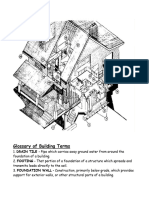
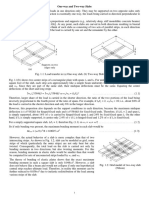
Parts of A Building
Diunggah oleh
Rai Rivera0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
97 tayangan17 halamanThis document defines key terms related to building design and construction. It discusses parts of buildings like roofs, trusses, crawl spaces, and attics. It also defines structural elements such as eaves, fascia boards, gutters, insulation, and ridges. Additionally, it provides definitions for architectural features including balconies, floor levels, setbacks, and height of buildings. Finally, it defines interior design terms such as baseboards, cornices, door jambs, windowsills, and stairwells.
Deskripsi Asli:
building
Judul Asli
parts of a building
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document defines key terms related to building design and construction. It discusses parts of buildings like roofs, trusses, crawl spaces, and attics. It also defines structural elements such as eaves, fascia boards, gutters, insulation, and ridges. Additionally, it provides definitions for architectural features including balconies, floor levels, setbacks, and height of buildings. Finally, it defines interior design terms such as baseboards, cornices, door jambs, windowsills, and stairwells.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
97 tayangan17 halamanParts of A Building
Diunggah oleh
Rai RiveraThis document defines key terms related to building design and construction. It discusses parts of buildings like roofs, trusses, crawl spaces, and attics. It also defines structural elements such as eaves, fascia boards, gutters, insulation, and ridges. Additionally, it provides definitions for architectural features including balconies, floor levels, setbacks, and height of buildings. Finally, it defines interior design terms such as baseboards, cornices, door jambs, windowsills, and stairwells.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 17
Building Design
Parts of the Building
PREPARED BY: ENGR. ALBERT PESTAO
TYPES OF ROOFS
TYPES OF TRUSSES
Definition of Terms
Site The geographic location of a construction project usually defined by legal
boundaries.
Sitework work done on site in preparation for a construction project, as excavation,
grading, shoring, backfilling, concreting, etc.
Property line One of the legally defined and recorded boundaries of a parcel of land.
Also called a lot line.
Easement A legal right by specified persons or public to make limited use of land of
another, as right of way.
Encroachment the unauthorized extension of a building, or part thereof, on the
property or domain of another.
Setback-the minimum required distance from every structure to the property lines of a
lot, established by the zoning ordinance to provide for air, light, solar access, and privacy.
Crawl space - A low or narrow space, such as one beneath the upper or lower story of a
building, that gives workers access to plumbing or wiring equipment.
Attic - any habitable space contained wholly within a roof pitched at not more than 36
degrees above the ceiling line of the storey immediately below, except for minor elements
such as dormer windows and the like.
Balcony means a small outdoor area, raised above the ground, directly accessible from
within the building and open except for a balustrade on at least one side.
Finished floor level (FFL) means the level of the upper surface of the relevant floor.
Finished ground level (FGL) means the ground level after completion of all excavation
and earthworks.
Definition of Terms
Habitable room means any room within a dwelling used or adapted to be used for the
purpose of living, sleeping, or the eating or cooking of food and includes lounge rooms, family
rooms, dining rooms, rumpus rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, but does not include
bathrooms, laundries, garages, or garden sheds.
Height of building means the vertical distance between natural ground level to the highest
point or points of the building.
Waterway means the drainage corridors, comprising natural streams, open drains and
floodways, dedicated for the primary purpose of drainage of urban areas.
Roofing - is the covering on the uppermost part of a building. A roof protects the building
and its contents from the effects of weather and the invasion of animals.
Eaves - is the edge of a roof. They normally project beyond the side of the building so they
can carry rain water away.
Fascia board - band running horizontally and situated vertically under a roof edge
Flashing construction material used to prevent passage of water around objects.
Roof Gutter - a narrow trough or duct which collects rainwater from the roof of a building
and diverts it away from the structure, typically into a drain.
Street gutter - a depression which runs alongside a city street, usually at the curb and
diverts rain and street-cleaning water away from the street and into a storm drain.
Roof Insulation material used to prevent heat coming from the roof towards the room or
ceiling below it.
Ridge the topmost part or covering of the roof, used to prevent passage of rainwater.
Downspout the pipe that collects rainwater coming from the roof towards the drain.
Wainscoting also known as wall paneling, is the inner wood covering of a wall.
Gazebo - is a pavilion structure, sometimes octagonal or turret-shaped, often built in a park,
garden or spacious public area.
