New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Classification
Diunggah oleh
EjanZulqadMaulanaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Classification
Diunggah oleh
EjanZulqadMaulanaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
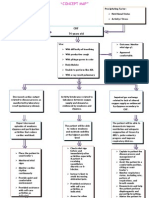
Canadian Cardiovascular Society Functional Classification of Stable Angina Pectoris
Class 1
Ordinary physical activity, such as walking and climbing stairs, does not cause angina.
Angina comes with strenuous or rapid or prolonged exertion at work or during recreation.
Class 2
Slight limitation of ordinary activity occurs walking or climbing stairs rapidly, walking
uphill, walking or stair climbing after meals, in cold, in wind, or when under emotional
stress, or only during the few hours after awakening. Walking more than two blocks on
level ground and climbing more than one flight of ordinary stairs at a normal pace and in
normal conditions triggers angina.
Class 3
Marked limitation of ordinary physical activity occurs walking one to two blocks on level
ground and climbing more than one flight of stairs under normal conditions.
Class 4
Patient is unable to carry on any physical activity without discomfort; anginal syndrome
may be present at rest.
New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Classification
Class Functional Capacity: How a patient with cardiac disease feels during physical activity
I
Patients with cardiac disease but resulting in no limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not
cause undue fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea or anginal pain.
II
Patients with cardiac disease resulting in slight limitation of physical activity. They are comfortable at rest.
Ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea or anginal pain.
III
Patients with cardiac disease resulting in marked limitation of physical activity. They are comfortable at rest.
Less than ordinary activity causes fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea or anginal pain.
IV
Patients with cardiac disease resulting in inability to carry on any physical activity without discomfort. Symptoms
of heart failure or the anginal syndrome may be present even at rest. If any physical activity is undertaken,
discomfort increases.
Class Objective Assessment
A No objective evidence of cardiovascular disease. No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity.
B
Objective evidence of minimal cardiovascular disease. Mild symptoms and slight limitation during ordinary
activity. Comfortable at rest.
C
Objective evidence of moderately severe cardiovascular disease. Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms,
even during less-than-ordinary activity. Comfortable only at rest.
D
Objective evidence of severe cardiovascular disease. Severe limitations. Experiences symptoms even while at
rest.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- MEDICAL CASE STUDIESDokumen4 halamanMEDICAL CASE STUDIESDarryl John Pasamba67% (3)
- Essentials of Internal MedicineDokumen832 halamanEssentials of Internal MedicineEmanuelMC100% (75)
- Concept Map - Abby !Dokumen2 halamanConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Nuero and Musculo Set B Answer KeyDokumen15 halamanNuero and Musculo Set B Answer KeyChristopher SarsozaBelum ada peringkat
- HIV Practice TestDokumen2 halamanHIV Practice TestJoslyn GrossBelum ada peringkat
- Shortness of Breath: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFDokumen1 halamanShortness of Breath: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFanz_4191Belum ada peringkat
- Epidemics: Fessahaye Alemseged (MD, MPHE)Dokumen34 halamanEpidemics: Fessahaye Alemseged (MD, MPHE)teklay100% (1)
- PHEM Basic Level Training Participants Module Final DraftDokumen53 halamanPHEM Basic Level Training Participants Module Final DraftKalifa Mohammed100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure OverviewDokumen12 halamanCongestive Heart Failure OverviewkazelleBelum ada peringkat
- MCQSDokumen13 halamanMCQSUzair Khan100% (1)
- Nurse assesses vascular clients and delegates tasksDokumen6 halamanNurse assesses vascular clients and delegates tasksticticBelum ada peringkat
- Addison and Cushing DMDokumen22 halamanAddison and Cushing DManon_391984943Belum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Study QuestionsDokumen13 halamanModule 1 Study QuestionsLuna AstanehBelum ada peringkat
