIDokumen19 halamanPFC Apdrp IIK Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- Nit 391 Ninl Erp TenderdocDokumen405 halamanNit 391 Ninl Erp TenderdocK Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- Sata Role of Telecommunications and Ics in Disaster ManagementDokumen26 halamanSata Role of Telecommunications and Ics in Disaster ManagementFatima AdabBelum ada peringkat
- Model Answer Key - State Service Preliminary Examination - 2013 - 13!8!2014Dokumen9 halamanModel Answer Key - State Service Preliminary Examination - 2013 - 13!8!2014skh_1987Belum ada peringkat
- ONE BHEL ERP Tender Document1 - 1Dokumen122 halamanONE BHEL ERP Tender Document1 - 1K Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- eGC Individual Assignment I & II - K Prashant CPEG IIM IndoreDokumen5 halamaneGC Individual Assignment I & II - K Prashant CPEG IIM IndoreK Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- Week 5 DetectiveDokumen2 halamanWeek 5 DetectiveK Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- FSGO Assignment - K Prashant CEPGDokumen4 halamanFSGO Assignment - K Prashant CEPGK Pra ShantBelum ada peringkat
- Summative TestDokumen2 halamanSummative TestDominador MasiragBelum ada peringkat
- The 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami DisasterDokumen15 halamanThe 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami DisasterCharles TranBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake G6Dokumen49 halamanEarthquake G6Debbie FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Term PaperDokumen7 halamanTerm Paperapi-241248438Belum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological University Disaster Management SUBJECT CODE: 3700002 Semester: I/IiDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological University Disaster Management SUBJECT CODE: 3700002 Semester: I/IiHardik Jograna100% (1)
- RED BookDokumen85 halamanRED BookGay Dugang-Ibañez100% (1)
- Exercise 3 Soal PAT 2021Dokumen13 halamanExercise 3 Soal PAT 2021William Chendra KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Explanation Text Beserta Generic Structure Dan Language Features. TsunamiDokumen3 halamanExplanation Text Beserta Generic Structure Dan Language Features. TsunamiValerina AzzahraBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 2nd Prelim ScienceDokumen4 halamanGrade 8 2nd Prelim ScienceJewo CanterasBelum ada peringkat
- Recaunt Text: Answer The QuestionsDokumen17 halamanRecaunt Text: Answer The QuestionsSonya ArteRy Na NokiBelum ada peringkat
- Title: Uplink Banda Aceh Authors: Uplink Banda Aceh and Gabriela SauterDokumen11 halamanTitle: Uplink Banda Aceh Authors: Uplink Banda Aceh and Gabriela SauterjimmiroytampubolonBelum ada peringkat
- Teks EksplanasiDokumen3 halamanTeks EksplanasisabrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Tsunamis: Presented By: Palak Arora 9 CDokumen17 halamanTsunamis: Presented By: Palak Arora 9 CVanita KhungerBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Risk and Risk Reduction: Dr. Walter Hays, Global Alliance For Disaster ReductionDokumen40 halamanUnderstanding Risk and Risk Reduction: Dr. Walter Hays, Global Alliance For Disaster ReductionjoelduparBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Teks ExplanationDokumen40 halamanContoh Teks ExplanationTelemedia GubugBelum ada peringkat
- National Disaster Response Plan For Earthquake and TsunamiDokumen109 halamanNational Disaster Response Plan For Earthquake and TsunamiLea Ibayan100% (1)
- Explanation Text - How Did The Tsunami HappenDokumen1 halamanExplanation Text - How Did The Tsunami HappenMita AradaBelum ada peringkat
- N H D: C, C M: Atural Azards AND Isasters Auses Onsequences AND AnagementDokumen25 halamanN H D: C, C M: Atural Azards AND Isasters Auses Onsequences AND AnagementHari KishanBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log: S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14Dokumen33 halamanDaily Lesson Log: S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14 S8Es-Iia-14SALVACION DURANBelum ada peringkat
- TsunamiDokumen17 halamanTsunamiedwinBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 9 1Dokumen7 halamanUnit 9 1Anh NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Task Family Preparedness Plan W9Dokumen5 halamanPerformance Task Family Preparedness Plan W9Psalm Ezrah LavadoBelum ada peringkat
- Based On Generic Structure and Language Feature Dominantly UsedDokumen18 halamanBased On Generic Structure and Language Feature Dominantly UsedFauzan Rizki NajiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment 1Amelia CahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 Day 2 TB DQAS 2nd QuarterDokumen9 halamanGrade 8 Day 2 TB DQAS 2nd QuarterNathan JangaoBelum ada peringkat
- Template Soal Bahasa Inggris AM-BINGDokumen30 halamanTemplate Soal Bahasa Inggris AM-BINGFikriBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics in Memory of Ragnar SigbjörnssonDokumen416 halamanEarthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics in Memory of Ragnar SigbjörnssonguillermoBelum ada peringkat
- ΕΕΕΕΓΜ ΝΕΑ ΑΡ 185 ΜΑΡΤΙΟΣ 2024Dokumen44 halamanΕΕΕΕΓΜ ΝΕΑ ΑΡ 185 ΜΑΡΤΙΟΣ 2024Costas SachpazisBelum ada peringkat
- Activty 8 - Problem Solving & ReasoningDokumen4 halamanActivty 8 - Problem Solving & ReasoningKarl paculanBelum ada peringkat