Drug Study CVD
Diunggah oleh
Irene Joy GomezJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study CVD
Diunggah oleh
Irene Joy GomezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IV.
Drug Study
DRUG ACTION INDICATION /
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING
RESPONSIBILITY
Aspirin (Aspilets)
80mg PO once daily
*decrease pain, inflammation, fever,
MI, absence of transient ischemic
attacks, thrombosis.
Relieves pain, reduce
inflammation by inhibition of
peripheral prostaglandin
synthesis. It acts on the
hypothalamic heat-
regulating center to relieve
fever, by promoting
sweating and vasodilation,
leading to heat loss and
cooling by evaporation.
Decreases platelet
aggregation by preventing
formation of thromboxane A,
a platelet aggregating
substance.
I : Treatment of mild to
moderate pain, fever,
inflammatory conditions;
reduce risk of death or MI in
patients with previous
infarction or unstable angina
pectoris or recurrent
transcient ischemia attacks
or stroke in men who have
had transient brain ischemia
cause by platelet thrombi.
C: Hypersensitivity to
salicylates or NSAIDs;
hemophilia, bleeding ulcers
or hemorrhagic states.
Dizziness, tinnitus,
nausea,dyspepsia,
heartburn, bleeding, anemia,
decreased iron
concentration, urticarial,
hives, angioedema and
anaphylactic shock
Give with food to decrease
gastric symptoms.
Do not crush enteric product.
Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
10mg PO QHS
* cholesterol at desired level after
8weeks.
Inhibits HMG-CoA
reductace enzyme, which
reduces cholesterol
synthesis.
I: For hypercholesterolemia,
mixed dyslipidemia and
hypertriglyceridemia. Lipid
lowering treatment.
C: Pregnancy,
hypersensitivity, acute liver
diease. Lactation.
Headache, myalgia,
asthenia, constipation,
dizziness, nausea,
abdominal pain, pruritus,
rash and urticarial,
myopathy, Rhabdomyolysis,
jaundice and hepatitis
May be taken with or without
food. Monitor adverse
reaction. Patient should have
periodic blood test to assess
effectiveness. Increase
exercise, fluids and fiber to
help with constipation.
Caution when
driving/engaged with
potentially hazardous tasks
until response to drug is
know.
Rifampicin+Ethambutol+Isoniazid
(Myrin) 150mg/300mg/75mg PO
2tabs BID
*decrease symptoms of TB.
Inhibits DNA-dependent
polymerase, decrease
replication
Treatment if all forms of
pulmonary and extra
pulmonary tuberculosis.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
anorexia, shortness of
breath, shock, gi bleeding,
erosive gastritis, ulcerative,
liver & kidney disfunction,
blurred vision, facial
flushing, elevations in BUN
acid and serum uric acid.
Stains soft contact lenses.
Perform mycobacterial
studies prior and during
therapy to detect resistance..
Monitor patient compliant to
treatment. Take rifampicin
on empty stomach, 1hr
before or 2hrs after meal. .
Medication will discolor
urine, stool, saliva, tears,
sweat and other body fluid a
red brown color.
DRUG ACTION INDICATION /
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
Cilostazol (Pletaal)
100mg PO BID
*decrease pain, adequate
tissue perfusion, increase
walking distance and duration.
Inhibits cellular cyclic AMP
phosphodiesterase III (PDE)
which results to increased
level of cyclic AMP. Increase
in the level of cAMP in
platelets and blood vessels
causes vasodilation and
inhibition of platelet
aggregation cause by
thrombin, ADP, collagen,
arachidonic acid, epinephrine
and shear stress.
I: treatment of ischemic
symptoms including ulcers,
pain and cold sensations in
chronic arterial occlusion.
Prevent cerebral infarction.
C: bleeding, chf,
hypersensitivity
Encephalorrhagia,
pneumorrhagia, fundus
bleeding, enteral bleeding.
Intestinal pneumonia, CHF,
angina pectoris, ventricular
tachycardia. CNS disorder,
kidney disorders, headache,
trauma.
Remind patient to take drug at
least 30mins before meal or
2hrs after breakfast and
dinner. Advise patient not to
take grapefruit juice while
taking drug. Report signs of
bleeding.
Betahistine (Serc)
24mg PO Q12
* relief from vertigo, dizziness
Direct stimulating effect on H1
receptors located on blood
vessels in the inner ear.
Strong affinity for histamine
H3 receptors and weak affinity
for histamine H1 receptors.
Powerful antagonistic effects
at H3 receptors and increases
the levels of neurotransmitters
release from the nerve
endings.
I: Menieres disease; Meniere-
like syndrome characterized
by attacks of vertigo, tinnitus
and progressive hearing loss.