- PHEM Basic Level Training Facilitator Module Final DraftDokumen69 halamanPHEM Basic Level Training Facilitator Module Final DraftYonas G.100% (1)
- NCLEX Practice Questions Quiz #4: Fundamentals of NursingDokumen12 halamanNCLEX Practice Questions Quiz #4: Fundamentals of NursingRegine Mae Encinada100% (1)
- Nurse Review: Medical-Surgical Nursing Endocrine System 2005Dokumen215 halamanNurse Review: Medical-Surgical Nursing Endocrine System 2005jonas2663Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Level III: PillsDokumen10 halamanNursing Level III: PillsMuluken BezabihBelum ada peringkat
- Inistitutional Assessementknowledge Test For Comprhenssive NursingDokumen19 halamanInistitutional Assessementknowledge Test For Comprhenssive NursingkassahunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10: Abdominal Disorders: Multiple ChoiceDokumen5 halamanChapter 10: Abdominal Disorders: Multiple ChoiceJamieBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17: Nutritional Support in The Older Adult: Multiple ChoiceDokumen3 halamanChapter 17: Nutritional Support in The Older Adult: Multiple ChoiceJamieBelum ada peringkat
- Main Applications of ECG DiagnosisDokumen19 halamanMain Applications of ECG DiagnosisMaria Rowena O. SalvoBelum ada peringkat
- Public Health COC ExamDokumen19 halamanPublic Health COC ExamTut Kong RuachBelum ada peringkat
- ILOCOS TRAINING AND REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER JUNIOR INTERNS’ EXIT EXAMINATIONDokumen6 halamanILOCOS TRAINING AND REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER JUNIOR INTERNS’ EXIT EXAMINATIONKai SibayanBelum ada peringkat
- Renal System Practice Quiz: D. Reversal of The Oliguria Occurs With Fluid ReplacementDokumen5 halamanRenal System Practice Quiz: D. Reversal of The Oliguria Occurs With Fluid Replacementمحمد حسينBelum ada peringkat
- Managing patient comfort and safety devicesDokumen296 halamanManaging patient comfort and safety devicesCHALIE MEQUBelum ada peringkat
- Lehne Nclex DMDokumen3 halamanLehne Nclex DMAmeliaM100% (2)
- 2 Nursing ProcessDokumen50 halaman2 Nursing ProcesssechzhenBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Patients With Cardiac DisordersDokumen4 halamanCare of Patients With Cardiac Disordersbugoff700Belum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Nursing 50 Questions PDF SurgerDokumen2 halamanPerioperative Nursing 50 Questions PDF Surgerpaulzkieyy100% (1)
- Exam 4Dokumen10 halamanExam 4pauchanmnlBelum ada peringkat
- Perform Nursing AssessmentDokumen81 halamanPerform Nursing AssessmentAhmanur SuleBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review Questions Part 3Dokumen8 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing Review Questions Part 3angelfire23phBelum ada peringkat
- DSS AIIIMS PREPRATION TEST SERIESDokumen24 halamanDSS AIIIMS PREPRATION TEST SERIESDr-Sanjay SinghaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Panay Healthcare ProtocolDokumen186 halamanPanay Healthcare ProtocolVian Arccenio100% (1)
- Cofidential DialloDokumen49 halamanCofidential DialloAbdulBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Maria Susan Z. MaglaquiDokumen24 halamanProf. Maria Susan Z. MaglaquiSusan MaglaquiBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation of Professional Nursing PracticeDokumen35 halamanFoundation of Professional Nursing PracticeJennifer Apostol100% (1)
- Internal Medicine 5th MidtermDokumen13 halamanInternal Medicine 5th MidtermIashdip iashdipBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Exercise and AssignmentsDokumen2 halamanIndividual Exercise and AssignmentsFilmOn Fufa50% (4)
- Diabetes MellitusquestionsDokumen3 halamanDiabetes Mellitusquestionscubicj100% (1)
- Pediatrics Nursing L5Dokumen89 halamanPediatrics Nursing L5MaxBelum ada peringkat
- Genito Urinary TractDokumen199 halamanGenito Urinary TractKim GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Staff Nurse - MCQ For NursesDokumen7 halamanStaff Nurse - MCQ For Nursesliya100% (1)
- 1.introduction of Ana & PhyDokumen7 halaman1.introduction of Ana & PhyCK SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter27-Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionDokumen31 halamanChapter27-Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionAhmed 123Belum ada peringkat
