QB - ME5635-Design of Jigs, Fixtures and Press Tools-Jan-May.2014
Diunggah oleh
Carlos Williamson0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
226 tayangan27 halamanQuestion Bank - April / May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools Saveetha School of Engineering Saveethu University Chennai - 602 105 Department of Mechanical Engineering Academic Year 20122013 / Even Semester.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
QB_ME5635-Design of Jigs, Fixtures and Press Tools-Jan-May.2014
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniQuestion Bank - April / May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools Saveetha School of Engineering Saveethu University Chennai - 602 105 Department of Mechanical Engineering Academic Year 20122013 / Even Semester.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
226 tayangan27 halamanQB - ME5635-Design of Jigs, Fixtures and Press Tools-Jan-May.2014
Diunggah oleh
Carlos WilliamsonQuestion Bank - April / May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools Saveetha School of Engineering Saveethu University Chennai - 602 105 Department of Mechanical Engineering Academic Year 20122013 / Even Semester.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 27
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
Saveetha School of Engineering
Saveetha University
Chennai 602 105
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Academic Year 2012- 2013 / Even Semester
QUESTION BANK
Sub. Code/Name: ME5635-Design of Jigs, Fixtures and Press Tools
Year/Sem: III/VI
(Use of approved design data book is permitted)
UNIT I PURPOSE, TYPES AND FUNCTIONS OF JIGS AND FIXTURES
Tool design objectives Production devices Inspection devices Materials used in J igs and
Fixtures Types of J igs Types of FixturesMechanical actuation Pneumatic and Hydraulic
Actuation Analysis of clamping force Tolerance and Error analysis.
Part A (2 Marks)
1. Define the term tool design.
Ans: Tool design is the process of designing and developing the tools, methods and techniques
necessary to improve manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
2. What are the types of tooling?
Ans: (i) Cutting tools (single and multiple point cutting tools), (ii) press tools, (iii) dies, (iv) jigs
and fixtures, and (v) gauges.
3. Define the term jig.
Ans: J ig is a work holding device that holds, supports and locates the workpiece and guides
cutting tool for a specific operation.
4. Define the term fixture.
Ans: Fixture is a work holding device that holds, supports and locates the workpiece for a
specific operation but does not guide the cutting tool.
5. Name any two materials commonly used in jigs and fixtures.
Ans: 1. HSS (High Speed Steel),
2. High Tensile Steel,
3. Oil Hardening Non-shrinking tool steel, and
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 1 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
4. Case Hardening Steel
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
6. What is fool proofing?
Ans: The locating system should positively prevent wrong loading of the workpiece in a fixture
by fool proofing.
Make the jig fool proof; That is, to arrange it so that work cannot be inserted except in correct
way.
7. What is meant by referencing?
Ans: Referencing is the process of properly positioning the part with respect to the cutter or other
tool.
8. Define degree of freedom?
Ans: An unrestricted object is free to move in any of the twelve possible directions. An object is
free to revolve around one move parallel to any axis in either direction.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 2 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
9. What is meant by 3-2-1 location or 6 point location?
mpletely restrained by providing three
0. Define locating devices.
ts of a jigs or fixture which help a workpiece to seat in proper
1. Name any four locators that are generally used.
rs and nest or cavity locators.
Ans: According to this principle, a workpiece can be co
location points in one plane, two location points in second plane and one location point in the
third plane. Therefore, it is called 3-2-1 principle of location.
1
Ans: Locators are those par
position in it. Depending on the type of work, locators are designed. There is a large variety of
locating devices or locators and methods of locating available to a jig and fixture designed. The
majority of workpieces can be located with these methods.
1
Ans: Pin and button locators, V-locators, bush locato
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 3 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
12. Define jack pin locator.
itions itself automatically by means of spring force according to the
3. Define clamping devices.
d to hold the workpiece in the correct relative position in the jig or
Ans: The locator which pos
need is known as jack pin locator.
1
Ans: clamping devices are use
fixture. It should ensure that the workpiece is not displaced under the action of cutting forces.
For efficient operation, firm clamping of the workpiece is must.
14. Sketch a Bayonet clamp.
Ans:
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 4 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
15. What is meant by fit?
tionship between mating parts with respect to the amount of clearance
6. Define and show the diagrammatic representation of clearance fit.
hole size for all possible
7. Show the diagrammatic representation of interference fit.
ize being larger than the maximum
Ans: Fit expresses the rela
or interference which exists when they are assembled together.
1
Ans: This fit results when the shaft size is always less than the
combinations within their tolerance ranges. Relative motion between shaft and hole is always
possible.