Peripheral vertigo.
C: patient with asthma or ulcer
in the stomach/intestines,
problem with heartburn or
gastroesophageal reflux
disease.
Nausea, vomiting. Mild gastric
complaints and skin rashes.
Best taken after meals.
Solution must be protected
from sunlight.
Citicoline (zynapse)
1g PO Q12
*Treat dizziness, memory
loss, poor concentration,
disorientation, trauma and
stroke.
Citicoline is a derivative of
choline and cytidine involved
in the biosynthesis of lecithin.
It is claimed to increase blood
flow and oxygen consumption
in the brain.
I: CVA in acute and recovery
phase. Symptoms and signs
of cerebral insufficiency ie
dizziness, headache, poor
concentration, memory loss
disorientation etc. Recent
cranial trauma, Parkinson
disease.
C: hypertonia of
parasympathetic nervous
system. Meclofenoxate.
Shock, hypersensitivity,
hypotension, insomnia,
excitement. Stimulates
parasympathetic action and
fleeting and discreet
hypotensor effect.
Must be administer with
medicaments containing
meclophenoxate. Caution that
large doses of citicoline cound
aggravate increase in cerebral
blood flow in episodes of
persistent intracranial
hemorrahage. Monitor BP,
RR, PR.
DRUG ACTION INDICATION /
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
Sitagliptin+metformin
(velmeta)
50/500mg PO BID
*management of DM2
Inhibitor of enzyme dipeptidyl
peptidase-4 (DPP-4), an
enzyme that slows inactivation
of incretin hormones such as
glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-
1) and glucose dependent
insulinotropic
polypeptide(GIP) which
regulates insulin secretion.
I: use for management of
dm2. Use with metformin in
dm2 who has not achieved
adequate glycemic control
with metformin.
C: dm1, diabetic ketoacidosis
Upper respiratory tract
infections, headache and
nasopharyngitis, peripheral
edema, pain, osteoarthritis,
anorexia, dizziness,
hypoglycemia.
Monitor blood glucose daily.
N-acetylcysteine (Fluimucil)
In 1/2glass water 600mg
PO once daily
*absence of purulent
pulmonary secretions, clear
bilateral sounds, prevents
hepatic damage, decreasing
blood toxicity.
Decrease viscosity of
respiratory tract secretion and
promote their removal by
breaking disulfide bonds. In
acetaminophen overdose, it
protects the liver from injury
by restoring glutathione levels
or by acting as alternate
substance for acetaminophen
metabolism.
I: treatment of respiratory
affections characterized by
thick and viscous
hypersecretions; acute and
chronic bronchitis and its
exacerbation, pulmonary
emphysema. Antidote in
poisoning caused by
paracetamol, carbon
tetrachloride, arsenic, metallic
mercury inhalation yellow
phosphorus (watusi) and for
cyclophosphamide-induced
hemorrhagic cystitis.
C: Hypersensitivity,
phenylketonuria (contains
aspartame)
Nausea, vomiting, generalized
urticarial with mild fever,
hypotension, wheezing,
dyspnea and stomatitis.
Assess fluid and electrolyte
status
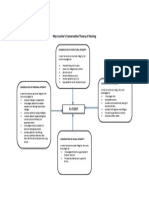
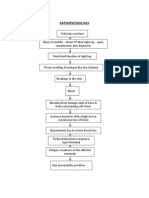
V. Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective:
Right hemiplegia
Limited ROM
Difficulty turning
Slowed
movement
Muscle strength
of
Right arm: 80/100
Right leg: 80/100
Left arm: 100/100
Right leg:
100/100
Postural
instability during
performance of
routine ADLs
Impaired
Physical Mobility
R/T
neuromuscular
involvement
secondary to
CVD infarct.
Short Term:
After 4hrs of
intervention pt is
willing to participate
in activities
necessary for the
patient.
Long Term:
After 3 days of
intervention pt will
be able to improve
and increase
strength and
function of affected
body part.
1.Note emotional/behavioral
responses to problems of
immobility.
2. Determine readiness to engage
in activities.
3. Assist patient reposition self in
regular schedule.
4. Provide for safety measure
including fall prevention.
5. Identify energy conserving
techniques for ADLs.
6. Involve patient and SO in care
assisting them to learn ways of
managing problems of immobility.
7. Assist patient to do passive
range of motion.
8. Provide restful environment for
patient after periods of exercise.
1. To assess functional ability.
2. To assess expected level of
participation.
3. To prevent complications.
4. To prevent injury.
5. Limit fatigue maximizing
participation.
6. To promote wellness.
7. To promote circulation and
prevent contracture.
