5
Diunggah oleh
YusephAwangSanaaniHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
5
Diunggah oleh
YusephAwangSanaaniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IVA.
DRUG STUDY
GENERIC NAME:
Cefuroxime
BRAND NAME:
Xefu
CLASSIFICATION:
Antibiotic
DOSAGE/FREQUENCY/ROUTE:
750 mg q8 hours ANST (negative)
for 4 doses
MECHANISM OF ACTION:
Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing
cell death.
INDICATION:
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis,infections of the urinary
andlower respiratory tracts, andskin and skin-
structureinfections caused byStreptococcus
pneumoniaeand S. pyogenes,Haemophillus
influenzae,Staphylococcus aureus,Escherichia coli.
CONTRADINDICATION:
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and related
antibiotics; pregnancy (category B), lactation.
SIDE EFFECTS:
Chills
diarrhea
fever
general feeling of illness or
discomfort
headache
itching of the vagina or genital area
pain during sexual intercourse
rigidity
sweating
thick, white vaginal discharge with no
odor or with a mild odor
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
Blistering, peeling, or loosening of
the skin
bloody, black, or tarry stools
clay-colored stools
cough or hoarseness
coughing up blood
decrease in urine output or decrease
in urine-concentrating ability
feeling of discomfort
fever with or without chills
general feeling of tiredness or
weakness
high fever
hives
increased menstrual flow or vaginal
bleeding
joint or muscle pain
large, hive-like swelling on the face,
eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands,
legs, feet, or sex organs
light-colored stools
NURSING RESPONSIBILITES:
Before:
Determine history of hypersensitivity
reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins,
and history of allergies, particularly to
drugs, before therapy is initiated.
Lab tests: Perform culture and sensitivity
tests before initiation of therapy and
periodically during therapy if indicated.
Therapy may be instituted pending test
results. Monitor periodically BUN and
creatinine clearance.
During:
Inspect IM and IV injection sites
frequently for signs of phlebitis.
Monitor for manifestations of
hypersensitivity (see Appendix F).
Discontinue drug and report their
appearance promptly.
Monitor I&O rates and pattern:
Especially important in severely ill
patients receiving high doses. Report any
significant changes.
Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea.
Although pseudomembranous colitis
(see Signs & Symptoms, Appendix F)
rarely occurs, this potentially life-
threatening complication should be
ruled out as the cause of diarrhea during
and after antibiotic therapy.
After:
Instruct patient to take medication around the
clock at evenly spaced times and to finish the
paralysis
prolonged bleeding from cuts
puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or
around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue
red or black, tarry stools
red or dark brown urine
red skin lesions, often with a purple
center
red, irritated eyes
seizures
swollen lymph glands
swollen or painful glands
unpleasant breath odor
upper right abdominal or stomach
pain
vomiting of blood
medication completely, even if feeling better
Advise patient to report signs of superinfection
and allergy
Instruct patient to notify health professional if
fever and diarrhea develop
Administraion :
After constitution, Cefuroxime may be given
intravenously or by deep IM injection into a large
muscle mass (such as the gluteus or lateral part
of the thigh). Before injecting intramuscularly,
aspiration is necessary to avoid inadvertent
injection into a blood vessel.
IVB. DRUG STUDY
GENERIC NAME:
Ranitidine
BRAND NAME:
None
CLASSIFICATION:
Therapeutic:
Anti-ulcer agents
DOSAGE/FREQUENCY/ROUTE:
1 amp IV now
MECHANISM OF ACTION:
Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2
receptor site located primarily in gastric
parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of
gastric acid secretion.
has some antibacterial action against
H. pylori.
INDICATION:
Treatment and prevention of heartburn,
acid indigestion, and sour stomach.
Prophylaxis of GI hemorrhage fromstress
ulceration.
CONTRADINDICATION:
Hypersensitivity, Cross-sensitivity may
occur; some oral liquids contain alcohol
and should be avoided in patients with
known intolerance.
SIDE EFFECTS:
Headache
dizziness
constipation
diarrhea
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
AV block; bradycardia; cardiac
arrhythmias; premature ventricular
beats.
Agitation; confusion; depression;
dizziness; fatigue; hallucinations;
headache; insomnia; malaise; motor
disturbances; somnolence; vertigo.
Alopecia; erythema multiforme; rash;
vasculitis.
Blurred vision.
Abdominal discomfort; constipation;
diarrhea; nausea; pancreatitis;
vomiting.
Acquired immune hemolytic anemia;
agranulocytosis; autoimmune
hemolytic or aplastic anemia;
granulocytopenia; leukopenia;
pancytopenia; thrombocytopenia.
Cholestatic or hepatocellular effects.
Arthralgias; myalgias.
Anaphylaxis; angioneurotic edema;
hypersensitivity reactions.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITES:
Instruct patient not to take new
medication w/o consulting physician.
