Single Phase Inverter
Diunggah oleh
BHALAJI BIRLA0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
206 tayangan7 halamanThe inverter is the power electronic circuit, which converts the DC voltage into AC voltage. The DC source is normally a battery or output of the controlled rectifi
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe inverter is the power electronic circuit, which converts the DC voltage into AC voltage. The DC source is normally a battery or output of the controlled rectifi
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
206 tayangan7 halamanSingle Phase Inverter
Diunggah oleh
BHALAJI BIRLAThe inverter is the power electronic circuit, which converts the DC voltage into AC voltage. The DC source is normally a battery or output of the controlled rectifi
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Single Phase I nverter
What is meant by Inverter?
The inverter is the power electronic circuit, which converts the DC voltage into AC voltage. The
DC source is normally a battery or output of the controlled rectifier.
The output voltage waveform of the inverter can be square wave, quasi-square wave or low
distorted sine wave. The output voltage can be controlled with the help of drives of the switches.
The pulse width modulation techniques are most commonly used to control the output voltage of
inverters. Such inverters are called as PWM inverters. The output voltage of the inverter contain
harmonics whenever it is not sinusoidal. These harmonics can be reduced by using proper
control schemes.
What are the various types of Inverters?
Inverters can be broadly classified into two types. They are
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
Current Source Inverter (CSI)
When the DC voltage remains constant, then it is called voltage inverter(VSI) or voltage fed
inverter (VFI). When input current is maintained constant, then it is called current source inverter
(CSI) or current fed inverter (CFI). Sometimes, the DC input voltage to the inverter is controlled
to adjust the output. Such inverters are called variable DC link inverters. The inverters can have
single phase or three-phase output.
A voltage source inverter is fed by a stiff dc voltage, whereas a current source inverter is fed
by a stiff current source.
A voltage source can be converted to a current source by connecting a series inductance and
then varying the voltage to obtain the desired current.
A VSI can also be operated in current-controlled mode, and similarly a CSI can also be
operated in the voltage control mode.
The inverters are used in variable frequency ac motor drives, uninterrupted power
supplies, induction heating, static VAR compensators, etc.
The following table gives us the comparative study between VSI and CSI
VSI CSI
VSI is fed from a DC voltage source having
small or negligible impedance.
CSI is fed with adjustable current from a DC
voltage source of high impedance.
Input voltage is maintained constant The input current is constant but adjustable.
Output voltage does not dependent on the load
The amplitude of output current is independent
of the load.
The waveform of the load current as well as its
magnitude depends upon the nature of load
impedance.
The magnitude of output voltage and its
waveform depends upon the nature of the load
impedance.
VSI requires feedback diodes The CSI does not require any feedback diodes.
The commutation circuit is complicated
Commutation circuit is simple as it contains
only capacitors.
Power BJT, Power MOSFET, IGBT, GTO with
self commutation can be used in the circuit.
They cannot be used as these devices have to
withstand reverse voltage.
Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter
It is also known as "inverter leg".
Basic building blocks for full bridge, three phase and higher order inverters.
There are 2 switches by dividing the dc source voltage into two parts with the capacitors.
Each capacitor has the same value and has voltage Vdc / 2.
The top (S1) and bottom (S2) switch must be complementary to each other. (When S1 is
closed, S2 must be opened and vise versa)
Feedback (freewheeling) diodes are required to provide continuity of current for
inductive loads.
It provides current to flow even switches are opened.
Single Phase Full Bridge Converter
Full bridge converter is also basic circuit to convert dc to ac.
An ac output is synthesized from a dc input by closing and opening switches in an
appropriate sequence.
There are also four different states depending on which switches are closed.
State
Switches
Closed
Vo
1 S1 & S2 + Vdc
2 S3 & S4 -Vdc
3 S1 & S3 0
4 S2 & S4 0
State 1 and State 2
State 3 and State 4
Switches S1 and S4 should not be closed at the same time. S2 and S3 should be be closed
in parallel too.
Otherwise, a short circuit would exist across the dc source.
Real switches do not turn on or off instantaneously. Hence, switching transition times
must be accommodated in the control of switches.
Overlap of switch "on" will cause short circuit (shoot-through fault) across the dc voltage
source.
The time allowed for switching is called blanking time.
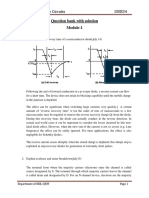
Square-wave Inverter
The figure below is the simple square-wave inverter to show the concept of AC waveform
generation.
The current waveform in the load depends on the load components.
The current waveform matches the shape of the output voltage for the resistive load.
