CHT Practical 1 KUK
Diunggah oleh
Dhruv Sharma0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
82 tayangan3 halamanStudy Motherboard CHT Practical
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniStudy Motherboard CHT Practical
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
82 tayangan3 halamanCHT Practical 1 KUK
Diunggah oleh
Dhruv SharmaStudy Motherboard CHT Practical
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Practical-1
Aim:- To study motherboard.
Motherboard: The main circuit board of a microcomputer. The motherboard contains the
connectors for attaching additional boards. Typically, the motherboard contains the CPU, BIOS,
memory, mass storage interfaces, serial and parallel ports, expansion slots, and all the controllers
required to control standard peripheral devices, such as the display screen, keyboard, and disk
drive. Collectively, all these chips that reside on the motherboard are known as the
motherboard's chipset.
The motherboard is the primary component of the entire system. In addition to hardware the
motherboard also contains some software .The system ROM actually contains three small but
very critical programs these are post, the BIOS and the setup program. This device provides,
even the C.P.U is enabled to function. In addition to hardware the motherboard also contain
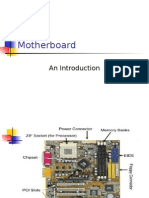
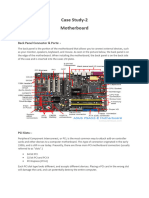
some software. The following is the picture of motherboard:
1. Mouse & keyboard: Keyboard Connectors are two types basically. All PCs have a Key
board port connected directly to the motherboard. The oldest, but still quite common type, is a
special DIN, and most PCs until recently retained this style connector. The AT-style keyboard
connector is quickly disappearing, being replaced by the smaller mini DIN PS/2-style keyboard
connector. You can use an AT-style keyboard with a PS/2-style socket (or the other way around)
by using a converter. Although the AT connector is unique in PCs, the PS/2-style mini-DIN is
also used in more modern PCs for the mouse. Fortunately, most PCs that use the mini-DIN for
both the keyboard and mouse clearly mark each mini-DIN socket as to its correct use. Some
keyboards have a USB connection, but these are fairly rare compared to the PS/2 connection
keyboards.
2. USB (Universal serial bus): USB is the General-purpose connection for PC. You can
find USB versions of many different devices, such as mice, keyboards, scanners, cameras, and
even printers. A USB connector's distinctive rectangular shape makes it easily
recognizable. USB has a number of features that makes it particularly popular on PCs. First,
USB devices are hot swappable. You can insert or remove them without restarting your system.
3. Parallel port: Most printers use a special connector called a parallel port. Parallel port
carries data on more than one wire, as opposed to the serial port, which uses only one wire.
Parallel ports use a 25-pin female DB connector. Parallel ports are directly supported by the
motherboard through a direct connection or through a dangle.
4. CPU Chip: The central processing unit, also called the microprocessor performs all the
calculations that take place inside a pc. CPUs come in Variety of shapes and sizes. Modern
CPUs generate a lot of heat and thus require a cooling fan or heat sink. The cooling device
(such as a cooling fan) is removable, although some CPU manufactures sell the CPU with a fan
permanently attached.
5. RAM slots: Random-Access Memory (RAM) stores programs and data currently being
used by the CPU. RAM is measured in units called bytes. RAM has been packaged in many
different ways. The most current package is called a 168-pin DIMM (Dual Inline Memory
module).
6. Floppy controller: The floppy drive connects to the computer via a 34-pin ribbon
cable, which in turn connects to the motherboard. A floppy controller is one that is used to
control the floppy drive.
7. IDE controller: Industry standards define two common types of hard drives: EIDE and
SCSI. Majority of the PCs use EIDE drives. SCSI drives show up in high end PCs such as
network servers or graphical workstations. The EIDE drive connects to the hard drive via a 2-
inch-wide, 40-pin ribbon cable, which in turn connects to the motherboard. IDE controller is
responsible for controlling the hard drive.
8. PCI slot: Intel introduced the Peripheral component interconnect bus protocol. The PCI
bus is used to connect I/O devices (such as NIC or RAID controllers) to the main logic of the
computer. PCI bus has replaced the ISA bus.
9. ISA slot: (Industry Standard Architecture) It is the standard architecture of the Expansion
bus. Motherboard may contain some slots to connect ISA compatible cards. The memory
address bus is to 32 bits .The bus speed is 8.33 MHZ and the bandwidth is 16 bits.
10. CMOS Battery: To provide CMOS with the power when the computer is turned off all
motherboards comes with a battery. These batteries mount on the motherboard in one of three
ways: the obsolete external battery, the most common onboard battery, and built-in battery.
11. AGP slot: If you have a modern motherboard, you will almost certainly notice a single
connector that looks like a PCI slot, but is slightly shorter and usually brown. You also
probably have a video card inserted into this slot. This is an Advanced Graphics Port
(AGP) slot
12. CPU slot: To install the CPU, just slide it straight down into the slot. Special notches in
the slot make it impossible to install them incorrectly. So remember if it does not go easily, it is
probably not correct. Be sure to plug in the CPU fan's power.