- مجموعه من الاسئلة التمريضيةDokumen75 halamanمجموعه من الاسئلة التمريضيةأبوأحمد الحكيمBelum ada peringkat
- QD Nurses PDFDokumen2 halamanQD Nurses PDFKaloy KamaoBelum ada peringkat
- CH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and PancreasDokumen28 halamanCH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and Pancreasjrflores1284Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Nutritional Consideration in The Prevention and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases, Educational PlatformDokumen18 halamanUnit 5 Nutritional Consideration in The Prevention and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases, Educational Platformzia ullah100% (1)
- McqsforentrancetestforbnmnmsnnursingDokumen70 halamanMcqsforentrancetestforbnmnmsnnursingNepkos SokpenBelum ada peringkat
- TPN for Major Burn InjuryDokumen31 halamanTPN for Major Burn InjuryBobet ReñaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDokumen4 halamanPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralBelum ada peringkat
- ContinueDokumen2 halamanContinuesamsonBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary System DisordersDokumen14 halamanUrinary System DisordersGideon P. CasasBelum ada peringkat
- ARELLANO UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING CAPP - 1 MIDTERM LONG TESTDokumen25 halamanARELLANO UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING CAPP - 1 MIDTERM LONG TESTmiracle kildoyleBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide For Med Surg 1Dokumen15 halamanStudy Guide For Med Surg 1desireemaenugentBelum ada peringkat
- TTS For APODokumen9 halamanTTS For APOJan Joseph BanzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Pleural Fluid AnalysisDokumen15 halamanPleural Fluid AnalysisNatalie Sarah MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Leadership Mcqs PaperDokumen6 halamanLeadership Mcqs PaperUmer IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric NursingDokumen2 halamanPsychiatric NursingRn nadeenBelum ada peringkat
- FON MCQs Vital SignsDokumen11 halamanFON MCQs Vital SignspriyaBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Night Sweats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandNight Sweats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Hasil TransleteDokumen2 halamanHasil TransleteEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- DapusDokumen1 halamanDapusEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen3 halamanDaftar PustakaEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Skenario e Blok 27 WiraDokumen25 halamanSkenario e Blok 27 WiraEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal SLEDokumen5 halamanJurnal SLEEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- ADokumen6 halamanAEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan LaboratoriumDokumen8 halamanPemeriksaan LaboratoriumEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationDokumen1 halamanNew York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel TTG Bell's PalsyDokumen4 halamanArtikel TTG Bell's PalsyEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary EdemaDokumen14 halamanPulmonary EdemaRizzamwah Catague100% (1)
- BronchoPulmonary Hygiene TechniquesDokumen88 halamanBronchoPulmonary Hygiene Techniques私 シャーロットBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokumen3 halamanImpaired Gas ExchangePaul VincentBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Systems FDDokumen1 halamanReview of Systems FDchronicidalBelum ada peringkat
- Decrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeDokumen3 halamanDecrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeRalph PelegrinoBelum ada peringkat
- Birth AsphyxiaDokumen2 halamanBirth AsphyxiaTeslim Raji100% (3)
- Respiratory Stimulants, Expectorants and Anti-TussivesDokumen16 halamanRespiratory Stimulants, Expectorants and Anti-TussivesAshish Mittal0% (3)
- New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationDokumen1 halamanNew York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationEjanZulqadMaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- First Tutorial: Brain StormingDokumen3 halamanFirst Tutorial: Brain Stormingsemicircularis0% (1)
- Amlodipine BP Heart DrugDokumen8 halamanAmlodipine BP Heart DrugChamCham Aquino75% (4)