The current will have more sinusoidal quality than the voltage for the inductive load because of
the filtering property of the inductance.
For a series RL load and a square wave output voltage, switches S1 and S2 is
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Voltage Source Converter: An IntroductionDokumen17 halamanVoltage Source Converter: An IntroductionChandrakant Tiwari100% (1)
- Classification of InvertersDokumen36 halamanClassification of InvertersMohammad ShoebBelum ada peringkat
- Single Phase AC Voltage ControllerDokumen6 halamanSingle Phase AC Voltage Controllermozaher1Belum ada peringkat
- Control Single-Phase IM Speed via Arduino PWMDokumen13 halamanControl Single-Phase IM Speed via Arduino PWMankitha0% (1)
- L9 Single Phase VSIDokumen114 halamanL9 Single Phase VSIPrashant Surana100% (1)
- Single Phase Series InverterDokumen9 halamanSingle Phase Series InverterDhivya NBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part IDokumen7 halamanExp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part Iusmpowerlab0% (1)
- Control of Single Phase To Three Phase AcDokumen10 halamanControl of Single Phase To Three Phase Acpriya dharshiniBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Dokumen69 halamanPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Single Phase PWM InverterDokumen56 halamanSingle Phase PWM InverterMary Paulson100% (2)
- Variable Voltage & Frequency Controlled 3 Phase Induction MotorDokumen6 halamanVariable Voltage & Frequency Controlled 3 Phase Induction MotorNAVEED ISHRAQBelum ada peringkat
- DC-AC Conversion - Lecture 10, 11 and 12Dokumen45 halamanDC-AC Conversion - Lecture 10, 11 and 12madiha100% (1)
- Single Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDokumen10 halamanSingle Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDeepu Chinna75% (4)
- Voltage Control of Single-Phase InvertersDokumen17 halamanVoltage Control of Single-Phase Invertersmailmanugs100% (1)
- Laboratory 12 - SMPSDokumen3 halamanLaboratory 12 - SMPSAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Electronic Circuits Question BankDokumen48 halamanAnalog Electronic Circuits Question BankchaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- HV Impulse CurrentDokumen9 halamanHV Impulse CurrentEdward CullenBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 328 Lecture 4Dokumen33 halamanEe 328 Lecture 4Eric KerrBelum ada peringkat
- DC - Ac Inv.Dokumen82 halamanDC - Ac Inv.Jegadeeswari GBelum ada peringkat
- Speed Control of Universal Motor Using 1 Phase SemiconverterDokumen2 halamanSpeed Control of Universal Motor Using 1 Phase SemiconverterscribsunilBelum ada peringkat
- On AC Voltage ControllersDokumen25 halamanOn AC Voltage ControllersSahil ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM for Constant PV Output VoltageDokumen6 halamanSimulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM for Constant PV Output Voltagekk_kamalakkannanBelum ada peringkat
- Synchronous Motor Drive Control MethodsDokumen17 halamanSynchronous Motor Drive Control MethodssidharthBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Open Book ExamDokumen4 halamanPower Electronics Open Book Examعبودي الامين100% (1)
- Chapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled RectifiersDokumen38 halamanChapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled Rectifiersyemane gebremichal100% (2)
- Buck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFDokumen13 halamanBuck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFsiti izyan100% (1)
- Lecture ThyristorsDokumen38 halamanLecture ThyristorsHamza Saeed AliBelum ada peringkat
- Single Phase PWM InverterDokumen11 halamanSingle Phase PWM InverterFoom A. Alshekh100% (2)
- L3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDokumen68 halamanL3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersSourabh KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- Four Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDokumen12 halamanFour Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- H-Bridge DC Motor Direction ControllerDokumen7 halamanH-Bridge DC Motor Direction ControllerKhan ElmeBelum ada peringkat
- DC-to-AC Converter Guide: Inverters ExplainedDokumen48 halamanDC-to-AC Converter Guide: Inverters ExplainedShanthu BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- DC Position ControlDokumen5 halamanDC Position ControlRamesh Babu100% (2)
- Electrical Machine-1 Manual PDFDokumen40 halamanElectrical Machine-1 Manual PDFsoumencha80% (5)
- DC-DC Converter FundamentalsDokumen63 halamanDC-DC Converter FundamentalsFaida HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Chopper Notes1Dokumen7 halamanChopper Notes1Ruthra DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation (SVPWM) For Three Phase Voltage Source Inverter Using Matlab Simulink - 24 PagesDokumen24 halamanImplementation of Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation (SVPWM) For Three Phase Voltage Source Inverter Using Matlab Simulink - 24 PagesMohamed Nabil100% (1)