Definition of Terms
Baseboard also called skirting board, skirting, mopboard, floor molding, as well as base
molding)
is a (generally wooden) board covering the lowest part of an interior wall. Its
purpose is to cover the joint between the wall surface and the floor.
Cornice any horizontal decorative moulding that crown the building, can be found over a
door or window, or in between a wall and a ceiling.
Door Jamb/Door Post - is the vertical portion of the frame onto which a door is secured.
Door Casing is an architectural design attached to the face of the door jamb. Also known
as door trim.
Door Header - is a support which is built in above a door, and it may be known simply as a
header. Windows also have headers.
Window Sill the lowest part of the window.
Soffit the underside of a ceiling, beam, slab, arch or eaves.
Ceiling Joists - are a number of horizontal beams, running parallel from one wall to the
opposite wall of the structure. The ceiling joist also support a flat roof, as well as the ceiling.
Floor Joists are a number of horizontal beams, running parallel from wall to wall and
support the floor of the structure.
Bridging cross bracing used between joists to stabilize them.
Studs a vertical member in the wall frame where the wall is attached to it.
Stairwell a vertical shaft in a building where the stair is built.
Dormer - is a structural element of a building that protrudes from the plane of
a sloping roof surface.
wainscoting
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Project InsuranceDokumen42 halamanProject InsuranceRajat PimplikarBelum ada peringkat
- Building LayoutDokumen10 halamanBuilding LayoutshayhaqBelum ada peringkat
- Port Concession Regime in Nigeria Issues and ChallengesDokumen11 halamanPort Concession Regime in Nigeria Issues and ChallengesAdefisayo HaastrupBelum ada peringkat
- General Contractor - RenFeel Rev03Dokumen10 halamanGeneral Contractor - RenFeel Rev03ridgell0% (1)
- All India Fire TarriffDokumen90 halamanAll India Fire Tarriffmib_santosh100% (2)
- Contractor's Safe Working Agreement: Assessing Occupational Health and Safety RiskDokumen5 halamanContractor's Safe Working Agreement: Assessing Occupational Health and Safety RiskAbinash Rout100% (1)
- Occupational Safety and Health Simplified For The Construction IndustryDokumen198 halamanOccupational Safety and Health Simplified For The Construction Industryhugo fariaBelum ada peringkat
- Road Users Handbook PDFDokumen180 halamanRoad Users Handbook PDFGaru VõBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Engineering Prospectus PDFDokumen310 halaman2020 Engineering Prospectus PDFChris WebbBelum ada peringkat
- Building Permit ChecklistDokumen28 halamanBuilding Permit ChecklistmrelfeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture1 IbDokumen10 halamanLecture1 IbJack JacintoBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To Osha HandoutDokumen28 halamanIntro To Osha HandoutEngr AliBelum ada peringkat
- 2006 Plan Review ChecklistDokumen21 halaman2006 Plan Review ChecklistmailreplyBelum ada peringkat
- Building A HouseDokumen11 halamanBuilding A HouseRichBelum ada peringkat
- NSPE Code of EthicsDokumen2 halamanNSPE Code of EthicsRizka WidyariniBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Management in Public Sector Buildings Manual May 2015 PDFDokumen61 halamanEnergy Management in Public Sector Buildings Manual May 2015 PDFzukchuBelum ada peringkat
- Nail Gun Safety: A Guide For Construction ContractorsDokumen20 halamanNail Gun Safety: A Guide For Construction Contractorswise222Belum ada peringkat
- Complete OSHA Safety and Management CourseDokumen8 halamanComplete OSHA Safety and Management Coursemansoor hussain100% (1)
- Working of Building ByelawsDokumen16 halamanWorking of Building ByelawsSree DevBelum ada peringkat
- R I A I ClausesDokumen3 halamanR I A I ClausesLetgo_010% (1)
- Emergency Preparedness ChecklistDokumen2 halamanEmergency Preparedness ChecklistDarrin Noble100% (1)
- 1.0 - Health Safety & Environment ManagementDokumen50 halaman1.0 - Health Safety & Environment ManagementNor Hafizah Azmiani100% (1)
- Intro To Construction Drawings NCCERDokumen46 halamanIntro To Construction Drawings NCCERsteverich2k6Belum ada peringkat
- Automatic Leveling TutorialDokumen8 halamanAutomatic Leveling TutorialMayseee06Belum ada peringkat
- Construction Check ListDokumen27 halamanConstruction Check ListUzank Mellitus100% (1)
