Bba 202 SUMMER 2014
Diunggah oleh
ManishSinghJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bba 202 SUMMER 2014
Diunggah oleh
ManishSinghHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DRIVE SUMMER 2014
ASSIGNMENT
PROGRAM- BBA
SEMESTER- 2
SUBJECT CODE & NAME
BBA 202
BUISNESS STRATEGY
BK ID- B1519
CREDITS 2
MARKS 30
NAME-SAGAR SINGH
ROLL-1308002677
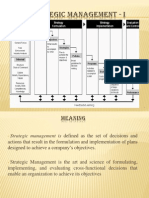
Q1.Define business policy? Explain the importance of business policy?Differentiate
between business policy and strategy.
Answer:
Business Policy
Business Policy defines the scope or spheres within which decisions can be taken by the subordinates in
an organization. It permits the lower level management to deal with the problems and issues without
consulting top level management every time for decisions. Business policies are the guidelines developed
by an organization to govern its actions. They define the limits within which decisions must be made.
Business policy also deals with acquisition of resources with which organizational goals can be achieved.
Business policy is the study of the roles and responsibilities of top level management, the significant
issues affecting organizational success and the decisions affecting organization in long-run.
Importance of Business Policy
An effective business policy must have following features-
1. Specific- Policy should be specific/definite. If it is uncertain, then the implementation will become
difficult.
2. Clear- Policy must be unambiguous. It should avoid use of jargons and connotations. There
should be no misunderstandings in following the policy.
3. Reliable/Uniform- Policy must be uniform enough so that it can be efficiently followed by the
subordinates.
4. Appropriate- Policy should be appropriate to the present organizational goal.
5. Simple- A policy should be simple and easily understood by all in the organization.
6. Inclusive/Comprehensive- In order to have a wide scope, a policy must be comprehensive.
7. Flexible- Policy should be flexible in operation/application. This does not imply that a policy
should be altered always, but it should be wide in scope so as to ensure that the line managers
use them in repetitive/routine scenarios.
8. Stable- Policy should be stable else it will lead to indecisiveness and uncertainty in minds of
those who look into it for guidance.
Difference between Policy and Strategy
The term policy should not be considered as synonymous to the term strategy. The difference
between policy and strategy can be summarized as follows-
1. Policy is a blueprint of the organizational activities which are repetitive/routine in nature. While
strategy is concerned with those organizational decisions which have not been dealt/faced before
in same form.
2. Policy formulation is responsibility of top level management. While strategy formulation is
basically done by middle level management.
3. Policy deals with routine/daily activities essential for effective and efficient running of an
organization. While strategy deals with strategic decisions.
4. Policy is concerned with both thought and actions. While strategy is concerned mostly with action.
5. A policy is what is, or what is not done. While a strategy is the methodology used to achieve a
target as prescribed by a policy.
Q2. What are the objectives of strategic management.? What are the causes for failure of
Strategic Management?
Answer: Objectives of strategic management
A broadly defined objective that an organization must achieve to make its strategy
succeed.
Strategic objectives are, in general, externally focused and (according to the management
guru Peter Drucker) fall into eight major classifications:
(1) Market standing: desired share of the present and new markets;
(2)Innovation: development of new goods and services, and of skills and methods required
to supply them;
(3) Human resources: selection and development of employees;
(4) Financial resources: identification of the sources of capital and their use;
(5) Physical resources: equipment and facilities and their use;
(6) Productivity: efficient use of the resources relative to the output;
(7) Social responsibility: awareness and responsiveness to the effects on the wider
community of the stakeholders;
(8) Profit requirements: achievement of measurable financial well-being and growth.
Causes for failure of Strategic Management
1 Having a plan simply for plans sake. Some organizations go through the
motions of developing a plan simply because common sense says every good
organization must have a plan
2. Not understanding the environment or focusing on results. Planning
teams must pay attention to changes in the business environment, set meaningful
priorities, and understand the need to pursue results.
