Animal Tissues Summary
Diunggah oleh
Caroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Animal Tissues Summary
Diunggah oleh
Caroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
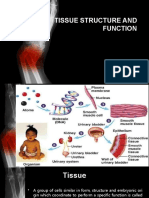
Animal Tissues
Kingdom Animalia are consists of multicellular eukaryotic organisms. And they are characterized by
complex tissue organization. Animal cells having similar structure and performing definite functions in
the animal body constitutes tissue. Various animal tissues having different functions are organized to
become organs.
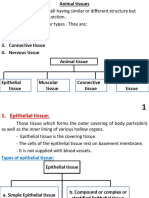
I. Epithelial Tissues- composed of cells which form a continuous layer of sheet covering the
body surface or lining cavities within the body. They perform protection secretion,
excretion, absorption, lubrication (glandular) sensory reception, and reproduction.
Examples: skin, lining of digestive tract, lining of kidney tubules, lining of windpipe and
lungs
A. According to shape of cells:
1. Squamous Cell- is a thin flattened cell resembling tiles in a floor or scale-like.
2. Cuboidal Cell- the height of cell body is about equal to the width, cube-like
appearance.
3. Columnar Cell- the height greatly exceeds the width resembling pillars.
4. Ciliated Cell- bears on its exposed surface numerous short hairlike extensions
called cilia.
5. Flagellated- have one or more whiplike cytoplasmic processes called flagella on
the exposed surface.
6. Spherical- rounded or oval in shape.
7. Polygonal- resembles a closed polygon.
B. Arrangement of Cells in Epithelial Sheets:
1. Simple- composed of a membrane but one cell in thickness.
2. Transitional- cells are arranged in two or more distinct layers of varied cell
shape that is the superficial layer is of large umbrella shaped cells, its middle
layer composed of several layers of polygonal cells and the basal layer
composed of low columnar cells or small polyhedral cells.
3. Stratified- cells are arranged in two or more distinct layers.
4. Pseudostratified- cells are arranged in two or more indistinct layers.
C. According to Shape and Arrangement:
1. Simple squamous or pavement epithelium- a single layer of flat cells or thin
platelike cells is arranged in a single layer.
2. Simple cuboidal epithelium- made up of line layer of cuboidal cells lining of
ducts, thyroid gland, and the kidney tubules such as the uriniferous tubules.
3. Simple columnar epithelium- a layer of columnar cells adhere to each other
along longitudinal or lateral surface
4. According to Function:
II. Connective and Supportive Tissues- composed of cells and interspersed fibers suspended in
a semi- fluid amorphous ground substances. There primary function is for support and for
binding the different parts of the body together.
III. Muscular and Contractile Tissues- movement of most animals result from the contraction of
elongate, cylindrical or spindle- shaped cells. The property of contractility is highly
developed in myofibrils in their cytoplasm which are capable of contraction in one direction
only.
IV. Nervous and Conductive Tissue- fundamental tissue that integrates the functions of various
organs of the body. Properties of irritability and conductivity (receive and transmit impulses)
are highly developed; arise from the ectoderm.
