Ass 2013
Diunggah oleh
api-252561013Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ass 2013
Diunggah oleh
api-252561013Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
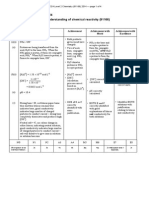
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 1 of 6
Assessment Schedule 2013
Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of thermochemical principles and the properties of particles and substances (91390)
Evidence Statement
Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit
Achievement with
Excellence
ONE
(a)
Se: [Ar]3d
10
4s
2
4p
4
or 4s
2
3d
10
4p
4
V: [Ar]3d
3
4s
2
or 4s
2
3d
3
V
3+
: [Ar]3d
2
where [Ar]: 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
TWO correct from (a).
(b)(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Se has more shells/electrons in energy levels further from the nucleus than O,
with increased shielding from inner shells. This means there is a weaker
electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the bonded electrons, so Se has
a lower electronegativity than O.
Cl
has an extra electron in its outermost/same energy level. This causes
increased repulsion between electrons in the valence shell, so the electrons
move further apart. This makes Cl
bigger than Cl. Both Cl and Cl
have the
same number of protons/attractive force of the nucleus remains the same.
Cl has more protons than Li. Therefore there is a greater attraction between the
nucleus and outer electrons/electrons held more tightly so it is harder to remove
an electron from Cl than Li.
Even though the valence electrons of Cl are in the 3rd energy level/has an extra
energy level the extra shielding is not as significant as the effect of the
increased nuclear charge, so Cl has a higher first ionisation energy than Li.
Two valid statements
from any of b(i) (ii) or
(iii).
Full discussion in one
of the three parts and
any two other valid
points.
Two full discussions and
one other valid point.
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 2 of 6
(c)(i)
(ii)
BrF
3
: T-shaped: PCl
6
: Octahedral
There is a difference in electronegativity between S and F, so the S-F bonds are
polar covalent. SF
4
has a see-saw shape (distorted tetrahedron) due to the
repulsions between four bonding regions and one non-bonding region of
charge, which is asymmetric therefore the polarities/dipoles do not cancel. As a
result, SF
4
is a polar molecule.
There is a difference in electronegativity between Xe and F, so the Xe-F bonds
are polar covalent. XeF
4
has a square planar shape, due to the repulsions
between four bonding regions and two non-bonding regions of charge;
therefore the polarities/dipoles do cancel. As a result, XeF
4
is a non-polar
molecule.
TWO correct Lewis
diagrams.
OR
TWO correct shapes.
OR
ONE correct Lewis
diagram and corresponding
name.
Both shapes correct OR
Both polarities correct OR
One shape and
corresponding polarity
Identifies polar bonds due
to F having a different
electronegativity to both
Xe and S. OR
Links polarity to
symmetrical or
asymmetrical arrangement
of polar bonds.
ALL correct
Both polarities correct and
full discussion of polarity
for both molecules. OR
Both shapes correct and
full discussion of shape
for both. OR
Shape and polarity correct
and full discussion for one
molecule. OR
Both shapes and polarities
correct with essentially
correct discussions but
omissions in both.
Correct discussion for
polarities of BOTH
molecules.
Not Achieved Achievement Merit Excellence
N
No response; no
relevant evidence.
N1
1a
N2
2a
A3
3a
A4
4a
M5
2m
M6
3m
E7
2e with minor
error/omission
E8
2e
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 3 of 6
Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit
Achievement with
Excellence
TWO
(a)(i)
(ii)
(iii)
The enthalpy change when one mole of liquid water is converted to gaseous
water under standard conditions. OR H
2
O(!) ! H
2
O(g)
Find H
2
(g) + ! O
2
(g) ! H
2
O(!)
Given H
2
O(!) ! H
2
O(g) "! = 44 kJ mol
1
(reverse)
H
2
(g) + ! O
2
(g) ! H
2
O(g) "H = -242 kJ mol
1
"
f
H(H
2
O(!)) = 44 + (242) = 286 kJ mol
1
At 100C, energy is used to change liquid water to water vapour.
At its boiling point, the heat energy is used to break the intermolecular forces
/hydrogen bonds between the H
2
O molecules.
Correct definition or
equation.
Correct process with minor
error.
OR
Writes 2 correct equations
Relates energy use to
change of state/breaking of
intermolecular forces
Correct working and
answer, with units.
Relates energy use to
change of state and
intermolecular forces
Both merit answers
(b)(i)
(ii)
q = mc"T = 50 # 4.18 # 6.5 = 1358.5 J = 1.3585 kJ
n = c x V = 1 x 0.025 = 0.025 mol
!
r
H =
q
n
=
"1.3585 kJ
0.025 mol
= "54.3kJ mol
"1
Conditions were not standard.
