Tablas Nefrologia PDF
Diunggah oleh
Thelma Cantillo RochaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tablas Nefrologia PDF
Diunggah oleh
Thelma Cantillo RochaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CREATININA IDEAL = Talla x K/FG
K:
<2500 0,33
RNAT 0,45
<2 aos 0,45
>2 aos 0,55
Adoles H 0,70 M 0,55
FILTRACION GLOMERULAR (FG)
1-2 das de vida
Preterminos 28-32 sem 10,7
32-34 sem 15,9
39-40 sem 20,8
4-6 dias de vida
32-34 sem 24,1
39-40 sem 46,4
6-7 dias de vida 50 +/- 6
3-5 semanas de vida
32-34 sem 37
39-40 sem 64 +/-5
3-4 meses de vida 85
5 meses de vida 87
Lactantes y escolares 85
Adolescente H 124 M 108
MEDIDA DEL FG
Depuracin de = cr urinaria mg%x vol min = X
creatinina cr plasmtica mg%
X. (1,73 / superficie corporal) /sc del paciente
= depuracin de creatinina en ml/min/1.73m
2
Valor normal: Dep Cr x 1,73: 90-120 ml/mto
(Mnimo en nios 90ml/min)
Otra formula:
Creatinuria x Volumen urinario/ Creatinina srica /1440 = 65+/-10 ml/mto/m2
INDICE DE SCHAWRTZ (IS) = TFG
IS= Kx Talla (cms) = Depuracin de creatinina ml/min/1,73
Cr plasmatica
Valores IS
Pretrmino 29-50
RNAT 30-60
0 a 2 aos 50-80
2 a 6 aos 60-100
6 a 13 aos 100
IRC
FG/ml/min x 1,73
>90 Normal
90-50 Leve
50-10 Moderada
10-5 Severa
<5 Terminal
INDICE DE HODSON (Tamao renal)
Talla cms x 0,057 + 2,646 +/- 2
Comparado con la Eco renal
INSUFICIENCIA RENAL
Gasto normal :
< 10 kg : 1-5 cc/k/h
>10 kg : 12 80 cc/m2/h
Oligurica:
< 10 kg : < 1 cc/k/h
> 10 kg: < 12 cc/m2/h
< 300 cc/m2/da
Anuria
<0,5 cc/kg/hora
<100 cc/m
2
/dia
Poliuria:
En IRA . > 2 cc/k/h
< 10 kg : > 5 cc/k/h
>10 kg :
> 80cc/m
2
/hora
> 2000cc/mt2/da
Agua endgena 200cc/m
2
VOLUMENURINARIO
Normal: 300-2000 cc/mt2/dia
Aguda: hasta 3 meses
Crnica: ms de 1 ao
Laboratorio Falla
PreRenal
NTA
Urea/ Creatinina > 20 10- 20
Densidad Urinaria > 1020 < 1010
Osmolaridad Urinaria > 500 < 350
Sodio urinario < 10 > 40
FENA* < 1% > 2%
Fe Urea < 30 > 50
Urea Urinaria / srica > 10 < 5
Na urinario
>40 meq/l: Insuf Renal
RNpuede ser normal
20-40 meq/L (normal)
RENOGRAMA Y FILTRACION GLOMERULAR
Filtracion glomerular: Valor normal segun edad sin corregir x 1.73 M2
Renograma diurtico: T Eliminacin 50%
Tiempo medio <15 min - Normal
15-20 min Indeterminado (pelvis complaciente,
obstruccin parcial, Fx renal Alterada)
>20 min = obstruccin
HIPERCALCIURIA
Normal <4mg/kg/dia (Recoleccion de 24 horas)
Relacin Calciuria/Creatinuria
>0,2 Hipercalciuria
0,18-0,2 Indeterminado
<0,18 Normal
<6m hasta 0,8
6-12 m hasta 0,6
Relacin Na/K (orina)
<2,5 Normal
2,5-4,5 Indeterminado
>4,5 Hipercalciuria
Dietario dependiente
Se piden gases venosos por sospecha de acidosis
tubular
PROTEINURIA
Proteinuria muestra aislada de PO
Significativa >15mg/dl
Severa >100mg/dl
Proteinuria segn la edad
Lactante 145mg/da
2-4 aos 155mg/da
4-10 aos 190mg/da
10-16 aos 250mg/da
Relacin Proteinuria/creatinuria
Normal Hasta 0.5 en <2aos luego
<0,2 Normal
0,2-0,5 Leve
0,5-2 Moderada
>2 Severa (Rango nefrtico)
Proteinuria PO
+ 30mg/dl
++ 100mg/dl
+++ 300mg/dl
++++ >1gr
Proteinuria: mg/24h/SC
Normal 0 - 4 mg/m
2
/h
Leve 4 - 10 mg/m
2
/h
Moderada 10- 40 mg/m
2
/h
Severa >40 masivo o rango nefrtico
Microalbuminuria=
1-14mcg /min/1,73m2 = proteinuria glomerular
Betaglobulina
Proteinuria tubular = >3m: <400mcg/l
Relacin albumina/ B2 micro:
200-300 normal
<300 proteinuria tubular
HEMATURIA
RTO HAMBURGUER: positivo si mayor de 1000
eritrocitos/orina de 3 horas
SINDROME ELIMINACION DISFUNCIONAL
RESIDUOVESICAL
Hipotticamente cero
Lactantes hasta 20cc
Pre y Escolares hasta 5cc
CAPACIDAD VESICAL
Edad (aos) + 2 x 30
10cc x Kg primeros 10 Kgs
VEJIGA NEUROGENICA
Residuo Mayor del 30%
IVU: CRITERIOSDXPARAIVU
PSP: cualquier recuento bacilos gram(-), Mas de
3.000 cocos gram(+) en adolescentes.
Cateterismo: > 50.000 confirmatorio
10.000 - 50.000: probable segun clinica y patogeno.
< 10.000: muy poco probable.
Miccion: >100.000: confirma.
>50.000 : tiene valor
>10.000: dudoso. Aconfirmar.
<10.000: poco probable.
RVU
GRADOI: urter solamente
GRADOII: urter, pelvis, clices sin dilatacin
GRADOIII: dilatacin leve a moderada y/o
tortuosidad del urter y leve dilacin de la pelvis
GRADOIV: dilatacin moderada y/o tortuosidad del
urter y leve-moderada dilacin de la pelvis renal mas
clices
GRADOV: Dilatacin gruesa y tortuosidad del urter,
gran dilatacin de la pelvis renal y los clices, sin
impresin papilar en la mayora de los clices
DIALISIS PERITONEAL
KTR/V= KRUX7 X1440/VD
Normal >2
KRU= (BUNurinario x Volumen urinario/1440) 60
VDpara nios
- Talla mayor 132,7 cms
Lts = -21,993 + 0,456 x peso + 0,209 x
Talla
- Talla menor 132,7cms
Lts = -1,927 + 0,485 x peso + 0,045 x
Talla
VDpara nias
- Talla menor 110 cms
Lts = 0,076 + 0,507 x peso + 0,013 x
Talla
- Talla mayor 110 cms
Lts = -10,213 x 0,252 x peso + 0,154 x
Talla
Lactante menor <0,65% peso
Lactante mayor >0,60% peso
Adulto 0,58%
Dosis recibida de Dianeal
KT/V UREA= DP UREAx Vol da x 7/VD
Volumen a administrar
KT/V deseado x VD/7 x D/P
Meta de aclaracin de UREA
Hemodilisis 1,2-1,3
CAPD 2,3-2,6
Rata catablica proteica
RCP = (6,49 x BUN urinario) + (0,294 x VD) + perdida proteica
dializado
SX NEFRITICO
Hematuria micro o macroscpica, HTA, edemas, con o sin oliguria
o alteraciones de la funcin renal
CAUSAS
1. Infecciosas
2. No infecciosas: a. Enf. Multisistmicas
b. Enf. Glomerular primaria
SINDROME NEFROTICO
Proteinuria > 40 mg M2 hora
Hipoalbuminemia: menor 2 gm
Edemas
Hipercolesterolemia: > 200 mg
TRANSTORNOS DE LIQUIDOS
SSIADH
DIABETES
INSIPIDA
ENC
PERDEDOR
SAL
Na serico <130 >150 <130
Na urinario >60 <40 >120
Osmolaridad
Serica
<275 >305 <275
Osmolaridad
Urinaria
<500 <250 >300
Densidad
Urinaria
<1020 <1000 >1010
Diuresis Disminuida aumentada aumentada
HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL EN NIOS
CLASIFICACION
NORMAL: < P90
PREHIPERTENSION: P90-P95
ESTADO 1 HT: P95-P99 +5
ESTADO 2 HT: >P99+5
ACIDOSIS TUBULAR RENAL
U/PHCO3 // U/PCr X 100
< 5% normal o distal tipo I
5-15% mixta
>15% Proximal o tipo II
Anion Gap serico= Na- (Cl + HCO3)
Normal: 12+/- 2
Anion Gap urinario= (Na+ urinario + K+ urinario) Cl urinario
pH< 6,5 (Na + K) Cl
(+) Incapacidad excrecion H+
:
: acidosis tubular tipo I
(-) Acidosi tub tipo II
Gap osmolar: Osmurin medida osmurin calculada:
> 200: buena capacidad de acidificacin
< 200: incapacidad para excretar H+, acidosis tubular distal
Delta CO2 : PCO2U-P
normal > 20 de PCO2U-P
Si < 20 = (Acidosis tubular) : menor Capacidad para excretar H
+
POTASIO
Excrecin fraccional de potasio:
VALORES NEFROPEDIATRIA REVISION 2011
Ricardo Gastelbondo MD , Zilac Espitaletta MD Claudia Quijano MD Magda puerta MD, Yeferson Alvarez MD
FeK+ = K+ urinario/ srico x 100
Creatinina U/ srica
RN< 8 %
Resto < 15 %
Si > entonces buena accin aldosterona
Gradiente transtubular de concentracin de K+
GTTK+= U/S K+ .
