Chap 001
Diunggah oleh
vivek11190 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan51 halamanmis
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inimis
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan51 halamanChap 001
Diunggah oleh
vivek1119mis
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 51
McGraw-Hill/I rwin
Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, I nc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 1
The Information Age
in Which You Live:
Changing the Face
of Business
1-2
STUDENT LEARNING
OUTCOMES
1. Define MIS and describe the three resources
within itpeople, information, and
information technology.
2. Describe how to use break-even analysis to
assess the financial impact of IT.
3. Describe how to use Porters Five Forces
Model to evaluate an industry.
4. Compare and contrast Porters three generic
strategies and the RGT framework as
approaches to the development of business
strategy.
1-3
Cell Phones Doom Phone
Revenues for Hotels
1-4
Cell Phones Doom Phone
Revenues for Hotels
The year 2000 typical hotel could
budget annual revenue of $1,274
per room for in-room phone charges
The year 2009 typical hotel could
budget annual revenue of only $178
per room for in-room phone charges
Cell phones and technologies of all
kinds are transforming entire
industries
1-5
Questions
1. When was the last time you used a pay
phone? How often have you used a pay
phone in the last year?
2. If you needed to use a pay phone,
would you know immediately where one
was located?
3. When was the last time you used your
cell phone? How often have you used
your cell phone in the last day?
1-6
INTRODUCTION
You live in a digital age
Average American relies on more
than 250 computers per day
How much do you rely on
technology in your daily life?
1-7
INTRODUCTION
Management information
systems (MIS) planning for,
development, management, and use
of information technology to help
people performs all tasks related to
information processing and
management.
Important field of study
Important business discipline
1-8
INTRODUCTION
MIS deals with the coordination and
use of 3 very important
organizational resources
1. People
2. Information
3. Technology
1-9
The Synergy among the Three
Resources of MIS
1-10
CHAPTER ORGANIZATION
1. MIS Resources: Information, People,
and Information Technology
Learning Outcome #1
2. Financial Impact of IT
Learning Outcome #2
3. Industry Impact of IT
Learning Outcome #3
4. Strategy Impact of IT
Learning Outcome #4
1-11
MIS RESOURCE #1:
INFORMATION
Intellectual asset hierarchy data,
information, and business
intelligence
Data raw facts that describe a
particular phenomenon such as the
current temperature, the price of
movie rental, or your age
Information data that have a
particular meaning within a specific
context
1-12
Information Resource
Information is
often
aggregated
data that has
meaning such
as average
age, youngest
and oldest
customer, and
a histogram of
customer ages
1-13
Information Resource
Business intelligence (BI)
collective information about
Customers
Competitors
Business partners
Competitive environment
BI is information on steroids
BI can help you make important,
strategic decisions
1-14
Information Resource
1-15
Information Resource Quality
Attributes
Timeliness
When you need it
Describing the right time period
Location (no matter where you are)
Form (audio, text, animation, etc)
Validity (credibility)
Lack of any of the above can create
GIGO (garbage-in, garbage-out)
in a decision-making process
1-16
Information Resource
Organizational Perspective
1-17
Information Resource Flows
of Information
Upward describes state of the
organization based on transactions
Downward strategies, goals, and
directives that originate at a higher
level and are passed to lower levels
Horizontal between functional
business units and work teams
Outward/inward from and to
customers, suppliers, etc
1-18
Information Resource What
It Describes
Internal information operational
aspects of the organization
External information environment
surrounding the organization
Objective information quantifiably
describes something that is known
Subjective information describe
something that is unknown
1-19
MIS RESOURCE #2: PEOPLE
People are the most important
resource in any organization, with a
focus on
Technology literacy
Information literacy
Ethical responsibilities
1-20
People Resource
Technology-literate knowledge worker
knows how and when to apply technology
Information-literate knowledge worker
Can define information needs
Knows how and where to obtain information
Understands information
Acts appropriately based on information
Ethics principles and standards that guide
our behavior toward other people
1-21
People Resource - Ethics
You always
want your
actions to fall
in Quadrant I
both ethical
and legal.
1-22
MIS RESOURCE #3:
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Information technology (IT)
computer-based tools that people
use to work with information
Hardware physical devices that
make up a computer
Software set of instructions that
your hardware executes to carry out a
specific task for you
1-23
Information Technology Hardware
1-24
Information Technology
Hardware
1. Input device tool for entering
information and commands
2. Output device tool for see or
hearing results
3. Storage device tool for storing
information
1-25
Information Technology
Hardware
4. CPU hardware that interprets and
executes instructions (RAM
temporarily stores information and
software for the CPU)
5. Telecommunications device for
sending info
6. Connecting devices like cables,
ports, etc.