Instruct patient to take as directed and
do not increase dose.
Allow 1 hour between any other antacid
and ranitidine.
Avoid excessive alcohol.
Assess patient for epigastric or
abdominal pain and frank or occult
blood in the stool,emesis, or gastric
aspirate.
Nurse should know that it may cause
false-positive results for urine protein;
test with sulfosalicylic acid.
Inform patient that it may cause
drowsiness or dizziness.
Inform patient that increased fluid and
fiber intake may minimize constipation.
Advise patient to report onset of black,
tarry stools; fever, sore throat;
diarrhea;dizziness; rash; confusion; or
hallucinations to health care professional
promptly.
Inform patient that medication may
temporarily cause stools and tongue to
appear gray black Instruct patients to
monitor for and report occurrence of
drug-induce dadverse reaction.
Administration:
For intravenous or intramuscular injection or,
after dilution, for intravenous infusion. Whenever
solution and container permit, parenteral drug
products should be inspected visually for
particulate matter and discolouration prior to
administration.
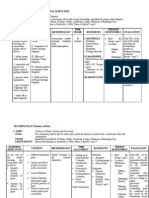
IVD. NURSING CARE PLAN
CUES/NSG.DX. OBJECTIVES OF CARE NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
Subjective Cues:
Medyo nanghihina ako
(I fell weak)
Natural ang hypertensive
sa pamilya namin
(hypertension runs in the
family)
As verbalized by the patient.
Objective Cues:
Variations in blood
pressure.
Edema
V/S taken as
follows:
T: 36.8
degrees
Celcius
P: 84
beats/min.
R: 23 rpm
BP: 150/85
NSG. DX.
Decreased cardiac output
related to decreased venous
return.
To make the patient
participate in activities
that reduce blood
pressure or cardiac
work load.
To help the patient to
achieve fast recovery
Independent:
Monitor blood pressure
of the patient. Measure
in both arms or thighs
three times, 3-5 minutes
apart while patient is at
rest, then sitting, then
standing for initial
evaluation.
Observe skin color,
moisture, temperature
and capillary refill time.
Note dependent or
general edema.
Provide calm, restful
surroundings,minimize
environmental activity or
noise.
Maintain activity
restrictions.
Instruct in relaxation
techniques, and guided
imagery.
Collaborative:
Implement dietary
sodium, fat, and
cholesterol
restrictions as
indicated.
Comparison of pressures
provides a more complete
picture of vascular
involvement or scope of
the problem.
Presence of pallor, cool,
moist skin and delayed
capillary refill time may be
due to peripheral
vasoconstriction
May indicate heart failure,
renal or vascular
impairment.
Help reduce sympathetic
stimulation, promotes
relaxation.
Reduces physical stress and
tension that affect blood
pressure and course of
hypertension.
Can reduce stressful
stimuli, produce calming
effect, thereby reduce
blood pressure.
These restrictions can help
manage fluid retention and
with associated
hypertensive response,
which decrease cardiac
workload.
Monitoring of blood
pressure of the patient
was conducted very fast
because patient isnt
feeling well. blood
pressure was noted
only 2 times in more
than 3-5 minutes apart
because patient took a
break for not feeling
well.
The patient agreed on
having her skin color
noted , capillary refill
time and temperature
taken.
Her mother and a nurse
was to assist her
whenever she needs
help to avoid physical
activities.
We quickly chaged the
bed linens
Patient was
informed about
her current BP
status and
made aware
that it is quite
high ranging in
140-150/85-90
Patient was
relieved to
know she has
normal body
temperature
Patient is
managing her
health well due
to more time to
rest and relax
with the aid of
her mother and
a nurse.
Patient was
glad to have a
fixed and clean
bed.
IVE. HEALTH TEACHING PLAN
SUBJECT MATTER: PRE-ECLAMPSIA AND ITS MANAGEMENT
TIME ALLOTMENT: 45 MINUTES
GENERAL OBJECTIVE: At the end of health teaching, the client will be able to acquire knowledge about the nature of illness, its causes and effective measures.
ASSESSMENT TEACHING OBJECTIVE CONTENT STRATEGY EVALUATION CRITERIA
LEARNING NEEDS:
Patient wants to know ways to
lower her blood pressure and ways
to have a fast recovery in the CS
unit.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
Decreased cardiac output related
to decreased venous return. (pre-
eclampsia,hypertension)
After the health education client
willbe able to:
verbalize own understanding
of what is pre-eclampsia.
be educated about vital
information regarding high
blood preassure.
be able to identify risk factors
that made the client more
susceptible to the disease
be able to enumerate ways to
prevent further rise in blood
pressure.
be able to enumerate common
drugs.
Preeclampsia is when a
pregnant woman develops high
blood pressure and protein in
the urine after the 20th week
(late 2nd or 3rd trimester) of
pregnancy.