U/S osmolaridad
HIPERKALEMIA: TTO
Salbutamol: inhalado o IV (4 - 5 g/kg x 15 min)
Keyaxalate (Sodiumpolystyrene sulfonate) o -Resincalcio
Bicarbonato de Sodio IV: 1 mEq/L x 10 a30 min
Gluconato de Calcio: (10%) IV: 0.5 to 1.0 mL/kgx 5 a 15 min
Glucosa 0.5 g/kg + Insulina 0.1 U/kg IV x 30 min
ESTADO ACIDO-BASE
Formulas de correccin:
Si se alteran las protenas: por cada gramo de descenso o aumento de la
albmina se disminuye o aumenta el anin Gap en 2mE/Lt
Acidosis metablica: por cadadescenso del bicarbonato, la PCO2 desciende
1,25 mmHg
Alcalosis metablica: por cada mEq/l de descenso del bicarbonato, la PCO2
asciende 0,7 mmHg
Acidosis Metablica:
o Aguda: por cada mmHg de ascenso de la PCO2, el bicarbonato
aumenta 0,1mE/lt
o Crnica: por cada mmHg de ascenso de la PCO2, el bicarbonato
aumenta 0,35mE/lt
Alcalosis Respiratoria: por cada mmHg de descenso de la PCO2, el
bicarbonato desciende 0,2mE/lt
SODIO
CORRECCIN DE LOS VALORES DEL SODIO PLASMTICO
Correccin en nios con hiperglicemia: por cada 100mg%de ascenso de la
glicemia, disminuye la natremia en 1,6mE/lt
Por triglicridos: tigliceridos mg%x 0,002. El resultado se suma a la
natremia obtenida.
Correccin de las anormalidades electrolticas:
mEq necesarios = (valor deseado valor paciente) x factor de distribucin x
peso en KG
Factor de distribucin:
Na+= 0,6
Cl- = 0,3
HCO3- = 0,41
Correccin de hipernatremia
Dficit de agua libre = 0,6 x Kg. x (Na+ del paciente -1)
140
La disminucin de la natremia no debe ser mayor a 0,5-1mEq/h
Correccin de hiponatremia
No debe aumentar ms de 0,5-1 mEq/h:
1. Estimar el dficit previo de sodio:
0,6 x Kg. x (Na+ terico Na+ real)
2. Estimar el exceso de agua con hiponatremia y LECnormal (euvolemica)
Exceso de agua= ACT (peso terico x0,6) x Na+ terico ACT
Na+ plasmtico
Expresa el exceso de ACT en litros que debe disminuirse en 48-72 horas
CALCIO
Correccin del calcio de acuerdo a la albuminemia
Ca++ corregido mg/dl =4-albuminax0.8+Ca paciente
Ca++ corregido nMoles/L = Ca++ medido mMol/L 0,025 x Albmina (gr/dl) + 1
Por protenas Totales
Ca++ corregido mg/dl = Ca++ / (0,6 + Protenas Totales (gr/dl)) / 19,4
Ca++ corregido nMoles/L = Ca++ / (0,6 + Protenas Totales (gr/dl)) / 19,4
HIPOCALCEMIA/ HIPERFOSFATEMIA: TTO
Carbonato de calcio 45 a 65 mg/k/da
Glucotano de Calcio (10%): 0.5 a 1 mL/kg (max 10 mL)
Si el paciente esta cursando con tetania o con arritmias cardiacas
FOSFORO
Excrecin fraccional de fsforo
FeP= P urinario/ srico x 100
Creatinina U/ srica
Reabsorcin tubular del fsforo (RTP) = 1 FeP
Normal mas de 80%
CLORO
Fe Cloro= [(Cl urinario/srico) / (creatinina U/S] x 100
Normal hasta 5%
5%: excrecin aumentada de Cl = tubulopata
TRASTORNOS OSMOLARES
Osmolaridad plasmticas =
Na+ x 2 + (Glucosa /18) + (Urea/6) + (BUN/2,8)
Tonicidad plasmtica = Na+x2 + glucosa mg/dl
18
Osmolaridad Urinaria = Densidad urinaria 1000 x 40
Osmol U= (Na+Urinario + K+ Urinario) x 2 + Urea
6
OsmGAP= Osmdel paciente por Osmometra
Osmx frmula
Valor normal = 10
Clearence Osmolar = Volumen x U/SOsm
Clearence agua libre = Volumen x(1- U/Sosm)
CCULO DE INGESTA PROTICA
Gr de protena ingerida=
(0,031gr/Kg + Urea urinaria gr/24h) x 6,25
2,03
ESTUDIO METABLICO EN ORINA
Citraturia
Varones= 9,76 mg/Kg/da 5,88
Mueres = 11,26 mg/Kg/da 6,10
Citraturia mg / calcio mg
Varones= 5,3 4,1
Mujeres= 8,2 10,1
Citraturia/ creatinuria > 400
439mg 49 mg/gr de creatinina
Adulto > 320 mg en 24 horas
cido rico
520 147 mg/da/1,73
13 2,5 mg/kg7da
cido rico mg/creatinina mg=
3-4 aos: 0,88 0,22
5-6 aos: 0,71 0,21
7-8 aos: 0,62 0,18
9-10 aos: 0,56 0,16
11-12 aos: 0,46 0,13
13-14 aos: 0,36 0,11
Adultos: 0,34 0,1
Magnesio
2,10 1,1 mg/kg/da
Magnesio mg/ creatinina mg
1-2 aos: 0,09 0,37
2-3 aos: 0,07 0,34
3-5 aos: 0,07 0,29
5-7 aos: 0,06 0,21
7-10 aos: 0,05 0,18
10-14 aos: 0,05 0,15
Fosfato
12,4 4,6 mg/kg/da
Fosfato mg/creatinina mg=
0-2 aos: 0,8 -2
3-5 aos: 0,33-2,17
5-7 aos: 0,33- 1,49
7-10 aos: 0,32 -0,97
Fosfaturia/Creatinuria
Hasta 0,63
Mayor es fosfaturia
Fosfaturia/kg/da: hasta 20mg/kg/da
TRP = (1 [Porina x
Crsangre/Psangre x Crorina]) x 100.
TmP/FG .Psangre (Porina x
Crsangre/ Crorina). Normal:> 3 mg/dl.
Oxalato
36,9 13,7 mg/da/ 1,73
25mg/mt2/da
Oxalato urinario/ creatinuria:
< 1 ao: 0,061
1-5 aos: 0,036
5-12 aos: 0,03
> 12 aos: 0,013
Sodio = 3,8 mg 13 mEq/Kg/da
> 2aos:0,2mEqNa+/mg de creatinina 0,07
Cistina
Nios: No debe haber en la orina.
Adultos <200mg/da
VALOR NORMAL EN ORINA
Densidad 1010 1030
pH4,5 6,5
Nitritos = negativp = 0
Hemoglobina = 0
Mioglobina = 0
VALORES NORMALES DE HEMOGLOBINA Y
HEMATOCRITO POR EDAD
Edad Hb
( g)
HTO% Leucocito
s/mm
RNPT 13.4 41.5 4.400
RNAT 18.5 56 18.100
2 semanas 16.6 53 11.400
1 mes 13.9 44 10.800
2 meses 11.2 35 10.800
6 meses 12.6 36 11.900
6 m- 2 aos 13.5 40 10.600
2 - 6 aos 12.5 37 8.500
6 12 aos 13.5 40 8.1000
12- 18 aos
Hombre
Mujer
14.5
14
43
41
7.800
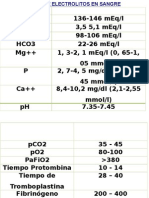
OTROS VALORES EN SANGRE
Muestras sricas
Medicin usual
Acido Homovanlico
Menores de 1 ao
De 2 a 4 aos
De 5 a 9 aos
De 10 a 14 aos
De 15 a 18 aos
< 35 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
< 13.5 a 23 mcg/mg de creatinina/24h
< 9 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
< 7 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
< 2 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
Acido Vanilmandlico
Menores de 1 ao
De 1 a 4 aos
De 5 a 9 aos
De 15 a 18 aos
< 27 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
< 13 a 18 mcg/mg de creatinina/24h
< 8.5 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
< 5 mcg/mg de creatinina/24 horas
Acido rico
Menores de 14 aos
2 7 mg/dl.
Amonio (venoso) 29 - 70 mcg/dl.
ASTOS < 200 unidades Todd
Colesterol total
VLDL
LDL
HDL
120 - 200 mg/dl.
< 170
62 - 130
35 - 135 (>25%de colesterol total)
Complemento total 41 - 90 unidades hemolticas
Cortisol 6 -18 mcg/dl.
C3
1 mes a 10 aos
> 10 aos
50 - 200 mg/dl.
83 -177 mg/dl.
C4
1 mes a 10 aos
> 10 aos
7 - 40 mg/dl.
15 - 45 mg/dl.
Deshidrogenasa
lctica (DHL)
1 mes a 2 aos
3 aos a 17 aos
200 570 U/L
100 360 U/L.
Protenas totales
Albmina
Globulinas
6.0 8.0 gm/dl.
3.5 5.5 gm/dl.
2.3 3.5 gm/dl.
Urea 5 - 25 mg/dl.