V. Blood or Vascular Tissue- consist of the blood and a circulating tissue which transport
nutrients, gases, waste materials and hormones; protects the body from disease causing
organisms (immunity), and blood clotting.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Structure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectDari EverandStructure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDokumen110 halamanAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Epithelial TissueDokumen30 halamanEpithelial Tissueعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحBelum ada peringkat
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDokumen6 halamanTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Struc. Organization in AnimalsDokumen47 halamanStruc. Organization in AnimalsathuBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyDokumen45 halamanAnatomyMB Loterte100% (1)
- Human Body OrganizationDokumen6 halamanHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenBelum ada peringkat
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDokumen74 halamanTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Study of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifDokumen60 halamanStudy of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifEntirety 4uBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 AnaphyDokumen3 halamanChapter 4 AnaphyKate MontenegroBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy - TissuesDokumen43 halamanAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDokumen4 halamanTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaBelum ada peringkat
- Animal TissueDokumen14 halamanAnimal TissueSagar GavasBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDokumen16 halamanMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- 3.tissue DmaDokumen111 halaman3.tissue DmaFaisal Mohamad100% (1)
- TissuesDokumen91 halamanTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezBelum ada peringkat
- TISSUESDokumen28 halamanTISSUESSamuel BordohBelum ada peringkat
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDokumen8 halamanHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKBelum ada peringkat
- STM 007Dokumen11 halamanSTM 007Carla PascuaBelum ada peringkat
- Tissues 2Dokumen2 halamanTissues 2Adeaga ElizabethBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDokumen25 halamanChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamit lakraBelum ada peringkat
- Tissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueDokumen12 halamanTissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueChristine BalanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Tissues 2023Dokumen70 halamanAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzBelum ada peringkat
- English Task 2Dokumen3 halamanEnglish Task 2Tiara ArmiliaBelum ada peringkat
- Animaltissues 180604115637Dokumen40 halamanAnimaltissues 180604115637proud.student2023Belum ada peringkat
- RudrakshDokumen3 halamanRudrakshAmartyaBelum ada peringkat
- Epithelial TissueDokumen12 halamanEpithelial Tissuenitesh.th15005Belum ada peringkat
- BIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerDokumen7 halamanBIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerBedecir, Schrister Hynes D.Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 The EpitheliumDokumen3 halamanChapter 3 The EpitheliumGela ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesDokumen27 halaman1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesrenatoamarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Dokumen40 halamanLecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Wll NasiibBelum ada peringkat
- Histology of The Epithelium TissueDokumen9 halamanHistology of The Epithelium TissueKelvin HillsBelum ada peringkat
- HistocologyDokumen10 halamanHistocologyKelvin HillsBelum ada peringkat
- Tissue and HistologyDokumen28 halamanTissue and HistologymagdangalmaryfrancessBelum ada peringkat
- Epithelial TissueDokumen3 halamanEpithelial TissueAmmar ShahidBelum ada peringkat
- Tissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Dokumen14 halamanTissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Thikshika . NBelum ada peringkat
- Expeeriment 2Dokumen4 halamanExpeeriment 2Ali RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Histology 2018 1Dokumen38 halamanHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Laboratory ManualDokumen39 halamanLaboratory ManualChelsea Chadwick100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresDokumen18 halamanGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Body TissuesDokumen10 halamanBody TissuesNaanmatha PuspanathanBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology IIDokumen6 halamanGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDokumen64 halamanYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- Tissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionDokumen13 halamanTissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionnagahushanamBelum ada peringkat
- Epithelial TissueDokumen2 halamanEpithelial Tissuesomya mathurBelum ada peringkat
- Elementary TissuesDokumen32 halamanElementary TissuesManjunath100% (1)
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDokumen10 halamanCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Tissues NEW 1Dokumen54 halamanAnimal Tissues NEW 1Jela AgengaBelum ada peringkat
- TissueDokumen20 halamanTissueJagruti MaratheBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Types 1Dokumen28 halamanCell Types 1IngridBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesDokumen22 halamanCh. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesLinda Yurani Carvajal AngaritaBelum ada peringkat