13. Power supply plug in: The Power supply, as its name implies, provides the necessary
electrical power to make the pc operate. The power supply takes standard 110-V AC power and
converts into +/-12-Volt, +/-5-Volt, and 3.3-Volt DC power.
The power supply connector has 20-pins, and the connector can go in only one direction.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Computer Hardware & Software Lab ManualDokumen66 halamanComputer Hardware & Software Lab ManualS Vrns100% (5)
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12Dari EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12Belum ada peringkat
- Hard Ware Note BookDokumen22 halamanHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluBelum ada peringkat
- Components of A MotherboardDokumen114 halamanComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDokumen12 halamanComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard Components... CSEDokumen28 halamanMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDokumen14 halamanIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Acer Schematic Collection for Laptop RepairDokumen25 halamanAcer Schematic Collection for Laptop RepairKJ-04 MUSISI LOKAL67% (3)
- Motherboard components and portsDokumen32 halamanMotherboard components and portsAnanduBelum ada peringkat
- MotherboardDokumen14 halamanMotherboardPalash Jain100% (1)
- How BIOS WorksDokumen6 halamanHow BIOS Worksramjee26Belum ada peringkat
- MotherboardDokumen27 halamanMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்Belum ada peringkat
- M640 CARD PCI GX System Instruction ManualDokumen15 halamanM640 CARD PCI GX System Instruction Manualjani100% (1)
- Microprocessor and Interfacing Douglas Hall 2nd EditionDokumen5 halamanMicroprocessor and Interfacing Douglas Hall 2nd EditionSushma Borkar29% (17)
- New Used Laptops For SaleDokumen7 halamanNew Used Laptops For SaleBourkiBelum ada peringkat
- MotherboardDokumen20 halamanMotherboardJeyc RapperBelum ada peringkat
- ATX Motherboard Components GuideDokumen4 halamanATX Motherboard Components GuideIgloo JainBelum ada peringkat
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDokumen40 halamanA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Notes 2Dokumen6 halamanBasic Notes 2jivan jyotBelum ada peringkat
- BIOS InstallationDokumen5 halamanBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsDokumen29 halamanComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDokumen39 halamanUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDokumen4 halamanMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen8 halamanReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- Experiment No.4Dokumen12 halamanExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheBelum ada peringkat
- Mohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7Dokumen3 halamanMohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7kmohammadalfaizBelum ada peringkat
- A+ Hardware Tutorial: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDokumen5 halamanA+ Hardware Tutorial: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationsakuraenriqueBelum ada peringkat
- Components of MotherboardDokumen4 halamanComponents of MotherboardParitosh BelekarBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard HandoutDokumen5 halamanMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDokumen9 halamanUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamBelum ada peringkat
- Give All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipDokumen7 halamanGive All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipjanBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of MotherboardDokumen86 halamanParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniBelum ada peringkat
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDokumen10 halamanG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDokumen3 halamanMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Motherboard: by John AnthonyDokumen3 halamanMotherboard: by John Anthonyraghu_534Belum ada peringkat
- IEEE 1394 PortDokumen4 halamanIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedDokumen5 halamanCOMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedStar Boy DavieBelum ada peringkat
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDokumen5 halamanThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Guide to Motherboard Components and TypesDokumen20 halamanEssential Guide to Motherboard Components and TypesAMIT SINGH100% (1)
- Hardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFDokumen8 halamanHardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFKrish NeupaneBelum ada peringkat
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDokumen10 halamanThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawBelum ada peringkat
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Dokumen4 halamanDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Ports and Components GuideDokumen5 halamanComputer Ports and Components GuidessssmailnatBelum ada peringkat
- CahmDokumen3 halamanCahmakkivish37Belum ada peringkat
- System Board, Baseboard, Planar Board or Logic Board, or Colloquially, A Mobo) Is TheDokumen5 halamanSystem Board, Baseboard, Planar Board or Logic Board, or Colloquially, A Mobo) Is TheluqmanBelum ada peringkat
