Instrumentation
Diunggah oleh
Joca Rivera0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
60 tayangan8 halamandsd
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inidsd
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
60 tayangan8 halamanInstrumentation
Diunggah oleh
Joca Riveradsd
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 8
INSTRUMENTATION
Accuracy the degree of exactness of
measurement when
compared to the expected value of the
variable being measured
Measurement the art, or process of
determining the existence
of knowing the magnitude of something,
directly or indirectly in
terms of a recognized standard
Test a procedure, or sequence of
operations for determining
whether a component or equipment is
functioning or working
normally
In measurement, accuracy is the degree of
exactness compared
to the expected value of the variable being
measured
A measure of consistency or repeatability of
measurements is
called precision
Precision is also known as reproducibility
In measurements, the sum of a set of
numbers divided by the total
number of pieces of data in the given set is
called arithmetic
mean
Error the deviation of a reading form the
expected value
I nstrument errors errors due to frictions
of the meter
movement, incorrect spring tension,
improper calibration or faulty
instruments
When an instrument is subjected to harsh
environments such as
high temperature, strong magnetic,
electrostatic, or
electromagnetic field, it may have a
detrimental effects and cause
errors known as environmental errors
Observation errors errors introduced by
the observer or user
Parallax error errors in analog meter
reading due to your
physical position with respect to the meter
scale
Deviation the difference between any
number within the set of
numbers and the arithmetic mean of that set
of numbers
Standard instrument/device an instrument
or device having
recognized permanent or stable value that is
used as a reference
Resolution the smallest change in a
measured variable to which
an instrument will respond
I nstrument a device or mechanism used to
determine the value
of a quantity under observation
Amepe is the basic unit for measuring
current flow
An instrument used to detect and measure
the presence of
electrical current is generally called
galvanometer
D Arsonoval is the common type of meter
moving
D Arsonoval meter movement a
permanent-magnet movingcoil
instrument
Moving-iron instrument an instrument
which depends on
current in one or more fixed-coils acting on
one of more pieces of
soft iron, at least one of which is movable
Moving-magnet instrument depends on
the action of a
movable permanent magnet, in aligning
itself in the resultant field,
produced either by a fixed permanent
magnet and an adjacent coil
or coils carrying current, or by two or more
current-carrying coils
whose axes are displaced by a fixed angle
Thermocouple ammeter is mostly used in
measuring highfrequency
currents
Measurement of high dc-voltages is usually
done by using electrostatic
Electrostatic measuring instrument that
can be used only to measure voltages
Pyrometer this instrument measures
temperatures by electric
means, especially temperatures beyond the
range of mercury
thermometers
Pyranometer this instrument refers to that
one, which measures
the intensity of the radiation, received from
any portion of the sky
I nfinity is the normal indication on a
megger (megaohmmeter)
when checking insulation
Megaohmmeter, megger Resistance
measuring instrument
particularly used in determining the
insulation resistance
Wattmeter an electrodynamic meter used
to measure power
Dynamometer a device used to
mechanically measure the
output power of a motor
Electrodynamometer an indicating
instrument whose movable
coils rotate between two stationary coils,
usually used as
wattmeter
Dynamometers are mostly used as
wattmeter
Air friction damping method is generally
used in dynamometers
Wattmeter dynamometer instrument has a
uniform scale
For a dynamometer to be able to measure
high current, a current
transformer should be used
Error in voltmeter reading is due to loading
Error in ammeter reading is due to insertion
An ohmmeter type of meter requires its own
power source
Error in ohmmeter reading is due to battery
aging
Decreasing the value of the shunt resistor of
an ammeter, its
current measuring capability increases
Increasing the value of the series resistor of
a voltmeter, its voltage
measuring capability increases
Clamp probe a device that is used to
measure current without
opening the circuit