Table 2 Drug doses for children with normal and reduced kidney
function. All doses are given for normal renal function, for a
glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 40 and 10 ml/min/1.73 m
2
, and
for anuric patients. The doses for reduced renal function are cal-
culated as a percentage of the normal dose and divided into the
indicated number of single doses (for example: normal dose
100 mg/kg/day in two single doses = 250 mg/kg daily; dose at a
GFR of 10 ml/min/1.73m
2
: 30% in one single dose = 130 mg/kg
daily)
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Aldosterone antagonists
Spironolactone PO: 15 mg/kg in 2 single doses 50%
(1 single
dose)
25%
(1 single
dose)
Contraindicated
IV: 5 mg/kg in 4 single doses
Analgesics/anti-inflammatory agents
Acetylsalicylic
acid
5(10) mg/kg as single dose
(max. 4/day)
75% 50% (in-
crease dose
interval)
50% (increase dose
interval)
Ibuprofen 2030 mg/kg in 34 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 1.2 g
Indomethacin 25 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses 50% (2 single doses)
Max. daily dose 200 mg
Metamizole 20 mg/kg as single dose
(max. 4/day)
Normal dose 75% 75% (increase dose
interval, short-time
use only)
Paracetamol 1020 mg/kg as single dose
(max. 4/day)
Normal dose 50% (in-
crease dose
interval)
50% (increase dose
interval)
Max. daily dose 4 g
Piritramide 0.050.1(0.2) mg/kg as single dose Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Tramadol 1 mg/kg as single dose Normal dose 50% (in-
crease dose
interval)
50% (increase dose
interval) Max. daily dose 400 mg
Antiallergics
Clemastine 0.05(0.1) mg/kg/day in 2 single
doses
Normal dose Normal dose 50% (1 single dose)
Dimethindene 0.1 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 6 mg
Terfenadine 2 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose Normal dose 50% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 120 mg
Antiasthmatics
Reproterol-HCl Perfusor: 0.1 g/kg/min Normal dose 80% 60%
Terbutaline PO: 0.2 mg/kg as single dose Normal dose 50% Avoid
IV: 0.15 mg/m
2
as single dose
Theophylline Loading dose 47 mg/kg Normal dose 50% 50%
Maintenance dose 1520 mg/kg/day
Continuous infusion: 1 mg/kg/h
Plasma levels: 520 mg/l
Antibiotics
Aminoglycosides
Amikacin 15 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose 40%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
20%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
10% (1 single dose);
loading dose
5 mg/kg;
33% after hemodialy-
sis (plasma levels!);
intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 25 mg/l,
maintenance dose
12 mg/l
Peak level 2030 mg/l
Trough level 2.510 mg/l
Max. daily dose 1 g
Gentamicin 35 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 60%
(2 single
doses)
Reduce
loading dose
10%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
5% (1 single dose),
loading dose
12 mg/kg;
15% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
loading dose 8 mg/l,
maintenance dose
4 mg/l
Peak level 510 mg/l
Trough level 0.52 mg/l
Max. daily dose 360 mg
Netilmicin 6 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose 60%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
15%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
10% (1 single dose);
loading dose IV
2 mg/kg
20% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
loading dose 8 mg/kg,
maintenance dose
4 mg/l
Peak level 510 mg/l
Trough level 0.52 mg/l
Max. daily dose 300 mg
Tobramycin 6 mg/kg in 1 single dose 60%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
10%
(1 single
dose)
Reduce
loading dose
5% (1 single dose);
loading dose
2 mg/kg
15% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
loading dose 8 mg/l,
maintenance dose
4 mg/l
Peak level <10 mg/l; trough
level 0.52 mg/l
Max. daily dose 360 mg
1677
AJUSTE DE MEDICAMENTOS EN FALLA RENAL
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Carbapenems
Imipenem +
cilastatin
60 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 75%
(3 single
doses)
25%
(2 single
doses)
15%
(1 single dose)
Intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 500 mg/l,
maintenance dose
2200 mg/l/day
<3 months: 40 mg/kg/day in 2 single
doses
Max. daily dose 4 g
Cephalosporins
Cefaclor 40 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Prophylaxis of recurrent urinary tract
infection: 10 mg/kg/day in 1 single
dose
Max. daily dose 3 g
Cefazolin 50100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 75%
(3 single
doses)
30%
(2 single
doses)
10%
(1 single dose)
Intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 500 mg/l,
maintenance dose
125 mg/l
Max. daily dose 12 g
Cefixime 8 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
50%
(1 single dose) Max. daily dose 400 mg
Cefotaxime 50100 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose 60%
(2 single
doses)
60%
(2 single doses)
Intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 500 mg/l,
maintenance dose
250 mg/l
Meningitis: 200 mg/kg/day in 4 single
doses
Max. daily dose 6 g
Cefotiam 50100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 100%
(2 single
doses)
50%
(2 single
doses)
20%
(1 single dose)
25% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
loading dose 250 mg/l;
maintenance dose
125 mg/l
Max. daily dose 4 g
Ceftazidime 50100 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses 50%
(2 single
doses)
15%
(1 single
dose)
10%
(1 single dose)
30% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
loading dose 250 mg/l,
maintenance dose
125 mg/l
Max. daily dose 6 g
Ceftriaxone 50100 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 80%
(1 single
dose)
50%
(1 single dose)
1 normal dose after
hemodialysis; intra-
peritoneal: loading
dose 250 mg/l, main-
tenance dose 125 mg/l
Max. daily dose 2 g
Cefuroxime 50100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
15%
(1 single dose)
30% after hemodialy-
sis; prophylaxis in
peritoneal dialysis:
250 mg/l
Max. daily dose 4.5 g
Cefuroxime
axetil
25 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose 33%
(1 single
dose)
25%
(1 single dose)
50% after hemodialy-
sis Max. daily dose 1 g
Glycopeptides
Teicoplanin Loading dose 20 mg/kg in 2 single
doses (1st day), maintenance dose 6
10 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose; trough
level >8 mg/l
40%
(1 single
dose)
10%
(1 single
dose)
IV: 1 loading
dose, monitor
plasma levels
Peritoneal dialysis:
loading dose 15 mg/
kg; intraperitoneal [34]
(days 1+8);
Max. daily dose 400 mg
Vancomycin 2040 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 30%
(1 single
dose)
5%
(1 single
dose)
IV loading dose
500 mg/l,
maintenance dose
30 mg/l 34
peak level: 2040 mg/l, trough level
510 mg/l
Max. daily dose 2 g
Gyrase inhibitors
Ciprofloxacin PO: 15 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
33%
(1 single dose)
Intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 50 mg/l,
maintenance dose
25 mg/l
IV: 10 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses
Max. daily dose 800 mg
Ofloxacin PO: 7.5 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses 50%
(1 single
dose)
15%
(1 single
dose)
15%
(1 single dose)
20% after hemodialy-
sis IV: 5 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses
Max. daily dose 800 mg
Macrolides
Azithromycin 10 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 500 mg
1678
Table 2 (continued)
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Clarithromycin 10(20) mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
50% (2 single doses)
Max. daily dose 1 g
Erythromycin 3050 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 60%
(3 single
doses)
60% (3 single doses)
Max. daily dose 2 g
Roxithromycin 5 mg/kg/day in 12 single doses Normal dose 60%
(2 single
doses)
60% (2 single doses)
Max. daily dose 300 mg
Nitroimidazoles
Metronidazole PO: 2030 mg/kg/day in 3 single
doses
Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
50% (2 single doses)
IV: 30 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses
Max. daily dose 1.5 g
Penicillins
Amoxicillin 50 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 30%
(2 single
doses)
15% (1 single dose) 30% after
hemodialysis Newborn: 1520 mg/kg/day
in 3 single doses
Max. daily dose 6 g
Amoxicillin +
clavulanic acid
IV: 60100 mg/kg/day in 3 single
doses
Normal dose 25%
(2 single
doses)
15% (1 single dose) 30% after
hemodialysis
PO: 40 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses
Newborn: 2 single doses
Max. daily dose 8 g
Ampicillin 100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 25%
(3 single
doses)
15% (12 single
doses)
30% after hemodialy-
sis; intraperitoneal:
maintenance dose
125 mg/l
Newborn: 50100 mg/kg/day
in 2 single doses
Max. daily dose 16 g
Benzylpenicillin 50250,000 IU/kg/day in 4 single
doses (>1 year) and/or 23 ED
(<1 year)
75%
(3 single
doses)
50%
(2 single
doses)
20% (2 single doses) 30% after
hemodialysis
Max. daily dose 20 MIU
Flucloxacillin 50100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 50%
(3 single
doses)
25% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 8 g
Phenoxymethyl-
penicillin
4080,000 IU/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
25% (2 single doses) Supplementary dose
after hemodialysis
= 1 normal dose
Newborn: 50250,000 in 2 single
doses
Max. daily dose 6 MIU
Other antibiotics
Clindamycin PO: 20 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose Normal dose 75% (accumulation