3. Partial commitment Without this knowledge, its tough to stay committed to
the process.
4. Not having the right people involved. Those charged with executing the
plan should be involved from the onset. Those involved in creating the plan will be
committed to seeing it through execution.
5. Writing the plan and putting it on the shelf. If a plan is to be an effective
management tool, it must be used and reviewed continually. Unlike Twinkies or a
fine vino, strategic plans dont have a good shelf life.
6. Unwillingness or inability to change. Your company and your strategic
plan must be nimble and able to adapt as market conditions change.
7. Having the wrong people in leadership positions The right individuals
include those who will advocate for and champion the strategic plan and keep the
company on track.
8. Ignoring marketplace reality, facts, and assumptions. Plan in advance
and youll be ready when the tide comes in.
9. No accountability or follow through. Be tough once the plan is developed
and resources are committed and ensure there are consequences for not delivering
on the strategy.
10. Unrealistic goals or lack of focus and resources. Strategic plans must be
focused and include a manageable number of goals, objectives, and programs.
Q3. Write brief notes on the following:
a) Core competencies and their importance
b) Strategic leadership.
Answer: Core Competencies and their Importance in Strategy Formulation
In their 1990 article entitled, The Core Competence of the Corporation, C.K.
Prahalad and Gary Hamel coined the term core competencies, or the collective
learning and coordination skills behind the firm's product lines. They made the case
that core competencies are the source of competitive advantage and enable the firm
to introduce an array of new products and services.
According to Prahalad and Hamel, core competencies lead to the development of
core products. Core products are not directly sold to end users; rather, they are
used to build a larger number of end-user products. For example, motors are a core
product that can be used in wide array of end products. The business units of the
corporation each tap into the relatively few core products to develop a larger
number of end user products based on the core product technology. This flow from
core competencies to end products
Strategic leadership:
While there are many different definitions of strategic leadership, we define it as the ability to influence
others in your organization to voluntarily make day-to-day decisions that lead to the organizations long-
term growth and survival, and maintain its short-term financial health.
The most important aspects of strategic leadership are shared values and a clear vision, both of which
will enable and allow employees to make decisions with minimal formal monitoring or control
mechanisms. With this accomplished, a leader will have more time and a greater capacity to focus on
other, ad hoc issues, such as adapting the vision to a changing business environment. In addition,
strategic leadership will incorporate visionary and managerial leadership by simultaneously allowing for
risk-taking and rationality.
An examination of the characteristics of managerial and visionary leadership styles will help understand
strategic leadership better.
In short, managerial leaders need order and stability, and to be able to control the details of the work
being performed. Mostly, these leaders have no personal attachment towards setting and using goals as
motivational tools, and they may have difficulty showing empathy when dealing with employees. They will
attempt to gain control through systems of rewards, punishment, and other forms of coercion. These
leader managers will be focused on the cost-benefit analysis of everyday actions and will therefore be
mostly linked to the short-term financial health of the organization, as reflected in its day-to-day stock
price. It is important to note that short-term gains are often a result of a least-cost approach, which might