Clamp-meter ammeter has no insertion error
To prevent damage of the multirange
ammeter during selection, an
Ayrton shunt should be used
For the greatest accuracy, the input
impedance of a VOM should be
as large as possible
Voltage measurement in a high impedance
circuit requires a
voltmeter with high input impedance
In order to make an accurate measurement
as possible, the
internal resistance of a voltmeter must be as
high as possible
The purpose of the rheostat in ohmmeter is
to compensate the
aging battery of the meter
The zero-adjust control in an analog type
ohmmeter is used to
compensate for the differing internal
battery voltage
The scale of a hot wire instrument is a
squared function
Moving iron instruments have a scale
function that is squared
To increase the measuring capability of a
moving-iron ac ammeter,
a different number of turns of operating
coil should be used
PMMC electrical instrument is the most
sensitive
Basically, a PMMC instrument can be used
only in dc
measurement
Spring action controlling torque in
PMMC
Eddy current damping method is used in
induction type
ammeter
Induction type instruments are mostly used
as watt-hour meter
In indicating instruments, the controlling
torque increases if the
deflection becomes greater
Controlling torque and deflecting torque
are forces that are
acting on the pointer of an indicating
instrument as it rest on its
final deflected position
Controlling, damping, and deflecting
torques are the forces
acting on the pointer of an indicating
instrument when it is in
motion
Aluminum material that is mostly used as
a pointer in indicating
instrument
A Kelvin electrostatic voltmeter uses fluid
friction method of
damping
Shunts in meters should have a very small
temperature
coefficient of resistance
In a moving coil ammeter, a swamping
resistor is connected in
series with the coil to compensate for
temperature variations
We use the dynamometer in dc and ac
Electrostatic instrument meter that
depends for its operation
on the forces of attraction and repulsion
between electrically
charged bodies
I nduction instrument instrument that
depends for its operation
on the reaction between magnetic flux set up
by currents in fixed
windings and other currents set up by
electromagnetic induction in
movable conduction parts
Permanent-magnet moving-coil instrument
a meter that for
its operation, it depends on a movable iron
vane which aligns itself
in the resultant field of a permanent magnet
and an adjacent
current carrying coil
Vane-type instrument uses the force of
repulsion between fixed
and movable magnetized iron vanes, or the
force between a coil
and a pivoted vane-shaped piece of soft iron
to move the indicating
pointer
Kelvin voltmeter its an electrostatic
voltmeter in which an
assembly of figure 8 shaped metal plates
rotates between the
plates of a stationary assembly when a
voltage is applied between
the assemblies. The length of the arc of
rotation is proportional to
the electrostatic attraction and thus, to the
applied voltage
Magnetometer is an instrument used for
measuring the strength
and direction of magnetic field
Varmeter and reactive volt-ampere meter
are the instrument
used for measuring reactive power in vars
Bridge is a circuit that has four or more
arms, by means of which
one or more of the electrical constants of an
unknown component
may be measured
Resistance bridge, wheatstone bridge a
four-arm bridge. All
arms of which are predominantly resistive;
used for measuring
resistance
Varley loop this is a method of using a
Wheatstone bridge to
determine the distance from the test point to
a fault in a telephone
or telegraph line or cable
Maxwell bridge this refers to a four-arm
ac bridge used for
measuring inductance against a standard
capacitance
Hay bridge refers to an ac bridge for
measuring the inductance
and Q of an inductor in terms of resistance,
frequency and a
standard capacitance
Kelvin double bridge this is a special
bridge for measuring very
low resistance (0.1 or less). The arrangement
of the bridge reduces
the effects of contact resistance, which
causes significant error
when such low resistance are connected to
conventional resistance
bridges
Schering bridge a type of four-arm
capacitance bridge in which
the unknown capacitance is compared with a
standard
capacitance. This bridge is frequently
employed in testing
electrolytic capacitors, to which a dc
polarizing voltage is applied
during the measurement
Wein bridge a frequency-sensitive bridge
in which two adjacent
arms are resistances and the other two arm
