MEC 2300 - Eng. Mechanics - Kinematics Final
Diunggah oleh
kwejkbaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MEC 2300 - Eng. Mechanics - Kinematics Final
Diunggah oleh
kwejkbaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Page 1 of 5
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
B.ENG.(HONS.) IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
YEAR II SEMESTER I
JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2014 SESSION OF EXAMINATIONS
MEC2300 Engineering Mechanics Kinematics 25
th
January, 2014
0915 - 1215 hours
This paper contains NINE questions. You are to attempt ALL questions.
Stationery: Use of calculators is allowed
Mathematical Booklets
Kinematics Data sheet
Graph Paper
1. The position of a particle moving along a straight line is given by
Where t is in seconds and s is in metres. Find:
(a) The position of the particle when t = 5 seconds
(1 mark)
(b) The velocity function of the particle at any time t
(2 marks)
(c) The acceleration function of the particle at any time t
(2 marks)
Page 2 of 5
2. The acceleration of a car starting from rest is given by the following equations:
For 0 s 50
For 50 s 120
Where s is in m and a is in m/s
2
Draw on graph paper
(a) The a s graph
(3 marks)
(b) The v s graph
(10 marks)
On your graphs show the relevant equations for each segment of the relationships.
3. The velocity of a particle is given by
( )
Where t is in s and v is in m/s
If the particle is at the origin when t = 0, find
(a) The particles acceleration when t = 3s
(2 marks)
(b) The x, y, z (i, j, k) position of the particle when t = 3s
(2 marks)
4. A particle is moving along a curved path defined by the curve
.
When it is at the coordinate position x = 2m the speed of the particle is 8m/s and the rate of
increase in speed is
. At this instant the particle is moving in the direction so that
x is decreasing.
Calculate the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the particle at this instant.
(10 marks)
Page 3 of 5
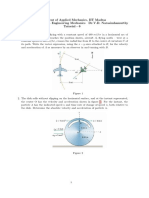
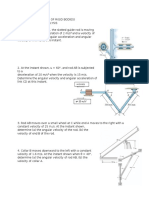
5. The rod OA shown in Figure 1 is rotating anticlockwise with an angular velocity
rad/s. The collar B moves along the rod with a speed of
. When t = 0, = 0 and
r = 0. Find:
(a) The velocity magnitude of collar B when = 50
o
(5 marks)
(b) The acceleration magnitude of collar B when = 50
o
(5 marks)
Figure 1
6. A disk having a radius of 0.6m is initially rotating at an angular speed of 8 rad/s and is
subjected to a constant angular acceleration of 6 rad/s
2
. A point B on the disk lies at a radius
of 0.45m. Find:
(a) The magnitude of velocity of point B just after the wheel rotates through 2 revolutions.
(2 marks)
(b) The acceleration (magnitude and direction) of point B just after the wheel rotates through
2 revolutions.
(2 marks)
Page 4 of 5
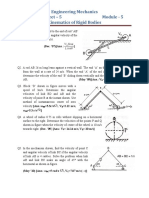
7. At the instant shown in Figure 2, car A travels along the straight portion of the road with a
constant speed of 30 m/s in the general direction towards the right hand side of the page.
At the same instant car B travels along the circular portion of the road with a constant speed
of 20 m/s also towards the general direction towards the right hand side of the page.
Find (at the instant depicted in Figure 2):
(a) The velocity of car B relative to car A
(6 marks)
(b) The acceleration of car B relative to car A
(6 marks)
Figure 2
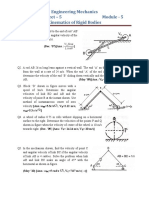
8. In Figure 3 the crank AB rotates in the anticlockwise direction with an angular velocity of
12 rad/s and with an anticlockwise angular acceleration of 1.5rad/s
2
. At the instant shown
= 30
o
. For the position and instant shown find:
(a) The angular velocity of the connecting rod BC
(12 marks)
(b) The angular acceleration of the connecting rod BC
(8 marks)
The dimensions a and b are 0.3m and 0.5m respectively.
Figure 3
Page 5 of 5
9. End A of the link ABC shown in Figure 4 is constrained to move in the vertical direction.
At the instant shown end A is moving downwards with a velocity of 1.5m/s and has a
downward acceleration of 0.5m/s
2
. Distance AB is equal to 0.6m, distance BC is equal to
0.5m, angle ABC is equal to 90
o
and the angle that AB makes with the horizontal is equal to
60
o
. Pivot B is a pin connected to a slider block. The slider block is constrained to move in the
horizontal guide as shown. For the instant shown find:
(a) The angular acceleration of the right angled link ABC.
(10 marks)
(b) The velocity and acceleration of the slider block.
(6 marks)
(c) Describe briefly how you would calculate the acceleration of point C. Mainly highlight
the equations to use, the known parameters to use in the equation and which parameters
need to be calculated.