1
Ans: This is a fit which always results in the minimum shaft s
hole size for all possible combinations within their tolerance ranges. Relative motion between the
shaft and hole is impossible.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 5 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
18. Define and show the diagrammatic representation of transition fit.
the same size. This fit is
9. What is meant by tolerance?
of an error of manufacturing. It is the acceptance of the fact
0. Distinguish between unilateral and bilateral tolerance.
irection from the nominal size, the
Ans: A pure transition fit occurs when the shaft and hole are exactly
theoretically the boundary between clearance and interference and is practically impossible to
achieve, but by selective assembly or careful machining methods, it can be approached within
very fine limits.
1
Ans: Tolerance is the acceptance
that a dimension cannot be economically made to the exact size specified by the designer.
Tolerance is the difference between the maximum limit of size and the minimum limit of size.
2
Ans: Unilateral tolerance is one that applies in one d
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 6 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
permissible variation in the other direction is zero. The bilateral tolerance, the tolerance is split
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
into two parts (equal or unequal) and applied on either side of the nominal size. The deviations
on either side are expressed as plus and minus values to the nominal size.
21. What are the different types of errors considered in design of jig?
Ans: 1. Locating errors, 2. Clamping error, and 3. Fixture error
Part B (16 Marks)
1. (a) Discuss in detail the principles employed in jigs and fixtures design. [8]
(b) List out the advantages of jigs and fixtures. [8]
2. (a) Explain briefly the main elements of jig and fixture. [6]
(b) Compute the fundamental deviations for a circular hole of 35 mm diameter finished to
H7 tolerance. [10]
3. Discuss in detail the locating principles. [16]
4. With a neat sketch explain air to hydraulic pressure booster for clamping application.
[16]
5. (a) Describe any two types of locating device with neat sketches. [8]
(b) Compute the fundamental deviations for a circular shaft of 60 mm diameter finished
to g6 tolerance. [8]
6. Sketch and explain any two of the mechanically actuated clamps. [16]
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 7 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
UNIT II JIGS
Drill bushes Different types of jigs Plate latch Channel, box- post- angle plate- angular
post- turnover- pot jigs Automatic drill jigs Rack and pinion operated Air operated J igs
components Design and development of J igs for given components.
PART A (2 Marks)
1. What are the elements of jigs?
Ans: J ig body, jig feet, jig bushing, jig plate or bush plate, locators, clamps, fool proof element.
2. List the construction methods of jigs?
Ans: Built up construction, Welded construction, cast construction.
3. List the types of jigs.
Ans:
a. Template J ig
b. Plate jig
c. Channel jig
d. Leaf jig
e. Pot jig
f. Turnover jig or table jig
g. Box jig or tumble jig
h. Trunnion jig
i. Indexing jig
j. Post jig
k. Sandwich jig
l. Nut cracker jig
m. Pumping or universal
n. Latch jig
o. Vise jig
p. Solid jig
q. Angle plate jig
r. Angular post jig.
4. What is the function of jig bushes?
Ans: Drill bushes are used to guide drills, reamers and other cutting tools to the workpiece.
5. What is an open press fit bush?
Ans: Press fit bushes are the most common type of bushes and are pressed by interference fit in
the bush plates also referred to as jig plates.
6. What is meant by renewable bush?
Ans: These bushes are generally used for continuous or for large batch production. These bushes
are used in liner bushings which are installed in the jig plate.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 8 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
7. How the rotation and movement of bush can be prevented? Show with sketch.
Ans: By providing set screws, the bushes are retained with the jig plate.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 9 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
8. Sketch the headed drill bush.
Ans:
9. Sketch a shaped drill bush.
Ans:
10. Sketch a channel jig.
Ans:
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 10 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
11. State the use of angular post jig.
Ans: These jigs are used to drill holes in the workpiece at some angles.
12. State the use of post jigs.
Ans: The post jig is used for drilling and reaming operations. It is named so because it has a solid
post to locate the workpiece from its bore. These jigs are mainly useful for hollow workpiece.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 11 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
13. Define sandwich jig.
Ans: These jigs are a form of plate jig with a back plate. This type of jig is ideal for thin or soft
parts that could bend or wrap in another style of jig. Here again, the use of bushings is
determined by the number of parts to be made.
14. State the provision made on latch or leaf jigs.
Ans: Leaf plate is capable of swinging about a fulcrum point so that it can open or close the load
or unload the workpiece.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 12 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
15. What are the advantages of trunnion jig?
Ans: (i) the workpiece is located and clamped to the carrier which also carries the drill plates.
(ii) the carrier is mounted on trunnion so that it can be rotated from face to face.
(iii) it can be positioned and locked using an indexing device.