- CMN Lab Expt-1Dokumen3 halamanCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghBelum ada peringkat
- M2 Yash AllabadiDokumen7 halamanM2 Yash Allabadidegijon661Belum ada peringkat
- Motherboard PartsDokumen4 halamanMotherboard PartsabelBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment CS by ABRARDokumen9 halamanAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioBelum ada peringkat
- SeminarDokumen30 halamanSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Class NotesDokumen12 halamanClass NotesHeart WeyganBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDokumen8 halamanMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerBelum ada peringkat
- REPORT ON MOTHERBOARD PRESENTATIONDokumen10 halamanREPORT ON MOTHERBOARD PRESENTATIONmanjeetsinghnavab100% (1)
- Ass 2Dokumen8 halamanAss 2wudase solomonBelum ada peringkat
- Computer MotherboardDokumen15 halamanComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of A MotherboardDokumen4 halamanParts of A MotherboardPamieDyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDokumen11 halamanLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Dokumen4 halamanParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Dokumen10 halamanMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual Computer Organization and Hardware MaintenanceDokumen28 halamanLab Manual Computer Organization and Hardware Maintenanceanshroy7373Belum ada peringkat
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Dokumen15 halamanAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of A MotherboardDokumen9 halamanParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462Belum ada peringkat
- What Are The Parts of A MotherboardDokumen2 halamanWhat Are The Parts of A MotherboardPRincess ScarLetBelum ada peringkat
- Firewire header speeds up data transfersDokumen4 halamanFirewire header speeds up data transfersVishnu TejaBelum ada peringkat
- अलसी की महिमा -डॉ - ओ.पी.वर्माDokumen19 halamanअलसी की महिमा -डॉ - ओ.पी.वर्माharibhagatBelum ada peringkat
- IC33 Sample QuestionsDokumen13 halamanIC33 Sample QuestionsKamleshwar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CS 2013Dokumen15 halamanCS 2013Vivek Vikram SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Live HappyDokumen2 halamanLive HappyDhruv SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Osmeña-Sto. Niño National High SchoolDokumen1 halamanOsmeña-Sto. Niño National High SchoolTobi MMBelum ada peringkat
- ARMOURY CRATE (Mobile) Connection Troubleshooting Guide: Laptop (A)Dokumen7 halamanARMOURY CRATE (Mobile) Connection Troubleshooting Guide: Laptop (A)Hathey OctaBelum ada peringkat
- SavingsAccount History 05072023114939Dokumen2 halamanSavingsAccount History 05072023114939Farid AyidBelum ada peringkat
- KKT Chillers Update Instruction For FW 3.3 10-12-2016Dokumen4 halamanKKT Chillers Update Instruction For FW 3.3 10-12-2016Eduardo JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Mic 8051Dokumen1 halamanMic 8051DaisyQueenBelum ada peringkat
- 21 36 05Dokumen7 halaman21 36 05Suanno ZomiBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Key: 1 Computer Hardware ADokumen2 halamanAnswer Key: 1 Computer Hardware AazabacheasturBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard Manual 8pe667u j-2Dokumen49 halamanMotherboard Manual 8pe667u j-2MichaelAlanEngCivilBelum ada peringkat
- Laptop Dell Latitude 5420 CTO BaseDokumen1 halamanLaptop Dell Latitude 5420 CTO Baselutfi mahfudBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Presentation On The Basis of SizeDokumen8 halamanComputer Presentation On The Basis of SizesanjamBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sasaran SMPDokumen122 halamanData Sasaran SMPSyahdan HudaBelum ada peringkat
- Debug 1214Dokumen14 halamanDebug 1214Abdul RozakBelum ada peringkat
- Kaye R. Rubica BSCS 3A 02 Task Performance 1Dokumen4 halamanKaye R. Rubica BSCS 3A 02 Task Performance 1kyle jezreel RubicaBelum ada peringkat
- Some Useful CrapDokumen18 halamanSome Useful CrapRade VojvodanovićBelum ada peringkat
- BIOS and UEFI guideDokumen3 halamanBIOS and UEFI guideAldwin ManalansanBelum ada peringkat
- RIT-LBX-MNT-28012022-01 System IssuesDokumen4 halamanRIT-LBX-MNT-28012022-01 System Issuesjoao abreuBelum ada peringkat
- Von Neumann ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanVon Neumann ArchitectureAditya JainBelum ada peringkat
- Microcontrollers For Embedded Systems Nec022r PDFDokumen2 halamanMicrocontrollers For Embedded Systems Nec022r PDFSudhir GoswamiBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital Converter in Pic Microcontroller Xc8Dokumen12 halamanAnalog To Digital Converter in Pic Microcontroller Xc8Erandi Brito100% (1)
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDokumen2 halamanIntroduction To Embedded Systemsvenkata satishBelum ada peringkat
- Eee MPMCDokumen2 halamanEee MPMCSekhar Reddy100% (1)
- Favorite Tech Devices: Laptops, SmartphonesDokumen4 halamanFavorite Tech Devices: Laptops, SmartphonesEcheverre LuisBelum ada peringkat
- Team 6 - Project ProposalDokumen4 halamanTeam 6 - Project ProposalAmritpal SangwanBelum ada peringkat
- Poop GPTDokumen312 halamanPoop GPTPatrick Ian BernardBelum ada peringkat
- Microcontroller With 16K/32K/64K Bytes In-System Programmable FlashDokumen28 halamanMicrocontroller With 16K/32K/64K Bytes In-System Programmable FlashJanos KrauszBelum ada peringkat