1-26
Information Technology
Software
Two types of software
Application software enables you to
solve specific problems and perform specific
tasks (Word, payroll, inventory management,
etc)
System software handles tasks specific
to technology management (operating
system, anti-virus, etc)
See Extended Learning Module A for a review of IT hardware and
software
1-27
FINANCIAL IMPACT OF
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Regardless of the resource, you must
always assess its financial impact
Many times, you will do so using
break-even analysis
IT can definitely impact break-even
analysis
1-28
Break-Even Analysis
Consider and chart the following
financial information
Fixed costs costs you incur even if you
dont sell anything
Variable costs costs you incur when
you sell something (COGS)
Revenue how much you sell one unit
for
1-29
Break-Even Analysis Example
Assume online movie poster business
$1,500 online store, domain name
registration, search engine placement,
etc (fixed costs)
$6 - $4 to buy poster from supplier
and $2 to ship to customer (var costs)
$9 price at which you sell a move
poster
1-30
Break-Even Analysis Example
1-31
Reducing Fixed Costs with IT
Digital storefronts no physical retail
space
Telecommuting fewer expenses
related to office space
VoIP using the Internet for phone
calls
1-32
Reducing Fixed Costs with IT
1-33
Reducing Variable Costs with
IT
Virtual goods because they are
digital, there is no cost to duplicate
and sell again and again
Crowdsourcing use non-paid non-
employees to create value
1-34
Reducing Variable Costs with
IT
1-35
Increasing Revenue with IT
Recommendation engines to drive
complementary sales
Long-tail economics to sell
products/services that are too
expensive for physical stores to carry
Physical stores only carry what they can
sell large amounts of
Because of fixed costs
1-36
INDUSTRY IMPACT OF
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Porters Five Forces Model helps
business people understand the relative
attractiveness of an industry and the
industrys competitive pressures in
terms of
1. Buyer power
2. Supplier power
3. Threat of substitute products or services
4. Threat of new entrants
5. Rivalry among existing competitors
1-37
PORTERS FIVE FORCES
MODEL
1-38
Buyer Power
Buyer power high when buyers
have many choices and low when their
choices are few
Competitive advantages are created to
get buyers to stay with a given
company
NetFlix set up and maintain your movie
list
United Airlines frequent flyer program
Apple iTunes buy/manage your music
1-39
Buyer Power
Competitive advantage providing
a product or service in a way that
customers value more than what the
competition is able to do
First-mover advantage significant
impact on gaining market share by
being the first to market with a
competitive advantage
All competitive advantages are fleeting
1-40
Supplier Power
Supplier power high when buyers
have few choices and low when choices
are many
The opposite of buyer power
1-41
Threat of Substitute Products
and Services
Threat of substitute products
and services high when there are
many alternatives for buyers and low
when there are few alternatives
Switching costs can reduce this
threat
Switching cost a cost that makes
buyers reluctant to switch to another
product/service
1-42
Threat of New Entrants
Threat of new entrants high
when it is easy for competitors to
enter the market and low when
entry barriers are significant
Entry barrier product or service
feature that customers have come to
expect and that must be offered by
an entering organization
Banking ATMs, online bill pay, etc
1-43
Rivalry Among Existing
Competitors
Rivalry among existing
competitors high when
competition is fierce and low when
competition is more complacent
General trend is toward more
competition in almost all industries
IT has certainly intensified
competition in all sectors of business
1-44
STRATEGY IMPACT OF
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Porter identified 3
generic business
strategies for
beating the
competition
1. Overall cost
leadership
2. Differentiation
3. Focus
1-45
Overall Cost Leadership
Overall cost leadership offering
the same or better quality product or
service at a price that is less than what
any of the competition is able to do
Walmart (Always Low Prices, Every Day
Low Prices)
Dell a computer the way you want it at
an affordable price
Hyundai and Kia reliable low-cost cars
Grocery stores high-volume, low-margin
1-46
Differentiation
Differentiation offering a
product or service that is perceived
as being unique in the