16. Define indexing device.
Ans: Device used for dividing the rotation of the circular workpiece into equal number of
portions is known as indexing device.
17. What are the various possibilities to operate automatic drill jigs?
Ans: (i) Mechanical
(ii) Pneumatic or air operated
(iii) Hydraulic operated
(iv) pneumo-hydraulic
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 13 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
Part B (16 Marks)
1. (a) Explain the important elements of jig. [8]
(b) Explain any two types of drill bush with neat sketch. [8]
2. With neat sketches explain the uses of plate and channel jigs. [16]
3. Explain the use of turnover jig with a neat diagram. [16]
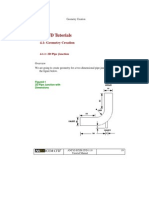
4. Design a drill jig for the use when drilling the 12 mm diameter hole in the shank of the adapter
show in Fig. 2.1. 16]
Fig. 2.1
5. Explain the box jig and angular post jig with neat sketch. [16]
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 14 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
6. Design and develop a jig which can be used for drilling holes on the web of a flange coupling
as shown in Fig. 2.3. [16]
Fig. 2.3
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 15 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
UNIT III FIXTURES
General principles of boring- lathe- milling and broaching Fixtures Grinding- planning and
shaping fixtures- assembly- Inspection and welding fixtures Modular fixtures Design and
development of fixtures for given component.
PART A (2 Marks)
1. What are fixtures and what are they used for?
Ans: Fixtures are used to hold work pieces during machining when they are to be produced in
large numbers. Fixtures are a form of tooling that are used to position parts relative to each other
for fabricating purposes.
2. What are the standard work holding devices used in lathes?
Ans: i) Chucks
ii) Collets
iii) Face plate
iv) Mandrels
3. State any four design points to be considered while designing a lathe fixture.
Ans: i) The fixture should be accurately balanced in order to avoid vibrations while revolving.
ii) Clamps and other holding devices should be designed in such a way that they will not be
loosened by centrifugal force.
iii) There should be no projections of the fixture which may cause injury to the operator.
iv) The fixture should be light in weight as far as possible, since it is rotating.
4. What is the function of mandrels in turning fixture?
Ans: It is used to hold the hollow workpiece and mandrels.
5. Mention the application of turning fixture.
Ans: The fixture body is designed to drill a hole in the face of a cubical shaped workpiece.
6. Mention any four essential features made on milling fixtures.
Ans: i) Base
ii) Tenon strips
iii) Setting block
iv) Locating elements
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 16 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
7. What are the factors to be considered while selecting string milling fixture?
Ans: i) The length depends on the size of the workpiece.
ii) Length of milling machine table
iii) Length of stroke of the table.
iv) The workpiece should be clamped properly to ensure accurate machining.
8. When are indexing fixtures used?
Ans: When a number of surfaces are to be milled on a periphery of a workpiece are gear teeth,
slots, splines in shafts, etc.
9. State the classification of boring bars.
Ans: i) Stub bar
ii) Single-piloted bar
iii) Double-piloted bar
10. What are the different types of broaching operations?
Ans: i) Keyway broaching
ii) Hole broaching
iii) Gear broaching
11. Define key way broaching fixture.
Ans: The fixture which is used for cutting internal key-ways in pulleys, gears, sprockets, etc are
known as key way broaching fixtures.
12. What are static fixtures?
Ans: The static fixtures are set-up clamping or fit-up fixtures used for accurate positioning of
workpieces and companion parts of the product assembly.
13. What are the steps involved in operating pressing fixtures?
Ans: i) Location arrangement of housing
ii) Locator for the part to be pressed
iii) System for alignment of the parts to be pressed with the housing
iv) Arrangement for application of press force to drive the part into the housing
14. What are inspection fixtures? State its types.
Ans: Inspection fixtures are used to check the quality of the workpieces as well as the
components or parts of the machines. Types:
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 17 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
a) In-process inspection fixtures
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
b) Off-line inspection fixtures
15. What are the important elements of inspection fixtures?
Ans: a) Locating element
b) Clamping element
c) Gauging element
d) Auxiliary element
16. Mention any two design principles applicable to welding fixture.
Ans: Welding spatter should not be allowed to fall on the threaded parts of the clamping
elements.
Welding fixture should not be so designed that it does not get overheated due to continuous
work.
17. What is the use of tack welding fixture?
Ans: Tack welding fixtures are used to locate the components of a weldment in their correct
relationship with proper clamps while a welder tacks them prior to their final welding.
18. State the main function of assembly fixtures
Ans: The main function is to hold different components together in their proper relative position
at the time of assembling them.