are RC combinations
When the capacitors of a Wien bridge are
replaced by inductors,
the bridge becomes Wein inductance bridge
Slide-wire bridge a simplified version of
the Wheatstone bridge
wherein, two of the ratio arms are replaced
by a 100 cm long
Manganin of uniform cross-sections and
provided with a slider
Radio-frequency bridge bridge used to
measure both inductive
and capacitive impedances at higher
frequencies
Balance bridge a bridge wherein all legs
are electrically
identical
Spectrum analyzer is an electronic
instrument capable of
showing on screen and maybe on print,
relative spacing of
transmitter carriers, their sidebands and
harmonics
Spectrum analyzer an instrument capable
of displaying
simultaneously the amplitude of signals
having different
frequencies
A spectrum analyzer is a real-time analyzer
Indications of spectrum analyzer is
presented by means of a CRT
Oscilloscope an electronic measuring
device that provide
instantaneous visual indication of voltage
excursions
Oscilloscope an instrument that is capable
of displaying
waveforms by means of a fluorescence in a
CRT
Storage oscilloscope types of
oscilloscopes that are able to
retain the display for a longer period for
analysis. The display is
retained by the use of flood gun
Sampling oscilloscope uses sampling
technique in processing
signals having frequencies beyond its
normal capabilities
Generally, oscilloscope uses electrostatic
deflection
Signal generators a device or instrument,
which delivers
signals of precise frequency and amplitude,
usually over a wide
range
The two most common audio oscillators are
Wein bridge and
phase-shift
The two most popular RF oscillators are
Colpitts and Hartley
Noise generator a device or instrument
able to generate noise
with accurate voltage for test purposes
You need a noise generator when evaluating
noise
characteristics of an amplifier
In RF or microwave system, reflectometer is
used to measure the
incidental and reflected signals
Reflectometer a type of photometer used
to measure reflection
Dip meter a tunable RF instrument, which,
by means of a sharp
dip of an indicating meter, indicates
resonance with an external
circuit under test
Grid-dip meter a type of dip meter
employing a vacuum tube
oscillator, whose indicating dc
microammeter is in the grid circuit
In meter movement, you prevent the meter
from oscillation and
overswing by damping
When the meter is insufficiently damped, it
is considered as
underdamped
A meter when overdamped will become
insensitive to small signals
Test and Measurement
An ammeter is an indicating instrument
As the deflection of the moving system
increases, the controlling
torque in an indicating instrument increases
DArsonval is the best type of meter
movement
Wattmeter dynamometer type has uniform
scale
When both deflecting and controlling torque
act, the pointer of an
indicating instrument comes to rest
The output voltage of a thermocouple
increases with
temperature
Analog instrument an instrument in which
the magnitude of the
measured quantity is indicated by means of
a pointer
If the pointer of an indicating instrument is
in motion, damping
and controlling torques oppose the
deflecting torque
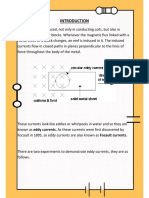
Electrical currents can be induced with a
coil and a magnet by
moving either the magnet or the coil
The fuse should never be replaced with a
higher rated unit
The pointer of an indicating instrument is
generally made of
aluminum
The time interval that a waveform is high (or
low) is the pulse
width of the signal
A Wheatstone bridge is balanced if the ratio
of resistors on one
side of the bridge equals the ratio of
resistors on the other
side
The pointer of an indicating instrument is in
the final deflected
position, the damping torque is zero
Deflecting force a moving system force in
analog instruments
which causes the moving system to deflect
from its zero position
Controlling force a moving system force
in analog instruments
which ensures that the deflection of the
pointer for a given value of
measured quantity always has the same
value
All voltmeters except electrostatic is
operated by the passage of
current
Disc is made of conductor and non-
magnetic material in eddy
current damping
The time interval between pulses is called
pulse delay
An oscilloscope provides easy measurement
of peak to peak
values
Fuse is an element in electronics which
serves as a protection
against overlead
Diode sensor provides a dc voltage
approximately 1V to 10 mW
Hot-wire instrument has a squared scale