marketplace
Hummer Like Nothing Else
Audi and Michelin safety
Lunds & Byerlys high-end grocery
store
Apple
1-47
Focus
Focus focusing on offering
products or services
To a particular segment or buyer group
Within a segment of a product line
To a specific geographic market
Examples
Restaurants
Physician offices
Legal offices
1-48
Run-Grow-Transform (RGT)
Framework
Run-grow-transform (RGT)
framework the allocation in
terms of percentages of IT dollars
on various types of business
strategies
1-49
RGT Framework
How will you allocate IT dollars to
Run optimizing execution of existing
processes
Grow increasing market share,
products, and service offerings
Transform innovating business
processes, products, and/or services
1-50
RGT Framework
1-51
Porter and RGT
Run = overall cost leadership
Grow = focus and differentiation
Transform = (new) differentiation
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Global 500 Full ListingDokumen33 halamanGlobal 500 Full Listingvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Conversion Gate02Dokumen18 halamanConversion Gate02Babacar Tall100% (1)
- Walmart Cost LeaderDokumen6 halamanWalmart Cost LeaderSylvia JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Drivers For Green Practices Among Manufacturers in Malaysia - Analysis Between Smes and LesDokumen10 halamanDrivers For Green Practices Among Manufacturers in Malaysia - Analysis Between Smes and Lesvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- SchlumbergerDokumen5 halamanSchlumbergervivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Interest Rates DerivativesDokumen4 halamanInterest Rates Derivativesvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Cost of CapitalDokumen6 halamanCost of Capitalvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Costco Strategy WareshousingDokumen16 halamanCostco Strategy WareshousingNuri SusantiBelum ada peringkat
- Traders Swerving On Rates Now Bet On Cut South Africa CreditDokumen2 halamanTraders Swerving On Rates Now Bet On Cut South Africa Creditvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Interest Rates DerivativesDokumen4 halamanInterest Rates Derivativesvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Cost of CapitalDokumen6 halamanCost of Capitalvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Gsm5500 Human Resource Management: Analysis On International CompanyDokumen8 halamanGsm5500 Human Resource Management: Analysis On International Companyvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Gordon's Dividend Valuation Model and Malaysian Share PriceDokumen2 halamanGordon's Dividend Valuation Model and Malaysian Share Pricevivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental Reporting Practices in Malaysia and AustraliaDokumen10 halamanEnvironmental Reporting Practices in Malaysia and Australiavivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- GSM 5421: Investment AnalysisDokumen4 halamanGSM 5421: Investment Analysisvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Modlin 18 QuestionsDokumen13 halamanModlin 18 Questionsvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Final Law Exam TipsDokumen6 halamanFinal Law Exam Tipsvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Dell v1.4Dokumen8 halamanDell v1.4vivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- GSM 5400 Financial Management and ControlDokumen9 halamanGSM 5400 Financial Management and Controlvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Connors GaoDokumen32 halamanConnors Gaovivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Corporate Environmental Performance On Financial Outcomes - Profits, Revenues and Costs: Evidence From The Czech Transition EconomyDokumen44 halamanThe Effect of Corporate Environmental Performance On Financial Outcomes - Profits, Revenues and Costs: Evidence From The Czech Transition Economyvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- AnswersDokumen10 halamanAnswersSajidZiaBelum ada peringkat
- Validity and ReliabilityDokumen6 halamanValidity and ReliabilityfarlynzBelum ada peringkat