not be good for long-term viability.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Diff BW Policy & StrategyDokumen2 halamanDiff BW Policy & StrategyJoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Policy and Strategy FormulationDokumen12 halamanPolicy and Strategy FormulationRahul BaruahBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Characteristics of A Good StrategyDokumen8 halamanWhat Are The Characteristics of A Good StrategyJayson Tom Briva CapazBelum ada peringkat
- Business Policy and Strategic AnalysisDokumen36 halamanBusiness Policy and Strategic AnalysisSandeep GhatuaryBelum ada peringkat
- Bus 401Dokumen21 halamanBus 401Seyon HunpeganBelum ada peringkat
- BPSM Unit 2Dokumen16 halamanBPSM Unit 2Prabha DineshBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Business PolicyDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To Business PolicyMazumder SumanBelum ada peringkat
- Bus 402 Business Policy APRIL SIX 2023Dokumen24 halamanBus 402 Business Policy APRIL SIX 2023jonelouis440Belum ada peringkat
- Mba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementDokumen42 halamanMba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementArjun GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Bba 6 SemesterDokumen46 halamanStrategic Management Bba 6 Semestermahika bishtBelum ada peringkat
- BUSINESS POLICY AND STRATEGIC PLANING Lesson 1 and TwoDokumen18 halamanBUSINESS POLICY AND STRATEGIC PLANING Lesson 1 and Twomoza salimBelum ada peringkat
- Planning: "Without The Activities Determined byDokumen137 halamanPlanning: "Without The Activities Determined byDamry Bin DaudBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-I: Concept of Strategy: The Term Strategy Is Derived From A Greek WordDokumen22 halamanUnit-I: Concept of Strategy: The Term Strategy Is Derived From A Greek Wordsumeetgoyal16Belum ada peringkat
- 202 Business StrategyDokumen8 halaman202 Business StrategyShashank PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Mba Iii Semester Strategic Management and Social Capital (MBA008A) ObjectivesDokumen20 halamanMba Iii Semester Strategic Management and Social Capital (MBA008A) ObjectivesGauravsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Business StrategyDokumen12 halamanChapter 1 - Business StrategyKateBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Strategy-7Dokumen51 halamanUnderstanding Strategy-7madhuragarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Strategic Management Change (Transition)Dokumen6 halamanIntroduction To Strategic Management Change (Transition)Anonymous g6wb11ypb3Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction - To - Strategic - ManagementDokumen6 halamanIntroduction - To - Strategic - ManagementTYBMS F 3023 JAIN RIYA PUKHRAJBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Mgt. Sem-6Dokumen64 halamanStrategic Mgt. Sem-6Aazam FarooqueBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management: SNR Degree College, JiganiDokumen50 halamanStrategic Management: SNR Degree College, Jiganibu butccmBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Business PolicyDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To Business PolicyMazumder Suman100% (1)
- BPSM Unit IDokumen12 halamanBPSM Unit Irohitkumarc4ppBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Planning - Uc2Dokumen16 halamanStrategic Planning - Uc2Aliyan Aman100% (1)
- 169 Sample PagesDokumen16 halaman169 Sample PagesShefferd Bernales100% (2)
- Bpsa NotesDokumen31 halamanBpsa Noteskrishna_medathatiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 PDFDokumen15 halamanUnit 1 PDFvBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Level StrategyDokumen47 halamanCorporate Level Strategycuty_phorum2160100% (1)
- Business Policy1Dokumen23 halamanBusiness Policy1Rahul SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Business Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Dokumen62 halamanBusiness Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Sanya GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- BBA202Dokumen6 halamanBBA202mreenal kalitaBelum ada peringkat
- Bps Final QuestionDokumen20 halamanBps Final Questionbharat khullarBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Strategy ExamDokumen11 halamanCorporate Strategy Examtiko sikharulidze100% (2)