For time measurements, horizontal scale of
the scope is used
Fluid friction damping is employed in
Kelvin electrostatic
voltmeter
Current range extension in moving coil
instruments can be
achieved by placing a low resistance
resistor in shunt with the
instrument
Permanent-magnet moving coil instrument
can be used in dc work
only
Control grid CRT element provides for
control of the number of
electrons passing farther into the tube
Orthogonal nulling refers to garaging the
two adjustments of an
AC bridge together in such a way that
changing one adjustment
changes the other in a special way, but
changing the second
adjustment does not change the first
When the vertical input is 0V, the electron
beam may be positioned
at the vertical center of the screen
The reason why the scale of a permanent-
magnet moving coli
instrument is uniform is because it is spring
controlled
Thermal converters a sensing element that
provides a dc
voltage less than 10mV with typical power
range of 0.1 to 100 mW
Tank circuit frequency can be measured by
Grid-dip meter
Shunts are generally made of Manganin
material
1 A meter is the most sensitive
A dynamometer instrument is mainly used
as a wattmeter
Dynamometer movement is the most
expensive
Attraction and repulsion instrument are
considered as movingiron
instruments
In wheatstone bridge, bridge balance is a
condition where there is
no current that flows through the load
The temperature coefficient of resistance of
the shunt material is
negligible
In VTVMS, zero adjust is used to balance
both halves of the
difference amplifier or cathode-coupled
amplifier
In an oscilloscope, intensity control adjusts
the brightness of the
spot by changing the voltage on the control
grid
Damping force a force in analog
instrument which quickly
brings the moving system to rest in its final
position
A small swamping resistance is connected in
series with operating
coil of a moving coil ammeter in order to
compensate for the
effects of temperature variation
The typical power range of diode sensor is
0.1 nW to 10 mW
A milliameter operates on the magnetic
attraction-repulsion
principles
Wheatstone bridge a dc bridge widely
used for the accurate
measurement of resistance
Potentiometer bridge is a dc bridge that is
very useful for
making extremely accurate voltage
measurements
Majority of the analog measuring instrument
utilizes magnetic
effect
Multimeter typically provides measurement
of rms values (for a
sinusoidal waveform)
Dynamometer type instrument can be used
for both dc and ac
works
Permanent-magnet moving coil is an
instrument in which
springs provide the controlling torque as
well as serve to lead
current into and out of the operating coil
In VTVMS, sensitivity refers to the smallest
signal that can be
reliably measured
The frequency of rotation in some rotating
machinery can be
measured by a Spectral meter
An instrument used for observing voltage
and current waveforms is
the oscilloscope
An electrostatic force does not act on the
moving systems of
analog instrument
When current through the operating coil of a
moving-iron
instrument is tripled the operating force
becomes nine times
50 mA is the typical full-scale deflection
current of a moving coil
instrument
Ammeter an instrument used for
measuring the amount of
current flowing in a circuit
DMM a type of meter that gives a precise
reading of voltage,
current or resistance where there is the
generation of samples at
the input and then feeds it to a digital read-
out
50 mV is the typical full-scale voltage across
a moving coil
voltmeter
The period of a repetitive signal is one cycle
of the waveform
Cathode an element of a CRT that releases
electrons when
heated indirectly by a filament
Moving-iron instrument has a squared scale
A pattern displayed by oscilloscope which
has a steady
characteristic is called Lissajous
Changing the number of turns of operating
coil extends the
range of a moving-iron ac ammter
Sawtooth generator is not a basic part of a
CRT
For amplitude measurements, vertical scale
is calibrated in either
volts per centimeter (V/cm), or millivolts
per centimeter (mV/cm)
Thermocouple ammter is used to measure
high-frequency
currents
Electrostatic is used for measuring high
direct voltage
A common technique for measuring power
at high frequency is to
employ a sensing element that converts the
RF power to a
measurable dc or low-frequency signal
The CRT provides the visual displaying
showing the form of the
signal applied as a waveform on the front
screen of a cathode ray
oscilloscope.