19. What are the sub-classification of special purpose fixtures?
Ans: a) Static fixtures
b) Mobile or dynamic fixtures
20. How are mobile fixtures classified?
Ans: a) Unitary fixtures
b) Multiple fixtures
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 18 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
Part B (16 Marks)
1. Design a suitable milling fixture to cut a keyway of size 3 x 3 mm on a solid shaft of 30 mm
diameter and 100 mm length.
2. With proper sketch explain the operation of a modular fixture with example used in practice.
3. Illustrate the working of a lathe fixture.
4. Illustrate the working of a Gang milling fixture.
5. Design a milling fixture to make a slot of 30 x 10 x 10 mm as shown in the following Fig.
3.1.
Fig. 3.1
6. Design a milling fixture to make a slot of 70 x 10 x 10 mm as shown in the Fig. 3.2.
Fig. 3.2
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 19 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
UNIT IV PRESS WORKING TERMINOLOGIES
Press working terminology Presses and press accessories Computation of capacities and
tonnage requirements Elements of progressive combination and compound dies Die block
die shoe Bolster plate Punch plate Punch holder Guide pins and bushes Strippers
Knockouts Stops Pilots Selection of standard die sets strip lay out Strip lay out
calculations.
Part A (2 Marks)
1. How is cutting operation carried out?
The work piece is stressed beyond its ultimate strength and cut-off into two Pieces.
2. List out the various cutting operations.
a. Blanking
b. Punching
c. Shearing
d. Parting off
3. Mention the three different ways of working sheet metal in presses.
a. Shearing
b. Bending
c. Drawing
4. Classify sheet metal operations
a. Cutting operations
b. Forming operations
5. State the advantages of press working operations.
a. Material economy
b. High productivity
c. Uniformity of parts
d. Use of less labour.
6. What are the applications of press working operations?
a. Electronic appliances
b. Steel furniture
c. Coach building
d. Automobile industry
7. Name some types of forming operations.
a. Bending
b. Drawing
c. Squeezing
d. Embossing
8. List out the press working terminology.
a. Base
b. Bolster plate
c. Die holder
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 20 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
d. Die
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
e. Stripper
f. Punch
g. Pitman
h. Stroke
i. Guide pin
j. Back up plate
9. When will be hydraulically driven presses used?
Whenever large force and slow speed are required in forming, pressing and drawing operation,
hydraulically driven presses are used.
10. How will you select the proper material for press tools?
a .Hardness
b. Compressive strength
c. Bending strength
d. Toughness
11. What factors are considered for selecting an appropriate press for a given job?
a. Force required to be cut the metal
b. Die space
c. Size and type of die
d. Stroke length
e. Shut eight
f. Type of operation
g. peed of operation
12. List down the material used for press working operations.
a. Mild steel
b. Stainless steel
c. Brass
d. Copper
e. Aluminium
f. Hard rubber
g. Fiber
13. What is a progressive die? When should a progressive die be used?
A die which is used to perform two or more operations at different stages every time when the
ram descends is called progressive die. It is mainly used where the accuracy of the products is
maintained.
14. Explain the function of bolster plate in press tool.
The bolster plate is the thick plate mounted on the base. It is used for locating and supporting the
die assembly. It is usually 5 to 12.5 mm thick plate.
15. What are the methods of holding pilots?
a. Direct pilots
b. Indirect pilots
16. What are the types of stock stop?
a. Lever or latch type
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 21 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
b. Automatic stop
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
c. Shoulder stop d. Starting stop
17. List down the various methods of arranging guide pins in the die set.
a. Back-post design
b. Centre-post design
c. Diagonal-post design
d. four-guide post design
18. What are the types of die set?
a. Precision die set
b. Commercial die set.
PART-B (16 Marks)
1. Describe briefly the various press working operations. (16)
2. What are the factors to be considered while selecting a press? (16)
3. Explain briefly the functions of following parts in press tool. (16)
(i) Stripper
(ii) Pilots
(iii) Shedder.
4. a) (i) explain briefly the function of the following parts applied to press working.
i) Stock stop
ii) Knockout rod (6)
(b) Sketch a suitable press tool to manufacture square component 40 mm side having a central
square hole 20 mm side, the material thickness being 1.5 mm. (10)
5. Explain step by step procedure for the computation of press capacities and tonnage
requirements for cutting and drawing operations. (10+6)
6. Design and sketch the views of compound die that produces steel washers. Dimensions of the
washer may be assumed suitably. (16)
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 22 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
UNIT V DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF DIES
Design and development of progressive and compound dies for Blanking and piercing operations
Bending dies Development of Bending Dies forming and Drawing Dies Development of
Drawing Dies Design considerations in Forging Extrusion Casting and Plastic Dies.
