Work Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash Goyal
Diunggah oleh
Akash GoyalDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Work Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash Goyal
Diunggah oleh
Akash GoyalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
[1] [1]
IITians TAPASYA, Pushpanj al i Pl ace, Bori ng Road Crossi ng, Opp. Al ankar Pl ace, Patna-1, Ph.: 0612-3225103 www.iitianstapasya.com
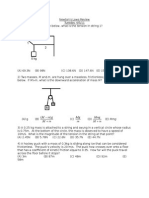
BATCH :. TARGET PHYSICS WORK ENERGY POWER
I I Ti ans TAPASYA
...IITians creating IITians
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM - 5
1. A motor drives a body along a straight line witha constant force. The power P developed by
the motor must vary with time t as
(A)
Y
P
O
X
t
(B)
Y
P
O
X
t
(C)
Y
P
O
X
t
(D)
Y
P
O
X
t
2. A stone is projected at time t = 0 with a speed V
0
and an angle u with the horizontal in a uniform
gravitational field. The rate of work done (P) by the gravitational force plotted against time (t)
will be as
(A)
P
O
t
(B)
P
O
t
(C)
P
O
t
(D)
P
O
t
Q. 3 to 4 related this Fig.
A suitcase of mass M is placed on a level conveyor belt at an airport. The coefficient of static
friction between the suitcase and the conveyor belt is
s
and the coefficient of kinetic friction is
k
, with
k s
. < The conveyor belt moves with constant speed u, and at time t = 0 the suitcase
is placed on the conveyor with speed v = 0. At a time t
f
, after moving a distance l, the suitcase
catches up with the conveyor belt, and starts to move at speed u with the conveyor belt. Gravity
acts downward with acceleration g > 0. Work can depend on ones frame of reference, so be
sure to answer the following questions in the frame of reference of the airport.
3. How much work does friction do on the suitcase during this period?
(A)
2
1
2
Mu
(B)
2
1
2
Mu
(C) Mgl (D)
s
Mgl
4. How much work does the force of friction from the suitcase do on the belt during this time
period?
(A)
k
Mgl (B)
k
Mgl (C)
k f
Mgut (D)
k f
Mgut
5. The net power of all the forces acting on a particle (P) versus time (t) curve is shown in
Fig. Work done upon the particle form A to B
P
A B
t
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) first increases then decreases
(D) first decreases then increases
BATCH :. TARGET PHYSICS WORK ENERGY POWER [2]
IITians TAPASYA, Pushpanj al i Pl ace, Bori ng Road Crossi ng, Opp. Al ankar Pl ace, Patna-1, Ph.: 0612-3225103 www.iitianstapasya.com
6. Massless springs, each with k = 1350 Nm
1
are attached to the left and right walls as shown in
Fig. A 1 kg block is initially held against the left-hand spring, compressing the spring by 0.1 m.
The block is released to move. The floor is frictionless except for the section AB. Coefficient of
friction for AB is 0.3. Find the distance (in cm) from point B where the block finally comes to
rest.
7. The frictional resistance to the motion of a train is always K times the total weight of the engine
and coaches. An engine of weight 2W works at constant horsepower throughtout and attains a
maximum speed u = 5 m/s when pulling six coaches each of weight W up the incline. Down the
same incline with only four coaches, the engine can attain a maximum speed 2u = 10 m/s.
Find the maximum speed (in m/s) of the engine when pulling two coaches on the horizontal
level.
8. A large block of mass M on a smooth inclined plane is connected via a string to a small block
m. which is attached to a relaxed spring of force cosntant k with its other end attached to the
ground (see Fig.) Which of the following forces do NEGATIVE work as the large block slides
down the incline?
(A) The tension force on m
(B) The gravitational force on m
(C) The spring force on m
(D) The tension force on M
9. An object has several forces acting on it. One of these forces is
F axy = i
, a force in the x-
direction whose magnitude depends on the position of the object, with o = 2.50 N/m
2
. Calcu-
late the work done on the object by this force for the following displacements of the object:
(a) The object starts at the point x = 2.00 m, y = 3.00 m and moves parallel to the x-axis to
the point x = 2.00 m, y = 3.00 m.
(b) The object starts at the point x = 2.00 m, y = 0 and moves in the y-direction to the point
x = 2.00 m, y = 3.00 m
(c) The object starts at the origin and moves on the line y = 1.5x to the point x = 2.00 m,
y = 3.00 m.
10. An elevator of heigth h moves upward at constant velocity v. Vibrations cause the elevators
light bulb to fall fro its fixture at time t = 0. The buld hits the floor at time t later. Let the mass of
the bulb be m.
(a) Find the initial kinetic energy of the bulb in ground
frame and elevator frame.