- Vidyarthiplus.com - for Educational WebsiteDokumen57 halamanVidyarthiplus.com - for Educational Websitec_h_v_k_rBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Single Phase H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Microcontroller Atmel 89c51Dokumen52 halamanDesign of Single Phase H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Microcontroller Atmel 89c51Sabir VeBelum ada peringkat
- Commutation TechniquesDokumen13 halamanCommutation TechniquesSantosh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report of Buck Boost RegulatorDokumen15 halamanProject Report of Buck Boost RegulatorAnshul YadavBelum ada peringkat
- TEE3211 DrivesDokumen126 halamanTEE3211 DrivesWebster Fungirai100% (1)
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDokumen5 halamanPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Chapter Eight: Dc-Ac Conversion: InvertersDokumen57 halamanChapter Eight: Dc-Ac Conversion: InvertersMd NazimBelum ada peringkat
- Step-Down Cycloconverter Explained - Electrical ConceptsDokumen5 halamanStep-Down Cycloconverter Explained - Electrical ConceptsMohammad HamamdBelum ada peringkat
- MRDokumen15 halamanMRSuresh UmadiBelum ada peringkat
- L08 Power Amplifier (Class A)Dokumen24 halamanL08 Power Amplifier (Class A)mkrasanBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Dokumen55 halamanEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 3 To Perform Delay Operation Using Push ButtonDokumen4 halamanExperiment No. 3 To Perform Delay Operation Using Push ButtonShashikant PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Chopper DC To DC ConverterDokumen37 halamanChopper DC To DC ConverterGautam Kumar100% (1)
- DC to DC Converter FundamentalsDokumen40 halamanDC to DC Converter FundamentalsJamir CalBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Source InverterDokumen77 halamanVoltage Source InverterSaied Aly SalamahBelum ada peringkat
- Single Phase SPWM InverterDokumen46 halamanSingle Phase SPWM Inverternitin aryaBelum ada peringkat
- Ed Lab ManualDokumen27 halamanEd Lab ManualBonnieBelum ada peringkat
- Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering Power System AnalysisDokumen59 halamanSaraswathi Velu College of Engineering Power System Analysissaran_0666100% (1)
- Submitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniDokumen22 halamanSubmitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniAbirami RajaBelum ada peringkat
- PPT Introduction To DC-DC ConvertersDokumen16 halamanPPT Introduction To DC-DC Convertersmuhamad.badar9285Belum ada peringkat
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsDokumen16 halamanIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- UNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: ApplicationsDokumen37 halamanUNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: Applicationsdivya k sBelum ada peringkat
- Tan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Dokumen18 halamanTan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Eden HazardBelum ada peringkat
- ApplicationDokumen1 halamanApplicationBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- FileDokumen12 halamanFileBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- FileDokumen12 halamanFileBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- IJCSE Template PDFDokumen5 halamanIJCSE Template PDFBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Partial Discharge - Open ElectricalDokumen2 halamanPartial Discharge - Open ElectricalBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- SG Industrial RepoetDokumen23 halamanSG Industrial RepoetBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- ApplicationDokumen1 halamanApplicationBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Training Report: ScadaDokumen4 halamanIndustrial Training Report: ScadaBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- IJCSE Template PDFDokumen5 halamanIJCSE Template PDFBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Partial Discharge - Open ElectricalDokumen2 halamanPartial Discharge - Open ElectricalBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- 01 Basic Electric MachinesDokumen30 halaman01 Basic Electric MachinesBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- 01 Basic Electric MachinesDokumen30 halaman01 Basic Electric MachinesBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- DiplomaDokumen5 halamanDiplomaBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- V Ex Sy 200612042116Dokumen11 halamanV Ex Sy 200612042116BHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Hydro-Electric Power Generation Plant: Submitted By:-Vijay Yadav Ex-Final YearDokumen1 halamanHydro-Electric Power Generation Plant: Submitted By:-Vijay Yadav Ex-Final YearBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- IntroductionDokumen2 halamanIntroductionBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Aryan NHDCDokumen4 halamanAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Aryan NHDCDokumen4 halamanAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Introduction:-: Scalar Control of Induction MachineDokumen2 halamanIntroduction:-: Scalar Control of Induction MachineBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Aryan NHDCDokumen4 halamanAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- GalvanometerDokumen4 halamanGalvanometerBHALAJI BIRLABelum ada peringkat
