Antes de Cojer Ss
Diunggah oleh
Natalia PadillaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Antes de Cojer Ss
Diunggah oleh
Natalia PadillaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
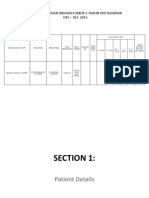
Contraception Contraception Contraception Contraception
Type of
contraceptive
Description Use Failure rate
per 100
women in
one year
Abstinence Refraining from
intercourse, anal sex,
and oral sex
Universally applicable. Also
prevents spread of sexually
transmitted diseases
0
Birth control
pill
Prescription pill
containing estrogen and
progestin that
suppresses ovulation
Must be taken daily,
regardless of the frequency
of intercourse
1-2
Cervical cap
with spermicide
Soft rubber cup that fits
around the cervix,
obtained by
prescription
Inserted before intercourse.
May be difficult to insert
17-23,
depending on
type
Condom,
female
Lubricated sheath that
is inserted into the
vagina. Similar in shape
to the male condom,
with a flexible ring
Applied immediately before
intercourse, for single use
21
Condom, male Latex or polyurethane
sheath placed over erect
penis, widely available
in drugstores
Applied immediately before
intercourse, for single use.
Best protection against
sexually transmitted
diseases
11
Depo-Provera
injection
Injection that inhibits
ovulation, obtained by
prescription
Injections performed at a
doctor's office, once every
three months
Less than 1
Diaphragm
with spermicide
Dome-shaped rubber
disk that covers the
cervix, obtained by
prescription
Inserted before intercourse
and left in place at least six
hours after
17
Douching Use an over-the-
counter feminine
douche immediately
after intercourse in an
effort to wash out the
sperm
Sperm travel quickly to the
cervix, making this an
ineffective method of birth
control
40
IUD
(intrauterine
device)
T-shaped device
inserted in the uterus
during a visit to the
doctor
Can remain in place for up
to one or 10 years,
depending on type
Less than 1
Name: Yili Natalia Padilla Flores ID: _A00999975__ List No. 24 Group: _1_
Homework Theme: _Contraceptive methods Date:__April 22th, 2013_ Biomedical Science Course
Morning-after
pill (emergency
contraceptive)
Pills similar to regular
birth control pills,
obtained by
prescription
Must be taken within 72
hours of unprotected
intercourse
80% reduction
in pregnancy
risk
Patch Adhesive patch worn on
the skin that releases
hormones preventing
ovulation. Obtained by
prescription
New patch is applied once a
week for three weeks,
followed by one week
without the patch
1-2
Periodic
abstinence
Refraining from
intercourse when
conception is likely
Requires regular menstrual
cycles and close monitoring
of body functions pertaining
to ovulation
20
Spermicide
alone
A foam, cream, jelly,
film, or suppository, or
tablet containing
nonoxynol-9
Depending on product,
inserted between five and 90
minutes before intercourse;
usually left in place at least
six to eight hours after
20-50,
depending on
product
Withdrawal Having intercourse, but
removing the male
penis before ejaculation
Not recommended for teens,
and some seminal fluid
leaks before ejaculation,
making it an ineffective
method of birth control
27
SOURCE : Food and Drug Administration, December 2003; Planned Parenthood,
March 2004; kidshealth.org, September 2001.
SOURCE : Food and Drug Administration, December 2003; Planned Parenthood,
March 2004; kidshealth.org, September 2001.
SOURCE : Food and Drug Administration, December 2003; Planned Parenthood,
March 2004; kidshealth.org, September 2001.
SOURCE : Food and Drug Administration, December 2003; Planned Parenthood,
March 2004; kidshealth.org, September 2001.
Hormonal methods: These use medications (hormones) to prevent ovulation.
Hormonal methods include birth control pills, Depo Provera injections, and
Norplant.
Barrier methods: These methods work by preventing the sperm from getting to
and fertilizing the egg. Barrier methods include male condom and female condom,
diaphragm, and cervical cap. The condom is the only form of birth control that also
protects against sexually transmitted diseases, including human immunodeciency
virus (HIV) that causes acquired immune deciency syndrome (AIDS).
Spermicides: These medications kill sperm on contact. Most spermicides contain
nonoxynyl-9. Spermicides come in many di!erent forms such as jelly, foam, tablets,
and even a transparent lm. All are placed in the vagina. Spermicides work best
when they are used at the same time as a barrier method.
Intrauterine devices (IUDs): These devices are inserted into the uterus, where they
stay from one to ten years. An IUD prevents the fertilized egg from implanting in
the lining of the uterus and may have other e!ects as well.
Name: Yili Natalia Padilla Flores ID: _A00999975__ List No. 24 Group: _1_
Homework Theme: _Contraceptive methods Date:__April 22th, 2013_ Biomedical Science Course
Tubal ligation: This medical procedure is a permanent form of contraception for
women. Each fallopian tube is either tied or burned closed. The sperm cannot reach
the egg, and the egg cannot travel to the uterus.
Vasectomy: This medical procedure is a the male form of sterilization and should
be considered permanent. In vasectomy, the vas defrens, the tiny tubes that carry
the sperm into the semen, are cut and tied o!.
References:
"Contraception - meaning, Definition, Purpose, Description, Risks." Encyclopedia of
Children's Health: Infancy Through Adolescence. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2013. <http://
www.healthofchildren.com/C/Contraception.html#b>.