8. To facilitate recuperation.
Short Term:
Patient shall have
participated in activities
necessary for the
patient. Goal met.
Long Term:
Pt shall have improved
and increase strength
and function of affected
body part.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective:
Need
assistance
eating,
getting
dress and
other
performing
ADLs
Self Care Deficit
R/T
musculoskeletal
impairment
secondary to
CVD
Short Term:
After 4hrs of NI, pt will be
able to identify personal
resources that can
provide assistance and be
able to verbalize
knowledge of health care
practices.
Long Term:
After 3days of NI, pt will
demonstrate
technique/lifestyle
changes to meet self care
needs,
1. Assess for type and severity of
immobility impairment, muscle
flaccidity, spasticity and
coordination, ability to walk,
sit, move in bed perform.
2. Passive ROM to all limbs and
progress to assistance and
then active ROM in all joints
four times a day.
3. Use assistive devices as
appropriate for ambulation,
clothing with zipper closures,
suction cups on personal
hygiene articles for brushing
teeth, combing hair, clothing
that is easy managed to dress
and undress.
1. Provides data regarding
mobility and ability to
perform activities with in
limitations without injury or
frustrations.
2. Promotes circulation,
muscle tone, joint flexibility,
prevents contractures and
weakness.
3. Provides safe support for
immobility and other safe
care activities to promote
independence.
Short Term:
Pt shall have identified
personal resources that
can provide assistance
and be able to
verbalize knowledge of
health care practices.
Long Term:
Pt shall have
demonstrated
technique/lifestyle
changes to meet self
care needs,
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective:
Right
hemiplegia
Risk for Injury
R/T hemiplegia
secondary to
CVD infarct
Short Term:
After 1 hour of NI, pt will
be able to seek help to
perform task that are
beyond her capabilities.
Long Term:
After 3 days of NI, pt will
be able to remain free
from injury/fall.
1. keep the side rails of bed
raised.
2. Remind client to walk slowly,
rest adequately between intervals
of walking use effective lighting.
3. inform pt so not to leave him in
the bathroom.
1. Protect from falling of bed.
2. To prevent injury.
3. For continuous monitoring
and guidance to the client.
Short Term:
Pt able to seek help to
perform task that are
beyond her
capabilities. Goal met
Long Term:
PT remained free from
injury/fall.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Carrot: This Article Is About The Cultivated Vegetable. For Other Uses, SeeDokumen10 halamanCarrot: This Article Is About The Cultivated Vegetable. For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Bannana Musa (Genus) : For The Plant Genus To Which Bananas Belong, See - For Other Uses, SeeDokumen10 halamanBannana Musa (Genus) : For The Plant Genus To Which Bananas Belong, See - For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment Options by StageDokumen2 halamanTreatment Options by StageIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Strawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeDokumen8 halamanStrawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Stab Wound: For Other Uses, SeeDokumen3 halamanStab Wound: For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Case ADokumen3 halamanCase AIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- A. Family Health HistoryDokumen2 halamanA. Family Health HistoryIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Theory CåonservationDokumen1 halamanNursing Theory CåonservationIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Outcome Activities EvaluationDokumen2 halamanPerformance Outcome Activities EvaluationIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Outcome Activities EvaluationDokumen1 halamanPerformance Outcome Activities EvaluationIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Study Pinpoints Issues That Leave ED Nurses Vulnerable: Sunday February 9, 2014Dokumen2 halamanStudy Pinpoints Issues That Leave ED Nurses Vulnerable: Sunday February 9, 2014Irene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Health TeachingsDokumen8 halamanHealth TeachingsIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Action Contraindication /indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDokumen1 halamanDrug Action Contraindication /indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Disturbed Thought Process Decreased Attention Span and Difficulty in Concentration Related To Accelerated ThinkingDokumen1 halamanDisturbed Thought Process Decreased Attention Span and Difficulty in Concentration Related To Accelerated ThinkingIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge Planning RevisedDokumen2 halamanDischarge Planning RevisedIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanFracture PathophysiologyIrene Joy Gomez100% (2)