possible; use
<14 days)
Intraperitoneal: load-
ing dose 300 mg/l,
maintenance dose
150 mg/l
IV: 40 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses
Max. daily dose 2.4 g
Doxycycline Loading dose 4 mg/kg/day
in 2 single doses
Normal dose Normal dose 70%
(2 single doses)
Maintenance dose
2(4) mg/kg/day in 12 single doses
Max. daily dose 200 mg
Linezolid Adults: PO/IV 15 mg/kg/day
in 2 single doses
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose, accu-
mulation of inactive
metabolites
Nitrofurantoin 35 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Contraindi-
cated
Contraindi-
cated
Contraindicated
Trimethoprim
(TMP) + sulfa-
methoxazole
(SMZ) (1:5)
PO/IV: 5 mg/kg/day TMP in 2 single
doses
Anthelmintics
Mebendazole Trichuriasis/ascaris: 2100 mg
for 3 days
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Enterobius: 1100 mg for 3 days,
repeat after 2 and 4 weeks
1679
Table 2 (continued)
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Antifungal agents
Amphotericin B 1st7th days 0.51 (liposomal
preparation: 4) mg/kg daily; later,
every 2nd day; peak level 1.52
Normal
dose;
liposomal
preparation
suggested
Normal
dose; liposo-
mal prepara-
tion suggest-
ed
Normal dose;
liposomal prepara-
tion suggested
Fluconazole 5 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
100% every
72 h
100% after each
hemodialysis;
intraperitoneal
36 mg/kg/day
100% after each
hemodialysis;
intraperitoneal:
36 mg/kg/day
Max. daily dose 400 mg
Flucytosin Loading dose 100150 mg/kg/day
in 4 single doses
50%
(2 single
doses)
20%
(1 single
dose)
100% after each
hemodialysis;
100% after each
hemodialysis
Maintenance dose 50 mg/kg/day
Itraconazole Prophylaxis: 5 mg/kg in 2 single doses Normal dose No data No data
Therapeutic: 510 mg/kg in 2 single
doses
Max. daily dose 600 mg
Ketoconazole <20 kg: 2.55 mg/kg/day in 1 single
dose
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
>20 kg: 510 mg/kg/day in 1 single
dose
Max. daily dose 600 mg
Antituberculous agents
Ethambutol PO: 15 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
50% after hemodi-
alysis, 25% every
non-hemodialysis
day
50% after hemodi-
alysis, 25% every
non-hemodialysis
day
Isoniazid PO/IV: 200 mg/m
2
/day in 1 to 3 doses;
not >10 mg/kg/day when combined
with rifampicin
Normal dose Normal dose 1st week 100%,
then 60% (1 single
dose)
Supplemental dose
after hemodialysis
5 mg/kg
Max. daily dose 300 mg
Pyrazinamide 30 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
1 normal dose
after hemodialysis
3/week
1 normal dose after
hemodialysis 3/week Max. daily dose 2.5 g
Rifampicin 350 mg/m
2
/day in 1 single dose Normal dose Normal dose 1st week 100%, then
75% (1 single dose) Max. daily dose 600 mg
Antivirals
Acyclovir VZV: 1,500 mg/m
2
/day in 3 single
doses; HSV: 750 mg/m
2
/day
in 3 single doses
60%
(2 single
doses)
20%
(1 single
dose)
15% (1 single dose) 4-h hemodialysis:
40% loss
Brivudine PO 15 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 33%
(2 single
doses)
25% (1 single dose)
Foscarnet Loading dose: 180 mg/kg/day
in 3 single doses as short infusion
40%
(2 single
doses)
20%
(1 single
dose)
13% (1 single dose)
Maintenance dose: 100 mg/kg/day
in 1 single dose
Ganciclovir IV: initial (14 days) 10 mg/kg/day
in 2 single doses, then 5 mg/kg/day
in 1 single dose
IV: 40%
(2 single
doses)
10%
(1 single
dose); orally
in 2 single
doses
1.25 mg/kg after
each hemodialysis
(or 5% during peri-
toneal dialysis); PO
in 2 single doses
1.25 mg/kg after each
hemodialysis (or 5%
during peritoneal dial-
ysis); PO in 2 single
doses
PO: 100 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses
PO dose at GFR<40: mg/kg = GFR;
max. daily dose 3 g PO
Indinavir 1,500 mg/m
2
/day in 3 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Lamivudine 8 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses 50%
(2 single
doses)
15%
(1 single
dose)
10% (1 single dose)
Loading dose
1.3 mg/kg
Max. daily dose 300 mg
Valacyclovir PO: 3,000 mg/m
2
/day in 3 single doses 60%
(2 single
doses)
20%
(1 single
dose)
15% (1 single dose) 4-h hemodialysis:
40% loss Max. daily dose 6 g
Zidovudine 450 mg/m
2
/day in 3 single doses Normal dose normal dose 50% (3 single doses)
Max. daily dose 800 mg/m
2
1680
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Anticonvulsive drugs
Carbamazepine PO: 1030 mg/kg/day in 3 single
doses
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Trough level 1040 M
Max. daily dose 1 g
Clonazepam 0.050.1(0.5) mg/kg/day
in 23 single doses
Normal dose Normal dose 75% (23 single
doses)
Max. daily dose 8 mg
Ethosuximide Loading dose 510 mg/kg/day Normal dose Normal dose 75%
Maintenance dose 1520 mg/kg/day
Lamotrigine 2 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses for
2 weeks, then 5 mg/kg for 2 weeks,
then 515 mg/kg/day
Normal dose Normal dose 75% (2 single doses)
Max. daily dose 400 mg
Phenobarbital Loading dose 10-20 mg/kg 80% 30% 25%
Maintenance dose 5 mg/kg/day
in 2 single doses
Trough level approx. 20(80) mg/l
Max. daily dose 800 mg
Phenytoin Loading dose 1520 mg/kg IV
over 30 min
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose; some-
times increased dose
necessary! Maintenance dose 5 mg/kg/day
in 12 single doses
Trough level 520 mg/l
(48 mg/l in uremia)
Sodium
valproate
Approx. 25(120) mg/kg/day in 24
single doses
Normal dose 75% No data
(plasma levels)
Trough level: 50100 mg/l; start
with low dose (10 mg/kg/day)
Sultiam 5(10) mg/kg/day in 2 single doses No data No data No data
Antihypertensives
ACE inhibitors
Captopril 0.35 mg/kg/day in 23 single doses 40%
(1 single
dose)
10%
(1 single
dose)
20% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 150 mg
Enalapril 0.10.2 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 25%
(1 single
dose)
15% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 40 mg
Ramipril 0.10.2 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 50%
(1 single
dose)
30% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 10 mg
Beta blockers
Atenolol 0.52 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 25% 2550%
Max. daily dose 100 mg
Bisoprolol 0.2 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose 66%
(1 single
dose)
50% (1 single dose)
Max. daily dose 10 mg
Propranolol PO: 0.51 (2) mg/kg/day in 3 single
doses
Normal dose 80%
(23 single
doses)
80% (23 single
doses)
Max. daily dose 320 mg
IV: 0.5 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses
Max. daily dose 10 mg
Calcium antagonists
Amlodipine 0.050.15 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 10 mg
Diltiazem 1 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
3(14) g/kg/min
Max. daily dose 360 mg
Nifedipine 0.52 mg/kg/day in 23 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
IV: 0.05 mg/kg/h
Max. daily dose 60 mg
Nitrendipine Adults: 2040 mg/day in 12 single
doses
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
1681
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Other hypotensive agents
Acetazolamide 30 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 50%
(2 single
doses)
30%
(2 single
doses)
20% (1 single dose)
Clonidine 530 g/kg/day Normal dose 75% 50%
Max. daily dose 900 g
Doxazosin Initial 0.5 mg/m
2
/day in 12 single
doses
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 8 mg
Losartan Adults: Max. daily dose 100 mg
in 1 single dose
Glycerol
trinitrate
Continuous infusion: 1 g/kg/min Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Nitroprusside
sodium
1(0.55) g/kg/min Normal dose Normal
dose; Cave
thiocyanate
Cave thiocyanate
accumulation (plas-
ma levels <10 mg%)
Prazosin 50500 g/kg/day in 4 single doses Normal dose Normal dose 75% (3 single doses)
Max. daily dose 20 mg
Urapidil Initial: 3.5 mg/kg/h for 30 min Normal dose 60% 50%; avoid
long-term use Continuous: 0.21 mg/kg/h
Antiemetics
Dimenhydrinate PO: 5 mg/kg/day in 4 single doses Normal dose Normal dose 75% (3 single doses)
IV: 150 mg/m
2
/day in 4 single doses
615 kg: 40 mg supp.
Max. daily dose 600 mg
Ondansetron 0.1 mg/kg as single dose
(max. 3/day)
Normal dose 75% 60%
Max. daily dose 24 mg
Anti-gout drugs
Allopurinol 10 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses 30% (every
48 h)
30%
(after hemodialysis)
30%
(after hemodialysis) Max. daily dose 800 mg
Colchicine Adults: start 12 mg/day
in 1 single dose
50%
Max. daily dose 8 mg
Antineoplastic agents
Azathioprine 1.52 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose (accu-
mulation of
metabolites possi-
ble)
Max. daily dose 5 mg/kg
Cisplatin 20 mg/m
2
in 1 single dose on
5 sequential days every 34 weeks or
Contraindi-
cated
Contraindi-
cated
Contraindicated
50120 mg/m
2
in 1 single dose every
34 weeks
Cyclophos-
phamide
Nephrotic syndrome: 2 mg/kg/day PO
in 1 single dose
Normal dose 50% 40% +20% after
hemodialysis
Ifosfamide Mostly 2,000 mg/m
2
in 1 single dose
on 5 sequential days
Avoid Contraindi-
cated
Contraindicated
Methotrexate Dose according to protocol Contraindi-
cated
Contraindi-
cated
Contraindicated
Calcium metabolism (bisphosphonates)
Clodronate PO: 1 g/m
2
in 1 single dose 75%
(1 single
dose)
25%
(1 single
dose)
Short-term
use only
15% (1 single dose)
IV: 200 mg/m
2
/day in 1 single dose
(infuse over 2 h)
Max. daily dose 3.2 g
Pamidronate Adults: 30 mg/week, 90 mg/day
infusion
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 90 mg
Cardiac glycosides
Medigoxin Loading dose 1 mg/m
2
75% 25% 25%
Maintenance dose approx.