PART A (2 Marks)
1. Write down the formula for calculating cutting forces required in a cutting operation.
Ans: Cutting force, for round holes
for other contours
D =Diameter of the hole to be cut
t =Thickness of material
=Ultimate shear strength of the material
=Shearing length
2. Write down the formula for calculating drawing force required in drawing operations.
Ans: Drawing force,
where
d =Outside diameter of the shell
t =Thickness of material
Yield strength of metal
Diameter of the blank to be cut
0.6 0.7 for ductile materials
3. What is the purpose of stock-stop?
Ans: It is used to stop the die at a required distance. It avoids over penetration of die in materials.
4. What is meant by bending allowance?
Ans: It is also called spring back allowance. Spring back allowance is defined as the tendency of
sheet metal to change the shape from final shape.
5. What is meant by flash and gutter?
Ans: The portion of extra metal near the parting line is known as flash. In addition to this, again
some extra metal is added with flash as extension is known as gutter.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 23 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
6. What are the various types of bending?
Ans: The various types of bending are:
a. Edge bending
b. V bending
c. U bending
7. What is spring back?
Ans: The tendency of the metal to resume its original position causing a decrease in bend
angle is known as spring back. The spring back varies from 0.5
o
to 5
o
for steel.
8. List the factors affecting spring back.
Ans:
a. Material type
b. Thickness
c. Hardness
d. Bend radius
9. List four factors affecting drawing
Ans:
a. Type of material
b. Ductility
c. Yield strength
d. Drawing speed
10. What are the types of drawing dies?
Ans: a. Single action dies
b. Double action dies
11. What are the methods used for bulging dies?
Ans:
a. Rubber
b. Urethane
c. Heavy grease
d. Oil
e. Water
12. What are the advantages of coining?
Ans: a. Excellent surface finish
b. Closer tolerances
13. What are the factors affecting bending?
Ans: a. Properties of material
b. Length of bend
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 24 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
c. Condition of cut edge at the ends of bend line
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
d. Direction of orientation of the axis of the bend to the direction in which material was
rolled
PART B (16 Marks)
1. Design and sketch any two views of a progressive die to manufacture the outer plate of a
cycle-chain links.
2. A steel cup of height 30 mm and internal diameter 40mm with a flange width of 10 mm is to
be deep drawn from a sheet 1 mm thick, determine the diameter of the blank and the drawing
force. What is the draw ratio? Can the cup be drawn in a single operation? Sketch any two views
of a draw die.
3. A rectangular steel component of size 20 mm x 60 mm is to be made from 4 mm thick sheet.
Sketch the scrap strip by layout and determine the percentage of stock used.
4. Design and draw any two views of a progressive die to make a steel washer of 30 mm outside
diameter with 15 mm hole from1.6 mm thick steel sheet. The ultimate shear stress of the material
is 320 N/mm
2
5. Sketch and design a drawing die as shown in the Fig. 5.1 from medium carbon steel F
t
=3600
kg/cm
2
All dimensions in cm.
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 25 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Fig. 5.1
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
6. Calculate the developed length of part as shown in theFig. 5.2.
All dimensions in cm.
Fig. 5.2
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 26 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
Question Bank April/May 2014 ME5635-Design of J igs, Fixtures And Press Tools
REFERENCES
1. Edward G Hoffman- J igs & Fixture Design, Thomson Delmar Learning, Singapore 2004
2. Donaldson. C, Tool Design, Tata McGrawHill, 1986
3. Kempster, J igs & Fixtures Design, The English Language Book Society, 1978
4. J oshi, P.H., J igs & Fixtures, Second Edition, Tata McGrawHill Publishing Company
Limited, New Delhi 2004
5. Hiram E Grant, J igs and Fixture Tata McGrawHill, New Delhi, 2003
6. Fundamentals of Tool Design, CEEE Edition, ASTME, 1983
Dept. of Mech. Engg. Page 27 of 27 SSE, Saveetha University
7. Design Data Handbook PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Jigs and Fixtures: Essential Guide to Locating, Clamping and Cutting Tool GuidanceDokumen47 halamanJigs and Fixtures: Essential Guide to Locating, Clamping and Cutting Tool GuidanceSaumya SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Blanking & Piercing (Handout)Dokumen50 halamanBlanking & Piercing (Handout)banana100% (1)