- Osteoarthritis PocDokumen4 halamanOsteoarthritis PocIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug StudyIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Exposing Instruments: Deaver Retractor Richardson Retractor Malleable or Ribbon Retractor Harrington RetractorDokumen3 halamanExposing Instruments: Deaver Retractor Richardson Retractor Malleable or Ribbon Retractor Harrington RetractorIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Theory Dorothea OremDokumen1 halamanNursing Theory Dorothea OremIrene Joy GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Review Article: Inhaled Therapy in Respiratory Disease: The Complex Interplay of Pulmonary Kinetic ProcessesDokumen12 halamanReview Article: Inhaled Therapy in Respiratory Disease: The Complex Interplay of Pulmonary Kinetic ProcessesliadiafaridaBelum ada peringkat
- Etiology, Classification and Clinical Approach: EndophthalmitisDokumen42 halamanEtiology, Classification and Clinical Approach: EndophthalmitisHieLdaJanuariaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Severe Hyperkalemia PDFDokumen6 halamanManagement of Severe Hyperkalemia PDFCarlos Navarro YslaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Reports in The Use of Vitamin C Based Regimen in Prophylaxis and Management of COVID-19 Among NigeriansDokumen5 halamanCase Reports in The Use of Vitamin C Based Regimen in Prophylaxis and Management of COVID-19 Among NigeriansAndi.Thafida KhalisaBelum ada peringkat
- TEACHING PLAN HypertensionDokumen2 halamanTEACHING PLAN Hypertensionpheochromocytoma59% (41)
- Pfizer Vaccine Explainer Version 2Dokumen9 halamanPfizer Vaccine Explainer Version 2nqosa neidscqBelum ada peringkat
- Femto LDV Z6Dokumen4 halamanFemto LDV Z6Francisco GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Ipd - Kelas Ac - Kad Dan Hhs - DR - DR.K Heri Nugroho HS, SP - PD, K-EmdDokumen51 halamanIpd - Kelas Ac - Kad Dan Hhs - DR - DR.K Heri Nugroho HS, SP - PD, K-EmdTeresia MaharaniBelum ada peringkat
- What Are NightmaresDokumen2 halamanWhat Are NightmaresCharlie BalucanBelum ada peringkat
- Congential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersDokumen7 halamanCongential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersNichole CollinsBelum ada peringkat
- Thrombocytopenia Brief DiscussionDokumen11 halamanThrombocytopenia Brief Discussionriel100% (3)
- Thorn Eh and OutDokumen24 halamanThorn Eh and OutNick MaxBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Level of Mental Health Problems of AdolescentDokumen3 halamanA Study On Level of Mental Health Problems of AdolescentEditor IJTSRDBelum ada peringkat
- Crash CartsDokumen11 halamanCrash CartsJohanna AbellanaBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture Blowout OrbitalDokumen6 halamanFracture Blowout OrbitalMasitha RahmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Otitis Media: Dr. Ajay Manickam Junior Resident RG Kar Medical College HospitalDokumen20 halamanAcute Otitis Media: Dr. Ajay Manickam Junior Resident RG Kar Medical College HospitalchawkatBelum ada peringkat
- Dentistry: A Case of Drug - Induced Xerostomia and A Literature Review of The Management OptionsDokumen4 halamanDentistry: A Case of Drug - Induced Xerostomia and A Literature Review of The Management OptionsSasa AprilaBelum ada peringkat
- ParasomniaDokumen27 halamanParasomniaVoltic AceroBelum ada peringkat
- Freedom Is Therapeutic Prof John FootDokumen2 halamanFreedom Is Therapeutic Prof John FootAna WongBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Optometry and Pediatric OptometryDokumen2 halamanGeriatric Optometry and Pediatric OptometryRony MathewsBelum ada peringkat
- Medrobotics Receives FDA Clearance For ColorectalDokumen2 halamanMedrobotics Receives FDA Clearance For ColorectalmedtechyBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine HyperstimulationDokumen2 halamanUterine HyperstimulationYwagar YwagarBelum ada peringkat
- Anesthesia Management For Pulmonary Hypertension PatientsDokumen18 halamanAnesthesia Management For Pulmonary Hypertension PatientsAliNasrallahBelum ada peringkat
- Medications Commonly Prescribed After A Stroke - GoodRxDokumen11 halamanMedications Commonly Prescribed After A Stroke - GoodRxAnonymous EAPbx6Belum ada peringkat
- Giotto Image3D BrochureDokumen16 halamanGiotto Image3D BrochureGriselda Maria Pinto SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Ss Ecg IntroDokumen0 halamanSs Ecg Introreusougenio4162Belum ada peringkat
- GBS Source 1Dokumen4 halamanGBS Source 1PJHG50% (2)
- The EBC 46 Cancer TreatmentDokumen9 halamanThe EBC 46 Cancer TreatmentAnimefan TheoBelum ada peringkat
- Louela C. Acedera, RN, MANDokumen18 halamanLouela C. Acedera, RN, MANelle seigdenBelum ada peringkat
- Minerva Anestesiol 2017 GruenewaldDokumen15 halamanMinerva Anestesiol 2017 GruenewaldMarjorie Lisseth Calderón LozanoBelum ada peringkat