7 g/kg/day; trough level 12 g/l
1682
Group/
subgroup
Normal daily dose,
number of single doses
Dose at GFR
(ml/min/1.73m
2
)
Dialysis
40 10 Anuric
Gastrointestinal drugs
Metoclopramide PO: 0.5 mg/kg/day in 3 single doses Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
50% (2 single doses) 100% on
hemodialysis day IV: 0.1 mg/kg/day as single dose,
max. 4/day
Max. daily dose 40 mg
Omeprazole 0.51 mg/kg/day in 1 single dose Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 200 mg
Ranitidine PO: 4 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose 50%
(2 single
doses)
50% (2 single doses)
IV: 2 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses
Max. daily dose 900 mg
Immunosuppressives
Cyclosporine Approx. 310 mg/kg/day in 2 (or 3)
single doses according to desired
trough level
Normal dose Normal dose
Mycophenolate
mofetil
1.2 g/m
2
in 2 single doses [35];
50% at WBC <4,000, stop at
WBC <2,000
Normal dose
[35]
Normal dose
[35]
Normal dose
(accumulation
of metabolites
possible) [35] Max. daily dose 2 g
Rapamycin Loading dose 57 mg/m
2
/day Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Maintenance dose 24 mg/m
2
/day
in 2 single doses (<13 years) or in
1 single dose (>14 years) according
to desired trough level (512 ng/ml)
Tacrolimus Approx. 0.15 mg/kg/day in 2 single
doses according to desired trough level
Normal dose Normal dose
Spasmolytics
Scopolamine/
hyoscyamine
PO/rectal: 12 mg/kg/day
in 34 single doses
Normal dose 75% 50%
IV: 0.8 mg/kg/day as single dose
(max. 3/day)
Max. daily dose 100 mg
Urospasmolytics
Oxybutynin >5 years: 10 mg/day in 2 single
doses
Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Propiverine 0.8 mg/kg/day in 2 single doses Normal dose Normal dose Normal dose
Max. daily dose 60 mg
Extracted and adapted from Daschner [43] and Daschner and Cochat [44], with permission
1683
Table 1 Antibiotic dosing recommendations. Administration should be via intraperitoneal route unless specified otherwise
Antibiotics Continuous therapy Intermittent therapy
b
Loading dose
a
Maintenance dose
Glycopeptides
Vancomycin 1000 mg/L 25 mg/L 30 mg/kg q 57 days
Teicoplanin
c
400 mg/L 20 mg/L 15 mg/kg q 57 days
Cephalosporins
Cefazolin/Cephalothin 500 mg/L 125 mg/L 15 mg/kg q 24 h
Cefuroxime 200 mg/L 125 mg/L 15 mg/kg q 24 h
Cefotaxime 500 mg/L 250 mg/L 30 mg/kg q 24 h
Ceftazidime 250 mg/L 125 mg/L 15 mg/kg q 24 h
Ceftizoxime 250 mg/L 125 mg/L
Antifungals
Amphotericin B 1 mg/kg IV 1 mg/kg/day IV
Fluconazole 3 6 mg/kg IP, IV or PO q
2448 h (max. dose 200 mg)
Flucytosine 50 mg/kg IV or PO
(max. dose 2.0 g)
2537.5 mg/kg PO/day
(max. dose 1.0 g)
Aminoglycosides
d
Amikacin 25 mg/L 12 mg/L
Gentamicin 8 mg/L 4 mg/L
Netilmicin 8 mg/L 4 mg/L
Tobramycin 8 mg/L 4 mg/L
Penicillins
d
Azlocillin 500 mg/L 250 mg/L
Piperacillin 250 mg/L 150 mg/kg IV q 12 h
Ampicillin 125 mg/L
Oxacillin 125 mg/L
Nafcillin 125 mg/L
Amoxicillin 250500 mg/L 50 mg/L
Quinolones
Ciprofloxacin 50 mg/L 25 mg/L
Combinations
Ampicillin/Sulbactam 1000 mg/L 100 mg/L
Imipenem/Cilastatin 500 mg/L 200 mg/L
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole 320/1600 mg/L 80/400 mg/L
Others
Clindamycin 300 mg/L 150 mg/L
Metronidazole 3550 mg/kg/day PO in 3 doses
Rifampin 20 mg/kg/day PO (max. dose 600 mg/day)
Aztreonam 1000 mg/L 250 mg/L
q, Every day; IV, Intravenously; IP, intraperitoneally; PO, orally
The therapeutic recommendations provided in this table are those of the ISPD Advisory Committee on Peritonitis Management in Pediatric
Patients and are, in large part, based upon adult experiences (used with permission from [11])
a
Loading dose should be administered during a standardized 3- to 6-h dwell period. Concentration-related loading doses assume usual patient-
specific fill volume (i.e. approximately 1100 mL/m
2
body surface area). If a smaller volume is instilled, the concentration must be increased to
ensure infusion of an equal mass of antibiotic. Intermittent antibiotic dosing should be administered over 6 h in one bag per day for continuous
ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients, or during a full fill volume daytime dwell for automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) patients,
unless otherwise specified
b
Accelerated glycopeptide elimination may occur in patients with residual renal function. Intermittent therapy is used in this setting. The second
dose of antibiotic should be time-based on a blood level obtained 35 days after the initial dose. Redosing should occur when the blood level
is <12 mg/L for vancomycin or 8 mg/L for teicoplanin. Intermittent therapy is not recommended for patients with residual renal function
unless serum drug levels can be monitored in a timely manner
c
Teicoplanin is not currently available in the USA
d
Aminoglycosides and penicillins should not be mixed in dialysis fluid because of the potential for inactivation
MEDICAMENTOS EN PERITONITIS
. Table 34-4
Treatment of crescentic glomerulonephritis
Induction phase (36 months) Maintenance phase (25 year)
Methylprednisolone 1520 mg/kg (maximum 1 g) IV daily for
36 doses
Azathioprine 1.52 mg/kg/day for 1218 months
Prednisone 1.52 mg/kg/day PO for 4 weeks; taper to 0.5 mg/kg daily
by 3 months; 0.51 mg/kg on alternate day for 3 months
Prednisone 0.51 mg/kg on alternate days;
later taper
a
Cyclophosphamide 500750 mg/m
2
IV every 34 weeks for 6 pulses Consider mycophenolate mofetil (1,0001,200 mg/
m
2
/day), if disease activity is not controlled
b
Plasmapheresis (double volume) on alternate days for 2-weeks
Agents for refractory disease
Intravenous immunoglobulin, TNF-a antibody (infliximab), anti CD20 (rituximab)
a
The dose of cyclophosphamide is increased to 750 mg/m
2
if no leukopenia. Dose reduction is necessary in patients showing impaired renal
function. Alternatively, the medication is given orally at a dose of 2 mg/kg daily for 12 weeks
b
Plasmapheresis should begin early, especially if patient is dialysis dependent at presentation or if biopsy shows severe histological changes
(>50% crescents). Plasma exchange is particularly useful in anti-GBM nephritis and ANCA-associated vasculitis. It might be considered in patients
with immune complex GN with unsatisfactory renal recovery after steroid pulses
TRATAMIENTO DE GMN RP O CRECENTICA
TABLE 9. Antihypertensive Drugs for Outpatient Management of Hypertension in Children 117 Years Old*
Class Drug Dose Dosing
Interval
Evidence FDA
Labeling
Comments
ACE inhibitor Benazepril Initial: 0.2 mg/kg per d up to 10 mg/d
Maximum: 0.6 mg/kg per d up to 40 mg/d
qd RCT Yes 1. All ACE inhibitors are contraindicated in pregnancy;
females of childbearing age should use reliable contraception.
2. Check serum potassium and creatinine periodically to
monitor for hyperkalemia and azotemia.
3. Cough and angioedema are reportedly less common with
newer members of this class than with captopril.
4. Benazepril, enalapril, and lisinopril labels contain information
on the preparation of a suspension; captopril may also be
compounded into a suspension.
5. FDA approval for ACE inhibitors with pediatric labeling is
limited to children 6 years of age and to children with
creatinine clearance 30 ml/min per 1.73m
2
.
Captopril Initial: 0.30.5 mg/kg/dose
Maximum: 6 mg/kg per d
tid RCT, CS No
Enalapril Initial: 0.08 mg/kg per d up to 5 mg/d
Maximum: 0.6 mg/kg per d up to 40 mg/d
qd-bid RCT Yes
Fosinopril Children 50 kg:
Initial: 510 mg/d
Maximum: 40 mg/d
qd RCT Yes
Lisinopril Initial: 0.07 mg/kg per d up to 5 mg/d
Maximum: 0.6 mg/kg per d up to 40 mg/d
qd RCT Yes
Quinapril Initial: 510 mg/d
Maximum: 80 mg/d
qd RCT, EO No
Angiotensin-receptor
blocker
Irbesartan 612 years: 75150 mg/d
13 years: 150300 mg/d
qd CS Yes 1. All ARBs are contraindicated in pregnancy; females of
childbearing age should use reliable contraception.
2. Check serum potassium, creatinine periodically to monitor
for hyperkalemia and azotemia.
3. Losartan label contains information on the preparation of
a suspension.
4. FDA approval for ARBs is limited to children 6 years of
age and to children with creatinine clearance 30 ml/min
per 1.73m
2
.
Losartan Initial: 0.7 mg/kg per d up to 50 mg/d
Maximum: 1.4 mg/kg per d up to 100 mg/d
qd RCT Yes
- and -Blocker Labetalol Initial: 13 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 1012 mg/kg per d up to
1200 mg/d
bid CS, EO No 1. Asthma and overt heart failure are contraindications.
2. Heart rate is dose-limiting.
3. May impair athletic performance.
4. Should not be used in insulin-dependent diabetics.
-Blocker Atenolol Initial: 0.51 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 2 mg/kg per d up to 100 mg/d
qd-bid CS No 1. Noncardioselective agents (propranolol) are
contraindicated in asthma and heart failure.
2. Heart rate is dose-limiting.
3. May impair athletic performance.
4. Should not be used in insulin-dependent diabetics.
5. A sustained-release formulation of propranolol is available
that is dosed once-daily.
Bisoprolol/HCTZ Initial: 2.5/6.25 mg/d
Maximum: 10/6.25 mg/d
qd RCT No
Metoprolol Initial: 12 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 6 mg/kg per d up to 200 mg/d
bid CS No
Propranolol Initial: 12 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 4 mg/kg per d up to 640 mg/d
bid-tid RCT, EO Yes
Calcium channel
blocker
Amlodipine Children 617 years: 2.55 mg once daily qd RCT Yes 1. Amlodipine and isradipine can be compounded into stable
extemporaneous suspensions.
2. Felodipine and extended-release nifedipine tablets must be
swallowed whole.
3. Isradipine is available in both immediate-release and
sustained-release formulations; sustained-release form is
dosed qd or bid.
4. May cause tachycardia.
Felodipine Initial: 2.5 mg/d
Maximum: 10 mg/d
qd RCT, EO No
Isradipine Initial: 0.150.2 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 0.8 mg/kg per d up to 20 mg/d
tid-qid CS, EO No
Extended-release
nifedipine
Initial: 0.250.5 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 3 mg/kg per d up to 120 mg/d
qd-bid CS, EO No
5
6
8
H
I
G
H
B
L
O
O
D
P
R
E
S
S
U
R
E
I
N
C
H
I
L
D
R
E
N
A
N
D
A
D
O
L
E
S
C
E
N
T
S
ANTIHIPERTENSIVOS
TABLE 9. Antihypertensive Drugs for Outpatient Management of Hypertension in Children 117 Years Old*
Class Drug Dose Dosing
Interval
Evidence FDA
Labeling
Comments
Central -agonist Clonidine Children 12 years:
Initial: 0.2 mg/d
Maximum: 2.4 mg/d
bid EO Yes 1. May cause dry mouth and/or sedation.
2. Transdermal preparation also available.
3. Sudden cessation of therapy can lead to severe rebound
hypertension.
Diuretic HCTZ Initial: 1 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 3 mg/kg per d up to 50 mg/d
qd EO Yes 1. All patients treated with diuretics should have electrolytes
monitored shortly after initiating therapy and periodically
thereafter.
2. Useful as add-on therapy in patients being treated with
drugs from other drug classes.
3. Potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene,
amiloride) may cause severe hyperkalemia, especially if
given with ACE inhibitor or ARB.
4. Furosemide is labeled only for treatment of edema but
may be useful as add-on therapy in children with resistant
hypertension, particularly in children with renal disease.
5. Chlorthalidone may precipitate azotemia in patients with
renal diseases and should be used with caution in those
with severe renal impairment.
Chlorthalidone Initial: 0.3 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 2 mg/kg per d up to 50 mg/d
qd EO No
Furosemide Initial: 0.52.0 mg/kg per dose
Maximum: 6 mg/kg per d
qd-bid EO No
Spironolactone Initial: 1 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 3.3 mg/kg per d up to 100 mg/d
qd-bid EO No
Triamterene Initial: 12 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 34 mg/kg per d up to
300 mg/d
bid EO No
Amiloride Initial: 0.40.625 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 20 mg/d
qd EO No
Peripheral
-antagonist
Doxazosin Initial: 1 mg/d
Maximum: 4 mg/d
qd EO No May cause hypotension and syncope, especially after first
dose.