- MB0052 - Solved Q.-4 To 6Dokumen4 halamanMB0052 - Solved Q.-4 To 6Ankur BhavsarBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic ManagementDokumen128 halamanStrategic ManagementKylaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 of ModuleDokumen15 halamanTopic 1 of ModuleJoseph Hernandez CumagunBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of Business PolicyDokumen5 halamanDefinition of Business PolicyJessica LaguatanBelum ada peringkat
- Planning: To Organize, No One To Activate and No Need To Control"Dokumen137 halamanPlanning: To Organize, No One To Activate and No Need To Control"Filipe BenjamimBelum ada peringkat
- Of Reaching There - Strategy Includes Both The Fixation of Objectives As Well The Medium To Be Used To Realize ThoseDokumen5 halamanOf Reaching There - Strategy Includes Both The Fixation of Objectives As Well The Medium To Be Used To Realize ThoseVishruti SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-1 Introduction To Strategy and Strategic ManagementDokumen13 halamanUNIT-1 Introduction To Strategy and Strategic Managementrakshith bond007Belum ada peringkat
- Module 1 The Nature of Strategic ManagementDokumen7 halamanModule 1 The Nature of Strategic ManagementdmangiginBelum ada peringkat
- MBA/4/CC/16 Business Policy and Strategic Management (BPSM)Dokumen35 halamanMBA/4/CC/16 Business Policy and Strategic Management (BPSM)dipu7dibyajyoti7haza100% (1)
- BBA Strategic Management - IDokumen135 halamanBBA Strategic Management - IbijayBelum ada peringkat
- Business and EconomicsDokumen13 halamanBusiness and Economicsbayissa biratuBelum ada peringkat
- Relationship Between A Company's Strategy and Its Business Model.Dokumen109 halamanRelationship Between A Company's Strategy and Its Business Model.Nantha Kumaran40% (5)
- Final Assessment in Strategic ManagementDokumen4 halamanFinal Assessment in Strategic ManagementJayvin FavorealBelum ada peringkat
- CH-1 Strategic ManagementDokumen14 halamanCH-1 Strategic ManagementMohammad ArifBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I Notes Business PolicyDokumen19 halamanUnit I Notes Business PolicyJunaid SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- Strama Learning Materials 1Dokumen8 halamanStrama Learning Materials 1Ella Marie BelgicaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic MGT KeytermsDokumen5 halamanStrategic MGT KeytermsWin BoBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management - 4Dokumen30 halamanStrategic Management - 4Pallavi.G.P. pallaviBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Strategic ManagementDokumen12 halamanUnit 1 - Introduction To Strategic Managementjalaja muniraju100% (1)
- BSBLDR811 SampleDokumen22 halamanBSBLDR811 SampleIrtaqa Raza100% (1)
- Business PolicyDokumen8 halamanBusiness PolicyOm PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- StrategicDokumen4 halamanStrategicShehab Eldin MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss Organizational Goals and Core Competencies and The Importance SHRM in Our Organization. Organizational GoalsDokumen11 halamanDiscuss Organizational Goals and Core Competencies and The Importance SHRM in Our Organization. Organizational Goalsconcerned studentBelum ada peringkat
- Concept of Obj., Mission & VisionDokumen18 halamanConcept of Obj., Mission & VisionPadmini KandulaBelum ada peringkat
- Making Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)Dari EverandMaking Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)Belum ada peringkat
- BBA404Dokumen7 halamanBBA404ManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bba 402Dokumen10 halamanBba 402ManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Drive Fall 2015 PROGRAM Bachelor of Business Administration-BBA Semester 4 SUBJECT CODE & NAME - BBA 403 - International MarketingDokumen12 halamanAssignment Drive Fall 2015 PROGRAM Bachelor of Business Administration-BBA Semester 4 SUBJECT CODE & NAME - BBA 403 - International MarketingManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- BBA401Dokumen12 halamanBBA401ManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bba301 3rd Semester 2015 SolvedDokumen7 halamanBba301 3rd Semester 2015 SolvedManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Drive Spring 2015 Program BBA - Semester 3 Subject Code & Name BBA302 - HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENTDokumen10 halamanAssignment Drive Spring 2015 Program BBA - Semester 3 Subject Code & Name BBA302 - HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENTManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bba301 3rd Semester 2015 SolvedDokumen7 halamanBba301 3rd Semester 2015 SolvedManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bba 205 Management Information SystemDokumen10 halamanBba 205 Management Information SystemManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bba 204 Marketing Management FreeDokumen9 halamanBba 204 Marketing Management FreeManishSingh100% (2)
- Bba201 Research Methods Summer 2014Dokumen7 halamanBba201 Research Methods Summer 2014ManishSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 IntelligenceDokumen4 halamanChapter 11 IntelligenceAdetola AbdulkadirBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2 The Meanings and Dimensions of Culture NewDokumen30 halamanLecture 2 The Meanings and Dimensions of Culture NewKanwal100% (1)
- Bill Bartmann - Self Esteem WorkbookDokumen46 halamanBill Bartmann - Self Esteem WorkbookMihai Vinatoru100% (4)
- Inter SubjectivityDokumen26 halamanInter SubjectivityElle Marie100% (1)
- Coaching and MentoringDokumen59 halamanCoaching and MentoringPaula JanBelum ada peringkat
- Charts-Broken Y Axis in An Excel ChartDokumen9 halamanCharts-Broken Y Axis in An Excel Chartversatile22Belum ada peringkat
- An Interview With Dr. Frank KinslowDokumen11 halamanAn Interview With Dr. Frank KinslowTruman DhanishBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDokumen4 halamanCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationKaaya GodfreyBelum ada peringkat
- SarcasmDokumen6 halamanSarcasmMarto FeBelum ada peringkat
- Daisy Bravo Lagunas - Junior Fieldwork Reflective Journal Template2Dokumen4 halamanDaisy Bravo Lagunas - Junior Fieldwork Reflective Journal Template2api-341650889Belum ada peringkat
- Continuous Comprehensive Evaluation - Group Controlled InstructionDokumen26 halamanContinuous Comprehensive Evaluation - Group Controlled InstructionBalakrishnan AriyambethBelum ada peringkat
- Michael RenovDokumen4 halamanMichael RenovLeila Maria Lopes Terceiro100% (1)
- Communication English A-B-CDokumen73 halamanCommunication English A-B-Cking star73% (11)
- Diagnostic Test in EAPPDokumen2 halamanDiagnostic Test in EAPPDANA91% (32)
- Narrative TextsDokumen9 halamanNarrative TextsborolomanBelum ada peringkat
- True Self, False Self, I and Me (Winicott and Mead), Kohlberg's Moral StageDokumen18 halamanTrue Self, False Self, I and Me (Winicott and Mead), Kohlberg's Moral Stagenicoleta5aldea100% (1)
- ReadDokumen4 halamanReadapi-26570979Belum ada peringkat
- Just Being Is Enough. NotDokumen128 halamanJust Being Is Enough. NotRajesh L Joshi100% (1)
- Effectiveness and Efficiency in Educational Management: Ana Georgiana CĂLUGĂRESCUDokumen8 halamanEffectiveness and Efficiency in Educational Management: Ana Georgiana CĂLUGĂRESCUgeorgianaBelum ada peringkat
- Big Five Personality QuestionnaireDokumen13 halamanBig Five Personality QuestionnaireNorashady100% (2)
- Concept Construct Variables RMDokumen69 halamanConcept Construct Variables RMmaramreddyleela100% (1)
- Mastering The Case InterviewDokumen42 halamanMastering The Case InterviewGoldy BhowmikBelum ada peringkat
- Logos Ethos Pathos KairosDokumen2 halamanLogos Ethos Pathos KairosbenjaminkamenBelum ada peringkat
- Dweck & Leggett (1988) A Social-Cognitive ApproachDokumen18 halamanDweck & Leggett (1988) A Social-Cognitive ApproachNicolásAlejandroCortésUaracBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts and Dynamics Of: ManagementDokumen23 halamanConcepts and Dynamics Of: ManagementnicabalacquitBelum ada peringkat
- Infp & Enfj GuideDokumen9 halamanInfp & Enfj GuideJason AlbertBelum ada peringkat
- 4Ps HandoutDokumen2 halaman4Ps Handoutjrivas2011Belum ada peringkat
- FALLACIESDokumen1 halamanFALLACIESErica Jane Garcia DuqueBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy SHS - What IsDokumen21 halamanPhilosophy SHS - What Isanon_254928515Belum ada peringkat
- Fixed and Growth MindsetDokumen30 halamanFixed and Growth MindsetSamuel DonkohBelum ada peringkat