"Blood pressure" is the force of
blood pushing against the walls
of the arteries as the heart
pumps blood. If this pressure
rises and stays high over time,
it can damage the body in
many ways one is pre-
eclampsia.
The exact cause of pre-eclampsia is
unknown.
Possible causes include:
Autoimmune disorders
Blood vessel problems
Your diet
Your genes
Risk factors include:
First pregnancy
Multiple pregnancy (twins or
more)
Obesity
Being older than age 35
History of diabetes, high
blood pressure, or kidney
disease.
Discussion: student nurse will
define pre-eclampsia based
from acquired knowledge and
will ask participation of
patient by giving the
definition in their own cue.
Discussion: student nurse will
talk about pre eclampsia and
blood pressure specially
hypertension so patient
would have an idea of the
relation of hypertension to
pre-eclampsia.
Picture presentation and
Discussion: letter-size bond
paper containing picture of
ways on how to avoid
hypertension
student nurse will explain the
different ways of avoiding
high blood pressure while
showing the picture and will
also ask the patient about the
different ways she
remembered
Discussion: student nurse will
now talk about the possible
causes of pre-eclampsia and
its risk factors also.
Direct Questioning:
After the first discussion
nursing student will asks
the client on what she think
pre-eclampsia is on her own
understanding.
On the second discussion
patient will be asked of
what she knows now of the
relation of hypertension to
pre-eclampsia.
On the third discussion
patient will be asked to give
ways on how to avoid
hypertension.
Next, patient will be asked
to give some possible causes
of pre-eclampsia and these
will be greatly emphasize for
her.
Patient will be asked to give
various ways to prevent
further rise of blood
pressure any will do, missed
ones will be reviewed for
her to remember again.
Patient will be asked to give
the names of the drugs that
Some ways to prevent further rise
in blood pressure are:
Lose extra pounds
Exercise regularly
Eat a healthy diet
Reduce sodium in your diet
Limit the amount of alcohol
you drink
Avoid tobacco products and
secondhand smoke
Cut back on caffeine
Reduce your stressMonitor
your blood pressure at home
and make regular doctor's
appointments
Get support from family and
friends
Medicines used to control chronic
high blood pressure during
pregnancy include:
Methyldopa
Nifedipine
Some high blood pressure
medicines are dangerous during
pregnancy.3 If you take high
blood pressure medicines, talk to
your doctor about the safety of
your medicine. Discuss this before
you become pregnant or as soon
as you learn you are pregnant.
Make sure that your doctor has a
complete list of all medicines that
you take.
Other blood pressure medicines
that may be used include:
Hydralazine - This is an
intravenous medicine
for quickly lowering
severely high blood
pressure during
pregnancy.
Labetalol - It's an
intravenous medicine
Discussion: student nurse now
will discuss about the ways to
prevent further rise of the
blood pressure emphasizing it
clearly for the patient.
Discussion: now student will
lastly discuss about the
various drugs used for the
treatment of pre-eclampsia.
could help in her recovery
from pre-eclampsia.
for quickly lowering
severely high blood
pressure in the
hospital. It's also an
oral medicine for
controlling high blood
pressure during
pregnancy.
Lowering blood pressure too much
or too fast can reduce blood flow
to the placenta, causing problems
for the baby. So medicine is
reserved for preventing severely
high blood pressure levels that
may be life-threatening to you or
your baby.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- AmoebiasisesusesDokumen9 halamanAmoebiasisesusesYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Rationale: DiagnosisDokumen2 halamanAssessment Rationale: DiagnosisYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen6 halamanChapter 2YusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Statement of Understanding in NCMDokumen1 halamanStatement of Understanding in NCMYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- What Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureDokumen9 halamanWhat Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Final Draft RevisedDokumen17 halamanFinal Draft RevisedYusephAwangSanaani100% (1)
- Case AnalysisDokumen26 halamanCase AnalysisYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Prenatal 1107Dokumen5 halamanPrenatal 1107YusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Otitis Media NCPDokumen2 halamanOtitis Media NCProneln100% (9)
- Prenatal Stuffs and Information StuffsDokumen31 halamanPrenatal Stuffs and Information StuffsYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- What Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureDokumen9 halamanWhat Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- What Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureDokumen9 halamanWhat Is An Episiotomy?: Reasons For The ProcedureYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To ComputersDokumen6 halamanAn Introduction To ComputersYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- DotsDokumen5 halamanDotsYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- What is an episiotomyDokumen11 halamanWhat is an episiotomyYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Family Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanFamily Nursing Care PlanJamil Lorca64% (14)