Prazosin Initial: 0.050.1 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 0.5 mg/kg per d
tid EO No
Terazosin Initial: 1 mg/d
Maximum: 20 mg/d
qd EO No
Vasodilator Hydralazine Initial: 0.75 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 7.5 mg/kg per d up to 200 mg/d
qid EO Yes 1. Tachycardia and fluid retention are common side effects.
2. Hydralazine can cause a lupus-like syndrome in slow
acetylators.
3. Prolonged use of minoxidil can cause hypertrichosis.
4. Minoxidil is usually reserved for patients with
hypertension resistant to multiple drugs.
Minoxidil Children 12 years:
Initial: 0.2 mg/kg per d
Maximum: 50 mg/d
Children 12 years:
Initial: 5 mg/d
Maximum: 100 mg/d
qd-tid CS, EO Yes
FDA indicates Federal Drug Administration; ARB indicates angiotensin-receptor blocker; bid, twice daily; HCTZ, hydrochlorothiazide; qd, once daily; qid, four times daily; tid, three times daily.
* Includes drugs with prior pediatric experience or recently completed clinical trials.
The maximum recommended adult dose should not be exceeded in routine clinical practice.
Level of evidence upon which dosing recommendations are based. CS indicates case series; EO, expert opinion; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
FDA-approved pediatric labeling information is available. Recommended doses for agents with FDA-approved pediatric labels are the doses contained in the approved labels. Even when pediatric
labeling information is not available, the FDA-approved label should be consulted for additional safety information.
Comments apply to all members of each drug class except where otherwise stated.
S
U
P
P
L
E
M
E
N
T
5
6
9
ANTIHIPERTENSIVOS
Drug Class Dose* Route Comments
Most useful
Esmolol -Blocker 100500 g/kg per min IV infusion Very short-acting; constant infusion
preferred. May cause profound
bradycardia. Produced modest
reductions in BP in a pediatric
clinical trial.
Hydralazine Vasodilator 0.20.6 mg/kg per dose IV, IM Should be given every 4 h when
given IV bolus. Recommended
dose is lower than FDA label.
Labetalol - and -Blocker Bolus: 0.21.0 mg/kg per
dose up to 40 mg/dose
Infusion: 0.253.0 mg/kg
per h
IV bolus or
infusion
Asthma and overt heart failure are
relative contraindications.
Nicardipine Calcium channel
blocker
13 g/kg per min IV infusion May cause reflex tachycardia.
Sodium
nitroprusside
Vasodilator 0.5310 g/kg per min IV infusion Monitor cyanide levels with
prolonged (72 h) use or in renal
failure; or coadminister with
sodium thiosulfate.
Occasionally useful
Clonidine Central -agonist 0.050.1 mg/dose, may be
repeated up to 0.8 mg
total dose
po Side effects include dry mouth and
sedation.
Enalaprilat ACE inhibitor 0.050.1 mg/kg per dose
up to 1.25 mg/dose
IV bolus May cause prolonged hypotension
and acute renal failure, especially
in neonates.
Fenoldopam Dopamine receptor
agonist
0.20.8 g/kg per min IV infusion Produced modest reductions in BP
in a pediatric clinical trial in
patients up to 12 years
Isradipine Calcium channel
blocker
0.050.1 mg/kg per dose po Stable suspension can be
compounded.
Minoxidil Vasodilator 0.10.2 mg/kg per dose po Most potent oral vasodilator, long-
acting.
FDA indicates Food and Drug Administration; IM, intramuscular; IV, intravenous; po, oral.
* All dosing recommendations are based on expert opinion or case series data except as otherwise noted.
Useful for hypertensive emergencies and some hypertensive urgencies.
Useful for hypertensive urgencies and some hypertensive emergencies.
570 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
MEDICAMENTOS EN HTA SEVERA DE 1 a 17 AOS
Antimicrobial
Agent
Dosage
Ceftriaxone 75 mg/kg, every 24 h
Cefotaxime 150 mg/kg per d,
divided every 68 h
Ceftazidime 100150 mg/kg per d,
divided every 8 h
Gentamicin 7.5 mg/kg per d,
divided every 8 h
Tobramycin 5 mg/kg per d,
divided every 8 h
Piperacillin 300 mg/kg per d,
divided every 68 h
TABLE 3 Some Empiric Antimicrobial Agents for Oral Treatment of UTI
Antimicrobial Agent Dosage
Amoxicillin-clavulanate 2040 mg/kg per d in 3 doses
Sulfonamide
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 612 mg/kg trimethoprim and 30-60 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole
per d in 2 doses
Sulsoxazole 120150 mg/kg per d in 4 doses
Cephalosporin
Cexime 8 mg/kg per d in 1 dose
Cefpodoxime 10 mg/kg per d in 2 doses
Cefprozil 30 mg/kg per d in 2 doses
Cefuroxime axetil 2030 mg/kg per d in 2 doses
Cephalexin 50100 mg/kg per d in 4 doses
602 FROM THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS
at Health Internetwork on September 1, 2011 pediatrics.aappublications.org Downloaded from
ANTIBIOTICOS EN ITU
TABLE 3. BP Levels for Boys by Age and Height Percentile
Age, y BP Percentile SBP, mm Hg DBP, mm Hg
Percentile of Height Percentile of Height
5th 10th 25th 50th 75th 90th 95th 5th 10th 25th 50th 75th 90th 95th
1 50th 80 81 83 85 87 88 89 34 35 36 37 38 39 39
90th 94 95 97 99 100 102 103 49 50 51 52 53 53 54
95th 98 99 101 103 104 106 106 54 54 55 56 57 58 58
99th 105 106 108 110 112 113 114 61 62 63 64 65 66 66
2 50th 84 85 87 88 90 92 92 39 40 41 42 43 44 44
90th 97 99 100 102 104 105 106 54 55 56 57 58 58 59
95th 101 102 104 106 108 109 110 59 59 60 61 62 63 63
99th 109 110 111 113 115 117 117 66 67 68 69 70 71 71
3 50th 86 87 89 91 93 94 95 44 44 45 46 47 48 48
90th 100 101 103 105 107 108 109 59 59 60 61 62 63 63
95th 104 105 107 109 110 112 113 63 63 64 65 66 67 67
99th 111 112 114 116 118 119 120 71 71 72 73 74 75 75
4 50th 88 89 91 93 95 96 97 47 48 49 50 51 51 52
90th 102 103 105 107 109 110 111 62 63 64 65 66 66 67
95th 106 107 109 111 112 114 115 66 67 68 69 70 71 71
99th 113 114 116 118 120 121 122 74 75 76 77 78 78 79
5 50th 90 91 93 95 96 98 98 50 51 52 53 54 55 55
90th 104 105 106 108 110 111 112 65 66 67 68 69 69 70
95th 108 109 110 112 114 115 116 69 70 71 72 73 74 74
99th 115 116 118 120 121 123 123 77 78 79 80 81 81 82
6 50th 91 92 94 96 98 99 100 53 53 54 55 56 57 57
90th 105 106 108 110 111 113 113 68 68 69 70 71 72 72
95th 109 110 112 114 115 117 117 72 72 73 74 75 76 76
99th 116 117 119 121 123 124 125 80 80 81 82 83 84 84
7 50th 92 94 95 97 99 100 101 55 55 56 57 58 59 59
90th 106 107 109 111 113 114 115 70 70 71 72 73 74 74
95th 110 111 113 115 117 118 119 74 74 75 76 77 78 78
99th 117 118 120 122 124 125 126 82 82 83 84 85 86 86
8 50th 94 95 97 99 100 102 102 56 57 58 59 60 60 61
90th 107 109 110 112 114 115 116 71 72 72 73 74 75 76
95th 111 112 114 116 118 119 120 75 76 77 78 79 79 80
99th 119 120 122 123 125 127 127 83 84 85 86 87 87 88
9 50th 95 96 98 100 102 103 104 57 58 59 60 61 61 62
90th 109 110 112 114 115 117 118 72 73 74 75 76 76 77
95th 113 114 116 118 119 121 121 76 77 78 79 80 81 81
99th 120 121 123 125 127 128 129 84 85 86 87 88 88 89
10 50th 97 98 100 102 103 105 106 58 59 60 61 61 62 63
90th 111 112 114 115 117 119 119 73 73 74 75 76 77 78
95th 115 116 117 119 121 122 123 77 78 79 80 81 81 82
99th 122 123 125 127 128 130 130 85 86 86 88 88 89 90
11 50th 99 100 102 104 105 107 107 59 59 60 61 62 63 63
90th 113 114 115 117 119 120 121 74 74 75 76 77 78 78
95th 117 118 119 121 123 124 125 78 78 79 80 81 82 82
99th 124 125 127 129 130 132 132 86 86 87 88 89 90 90
12 50th 101 102 104 106 108 109 110 59 60 61 62 63 63 64
90th 115 116 118 120 121 123 123 74 75 75 76 77 78 79
95th 119 120 122 123 125 127 127 78 79 80 81 82 82 83
99th 126 127 129 131 133 134 135 86 87 88 89 90 90 91
13 50th 104 105 106 108 110 111 112 60 60 61 62 63 64 64
90th 117 118 120 122 124 125 126 75 75 76 77 78 79 79
95th 121 122 124 126 128 129 130 79 79 80 81 82 83 83
99th 128 130 131 133 135 136 137 87 87 88 89 90 91 91
14 50th 106 107 109 111 113 114 115 60 61 62 63 64 65 65
90th 120 121 123 125 126 128 128 75 76 77 78 79 79 80
95th 124 125 127 128 130 132 132 80 80 81 82 83 84 84
99th 131 132 134 136 138 139 140 87 88 89 90 91 92 92
15 50th 109 110 112 113 115 117 117 61 62 63 64 65 66 66
90th 122 124 125 127 129 130 131 76 77 78 79 80 80 81
95th 126 127 129 131 133 134 135 81 81 82 83 84 85 85
99th 134 135 136 138 140 142 142 88 89 90 91 92 93 93
16 50th 111 112 114 116 118 119 120 63 63 64 65 66 67 67
90th 125 126 128 130 131 133 134 78 78 79 80 81 82 82
95th 129 130 132 134 135 137 137 82 83 83 84 85 86 87
99th 136 137 139 141 143 144 145 90 90 91 92 93 94 94
17 50th 114 115 116 118 120 121 122 65 66 66 67 68 69 70
90th 127 128 130 132 134 135 136 80 80 81 82 83 84 84
95th 131 132 134 136 138 139 140 84 85 86 87 87 88 89
99th 139 140 141 143 145 146 147 92 93 93 94 95 96 97
The 90th percentile is 1.28 SD, the 95th percentile is 1.645 SD, and the 99th percentile is 2.326 SD over the mean.