- Design of Piercing and PunchingDokumen41 halamanDesign of Piercing and Punchingjacky hansdahBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsDokumen27 halamanASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsCarlos Pinto Pradilla88% (8)
- Queuing Theory PresentationDokumen156 halamanQueuing Theory PresentationRaghavendra Pratap SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs Fixtures Accurately Manufacture Duplicate PartsDokumen8 halamanJigs Fixtures Accurately Manufacture Duplicate PartsHafizuddin NasirBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures Tools Design GuideDokumen37 halamanJigs and Fixtures Tools Design GuideYann YeuBelum ada peringkat
- FixturesDokumen12 halamanFixturesakshay2761Belum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures Design PrinciplesDokumen38 halamanJigs and Fixtures Design PrinciplesrajatjainkkjBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Jig and Fixture For Drilling and Milling OperationsDokumen8 halamanStudy of Jig and Fixture For Drilling and Milling OperationsSulficker AliBelum ada peringkat
- Differences and Uses of Jigs and FixturesDokumen2 halamanDifferences and Uses of Jigs and FixturesShichibukai WarlordBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures Clamping GuideDokumen15 halamanJigs and Fixtures Clamping GuidenilamBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs & FixturesDokumen63 halamanJigs & FixturesRishikesh KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-23 Jig and FixturesDokumen51 halamanCh-23 Jig and FixturesrajaBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs Fixtures MainDokumen30 halamanJigs Fixtures MainPrashanth RamakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Applications For Jigs and FixturesDokumen10 halamanApplications For Jigs and FixturesAntay Korakot100% (1)
- G.25-GEMSS-G-02 Rev 01plant Design CriteriaDokumen13 halamanG.25-GEMSS-G-02 Rev 01plant Design Criteriamohammad kassarBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs - and Fixtures PDFDokumen29 halamanJigs - and Fixtures PDFNiel Cool100% (1)
- Digital Die Design SystemDokumen17 halamanDigital Die Design Systemjagas123455123Belum ada peringkat
- GD&T Definitions GuideDokumen5 halamanGD&T Definitions GuideLokesh NarasimhaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs&FixtureDokumen14 halamanJigs&FixtureBikram MuduliBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures: DR Arslan AhmedDokumen18 halamanJigs and Fixtures: DR Arslan AhmedKNOWLEDGE WORLDBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Jigs and FixturesDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To Jigs and Fixturesabhilash karanBelum ada peringkat
- Generation Motions of Machine Tools, Requirements of Machine Tools, Fundamental of Machine Tool DesignDokumen50 halamanGeneration Motions of Machine Tools, Requirements of Machine Tools, Fundamental of Machine Tool DesignDeepan RajBelum ada peringkat
- 02-Us-Introduction To Jigs and FixturesDokumen72 halaman02-Us-Introduction To Jigs and FixturesShreyas ParabBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and FixtureDokumen4 halamanJigs and FixtureCK FaridahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4-EDokumen42 halamanChapter 4-EMahrouz MadoBelum ada peringkat
- Jig and FixtureDokumen24 halamanJig and FixtureprabhjotbhangalBelum ada peringkat
- Fitting (Bench Working) ShopDokumen26 halamanFitting (Bench Working) ShopBhaskar KandpalBelum ada peringkat
- Jigsfixtures Kuliah 1 Sesi Jun 2010Dokumen79 halamanJigsfixtures Kuliah 1 Sesi Jun 2010JahazielBelum ada peringkat
- RPVP Puerto PrincesaDokumen8 halamanRPVP Puerto PrincesaRanny LomibaoBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion in Oil and Gas Industry A Perspective On Corrosion InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanCorrosion in Oil and Gas Industry A Perspective On Corrosion InhibitorsAsma Sed100% (1)
- Introduction To Jig & Fixture Design by KempsterDokumen54 halamanIntroduction To Jig & Fixture Design by Kempstersk9145100% (10)
- Lab Session 1 & 2& 3Dokumen24 halamanLab Session 1 & 2& 3Ali RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFDokumen2 halamanFire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFpequenita34100% (1)
- Jig and Fixture Design GuideDokumen53 halamanJig and Fixture Design Guidettetslm100% (2)
- MBEYA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY KINEMATICS OF MACHINE TOOLSDokumen37 halamanMBEYA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY KINEMATICS OF MACHINE TOOLSSadikiel100% (1)
- Ricoh 2090Dokumen832 halamanRicoh 2090cosmin176100% (1)
- Presentation On Jigs and Fixtures by Group G - 2Dokumen31 halamanPresentation On Jigs and Fixtures by Group G - 2Michael Castro AbuduBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs QuestionDokumen13 halamanJigs QuestionShanmugavel MallaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixture Sem III FinalDokumen127 halamanJigs and Fixture Sem III Finalnikhil sidBelum ada peringkat