- 360 Value Reconstruction Older HomesDokumen2 halaman360 Value Reconstruction Older HomesbenBelum ada peringkat
- Driver Qualification HandbookDokumen116 halamanDriver Qualification HandbookRavi Kalyana SundaramBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Vapor Intrusion Mitigation? How Does It Work?Dokumen2 halamanWhat Is Vapor Intrusion Mitigation? How Does It Work?ul84Belum ada peringkat
- Variation FormatDokumen9 halamanVariation FormatmohandiazBelum ada peringkat
- A Survey of Transferable Development Rights Mechanisms in New York City ResearchDokumen55 halamanA Survey of Transferable Development Rights Mechanisms in New York City ResearchcrainsnewyorkBelum ada peringkat
- Greenport Parking StudyDokumen32 halamanGreenport Parking StudyRiverhead News-ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- Proper and Safe Use of Scissor LiftsDokumen3 halamanProper and Safe Use of Scissor LiftsJulius SablayanBelum ada peringkat
- CA - RFIs by ContractorDokumen4 halamanCA - RFIs by Contractorრაქსშ საჰაBelum ada peringkat
- Dubai LawDokumen16 halamanDubai LawJohn WilliamBelum ada peringkat
- Basement WaterproofingDokumen14 halamanBasement WaterproofingkannanBelum ada peringkat
- Building Code Regulations - Building Code Act (Nova Scotia)Dokumen93 halamanBuilding Code Regulations - Building Code Act (Nova Scotia)Angel E. German100% (1)
- Section 1 Notes: Approach The VehicleDokumen8 halamanSection 1 Notes: Approach The VehicleSam RobertsBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokumen3 halamanNew Microsoft Word DocumentMekhalaRameshBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 18 - Trusses: A Truss Is An Assemblage of Members Making TrianglesDokumen14 halamanLecture 18 - Trusses: A Truss Is An Assemblage of Members Making TrianglesNilesh Yerawar100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryDokumen52 halamanLecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryWong Yi RenBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Home Electrical Inspection Checklist: OutletsDokumen2 halamanSample Home Electrical Inspection Checklist: OutletsjoookingBelum ada peringkat
- Contractor NotesDokumen2 halamanContractor NotesMICHAEL PRITCHARDBelum ada peringkat
- BCM 524 Lecture 1 PDFDokumen11 halamanBCM 524 Lecture 1 PDFAnonymous wTTx1LBelum ada peringkat
- Lect. 01.Dokumen82 halamanLect. 01.Kzy ayanBelum ada peringkat
- 0932-2 Garage - Pricing Specs 10 - 0517Dokumen674 halaman0932-2 Garage - Pricing Specs 10 - 0517blutec13Belum ada peringkat
- Fidic Conditions of ContractDokumen57 halamanFidic Conditions of ContractAbhishek Rajendrakumar Ram67% (3)
- Engineering GraphicsDokumen7 halamanEngineering GraphicsDEEPANGaeBelum ada peringkat
- Fahss High Res 2018Dokumen8 halamanFahss High Res 2018SubashBelum ada peringkat
- Estimating in Building Construction 7th Ed. - F. Dagostino, S. Peterson (Pearson, 2011) BBSDokumen24 halamanEstimating in Building Construction 7th Ed. - F. Dagostino, S. Peterson (Pearson, 2011) BBSNaeem HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Work Breakdown StructureDokumen8 halamanWork Breakdown StructurerenshagullBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 007Dokumen20 halamanChap 007Adi SusiloBelum ada peringkat
- Demand ManagementDokumen22 halamanDemand Managementpatil_962113756Belum ada peringkat
- Architectural Structural TerminologiesDokumen25 halamanArchitectural Structural TerminologiesMario RufinoBelum ada peringkat
- Architectural GlossaryDokumen5 halamanArchitectural Glossaryjomer llanosBelum ada peringkat
- Construction Terms For The Non - BuildersDokumen4 halamanConstruction Terms For The Non - BuildersRian Jose EscameBelum ada peringkat
- Carpentry TermsDokumen4 halamanCarpentry TermsSameh SamehBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Components A Building StructureDokumen25 halamanBasic Components A Building StructureSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- Ceiling FinishesDokumen7 halamanCeiling FinishesstenkchaiBelum ada peringkat
- Building TermsDokumen3 halamanBuilding TermsArianne CostalesBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Aided Design CE-388: Components of Building Components of BuildingDokumen25 halamanComputer Aided Design CE-388: Components of Building Components of Buildingfaizankhan23Belum ada peringkat