"Oral Contraceptives - swollen, symptoms, Definition, Description, General use,
Precautions." Encyclopedia of Children's Health: Infancy Through Adolescence. N.p., n.d.
Web. 22 Apr. 2013. <http://www.healthofchildren.com/N-O/Oral-Contraceptives.html>.
Name: Yili Natalia Padilla Flores ID: _A00999975__ List No. 24 Group: _1_
Homework Theme: _Contraceptive methods Date:__April 22th, 2013_ Biomedical Science Course
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Lasers: Effect of Laser Therapy On Chronic Osteoarthritis of The Knee in Older SubjectsDokumen8 halamanLasers: Effect of Laser Therapy On Chronic Osteoarthritis of The Knee in Older SubjectsBasith HalimBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS of Soda AshDokumen3 halamanMSDS of Soda AshAtif IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Humanistic and Experiential Theories of Psychotherapy PDFDokumen32 halamanHumanistic and Experiential Theories of Psychotherapy PDFpsicandreiaBelum ada peringkat
- Bped 100 Act 1Dokumen2 halamanBped 100 Act 1DAVIE ELSISURABelum ada peringkat
- Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) - Photobiomodulation (PBM) - Red - NIR Phototherapy Studies - A Comprehensive Database by Vladimir Heiskanen - Taulukko1Dokumen76 halamanLow Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) - Photobiomodulation (PBM) - Red - NIR Phototherapy Studies - A Comprehensive Database by Vladimir Heiskanen - Taulukko1nepretipBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Utk State Meetng (DR DAUD)Dokumen45 halamanPresentation Utk State Meetng (DR DAUD)Mohd Daud Che YusofBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle Energy Technique: Dr. Nistara S. Chawla Miap, CSTMT MPT NeurologyDokumen32 halamanMuscle Energy Technique: Dr. Nistara S. Chawla Miap, CSTMT MPT NeurologyNistara Singh ChawlaBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Implementing A Safety Nursing Measures On Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardial InfarctionDokumen25 halamanThe Effect of Implementing A Safety Nursing Measures On Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardial InfarctionnurulfahmiBelum ada peringkat
- Coco Sugar Marketing Plan Targets Health-Conscious ConsumersDokumen12 halamanCoco Sugar Marketing Plan Targets Health-Conscious Consumersqwerttrewq100% (2)
- Breast MassDokumen38 halamanBreast MassLester Paul SivilaBelum ada peringkat
- Listening and Reading Comprehension TestDokumen12 halamanListening and Reading Comprehension TestPrimaIstianaBelum ada peringkat
- Ebola Virus Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen15 halamanEbola Virus Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAlvin AlmazanBelum ada peringkat
- Emailing 11. Dr. Manoj Gupta - Pelvic RT PlanningDokumen69 halamanEmailing 11. Dr. Manoj Gupta - Pelvic RT PlanningafshanBelum ada peringkat
- Braverman 2007 PMS and Dysphoric DisorderDokumen10 halamanBraverman 2007 PMS and Dysphoric DisorderCarolina GómezBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Pregnancy-Related Lumbar and Pelvic Girdle Pain by The Yoga Method: A Randomized Controlled StudyDokumen8 halamanTreatment of Pregnancy-Related Lumbar and Pelvic Girdle Pain by The Yoga Method: A Randomized Controlled StudyJosephineeBelum ada peringkat
- Alsoufi 2018Dokumen2 halamanAlsoufi 2018nidaakkusBelum ada peringkat
- Polydactyly of The Foot A Review.92Dokumen10 halamanPolydactyly of The Foot A Review.92mamyeu1801Belum ada peringkat
- PsychopathiaDokumen26 halamanPsychopathiaKunal KejriwalBelum ada peringkat
- Hazardous Waste Generator Online RegistrationDokumen12 halamanHazardous Waste Generator Online RegistrationTricia LacuestaBelum ada peringkat
- Bio OssDokumen4 halamanBio OssVizi AdrianBelum ada peringkat
- Chinese Pastoral Counselling Course SyllabusDokumen13 halamanChinese Pastoral Counselling Course SyllabusAbinayaBelum ada peringkat
- Gases Toxicos Irritantes PDFDokumen6 halamanGases Toxicos Irritantes PDFLUIS ANDRES JUAREZ CALLEBelum ada peringkat
- ADHD Strategies and TipsDokumen26 halamanADHD Strategies and Tipsgerfelc03Belum ada peringkat
- Research: Uterine Artery Doppler Study in Second Trimester of PregnancyDokumen8 halamanResearch: Uterine Artery Doppler Study in Second Trimester of PregnancyedelinBelum ada peringkat
- A Fluids and ElectrolytesDokumen8 halamanA Fluids and ElectrolytesAnastasiafynnBelum ada peringkat
- DokumenDokumen4 halamanDokumenFkep2015Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Adrenergic AgonistsDokumen9 halamanPharmacology of Adrenergic Agonistsfiena92Belum ada peringkat
- Compulsive Sexual Behavior Compulsive Sexual Behavior Compulsive Sexual BehaviorDokumen3 halamanCompulsive Sexual Behavior Compulsive Sexual Behavior Compulsive Sexual BehaviorAnand KirtiBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022Dokumen60 halaman2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022syedBelum ada peringkat
- Kapitel 6Dokumen125 halamanKapitel 6Jai Murugesh100% (1)