Needed to carry out under standard conditions.
OR
Heat lost to atmosphere / beaker / surroundings.
Insulate equipment; ensure all / as much of the energy produced as possible is
collected and measured.
Calculates energy correctly.
OR
Calculates number of moles
correctly.
Provides a valid reason for
the discrepancy in the
result AND suggests an
improvement.
Correct answer. May
have poor rounding
/incorrect units/sign
OR
Incorrect moles as the
only error.
Correct calculation, with
sign, units and appropriate
significant figures.
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 4 of 6
Not Achieved Achievement Merit Excellence
N
No response; no
relevant evidence.
N1
1a
N2
2a
A3
3a
A4
4a
M5
2m
M6
3m
E7
e in (b) and m in
(a)(ii) or (iii)
E8
2e
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 5 of 6
Q
Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit
Achievement with
Excellence
THREE
(a)
N
2
H
4
is a polar molecule. (Due the presence of the highly polar N-H bonds), there is
hydrogen bonding between N
2
H
4
molecules.
CH
3
F is also a polar molecule. (Due to the presence of the C-F bond), there are
permanent dipole attractions between the CH
3
F molecules.
The attractive forces due to permanent dipoles in CH
3
F must be weaker than the
attractive forces due to hydrogen bonding in N
2
H
4
, because CH
3
F boils at a lower
temperature and they are similar masses so temporary dipole attractions are similar.
C
10
H
22
is a non-polar molecule. The only attractive forces between the C
10
H
22
molecules are due to temporary dipoles. However, since C
10
H
22
is a significantly larger
molecule than N
2
H
4
, and CH
3
F, it is more polarisable / has more electrons / greater
molar mass, so its temporary dipole attractions are even stronger than the hydrogen
bonds in N
2
H
4
. As a result, C
10
H
22
requires the most heat energy to break its
intermolecular forces and therefore has the highest boiling point.
Identifies most
significant type of
intermolecular bonding
for ONE molecule.
Recognises that more
electrons cause
stronger temporary
dipoles.
OR
The stronger the
intermolecular force
the higher the boiling
point/more energy
required
Correct process
(evidence of
10 # 393, 11 # 286
and 1 # 250)
Recognises entropy
increases which favour
the reaction.
OR
Recognises reaction is
exothermic which
favours the reaction.
Correct description of
intermolecular bonding
for two molecules and
a valid comparison.
Correct calculation,
with correct units and
sign.
Partial explanation
refers to both entropy
and enthalpy changes.
OR
Full explanation for
enthalpy or entropy
change.
Full discussion for all
THREE molecules.
Full explanation.
(b) "
c
H = $"
f
H(products) $"
f
H(reactants)
=[(10 # 393) + (11 # 286)] (250)
= 6 826 kJ mol
1
or (6 830 kJ mol
1
)
(c) Enthalpy change: The combustion of liquid hydrazine is an exothermic process since
"
c
H is negative. Exothermic reactions form products that have lower energy than the
reactants / energy is released and this favours the spontaneous / forward reaction.
Entropy change: Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings, which makes
the entropy change of the surroundings positive. As both the surroundings and the
system gain entropy, this favours the spontaneous / forward reaction.
OR
The combustion reaction has more gas molecules in the products / goes from liquid to
gas / increase in number of particles. Therefore the entropy of the system increases and
this favours the spontaneous / forward reaction.
As both enthalpy and entropy are favoured, then hydrazine readily burns / the reaction
is spontaneous.
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91390) 2013 page 6 of 6
Not Achieved Achievement Merit
Excellence
N
No response; no
relevant evidence.