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDokumen4 halamanAdvantages and Disadvantagesapi-460929148Belum ada peringkat
- Medal Log 20230820Dokumen11 halamanMedal Log 20230820Pedro HenriqueBelum ada peringkat
- Icx C360exp RetailDokumen183 halamanIcx C360exp Retail韩勇Belum ada peringkat
- VDISP subroutine for boundary conditionsDokumen4 halamanVDISP subroutine for boundary conditionsNrl SyafiniBelum ada peringkat
- Implement Oracle Configurator Functional FlowDokumen28 halamanImplement Oracle Configurator Functional FlowAntoineBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Nursing Lecture NotesDokumen203 halamanSurgical Nursing Lecture NotesKwabena AmankwaBelum ada peringkat
- Wish and If Only HandoutDokumen2 halamanWish and If Only HandoutAntonio MoraesBelum ada peringkat
- Nehru Place CTC PricelistDokumen7 halamanNehru Place CTC PricelistAnonymous nqIC9a8BIBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis Tours and TravelsDokumen21 halamanSynopsis Tours and TravelsRaj Bangalore38% (13)
- Solution Manual For Concepts of Database Management 9th Edition Joy L Starks Philip J Pratt Mary Z LastDokumen36 halamanSolution Manual For Concepts of Database Management 9th Edition Joy L Starks Philip J Pratt Mary Z Lastbuffyycleped3j28100% (41)
- SIMATIC S7 Connector Configurator enUS en-USDokumen104 halamanSIMATIC S7 Connector Configurator enUS en-USnemarc08Belum ada peringkat
- Converting To Base 256 From DecimalDokumen4 halamanConverting To Base 256 From DecimalZohaibAltafKhanBelum ada peringkat
- Choosing the Correct SensorDokumen11 halamanChoosing the Correct Sensorkarim mohamedBelum ada peringkat
- O365 and M365 Comparison Table - April - 2020 - USDDokumen1 halamanO365 and M365 Comparison Table - April - 2020 - USDDaniel SherwoodBelum ada peringkat
- Qoutation of Vehicle Tracking (GPS)Dokumen4 halamanQoutation of Vehicle Tracking (GPS)Tabrez ahmed100% (1)
- MicroTech III For Water Cooled Screw Chillers - D-EOMWC00A07-16EN - Operation Manuals - EnglishDokumen79 halamanMicroTech III For Water Cooled Screw Chillers - D-EOMWC00A07-16EN - Operation Manuals - EnglishchristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2: Understanding Local NetworksDokumen12 halamanUnit 2: Understanding Local Networksglenn.tabucanonBelum ada peringkat
- Purvanchal Vidyut Vitaram Nigam LTDDokumen1 halamanPurvanchal Vidyut Vitaram Nigam LTDVIKAS MISHRABelum ada peringkat
- Choco SolverDokumen47 halamanChoco SolverHenne PopenneBelum ada peringkat
- Records Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Dokumen9 halamanRecords Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Patricia Lorayne YapBelum ada peringkat
- End Sem - Solution & Marking SchemeDokumen41 halamanEnd Sem - Solution & Marking SchemeHaryanvi ChhoraBelum ada peringkat
- World Chess Championship Kramnik-Leko Brissago 2004Dokumen88 halamanWorld Chess Championship Kramnik-Leko Brissago 2004Guilherme Carelli100% (10)
- ReleaseNote - FileList of X441MAR - 2009 - X64 - V1.00Dokumen7 halamanReleaseNote - FileList of X441MAR - 2009 - X64 - V1.00Johanis.WBelum ada peringkat
- TreeSize Professional - Folder Contents of - CDokumen1 halamanTreeSize Professional - Folder Contents of - CHenrique GilBelum ada peringkat
- 1KW-6KW Low Frequency Solar Inverter/Charger With 80A MPPT Solar Charge ControllerDokumen1 halaman1KW-6KW Low Frequency Solar Inverter/Charger With 80A MPPT Solar Charge ControllerLenin Portugal QuitoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Information Theory's Noisy Channel Coding TheoremDokumen6 halamanIntroduction to Information Theory's Noisy Channel Coding TheoremasBelum ada peringkat
- Unified Modeling Language (UML) : An OverviewDokumen37 halamanUnified Modeling Language (UML) : An OverviewRaddad Al KingBelum ada peringkat
- How Do I Read My Friend'S Whatsapp Chat Without Taking His Phone?Dokumen6 halamanHow Do I Read My Friend'S Whatsapp Chat Without Taking His Phone?Mahesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Abbreviation SlidesDokumen23 halamanAbbreviation SlidesHind ChehabeddineBelum ada peringkat
- DC Motor DrivesDokumen11 halamanDC Motor DrivesVikram NikhilBelum ada peringkat