- DotsDokumen5 halamanDotsYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Sanaani, Yuseph Crispe A. Bsn-2b (Summer) InfolabDokumen12 halamanSanaani, Yuseph Crispe A. Bsn-2b (Summer) InfolabYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Family Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanFamily Nursing Care PlanJamil Lorca64% (14)
- Individual Daily Program: Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University COLLEGE OF NursingDokumen1 halamanIndividual Daily Program: Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University COLLEGE OF NursingYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Informatics Lab.Dokumen8 halamanInformatics Lab.YusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of The NeonateDokumen12 halamanNursing Care of The NeonateYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of The NeonateDokumen12 halamanNursing Care of The NeonateYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- NH11functionalpatterns PADokumen4 halamanNH11functionalpatterns PAYusephAwangSanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching PlanDokumen16 halamanTeaching Plandeklear100% (6)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Reaction PaperDokumen2 halamanReaction PaperLinzie CariquetanBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Procedure Checklist: Administering Oral MedicationsDokumen2 halamanNursing Procedure Checklist: Administering Oral MedicationsOrl Trinidad100% (1)
- Seafarer Health Forms for COVID-19 ClearanceDokumen3 halamanSeafarer Health Forms for COVID-19 ClearanceYuraBelum ada peringkat
- Robinson Mesothelioma LIVRODokumen381 halamanRobinson Mesothelioma LIVROdocBelum ada peringkat
- Doctor LLLLL 4Dokumen54 halamanDoctor LLLLL 4loveBelum ada peringkat
- The New Science of Strong TeethDokumen4 halamanThe New Science of Strong TeethThe Bioclear ClinicBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Quiz 1. MCNDokumen4 halamanChapter Quiz 1. MCNAngie SaquingBelum ada peringkat
- Memorandum of Agreement Sample 124Dokumen3 halamanMemorandum of Agreement Sample 124Luther Torres CaloringBelum ada peringkat
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanTranexamic Acid Drug Studyswitchlers anneBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Development EssayDokumen5 halamanDrug Development EssayDoyin AwodeleBelum ada peringkat
- Zinc DeficiencyDokumen24 halamanZinc DeficiencyElita Maritan SBelum ada peringkat
- Course Module on Health Appraisal and Safety GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanCourse Module on Health Appraisal and Safety GuidelinesKate AlindajaoBelum ada peringkat
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis AdultDokumen3 halamanType 2 Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis AdultSiti Kurniah 'nsm'Belum ada peringkat
- Vaccine Adverse Reaction Reporting System by Vaccine and MaufacturerDokumen1.191 halamanVaccine Adverse Reaction Reporting System by Vaccine and MaufacturerGuy RazerBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDokumen13 halamanAnemia of Chronic Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Treatmentmaverick mazeBelum ada peringkat
- Feature WritingDokumen2 halamanFeature WritingRoselle PangilinanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study AmoxicillinDokumen3 halamanDrug Study AmoxicillinJanzelvine Lee MontenegroBelum ada peringkat
- Dentist-Patient Communication-A Maior Factor in Treatment PrognosisDokumen3 halamanDentist-Patient Communication-A Maior Factor in Treatment Prognosis'Montserrat Orozco GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- ParestesiDokumen1 halamanParestesiYolanda YiBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Health Record: Department of EducationDokumen1 halamanDental Health Record: Department of EducationBriones Tiamzon Jordan0% (1)
- Intern Journal reading-MRI-osteomyelitis-OOOE-2008Dokumen6 halamanIntern Journal reading-MRI-osteomyelitis-OOOE-2008yuni madjidBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Medication History Interview: Dr. Vijay B. Lambole Associate Professor, SNLPCP, UmrakhDokumen20 halamanPatient Medication History Interview: Dr. Vijay B. Lambole Associate Professor, SNLPCP, Umrakhvijaylambole0% (1)
- FSSAI extends tenure of Hygiene Rating Audit AgenciesDokumen1 halamanFSSAI extends tenure of Hygiene Rating Audit Agenciessheela bethapudiBelum ada peringkat
- Fosfomycin Susceptibility in Urinary Tract EnterobacteriaceaeDokumen3 halamanFosfomycin Susceptibility in Urinary Tract EnterobacteriaceaeNawwal NaeemBelum ada peringkat
- Penerapan Telenursing Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan: Literature ReviewDokumen8 halamanPenerapan Telenursing Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan: Literature ReviewAdi RiskiBelum ada peringkat
- DPT VaccinesDokumen2 halamanDPT VaccinesSowmiyaBelum ada peringkat
- EOB Code Crosswalk To HIPPA Standard CodesDokumen1.665 halamanEOB Code Crosswalk To HIPPA Standard CodesVikas TomarBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs and Cosmetics ActDokumen29 halamanDrugs and Cosmetics ActRanvidsBelum ada peringkat
- What is AnencephalyDokumen11 halamanWhat is AnencephalyAnironOrionBelum ada peringkat
- CD Post TestDokumen11 halamanCD Post TestNia KayeBelum ada peringkat