- Epithelial TissueDokumen10 halamanEpithelial TissueMichael NyaongoBelum ada peringkat
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Dokumen4 halamanZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeBelum ada peringkat
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDokumen62 halamanTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJBelum ada peringkat
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Dokumen22 halamanHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision NotesDokumen32 halamanClass 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision Notesshusa harsha100% (1)
- Tissues NotesDokumen7 halamanTissues NotesHarshitBelum ada peringkat
- Epithelial Tissue..Dokumen32 halamanEpithelial Tissue..Uzma KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Year 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesDokumen49 halamanYear 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesZoonieFR0% (1)
- November 28-29, 2019 I. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Dokumen3 halamanNovember 28-29, 2019 I. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Caroline Joy Baldomaro Picardal100% (1)
- Atmospheric Pressure, Winds, and PrecipitationDokumen3 halamanAtmospheric Pressure, Winds, and PrecipitationCaroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Technique ExercisesDokumen1 halamanTrial Technique ExercisesCaroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Creative Writing Elements of Creative WritingDokumen58 halamanElements of Creative Writing Elements of Creative WritingCaroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalBelum ada peringkat
- Unclaimed Balances Law (PD 679)Dokumen3 halamanUnclaimed Balances Law (PD 679)MaricrisBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Creative Writing Elements of Creative WritingDokumen58 halamanElements of Creative Writing Elements of Creative WritingCaroline Joy Baldomaro PicardalBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesDokumen9 halamanBlood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesEduardo Rios DuboisBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine GlandDokumen9 halamanEndocrine GlandKUNAL1221Belum ada peringkat
- Journal IPSG 5Dokumen7 halamanJournal IPSG 5marissa ulkhairBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro Lab ManualDokumen28 halamanGastro Lab ManualYeniBelum ada peringkat
- Dissection Guide On The Frog Muscular SystemDokumen6 halamanDissection Guide On The Frog Muscular SystemNeileene Joy Simeon DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Statement For Animal ResearchDokumen5 halamanThesis Statement For Animal Researchtit0feveh1h3100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Dokumen25 halamanMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Gaia PhyllisBelum ada peringkat
- What Bugs Hawaii: RoachesDokumen1 halamanWhat Bugs Hawaii: RoachesHonolulu Star-AdvertiserBelum ada peringkat
- Unacadmey Basic Organic Chemistry PDFDokumen92 halamanUnacadmey Basic Organic Chemistry PDFAbhishek VermaBelum ada peringkat
- PNS - Bafs 267.2019 Code of Good Animal Husbandry Practice For SwineDokumen20 halamanPNS - Bafs 267.2019 Code of Good Animal Husbandry Practice For Swinejoriz klenz sabeteBelum ada peringkat
- Kumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Dokumen7 halamanKumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Karki KedarBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics For Elementary Teachers 5th Edition Beckmann Test BankDokumen26 halamanMathematics For Elementary Teachers 5th Edition Beckmann Test BankDonnaMoorefspo98% (59)
- DOGS TableDokumen12 halamanDOGS TableUna CharismaBelum ada peringkat
- SalpingitisDokumen25 halamanSalpingitisAnonymous NDAtNJyKBelum ada peringkat
- Savage Worlds Cheatsheets PowersDokumen15 halamanSavage Worlds Cheatsheets Powersschwartz5350Belum ada peringkat
- Skilled Birth Attendant PostersDokumen16 halamanSkilled Birth Attendant PostersPrabir Kumar Chatterjee100% (1)
- Biology Project PDFDokumen18 halamanBiology Project PDFSuyash Baghel86% (7)
- Module in Science 9: First Quarter/Week 1/day4Dokumen5 halamanModule in Science 9: First Quarter/Week 1/day4Frederick EspejoBelum ada peringkat
- Schilling Test BrochureDokumen2 halamanSchilling Test BrochureLyn OdchigueBelum ada peringkat
- Dwnload Full Database Concepts 8th Edition Kroenke Solutions Manual PDFDokumen35 halamanDwnload Full Database Concepts 8th Edition Kroenke Solutions Manual PDFhudsons6opk100% (12)
- Sense OrgansDokumen6 halamanSense Organsannmarie100% (1)
- Science Illustrated July-August 2008Dokumen79 halamanScience Illustrated July-August 2008lelo2k30% (1)
- Sains t2 PDFDokumen6 halamanSains t2 PDFSJK CHUNG HUA 4 1/2 四哩半中公Belum ada peringkat
- HIV-Associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSDokumen13 halamanHIV-Associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSmauroignacioBelum ada peringkat
- Aarthi Minor AllDokumen52 halamanAarthi Minor AllVenkatesan Vidhya100% (1)
- Gibberish WordsDokumen4 halamanGibberish WordsDaniel PopaBelum ada peringkat
- Veterinary Medical Guide To Dog and Cat Breeds PDFDokumen673 halamanVeterinary Medical Guide To Dog and Cat Breeds PDFAndra Elena Pricop83% (6)
- Animal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Dokumen2 halamanAnimal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Chinmay KotkarBelum ada peringkat
- All Questions PhysiologyDokumen25 halamanAll Questions Physiologyfilchibuff100% (6)