(b) Find the kinetic energy of the bulb just before it hits
the floor in ground frame and elevator frame.
(c) Find the work done by gravity in ground frame and
elevator frame.
ANSWER KEY
1. (A) 2. (D) 3. (A) 4. (D) 5. (A)
6. 25 7. 12 8. (B,C,D) 9. 15 J, zero, 10 J
10. (a)
2
1
0
2
mv ,
(b)
2
2
2
v
m gh gh ,mgh
(
+
(
(c)
2h
mg h v ,mgh
g
( | |
( |
|
(
\
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Dokumen311 halamanUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDokumen12 halamanWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- Examples MomentumDokumen9 halamanExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- As Newtons Laws and Momentum QuestionsDokumen61 halamanAs Newtons Laws and Momentum Questionshasan_shahryar2008Belum ada peringkat
- Buckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessDokumen24 halamanBuckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessCole VincentBelum ada peringkat
- Nissan 720 L4-2.0-Z20 1983-86 Manual PDFDokumen641 halamanNissan 720 L4-2.0-Z20 1983-86 Manual PDFEduardo Ariel JuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Mit ExamDokumen11 halamanMit ExamAli RostamiBelum ada peringkat
- DPP 15-17 PDFDokumen5 halamanDPP 15-17 PDFAnkur GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen4 halamanAssignmentKhyzer HayyatBelum ada peringkat
- NL CQ 6 SSPDokumen4 halamanNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathBelum ada peringkat
- AP Mechanics FLT2 PDFDokumen21 halamanAP Mechanics FLT2 PDFXtreme VitthalBelum ada peringkat
- Work Power and Energy MCQs TestDokumen26 halamanWork Power and Energy MCQs Testrizal123100% (1)
- Practice Physics TestDokumen7 halamanPractice Physics Testthey12Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment#1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment#1Anoosha ArshadBelum ada peringkat
- MotionDokumen17 halamanMotionJohnBelum ada peringkat
- All AnswersDokumen22 halamanAll AnswersNadiatul JannahBelum ada peringkat
- Question 1Dokumen12 halamanQuestion 1eka123Belum ada peringkat
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDokumen14 halaman2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewDokumen6 halamanAP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewJordana BrenesBelum ada peringkat
- Wpe ExerciseDokumen19 halamanWpe ExerciseMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Lows of MotionDokumen20 halamanLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaBelum ada peringkat
- SpringerDokumen10 halamanSpringerMonico AlejoBelum ada peringkat
- (Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDokumen5 halaman(Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDeepak BaliyanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDokumen8 halamanChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNBelum ada peringkat
- Day 2 Newtons Laws ReviewDokumen6 halamanDay 2 Newtons Laws Reviewnoel castilloBelum ada peringkat
- Three Identical BallsDokumen5 halamanThree Identical BallsharshanauocBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Laws Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Dokumen5 halamanNewton's Laws Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- Physics 71 2nd LE ReviewerDokumen3 halamanPhysics 71 2nd LE ReviewerAnne Glydel Cruzado DalaganBelum ada peringkat
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa1 2014 PDFDokumen4 halamanCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa1 2014 PDFbhag singhBelum ada peringkat
- Int Mech Practice Exam 2Dokumen9 halamanInt Mech Practice Exam 2Kevin ApodacaBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDokumen3 halamanGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAssignmentAishley MatharooBelum ada peringkat
- Recitation-4: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy and Conservation of EnergyDokumen12 halamanRecitation-4: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy and Conservation of EnergyAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise - 1 To 3 English GcVoQ2eDokumen23 halamanExercise - 1 To 3 English GcVoQ2ewanderedBelum ada peringkat
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDokumen4 halamanEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Momentum NotesDokumen59 halamanLinear Momentum NotesruukiBelum ada peringkat
- Mu M+M Mu M+M Mu M M Mu M M: Topics Covered Physics: Kinemtics, Laws of Motion, Work Power EnergyDokumen6 halamanMu M+M Mu M+M Mu M M Mu M M: Topics Covered Physics: Kinemtics, Laws of Motion, Work Power EnergyRohit DewanBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Sheet WPEDokumen9 halamanPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferBelum ada peringkat
- 05 - Work, Energy and PowerDokumen6 halaman05 - Work, Energy and PowerAñîkët KãmãlBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 4A Chapter 5 HW ProblemsDokumen3 halamanPhysics 4A Chapter 5 HW Problemstannguyen8Belum ada peringkat