For research purposes, the SDs in Table B1 allow one to compute BP Z scores and percentiles for boys with height percentiles given in
Table 3 (ie, the 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles). These height percentiles must be converted to height Z scores given
by: 5% 1.645; 10% 1.28; 25% 0.68; 50% 0; 75% 0.68; 90% 1.28; and 95% 1.645, and then computed according to the
methodology in steps 2 through 4 described in Appendix B. For children with height percentiles other than these, follow steps 1 through
4 as described in Appendix B.
PERCENTILES DE TA EN NIOS
TABLE 4. BP Levels for Girls by Age and Height Percentile
Age, y BP Percentile SBP, mm Hg DBP, mm Hg
Percentile of Height Percentile of Height
5th 10th 25th 50th 75th 90th 95th 5th 10th 25th 50th 75th 90th 95th
1 50th 83 84 85 86 88 89 90 38 39 39 40 41 41 42
90th 97 97 98 100 101 102 103 52 53 53 54 55 55 56
95th 100 101 102 104 105 106 107 56 57 57 58 59 59 60
99th 108 108 109 111 112 113 114 64 64 65 65 66 67 67
2 50th 85 85 87 88 89 91 91 43 44 44 45 46 46 47
90th 98 99 100 101 103 104 105 57 58 58 59 60 61 61
95th 102 103 104 105 107 108 109 61 62 62 63 64 65 65
99th 109 110 111 112 114 115 116 69 69 70 70 71 72 72
3 50th 86 87 88 89 91 92 93 47 48 48 49 50 50 51
90th 100 100 102 103 104 106 106 61 62 62 63 64 64 65
95th 104 104 105 107 108 109 110 65 66 66 67 68 68 69
99th 111 111 113 114 115 116 117 73 73 74 74 75 76 76
4 50th 88 88 90 91 92 94 94 50 50 51 52 52 53 54
90th 101 102 103 104 106 107 108 64 64 65 66 67 67 68
95th 105 106 107 108 110 111 112 68 68 69 70 71 71 72
99th 112 113 114 115 117 118 119 76 76 76 77 78 79 79
5 50th 89 90 91 93 94 95 96 52 53 53 54 55 55 56
90th 103 103 105 106 107 109 109 66 67 67 68 69 69 70
95th 107 107 108 110 111 112 113 70 71 71 72 73 73 74
99th 114 114 116 117 118 120 120 78 78 79 79 80 81 81
6 50th 91 92 93 94 96 97 98 54 54 55 56 56 57 58
90th 104 105 106 108 109 110 111 68 68 69 70 70 71 72
95th 108 109 110 111 113 114 115 72 72 73 74 74 75 76
99th 115 116 117 119 120 121 122 80 80 80 81 82 83 83
7 50th 93 93 95 96 97 99 99 55 56 56 57 58 58 59
90th 106 107 108 109 111 112 113 69 70 70 71 72 72 73
95th 110 111 112 113 115 116 116 73 74 74 75 76 76 77
99th 117 118 119 120 122 123 124 81 81 82 82 83 84 84
8 50th 95 95 96 98 99 100 101 57 57 57 58 59 60 60
90th 108 109 110 111 113 114 114 71 71 71 72 73 74 74
95th 112 112 114 115 116 118 118 75 75 75 76 77 78 78
99th 119 120 121 122 123 125 125 82 82 83 83 84 85 86
9 50th 96 97 98 100 101 102 103 58 58 58 59 60 61 61
90th 110 110 112 113 114 116 116 72 72 72 73 74 75 75
95th 114 114 115 117 118 119 120 76 76 76 77 78 79 79
99th 121 121 123 124 125 127 127 83 83 84 84 85 86 87
10 50th 98 99 100 102 103 104 105 59 59 59 60 61 62 62
90th 112 112 114 115 116 118 118 73 73 73 74 75 76 76
95th 116 116 117 119 120 121 122 77 77 77 78 79 80 80
99th 123 123 125 126 127 129 129 84 84 85 86 86 87 88
11 50th 100 101 102 103 105 106 107 60 60 60 61 62 63 63
90th 114 114 116 117 118 119 120 74 74 74 75 76 77 77
95th 118 118 119 121 122 123 124 78 78 78 79 80 81 81
99th 125 125 126 128 129 130 131 85 85 86 87 87 88 89
12 50th 102 103 104 105 107 108 109 61 61 61 62 63 64 64
90th 116 116 117 119 120 121 122 75 75 75 76 77 78 78
95th 119 120 121 123 124 125 126 79 79 79 80 81 82 82
99th 127 127 128 130 131 132 133 86 86 87 88 88 89 90
13 50th 104 105 106 107 109 110 110 62 62 62 63 64 65 65
90th 117 118 119 121 122 123 124 76 76 76 77 78 79 79
95th 121 122 123 124 126 127 128 80 80 80 81 82 83 83
99th 128 129 130 132 133 134 135 87 87 88 89 89 90 91
14 50th 106 106 107 109 110 111 112 63 63 63 64 65 66 66
90th 119 120 121 122 124 125 125 77 77 77 78 79 80 80
95th 123 123 125 126 127 129 129 81 81 81 82 83 84 84
99th 130 131 132 133 135 136 136 88 88 89 90 90 91 92
15 50th 107 108 109 110 111 113 113 64 64 64 65 66 67 67
90th 120 121 122 123 125 126 127 78 78 78 79 80 81 81
95th 124 125 126 127 129 130 131 82 82 82 83 84 85 85
99th 131 132 133 134 136 137 138 89 89 90 91 91 92 93
16 50th 108 108 110 111 112 114 114 64 64 65 66 66 67 68
90th 121 122 123 124 126 127 128 78 78 79 80 81 81 82
95th 125 126 127 128 130 131 132 82 82 83 84 85 85 86
99th 132 133 134 135 137 138 139 90 90 90 91 92 93 93
17 50th 108 109 110 111 113 114 115 64 65 65 66 67 67 68
90th 122 122 123 125 126 127 128 78 79 79 80 81 81 82
95th 125 126 127 129 130 131 132 82 83 83 84 85 85 86
99th 133 133 134 136 137 138 139 90 90 91 91 92 93 93
* The 90th percentile is 1.28 SD, the 95th percentile is 1.645 SD, and the 99th percentile is 2.326 SD over the mean.
For research purposes, the SDs in Table B1 allow one to compute BP Z scores and percentiles for girls with height percentiles given in
Table 4 (ie, the 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles). These height percentiles must be converted to height Z scores given
by: 5% 1.645; 10% 1.28; 25% 0.68; 50% 0; 75% 0.68; 90% 1.28; and 95% 1.645 and then computed according to the
methodology in steps 2 through 4 described in Appendix B. For children with height percentiles other than these, follow steps 1 through
4 as described in Appendix B.