N1
1a
N2
2a
A3
3a
A4
4a
M5
2m
M6
3m
E7
2e, with minor
error / omission
E8
2e
Judgement Statement
Not Achieved Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
Score range 0 7 8 12 13 18 19 24
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ass 2014Dokumen5 halamanAss 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91165Dokumen2 halamanLearning Objectives As91165api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Exm 2014Dokumen12 halamanExm 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91392Dokumen1 halamanLearning Objectives As91392api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Exm 2014Dokumen16 halamanExm 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Ass 2013Dokumen6 halamanAss 2013api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91389Dokumen2 halamanAs 91389api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91390Dokumen2 halamanLearning Objectives As91390api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91165Dokumen3 halamanAs 91165api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Exm 2013Dokumen12 halamanExm 2013api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Ass 2014Dokumen4 halamanAss 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Ass 2012Dokumen6 halamanAss 2012api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91167Dokumen1 halamanLearning Objectives As91167api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91167Dokumen2 halamanAs 91167api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Ass 2014Dokumen5 halamanAss 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Ass 2014Dokumen4 halamanAss 2014api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91390Dokumen3 halamanAs 91390api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91161Dokumen1 halamanLearning Objectives As91161api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91435Dokumen3 halamanAs 91435api-271057641Belum ada peringkat
- As 91393Dokumen2 halamanAs 91393api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91391Dokumen4 halamanLearning Objectives As91391api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91162Dokumen2 halamanAs 91162api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91164Dokumen2 halamanLearning Objectives As91164api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91161Dokumen2 halamanAs 91161api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives As91388Dokumen1 halamanLearning Objectives As91388api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Testing For Cations Flow ChartDokumen2 halamanTesting For Cations Flow Chartapi-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- As 91164Dokumen3 halamanAs 91164api-252561013Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- 0901 B 803808 e 4479Dokumen7 halaman0901 B 803808 e 4479SiddharthapachisiaBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Manual: 2700 Series Benchtop MetersDokumen60 halamanInstruction Manual: 2700 Series Benchtop Meterssebastian florez sernaBelum ada peringkat
- 99ebook Com Msg00388 PDFDokumen15 halaman99ebook Com Msg00388 PDFM Sarmad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Autolab Brochure 2013 en LRDokumen40 halamanAutolab Brochure 2013 en LRdanidondoniBelum ada peringkat
- Urt 2Dokumen3 halamanUrt 2Reham HishamBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Parte Bomba Gorman RuppDokumen38 halamanManual de Parte Bomba Gorman RuppLuis Fernando Arias FlorezBelum ada peringkat
- Increasing The Performance of Chain Sprocket by Using Cryogenic Treated and Normalizing in Superficial Heat TreatmentDokumen25 halamanIncreasing The Performance of Chain Sprocket by Using Cryogenic Treated and Normalizing in Superficial Heat Treatmentthai avvaiBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced in Viscid Problems SolutionsDokumen12 halamanAdvanced in Viscid Problems SolutionssalahBelum ada peringkat
- 12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetDokumen1 halaman12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetAmen RaipurBelum ada peringkat
- Sedimentation 1Dokumen25 halamanSedimentation 1JatskinesisBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment For BCH3356Dokumen2 halamanAssignment For BCH3356farehaBelum ada peringkat
- Coatings Word August 2010Dokumen52 halamanCoatings Word August 2010sami_sakrBelum ada peringkat
- Review Problems PDFDokumen22 halamanReview Problems PDFArman Malekloo0% (1)
- Study Plan For The Mechanical PE ExamDokumen2 halamanStudy Plan For The Mechanical PE ExamMatthew Leaper100% (2)
- Standard SpecificationsDokumen5 halamanStandard SpecificationsIan54321Belum ada peringkat
- Model Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16Dokumen1 halamanModel Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16vrkoradaBelum ada peringkat
- Sublimation and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidDokumen4 halamanSublimation and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Engine Apparatus ManualDokumen23 halamanHeat Engine Apparatus ManualRomeo DequitoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Ecology Principle and ConceptDokumen96 halamanBasic Ecology Principle and ConceptRhoxie RoxasBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Stability of Cubipod Armour Units in Breaking ConditionsDokumen149 halamanHydraulic Stability of Cubipod Armour Units in Breaking ConditionsCamille CuadraBelum ada peringkat
- General Pharmacology MCQDokumen6 halamanGeneral Pharmacology MCQShrikant ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- FireResistiveDokumen25 halamanFireResistiveAdil KhanBelum ada peringkat
- THE TITLE OF EXPERIMENT Ion ExchangeDokumen18 halamanTHE TITLE OF EXPERIMENT Ion Exchangeputri wildanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - NewDokumen25 halamanChapter 5 - NewJW MBelum ada peringkat
- The Latent Heat of Fusion of IceDokumen4 halamanThe Latent Heat of Fusion of Iceeid elsayedBelum ada peringkat
- Flow Simulation and Static Structural Analysis On Pelton TurbineDokumen7 halamanFlow Simulation and Static Structural Analysis On Pelton TurbineRahul ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Exam 2.4Dokumen6 halamanPractice Exam 2.4jamalBelum ada peringkat
- Tata Steel Is - 26MnB5 HR - Data Sheet enDokumen2 halamanTata Steel Is - 26MnB5 HR - Data Sheet enGopi KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- HPTLCDokumen46 halamanHPTLCVedha K Chalam100% (1)
- Octahedral Molecular GeometryDokumen24 halamanOctahedral Molecular GeometryAnonymous gUjimJKBelum ada peringkat