- Memo 097.7 - 070219 - Standard Labor Rates Regional District Engineering OfficesDokumen126 halamanMemo 097.7 - 070219 - Standard Labor Rates Regional District Engineering OfficesRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- BOD - Final Rates StandardizationDokumen35 halamanBOD - Final Rates StandardizationRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Sheets (Road Construction)Dokumen542 halamanCost Sheets (Road Construction)Rai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Contract Time Suspension: Checklist of Supporting Documents and Attachments For DotsDokumen6 halamanContract Time Suspension: Checklist of Supporting Documents and Attachments For DotsRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Design of PurlinDokumen14 halamanDesign of PurlinRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Base Plate, Pedestal and FootingDokumen8 halamanBase Plate, Pedestal and FootingRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Insert Values On Yelow TabDokumen12 halamanInsert Values On Yelow TabRai RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Calculus Exercise ProblemsDokumen159 halamanDifferential Calculus Exercise ProblemsRai Rivera100% (1)
- Artikel 03 ENGDokumen7 halamanArtikel 03 ENGbureta20011385Belum ada peringkat
- FF SpecificationDokumen42 halamanFF SpecificationRaoofBelum ada peringkat
- Staircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-0Dokumen30 halamanStaircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-0Anish KumarBelum ada peringkat
- PowerpointDokumen9 halamanPowerpointTudosa MihaiBelum ada peringkat
- E02 Standard Duty Data SheetDokumen2 halamanE02 Standard Duty Data SheetMuhammad Nurul AminBelum ada peringkat
- CMHC - Durable Wood Frame Construction For All ClimatesDokumen238 halamanCMHC - Durable Wood Frame Construction For All ClimatesSadaf SalehiBelum ada peringkat
- Rule of Thumb For RC DesignDokumen12 halamanRule of Thumb For RC DesignJeefry Arranguez50% (2)
- Building Materials Module 3 & 4 by SDokumen57 halamanBuilding Materials Module 3 & 4 by SNagendra GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Farhan AkiraDokumen2 halamanTugas Bahasa Inggris Farhan AkiraFarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Tulip Infratech P LTD.: Work OrderDokumen12 halamanTulip Infratech P LTD.: Work Orderchanderp_15Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Conceptual Framework 6 8Dokumen3 halaman11 Conceptual Framework 6 8Glenn MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Diskusi 2 BingDokumen3 halamanDiskusi 2 BingSilvia LarasatiBelum ada peringkat
- 0 3 Stuctural Design TablesDokumen5 halaman0 3 Stuctural Design Tablesosbo1611Belum ada peringkat
- Vitrified TilesDokumen3 halamanVitrified Tilesamitdey_dey18164Belum ada peringkat
- Suspended Ceiling SystemDokumen12 halamanSuspended Ceiling SystemcruxifixoBelum ada peringkat
- Curse of Strahd Castle Ravenloft Map FlowchartDokumen2 halamanCurse of Strahd Castle Ravenloft Map Flowchartakikumon100% (1)
- 10 Chapter 5Dokumen8 halaman10 Chapter 5Danish YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- IBS Note Topic 1 For Polytechnic StudentDokumen21 halamanIBS Note Topic 1 For Polytechnic StudentShazey HenixyBelum ada peringkat
- RC Design IIDokumen58 halamanRC Design IIvenkatesh19701Belum ada peringkat
- Unitized Curtain Wall SystemDokumen38 halamanUnitized Curtain Wall Systems.senthil nathan100% (1)
- ServiceabilityDokumen5 halamanServiceabilityAshwin B S RaoBelum ada peringkat
- StaircaseDokumen18 halamanStaircaseSwapna PandeBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook For Structural Engg - SP - 6 (5) - 1980Dokumen127 halamanHandbook For Structural Engg - SP - 6 (5) - 1980pradeepqBelum ada peringkat
- ProjectDokumen20 halamanProjectRakesh Rosan SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of High Rise Building in VancouverDokumen8 halamanEvolution of High Rise Building in VancouverTeo Peng KeatBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing & Sanitary BOQDokumen12 halamanPlumbing & Sanitary BOQsooricivil0% (1)
- Mr. MUNIRAJU'S 07-01-2023Dokumen5 halamanMr. MUNIRAJU'S 07-01-2023Naveen Kumar T SBelum ada peringkat
- Maison T Basic (Feel Free) EngDokumen9 halamanMaison T Basic (Feel Free) EngvasiBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Corrugated Metal Pipe For Tunnels-ContechDokumen8 halamanUse of Corrugated Metal Pipe For Tunnels-ContechRenanBelum ada peringkat
- Opera House Car ParkDokumen8 halamanOpera House Car ParkkrainajackaBelum ada peringkat