PERCENTILES DE TA EN NIAS
COMPOSICION DE DIANEAL
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Absorción con filtro BK como terapia eficaz en el riñón del mieloma múltipleDari EverandAbsorción con filtro BK como terapia eficaz en el riñón del mieloma múltipleBelum ada peringkat
- Hemofiltración Cont-APC PDFDokumen6 halamanHemofiltración Cont-APC PDFCaronteno24Belum ada peringkat
- Dosis de HemodialisisDokumen9 halamanDosis de Hemodialisisliliana del rocio santillan salazarBelum ada peringkat
- Dialisis de Urgencia, Bases ClinicasDokumen16 halamanDialisis de Urgencia, Bases ClinicasMajo QuirozBelum ada peringkat
- Sindrome HepatorrenalDokumen15 halamanSindrome HepatorrenalSissy CrisantoBelum ada peringkat
- Guía de Cuidados para El Enfermo Renal PDFDokumen32 halamanGuía de Cuidados para El Enfermo Renal PDFAida Perez100% (1)
- TRRADokumen82 halamanTRRALeonel Gonzalez SotoBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Hemodialisis V.V.C. Lenta 12 de MayoDokumen13 halaman2 Hemodialisis V.V.C. Lenta 12 de MayoKEVIN ANGELO CASTILLO PATIÑOBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Post Operatoria ColelapDokumen3 halamanNota Post Operatoria ColelapEPICRISIS HQN1Belum ada peringkat
- Diamaxecuador PDFDokumen1 halamanDiamaxecuador PDFHector LuisBelum ada peringkat
- Tecnicas DialiticasDokumen71 halamanTecnicas DialiticasMariel Mireles100% (1)
- Taller Sobre Manejo de La Tecnica de DialisisDokumen21 halamanTaller Sobre Manejo de La Tecnica de DialisisAdriana Landero Porta100% (1)
- Complicaciones en DialisisDokumen60 halamanComplicaciones en DialisisEduardo ArmijosBelum ada peringkat
- NEFRONADokumen18 halamanNEFRONABaruch Arteaga Marquez100% (2)
- Complicaciones de La HemodialisisDokumen5 halamanComplicaciones de La HemodialisisGerardo FariñasBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad 19-Perfil RenalDokumen69 halamanUnidad 19-Perfil RenalConcepStore Py0% (1)
- Hepatitis C Cronica - Guia Practica ClinicaDokumen66 halamanHepatitis C Cronica - Guia Practica ClinicaMARIELA BUENDIABelum ada peringkat
- Insuficiencia RenalDokumen39 halamanInsuficiencia RenalMarioxi Rosana Campos SalinasBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes InsipidaDokumen25 halamanDiabetes InsipidaElvis Valdez MecaBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrolitosDokumen52 halamanElectrolitosJorge Guillen GómezBelum ada peringkat
- Lesion Renal Aguda y Urgencia DialiticaDokumen3 halamanLesion Renal Aguda y Urgencia DialiticaManuel López CobosBelum ada peringkat
- Heparina en HemodialisisDokumen33 halamanHeparina en HemodialisisAlexander DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodialisis TORAYDokumen31 halamanHemodialisis TORAYAdrianMontalvoBelum ada peringkat
- Enfermedad Arterial Periferica Diapos Final #Dokumen42 halamanEnfermedad Arterial Periferica Diapos Final #Jenny MorochoBelum ada peringkat
- Manejo de Pacientes en Hemodialisis Con Enfermedades InfectocontagiosasDokumen12 halamanManejo de Pacientes en Hemodialisis Con Enfermedades Infectocontagiosasmel_mendoza77Belum ada peringkat
- Tratamiento en Pacientes Con Vih Actual de La Hepatitis CDokumen28 halamanTratamiento en Pacientes Con Vih Actual de La Hepatitis CJos Brnal100% (1)
- TCRRDokumen57 halamanTCRRJosé María Bellido DomínguezBelum ada peringkat
- Adecuación de HemodiálisisDokumen18 halamanAdecuación de HemodiálisisLuis TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodializadores y Oxigenadores de SangreDokumen44 halamanHemodializadores y Oxigenadores de SangreErick ToledoBelum ada peringkat
- Indicaciones de HemodiafiltraciónDokumen47 halamanIndicaciones de HemodiafiltraciónGabriel GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Hemodialisis PDFDokumen182 halamanManual Hemodialisis PDFLuis GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Cinética de La UreaDokumen14 halamanCinética de La UreaLaura La RosarinaBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Acceso VascularDokumen91 halamanGuia de Acceso VascularRoElRaIsBelum ada peringkat
- Liquidos y ElectrolitosDokumen23 halamanLiquidos y ElectrolitosMarisa PedregalBelum ada peringkat
- Caso Clínico Insuficiencia RenalDokumen9 halamanCaso Clínico Insuficiencia RenalClara EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Hiponatremia e HiperglicemiaDokumen6 halamanHiponatremia e HiperglicemiaAnnie VictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Ventilacion Mecanica en El Embarazo FinalDokumen21 halamanVentilacion Mecanica en El Embarazo Finalyeison villanueva molina50% (2)
- Enfermedad Vascular OclusivaDokumen3 halamanEnfermedad Vascular OclusivaLaury MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Dializadores y Membranas de HemodiálisisDokumen10 halamanDializadores y Membranas de HemodiálisisPriscila RodBelum ada peringkat
- Complicaciones de La HemodialisisDokumen33 halamanComplicaciones de La HemodialisisYsmarlinBelum ada peringkat
- Hepatitis CDokumen21 halamanHepatitis CmelizaBelum ada peringkat
- Tesis ExamenDokumen15 halamanTesis ExamenMonica UribeBelum ada peringkat
- Rabdomiolisis e Insuficiencia Renal Aguda Por El Consumo de Cocaína Caso ClinicoDokumen4 halamanRabdomiolisis e Insuficiencia Renal Aguda Por El Consumo de Cocaína Caso ClinicoZxMijailxz CorreaBelum ada peringkat
- HemodialisisDokumen49 halamanHemodialisisRocio Virginia ViAz100% (1)
- Taller Funcion RenalDokumen18 halamanTaller Funcion RenalDavid Peña AriasBelum ada peringkat
- Malformaciones ArteriovenosasDokumen25 halamanMalformaciones Arteriovenosasangeliux25100% (1)
- Liquidos Corporales y Balance Hidrico AcDokumen8 halamanLiquidos Corporales y Balance Hidrico Acjorge bravoBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Del ParticipanteDokumen96 halamanManual Del ParticipanteAndrés TajanBelum ada peringkat
- S23 SEI Crisis Vs Emergencia HipertensivaDokumen21 halamanS23 SEI Crisis Vs Emergencia HipertensivaRosa BruckmannBelum ada peringkat
- Accesos Vasculares HemodiálisisDokumen31 halamanAccesos Vasculares Hemodiálisisjorge_alonzoBelum ada peringkat
- M1C5 PPT Electrolitos PDFDokumen145 halamanM1C5 PPT Electrolitos PDFLoreto Valenzuela VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Manejo de Paciente CriticoDokumen51 halamanManejo de Paciente CriticoGabriela Horna HuamánBelum ada peringkat
- Abordando Al Paciente RenalDokumen81 halamanAbordando Al Paciente RenalBaltazar Ibarra100% (1)
- Estrategias para El Control de La Hipotension en HemodialisisDokumen14 halamanEstrategias para El Control de La Hipotension en HemodialisisRuben Moran LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Clase 3 - Funcion TubularDokumen39 halamanClase 3 - Funcion TubularlobocazadorMHBelum ada peringkat
- Normas ModificadasDokumen15 halamanNormas ModificadasjoseBelum ada peringkat
- HipernatremiaDokumen25 halamanHipernatremiaAbril AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Gasometria ArterialDokumen19 halamanGasometria ArterialMaryanNelaChBelum ada peringkat
- Tabla de Valores Nefrologia PediatricaDokumen6 halamanTabla de Valores Nefrologia Pediatricareichell rojasBelum ada peringkat
- Crisis Hipertensiva en PediatriaDokumen40 halamanCrisis Hipertensiva en PediatriaThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- Casos Clinicos en Patologia Hemodinamica 2012Dokumen171 halamanCasos Clinicos en Patologia Hemodinamica 2012Thelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- 18 Apuntes de Clínicas Quirúrgicas 2011 FINAL PDFDokumen157 halaman18 Apuntes de Clínicas Quirúrgicas 2011 FINAL PDFThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- Eunacom - Preparacion - CardiologiaDokumen11 halamanEunacom - Preparacion - CardiologiaThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- EUNACOM - Salud PublicaDokumen4 halamanEUNACOM - Salud PublicaThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- Eunacom Cardiologa 110531020003 Phpapp02Dokumen257 halamanEunacom Cardiologa 110531020003 Phpapp02Alexis Fco Cerda Bizama100% (4)
- Codigo de NurembergDokumen2 halamanCodigo de NurembergThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- Libro BuenoDokumen66 halamanLibro BuenoThelma Cantillo RochaBelum ada peringkat
- SEDALMERCKDokumen4 halamanSEDALMERCKMiloZcorpioBelum ada peringkat
- Sevorane 2Dokumen12 halamanSevorane 2Giordy DlCruzBelum ada peringkat
- AnyelinaDokumen1 halamanAnyelinaJulio Coronado AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Guía de Aprendizaje Farmacología TSF (RHV)Dokumen4 halamanGuía de Aprendizaje Farmacología TSF (RHV)valeldc12pBelum ada peringkat
- Principios ActivosDokumen21 halamanPrincipios ActivosCultura cientifica 1º bachilleratoBelum ada peringkat
- Vademecum2 PDFDokumen336 halamanVademecum2 PDFNatalia López Rodríguez100% (1)
- Hipervitaminosis A Informe Cayetano HerediaDokumen49 halamanHipervitaminosis A Informe Cayetano HerediaRaul Puyen Rivera100% (3)
- Caso Clinicos Diabetes-15Dokumen3 halamanCaso Clinicos Diabetes-15YomiraHuamaniSimonBelum ada peringkat
- Modelo de RamDokumen1 halamanModelo de RamJesus BlancoBelum ada peringkat
- Clonixinato de LisinaDokumen24 halamanClonixinato de LisinaGeordy Villanueva100% (2)
- M2-Taller Escrito 1 - ImcDokumen3 halamanM2-Taller Escrito 1 - ImcNayli CobosBelum ada peringkat
- Informe Final Completo Análisis Comparativo Entre La Ley 50-88 de RD y La Ley 30-86 de ColombiaDokumen89 halamanInforme Final Completo Análisis Comparativo Entre La Ley 50-88 de RD y La Ley 30-86 de ColombiasanpeviBelum ada peringkat
- CV PaolaDokumen4 halamanCV PaolaKatherine ObregonBelum ada peringkat
- Nforme de Interacción FarmacológicaDokumen315 halamanNforme de Interacción FarmacológicaAlberto Junior Quispe YayaBelum ada peringkat
- Paso 4 - Lista de ChequeoDokumen2 halamanPaso 4 - Lista de ChequeofreyserBelum ada peringkat
- Matriz ServiciosDokumen21 halamanMatriz ServiciosRUBEN DARIO GELPUD BOTINABelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen121 halamanUntitledJhony AriasBelum ada peringkat
- I-Af-003 Instructivo de Seguimiento Farmacoterapeutico PDFDokumen9 halamanI-Af-003 Instructivo de Seguimiento Farmacoterapeutico PDFYkita Loaiza100% (1)
- Miperat ProspDokumen3 halamanMiperat ProspMauro NicoliniBelum ada peringkat
- PRUEBA DIAGNOSTICA Matematicas Grado 5Dokumen2 halamanPRUEBA DIAGNOSTICA Matematicas Grado 5DEISY LILIANA RICO TORRESBelum ada peringkat
- El Real Decreto Legislativo 1Dokumen9 halamanEl Real Decreto Legislativo 1Desirée GRBelum ada peringkat
- Practica N 4 ToxicologiaDokumen27 halamanPractica N 4 ToxicologiaDiomedes Rojas75% (8)
- Medicamentos para AlbunDokumen5 halamanMedicamentos para AlbunSonia Nancy Huatangari MundacaBelum ada peringkat
- Etapas de La Historia de La Farmacia 1076497Dokumen13 halamanEtapas de La Historia de La Farmacia 1076497Jhon Araque100% (1)
- Farmacología Básica PresentacionDokumen40 halamanFarmacología Básica PresentacionHenry Fica Sanhueza100% (1)
- Clases de BetalactamicosDokumen46 halamanClases de BetalactamicosSKarol SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Pasta Lassar 1Dokumen5 halamanPasta Lassar 1Miguel PallardeliBelum ada peringkat
- CUESTIONARIO 2 DE LABORATORIO DE FARMACOLOGIA YullDokumen9 halamanCUESTIONARIO 2 DE LABORATORIO DE FARMACOLOGIA YullLuis Alberto CjunoBelum ada peringkat
- Estabilidad Del IbuprofenoDokumen13 halamanEstabilidad Del IbuprofenoLuisha Cop AguiBelum ada peringkat
- Tesis FarmaciaDokumen85 halamanTesis FarmaciaMaria Huaman NovilloBelum ada peringkat