Electrostatic instruments are exclusively
used as voltmeters
0.1 W to100 W is the typical power range
of thermocouple
sensors
An electric pyrometer is an instrument used
to measure high
temperature
Permanent-magnet moving coil is the most
sensitive
I nduction watt-hour meter is the most
commonly used induction
type instrument
An integrating type of instrument is the
watt-hour meter
Indicating instrument is assumed to be most
accurate at half of
full part of the scale
On a simple ohmmeter, the 0 ohm mark is
located at far right of
the scale
One of the basic functions of electronic
circuit is the generation
and manipulation of electronic waveshapes
Cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) provides a
visual presentation
of any waveform applied to the input
terminals
The interval of a pulse from start to end is
the period of the pulse
Cathode ray tube (CRT) is considered as the
heart of the
cathode ray oscilloscope
Phosphor a material that glows when
struck by the energetic
electrons in a CRT
Thermiston sensor provides a change of
resistance with typical
power range of 1 W to 10 mW and with
maximum frequency
greater than 100 GHz
Most AC voltmeters have an rms scale
which is valid only if the
input signal being measured is a sinusoidal
signal
Wheatstone bridge measures dc resistance
Hay bridge is used to measure high-Q
inductors (Q>10)
Maxwell bridge measures an unknown
inductance in terms of
known capacitance
Maxwell bridge is used for measuring
medium Q coils (1<Q<10)
Wien bridge has a series RC combination in
one arm and a
parallel RC combination in the adjoining
arm and used as a notch
filter in harmonic distortion analyzer
Sensitivity of a voltmeter is express in
ohm/volt
The smallest change in applied stimulus that
will indicate a
detectable change in deflection in an
indicating instrument is called
resolution
Insulation material is measured by Megger
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fl530619 Gr3 Math TB WT r2gDokumen98 halamanFl530619 Gr3 Math TB WT r2gdmtriBelum ada peringkat
- Math Standards PDFDokumen93 halamanMath Standards PDFjason1989Belum ada peringkat
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDokumen33 halamanAmplifier Frequency ResponseHidayah HadiBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Equations For LinesDokumen5 halamanWriting Equations For LinesJoca RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Newtons Law of MotionDokumen25 halamanNewtons Law of MotionJoca RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDokumen33 halamanAmplifier Frequency ResponseHidayah HadiBelum ada peringkat
- 4 3 PermutationsDokumen48 halaman4 3 PermutationsBenedict AstrologoBelum ada peringkat
- 79e4150ca6bd826651 PDFDokumen24 halaman79e4150ca6bd826651 PDFJoca RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- P546 PDFDokumen0 halamanP546 PDFJoca RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Problem Set1 SolnsDokumen16 halamanThermodynamics Problem Set1 SolnsGopi NathBelum ada peringkat
- Signal System ObjectiveDokumen82 halamanSignal System ObjectiveNitin Kathuria100% (3)
- Electromagnetics PDFDokumen33 halamanElectromagnetics PDFJoca RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- PPSC Physics Lecturer Test Past Papers Solved by Muneer Hayat, PDFDokumen18 halamanPPSC Physics Lecturer Test Past Papers Solved by Muneer Hayat, PDFlog man60% (10)
- 8320-Method of Tests For Lead Acid Storage BatteriesDokumen13 halaman8320-Method of Tests For Lead Acid Storage Batteriesbalkudru100% (1)