- Cs15 Gas Tank Cleaning Degassing 1997Dokumen12 halamanCs15 Gas Tank Cleaning Degassing 1997kirandevi1981100% (2)
- Unit 3 Press and Press Tools: StructureDokumen14 halamanUnit 3 Press and Press Tools: StructurePranav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Jigs and Fixtures - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDokumen16 halamanDesign of Jigs and Fixtures - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M100% (1)
- JigDokumen6 halamanJigArun ManoBelum ada peringkat
- Jig and Fix Model QPDokumen4 halamanJig and Fix Model QPDharmaraj ParamasivamBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs Fixtures QuizDokumen1 halamanJigs Fixtures QuizMalcolm DiamondBelum ada peringkat
- DJF - Model Question PaperDokumen6 halamanDJF - Model Question PaperMohammedRafficBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Jigs QP Upto 2010Dokumen20 halamanDesign of Jigs QP Upto 2010Naresh Dharma100% (1)
- SPINTRONICSDokumen33 halamanSPINTRONICSSyam Pradeep ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures Design GuideDokumen36 halamanJigs and Fixtures Design GuideThulasi RamBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and FixturesDokumen20 halamanJigs and FixturesRenjith RajendraprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Single Point Cutting ToolDokumen11 halamanDesign of Single Point Cutting ToolSiddharth DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- GERE Axum 8Dokumen36 halamanGERE Axum 8Misge Chekole100% (1)
- Jigs and FixturesDokumen44 halamanJigs and Fixturespradeep_i19100% (3)
- Advanced Tool Design PDFDokumen4 halamanAdvanced Tool Design PDFgsudhanta1604Belum ada peringkat
- ME2029 DJF 2 Marks +16 Mark QuestionsDokumen15 halamanME2029 DJF 2 Marks +16 Mark QuestionssureshkumarBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Die Blocks PDFDokumen26 halaman01 Die Blocks PDFLibardo Cardenas PBelum ada peringkat
- Tumble Jig: Presented by Bharat.k.manvi Reg No: 100926022Dokumen29 halamanTumble Jig: Presented by Bharat.k.manvi Reg No: 100926022Bharat ManviBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Angular Post JigDokumen41 halamanDesign of Angular Post JigRobo Raja100% (2)
- Jig-Fixture DesignDokumen11 halamanJig-Fixture DesignVikramChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and FixturesDokumen26 halamanJigs and FixturesAumBelum ada peringkat
- "Design For Manufacturing and Assembly": 1 DfmaDokumen40 halaman"Design For Manufacturing and Assembly": 1 DfmasaiBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures For Machine Shops: Instructional ObjectivesDokumen21 halamanJigs and Fixtures For Machine Shops: Instructional ObjectivesRinkuBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs and Fixtures Question BankDokumen27 halamanJigs and Fixtures Question BankCarlos Williamson100% (1)
- WMP Lab Manual-2023 Aiml-ADokumen78 halamanWMP Lab Manual-2023 Aiml-ASentinel PlaysBelum ada peringkat
- Jigs, Fixtures and GuagesDokumen5 halamanJigs, Fixtures and GuagesRajuBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Chapter 2 Design of LocatorDokumen39 halaman2 Chapter 2 Design of LocatorKhaled HamdyBelum ada peringkat
- Tool Engg Lab ManualDokumen24 halamanTool Engg Lab ManualJenish Patel100% (3)
- CMPPDokumen74 halamanCMPPCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Generative CAPP Examples and BenefitsDokumen4 halamanGenerative CAPP Examples and BenefitsCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Generative CAPP Examples and BenefitsDokumen4 halamanGenerative CAPP Examples and BenefitsCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- GT and Part FamiliesDokumen9 halamanGT and Part FamiliesCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges in ManufacturingDokumen15 halamanChallenges in ManufacturingCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDokumen31 halamanNuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDr. B. Ramesh0% (1)
- Nuclear Power Plant: LoungeDokumen38 halamanNuclear Power Plant: LoungeRaveendran KBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDokumen31 halamanNuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDr. B. Ramesh0% (1)