- Answers To Sample Questions For FinalDokumen8 halamanAnswers To Sample Questions For Finalvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Subprime Crisis On The Financing Entreprenuerial Activities by Islamic BanksDokumen14 halamanThe Effect of Subprime Crisis On The Financing Entreprenuerial Activities by Islamic Banksvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Nespresso 2014 DEC 16Dokumen1 halamanNespresso 2014 DEC 16vivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Chap1 IntroDokumen16 halamanChap1 Introvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S1877042812051671 MainDokumen6 halaman1 s2.0 S1877042812051671 Mainvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- SME's Preparedness To Face Economic Crisis - A Proposed FrameworkDokumen7 halamanSME's Preparedness To Face Economic Crisis - A Proposed Frameworkvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Subprime Crisis On The Financing Entreprenuerial Activities by Islamic BanksDokumen14 halamanThe Effect of Subprime Crisis On The Financing Entreprenuerial Activities by Islamic Banksvivek1119Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Compiler Design Lab ManualDokumen36 halamanCompiler Design Lab ManualDHANA SRIBelum ada peringkat
- Donorperfect Littlegreenlight Chart PDFDokumen4 halamanDonorperfect Littlegreenlight Chart PDFAnthony CrespoBelum ada peringkat
- Maryland Teacher Technology Standards and ArtifactsDokumen4 halamanMaryland Teacher Technology Standards and ArtifactsLauren ZizwarekBelum ada peringkat
- Expression Language in UI Personalization - EM WP PDFDokumen11 halamanExpression Language in UI Personalization - EM WP PDFJihad Darwish100% (1)
- VERTIV Liebert EXS 10kVA-20kVA - V1.0Dokumen108 halamanVERTIV Liebert EXS 10kVA-20kVA - V1.0Jayz JDKBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary Heat Recovery Unit for Commercial BuildingsDokumen2 halamanRotary Heat Recovery Unit for Commercial BuildingsDamian OvidiuBelum ada peringkat
- A Blockchain-Based Self-Tallying Voting Protocol With Maximum Voter PrivacyDokumen13 halamanA Blockchain-Based Self-Tallying Voting Protocol With Maximum Voter PrivacyTango CharlieBelum ada peringkat
- Norsok AnnexaDokumen3 halamanNorsok AnnexaBalamurugan HBelum ada peringkat
- CCAA Environmental Guideline FinalDokumen13 halamanCCAA Environmental Guideline FinalRaza Muhammad SoomroBelum ada peringkat
- Automation Studio Starting GuideDokumen20 halamanAutomation Studio Starting GuidesyaifulBelum ada peringkat
- SB Pharma Proposal 01Dokumen7 halamanSB Pharma Proposal 01Badar RizwanBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTRONICS TRICKS and TIPS - DT 830D Digital Multimeter Fault Finding PCB ComponentDokumen6 halamanELECTRONICS TRICKS and TIPS - DT 830D Digital Multimeter Fault Finding PCB Componentmuntashir mamunBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing Clock Trees: Jeff ShabelDokumen28 halamanAnalyzing Clock Trees: Jeff ShabelarunsrlBelum ada peringkat
- PMD - Front Sprint2021-20 ScenariosDokumen42 halamanPMD - Front Sprint2021-20 ScenariosHuy Quang PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Effectiveness of Workers Participation in ManagementDokumen59 halamanEffectiveness of Workers Participation in ManagementᏒ.Gᴀɴᴇsн ٭ʏт᭄Belum ada peringkat
- E16538 Rog Strix Z490-E Gaming Um V2 WebDokumen78 halamanE16538 Rog Strix Z490-E Gaming Um V2 WebMario Arancibia SepulvedaBelum ada peringkat
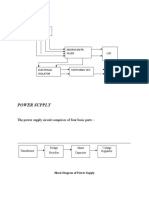
- Power SupplyDokumen3 halamanPower SupplytejisainiBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Theme 2.0Dokumen8 halamanThesis Theme 2.0PaperWritingWebsitePalmBay100% (2)
- Sekonda UputstvoDokumen2 halamanSekonda Uputstvohellios81Belum ada peringkat
- b66042 - Programmer's GuideDokumen362 halamanb66042 - Programmer's GuideMiroserh100% (1)
- PT Agincourt Resources - 2 PDFDokumen7 halamanPT Agincourt Resources - 2 PDFRifqi AdhikaraBelum ada peringkat
- Guide to The ISO 27000 Series of Information Security StandardsDokumen2 halamanGuide to The ISO 27000 Series of Information Security StandardswahidBelum ada peringkat
- BIG-IP F5 AFM Operations GuideDokumen115 halamanBIG-IP F5 AFM Operations GuidePadam DhamiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic FeaturesDokumen19 halamanBasic FeaturesumangBelum ada peringkat
- Project SynopsisDokumen23 halamanProject SynopsisRahul Raj SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Documentation Haptic TechnologyDokumen27 halamanDocumentation Haptic TechnologyLavan saikumar20% (5)
- Lab # 01 To Study The Transient Response of RL Series Circuit MaterialsDokumen4 halamanLab # 01 To Study The Transient Response of RL Series Circuit MaterialsYasir100% (1)
- Integrating The ISO 14034 Standard As A PlatformDokumen11 halamanIntegrating The ISO 14034 Standard As A PlatformTheerapan CBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica 320D3 GCDokumen12 halamanFicha Tecnica 320D3 GCanahdezj88Belum ada peringkat
- Ajuste Del Freno Estacionamiento ProbarDokumen2 halamanAjuste Del Freno Estacionamiento ProbarVictor NunezBelum ada peringkat