- What Is Static ElectricityDokumen8 halamanWhat Is Static ElectricityBrandon LeeBelum ada peringkat
- STD 1100-2005 - Part1Dokumen9 halamanSTD 1100-2005 - Part1Ankur SangwanBelum ada peringkat
- Commissioning Test Procedure Subtransmission CablesDokumen8 halamanCommissioning Test Procedure Subtransmission Cablesjkhgvdj mnhsnjkhgBelum ada peringkat
- Step by Step® Oral RadiologyDokumen448 halamanStep by Step® Oral RadiologyCynthia Octavia100% (6)
- Is 3043 Code Practice of EarthingDokumen86 halamanIs 3043 Code Practice of EarthingAshish JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Insulated Conductor Rail Single Powerline Program 0812: WWW - Conductix.UsDokumen36 halamanInsulated Conductor Rail Single Powerline Program 0812: WWW - Conductix.UsHéctor FuentesBelum ada peringkat
- Antenna FundamentalsDokumen37 halamanAntenna FundamentalsMarco Aurelio PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Rife Frequencies, The Skin Effect and Bio-Electrical Impedance AnalysisDokumen3 halamanRife Frequencies, The Skin Effect and Bio-Electrical Impedance AnalysisKhalid IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure Vessels - Sept 2018Dokumen28 halamanPressure Vessels - Sept 2018Haziq MansorBelum ada peringkat
- Nema-C12.1 2008Dokumen120 halamanNema-C12.1 2008Diego Ernesto Mariño SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2, Traffic Detector Handbook - Third Edition-Volume I - FHWA-HRT-06-108Dokumen45 halamanChapter 2, Traffic Detector Handbook - Third Edition-Volume I - FHWA-HRT-06-108Amarnath M Damodaran100% (1)
- High Voltage Engineering PDFDokumen669 halamanHigh Voltage Engineering PDFMlađan Crkvenjaš100% (6)
- Eee Unit 1 For Video LectureDokumen56 halamanEee Unit 1 For Video LecturePatel DipenBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Project Metal Detector Class 12 BoardsDokumen11 halamanPhysics Project Metal Detector Class 12 Boardsaditya agarwal100% (2)
- 2006 Longitudinal InductionDokumen8 halaman2006 Longitudinal InductionmaheshBelum ada peringkat
- G3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.13 So Much EnergyDokumen14 halamanG3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.13 So Much EnergyPhạm SửuBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion TextDokumen40 halamanCorrosion TextAlex PazmiñoBelum ada peringkat
- Tachick Isolation Overview PDFDokumen52 halamanTachick Isolation Overview PDFmoosuhaibBelum ada peringkat
- Ec100 Model Question Paper With AnswersDokumen35 halamanEc100 Model Question Paper With AnswersSanjay P NambiarBelum ada peringkat
- 3043 (Earthing)Dokumen82 halaman3043 (Earthing)pratap kumar nayakBelum ada peringkat
- Hitachi Cmp5000wxe Plasma TV SMDokumen159 halamanHitachi Cmp5000wxe Plasma TV SMricardoBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Battery Charger Circuit SetupDokumen2 halamanAutomatic Battery Charger Circuit Setupajith_b88100% (1)
- Applying IGBTs - 5SYA 2053-04 PDFDokumen22 halamanApplying IGBTs - 5SYA 2053-04 PDFbacuoc.nguyen356Belum ada peringkat
- Auto Electrical System Module PDFDokumen132 halamanAuto Electrical System Module PDFcharlon castidadesBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 Catalogue-SpanishDokumen101 halaman2016 Catalogue-SpanishwgonzalesmBelum ada peringkat
- 33kV Cable Sizing Report SummaryDokumen13 halaman33kV Cable Sizing Report Summarysrigirisetty208Belum ada peringkat
- Pragathi Full Test 5 Question Paper PDFDokumen20 halamanPragathi Full Test 5 Question Paper PDFAkash A100% (2)
- Noise in Communication SystemDokumen64 halamanNoise in Communication SystemShahrim MohdBelum ada peringkat