- Essay QuestionDokumen8 halamanEssay QuestionharshanauocBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 2Dokumen7 halamanPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaBelum ada peringkat
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDokumen26 halaman2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25Belum ada peringkat
- WPEDokumen6 halamanWPESanjeev KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Dokumen21 halamanCH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Christian ChiuBelum ada peringkat
- STPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsDokumen9 halamanSTPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsSouseiseki ChromeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics I Problems PDFDokumen1 halamanPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenBelum ada peringkat
- M1 BookletDokumen11 halamanM1 BookletRadu PopescuBelum ada peringkat
- UP Diliman Physics 71 Long Exam#2 Sample ExamDokumen12 halamanUP Diliman Physics 71 Long Exam#2 Sample Examjerard999Belum ada peringkat
- Work Power EnergyDokumen9 halamanWork Power EnergySanmati Jain100% (1)
- End of Term 2 s.5 PhyDokumen6 halamanEnd of Term 2 s.5 PhyMubiruIvanSnrBelum ada peringkat
- DynDokumen7 halamanDynRyan LumBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment - 1 Fall 2022Dokumen4 halamanAssignment - 1 Fall 2022junaidBelum ada peringkat
- Wpe 1Dokumen11 halamanWpe 1KkBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDokumen6 halamanSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Phys1101 Worksheeti 2014 EDokumen6 halamanPhys1101 Worksheeti 2014 Ejhxnrx48f8Belum ada peringkat
- AP Physics C 2004 With AnswersDokumen18 halamanAP Physics C 2004 With AnswersjhbmleeBelum ada peringkat
- BB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionDokumen108 halamanBB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionSunil DahaleBelum ada peringkat
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Types of WinesDokumen91 halamanTypes of Winesrajanrld19880% (1)
- Case Study (Co2 Flooding)Dokumen10 halamanCase Study (Co2 Flooding)Jessica KingBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Revolution OutlineDokumen8 halamanIndustrial Revolution OutlineGeraldine GuarinBelum ada peringkat
- Oasis AirlineDokumen5 halamanOasis AirlineRd Indra AdikaBelum ada peringkat
- Science: The Menstrual CycleDokumen4 halamanScience: The Menstrual CycleLena Beth Tapawan YapBelum ada peringkat
- Pelton2014 Para-Equilibrium Phase DiagramsDokumen7 halamanPelton2014 Para-Equilibrium Phase DiagramsAbraham Becerra AranedaBelum ada peringkat
- Aci 522R-06 PDFDokumen25 halamanAci 522R-06 PDFaldi raimon100% (2)
- SVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoDokumen3 halamanSVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoChejarla Naveen KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet - Labeling Waves: NameDokumen2 halamanWorksheet - Labeling Waves: NameNubar MammadovaBelum ada peringkat
- LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxDokumen56 halamanLINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxFalley FasterBelum ada peringkat
- Water Reuse RoundtableDokumen10 halamanWater Reuse RoundtableajiiithBelum ada peringkat
- SweetenersDokumen23 halamanSweetenersNur AfifahBelum ada peringkat
- AeonDokumen4 halamanAeonsancsa_74Belum ada peringkat
- Massage Techniques in SpaDokumen1 halamanMassage Techniques in SpaALISA SAITABelum ada peringkat
- Equipment in The NICUDokumen7 halamanEquipment in The NICUGheDine PeracionBelum ada peringkat
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDokumen13 halamanExcretory Products and Their Eliminationaravind kishanBelum ada peringkat
- HACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)Dokumen6 halamanHACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)kerem__22Belum ada peringkat
- Tyba S4 Syntax PDFDokumen107 halamanTyba S4 Syntax PDFIndahBelum ada peringkat
- Unemployment in IndiaDokumen9 halamanUnemployment in IndiaKhushiBelum ada peringkat
- Ield Methods: A Typical Field Mapping Camp in The 1950sDokumen4 halamanIeld Methods: A Typical Field Mapping Camp in The 1950sshivam soniBelum ada peringkat
- QIAGEN Price List 2017Dokumen62 halamanQIAGEN Price List 2017Dayakar Padmavathi Boddupally80% (5)
- JMO 2023 (7, 8) Question PaperDokumen2 halamanJMO 2023 (7, 8) Question PaperSuryanshu BhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- Medical CodingDokumen5 halamanMedical CodingBernard Paul GuintoBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Electronica HardbookDokumen970 halamanManual de Electronica HardbookninoferBelum ada peringkat
- PT4115EDokumen18 halamanPT4115Edragom2Belum ada peringkat
- ESM-4810A1 Energy Storage Module User ManualDokumen31 halamanESM-4810A1 Energy Storage Module User ManualOscar SosaBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation Formula SheetDokumen5 halamanRadiation Formula SheetJakeJosephBelum ada peringkat