- Disposal of Radioactive WasteDokumen19 halamanDisposal of Radioactive WasteCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Clustering Methods and Process PlanningDokumen14 halamanClustering Methods and Process PlanningCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclearpowerplant 170804051105Dokumen31 halamanNuclearpowerplant 170804051105Carlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclearpowerplant 170804051105Dokumen31 halamanNuclearpowerplant 170804051105Carlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Radioactive Waste Disposal MethodsDokumen23 halamanRadioactive Waste Disposal MethodsCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Medium Pressure Boiler Water Chemistry OptimizatioDokumen8 halamanMedium Pressure Boiler Water Chemistry OptimizatioCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear WasteDokumen17 halamanNuclear WasteCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV Off Site Processing: SyllabusDokumen77 halamanUnit IV Off Site Processing: SyllabusCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Queuingtheory 141114115954 Conversion Gate02 PDFDokumen19 halamanQueuingtheory 141114115954 Conversion Gate02 PDFCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant: Nishkam Dhiman Asst Prof: Electrical and Electronics Engineering Chitkara University, PunjabDokumen38 halamanNuclear Power Plant: Nishkam Dhiman Asst Prof: Electrical and Electronics Engineering Chitkara University, PunjabCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To CFD Analysis: Fluent User Services CenterDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To CFD Analysis: Fluent User Services CenterAravindanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - SF AnwerDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - SF AnwerKishore ChandBelum ada peringkat
- Mae423 Notes Update Feb7 12 PDFDokumen21 halamanMae423 Notes Update Feb7 12 PDFCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Programming-1Dokumen67 halamanLinear Programming-1Carlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Queueingtheory (1) 1Dokumen61 halamanQueueingtheory (1) 1ashwin josephBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To CFD ProblemDokumen1 halamanIntro To CFD ProblemlinoBelum ada peringkat
- 2dpipe Ge31111313131omDokumen13 halaman2dpipe Ge31111313131omnilesh0001Belum ada peringkat
- Queuingtheory 141114115954 Conversion Gate02 PDFDokumen19 halamanQueuingtheory 141114115954 Conversion Gate02 PDFCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Database Management SystemsDokumen11 halamanDatabase Management SystemsCarlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8Dokumen26 halamanChapter 8Carlos WilliamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Tu 1-5Dokumen8 halamanTu 1-5Made easy classes0% (2)
- 625-NR Consolidated NovemberDokumen321 halaman625-NR Consolidated NovemberArturoBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Quality Control of Emission From Diesel Engines Regulations 1996 - P.U.a 429-96Dokumen22 halamanEnvironmental Quality Control of Emission From Diesel Engines Regulations 1996 - P.U.a 429-96scribdledeeBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Can Am Off Road - Apache Track Kits Leaflet - enDokumen7 halaman2020 Can Am Off Road - Apache Track Kits Leaflet - enNicolas VillamayorBelum ada peringkat
- PactFocus Report - Sample - LPGDokumen27 halamanPactFocus Report - Sample - LPGIqbal HussainBelum ada peringkat
- 350q-5 Operation ManualDokumen97 halaman350q-5 Operation ManualCesar Mora100% (2)
- Custom Validation ExampleDokumen4 halamanCustom Validation ExampleAbdul Bais StanikzaiBelum ada peringkat
- Pure Chem p2 - 26pgDokumen26 halamanPure Chem p2 - 26pgJhomer CrespoBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation - Beton - Dreux - Gorisse Good - Fr.enDokumen9 halamanFormulation - Beton - Dreux - Gorisse Good - Fr.enRabnawaz ImamBelum ada peringkat
- Ansul Wheeled RedLine 150lb F-2002046Dokumen4 halamanAnsul Wheeled RedLine 150lb F-2002046German Duvan HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- How To Fix Samsung CorbyDokumen2 halamanHow To Fix Samsung CorbyMohd Sariffudin DaudBelum ada peringkat
- A ProcessDokumen41 halamanA ProcessjulioBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and Systems - MjrobertsDokumen3 halamanSignals and Systems - Mjrobertspriyakanthr5883100% (1)
- Linthwaite: Conservatio N AreaDokumen26 halamanLinthwaite: Conservatio N Areabill baileyBelum ada peringkat
- Brandt M FR Btd500blnDokumen74 halamanBrandt M FR Btd500blnStéphane JoussetBelum ada peringkat
- FTS ScaleoEUserManualEN 10 1082177Dokumen2.044 halamanFTS ScaleoEUserManualEN 10 1082177JBelum ada peringkat
- TI Oxydur PTB 206 - en PDFDokumen5 halamanTI Oxydur PTB 206 - en PDFgonzalogvargas01100% (1)
- Mock Test Jee MainDokumen142 halamanMock Test Jee MainAkash Ghosh0% (1)
- Axle, Front - Differential and Carrier - Jee0123251Dokumen3 halamanAxle, Front - Differential and Carrier - Jee0123251Husi NihaBelum ada peringkat
- DWTS, WDWTS: Improving MRI Image Reconstruction with Directional Wavelet ThresholdingDokumen1 halamanDWTS, WDWTS: Improving MRI Image Reconstruction with Directional Wavelet ThresholdingSumit ChakravartyBelum ada peringkat
- Power Tool Switches: Catalog 1308650 Issued 1-01Dokumen18 halamanPower Tool Switches: Catalog 1308650 Issued 1-01Gamal AhmadBelum ada peringkat