(6 marks)
Figure 4
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fluid Service CategoriesDokumen5 halamanFluid Service CategoriesKodali Naveen Kumar100% (1)
- Inelastic Analysis of StructuresDokumen9 halamanInelastic Analysis of StructuresNaim Demiri0% (1)
- Lateral Earth Pressure Due To Vibratory Rollers PDFDokumen11 halamanLateral Earth Pressure Due To Vibratory Rollers PDFchutton681Belum ada peringkat
- MF 440 Xtra Narrow (Tier II) PDFDokumen2 halamanMF 440 Xtra Narrow (Tier II) PDFlmn_grss100% (1)
- DPP Nlm-IiDokumen8 halamanDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- DTC P1120/19 Accel. Position Sensor Circuit (Open/Short)Dokumen7 halamanDTC P1120/19 Accel. Position Sensor Circuit (Open/Short)Jehuty88Belum ada peringkat
- LEC. (1) - Kinematics of Rigid Bodies-Definitions-Translation-Rotational Motion-ExamplesDokumen7 halamanLEC. (1) - Kinematics of Rigid Bodies-Definitions-Translation-Rotational Motion-ExamplesfadyBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematic Analysis of Simple Mechanisms Using Graphical and Analytical MethodsDokumen21 halamanKinematic Analysis of Simple Mechanisms Using Graphical and Analytical MethodsRamanathan DuraiBelum ada peringkat
- Circular MotionDokumen37 halamanCircular MotionSaurav Biyani100% (1)
- Modelling and Field-Oriented Control of A Synchronous ReluctanceDokumen215 halamanModelling and Field-Oriented Control of A Synchronous ReluctanceSneha ShendgeBelum ada peringkat
- ME 188 - Combined Brayton & Rankine CyclesDokumen44 halamanME 188 - Combined Brayton & Rankine CyclesAzherRoiFerrerBelum ada peringkat
- GPG291 Designer's Guide To The Options For Ventilation and Cooling 2001Dokumen40 halamanGPG291 Designer's Guide To The Options For Ventilation and Cooling 2001IppiBelum ada peringkat
- Design & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneDokumen57 halamanDesign & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneFatima Nasir R:29Belum ada peringkat
- Home Test 1 PDFDokumen3 halamanHome Test 1 PDFGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiin0% (1)
- Transmission Angles and Four-Bar LinkagesDokumen30 halamanTransmission Angles and Four-Bar LinkagesBivas Panigrahi0% (1)
- API LIcenseDokumen9 halamanAPI LIcenseNadeem AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics 04 Kinematics of Rigid Body 1Dokumen9 halamanDynamics 04 Kinematics of Rigid Body 1Pongsakorn AjdchariyasakchaiBelum ada peringkat
- M1 SpecimenDokumen4 halamanM1 SpecimenTaqsim RajonBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics of Rigid BodyDokumen4 halamanKinematics of Rigid BodyAbishek AdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- ME306-Fall 2013 - Chapter (3) - Velocities Analysis of Mechanisms PDFDokumen13 halamanME306-Fall 2013 - Chapter (3) - Velocities Analysis of Mechanisms PDFmurad_ashourBelum ada peringkat
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1Dokumen3 halamanPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1AlbertBelum ada peringkat
- Circular Motion and Rotational DynamicsDokumen2 halamanCircular Motion and Rotational DynamicsChasel Jane LaygoBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment - 3lord AssignmentDokumen7 halamanAssignment - 3lord Assignmentujdnbzdb hcBelum ada peringkat
- VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSISDokumen60 halamanVELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSIStarasasankaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 03 AE688Dokumen7 halamanAssignment 03 AE688Mhmoud Al-TamimiBelum ada peringkat
- D Dynamics: Lecture Notes 05: Kinematics of The Rigid Body Rigid BodyDokumen15 halamanD Dynamics: Lecture Notes 05: Kinematics of The Rigid Body Rigid BodyKish ShenoyBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomDokumen6 halamanMechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomIoana BoilaBelum ada peringkat
- Velocity and AccelartionDokumen56 halamanVelocity and Accelartionadus lakshmanBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallDokumen24 halamanLinear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallKarthikeyanRamanujamBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ProblemsDokumen6 halamanMechanical Engineering Dynamics Problemsizel valerianoBelum ada peringkat
- GCE Mech M1 M5 Specimen Paper MkschemeDokumen46 halamanGCE Mech M1 M5 Specimen Paper MkschemeAlbert RlBelum ada peringkat
- Kinema TicsDokumen3 halamanKinema TicsSpammerBelum ada peringkat
- Module 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsDokumen7 halamanModule 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsLeo TallerBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDokumen7 halamanEngineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesLeo TallerBelum ada peringkat
- FizikDokumen11 halamanFizikorangramaiBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics of Machines: Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisDokumen94 halamanKinematics of Machines: Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisUpender DhullBelum ada peringkat
- Relative Motion of Rigid BodiesDokumen1 halamanRelative Motion of Rigid BodiesGlass-Half-EmptyBelum ada peringkat
- T4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFDokumen5 halamanT4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFNurul AsyilahBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz KomDokumen5 halamanQuiz Komchellakutti tBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - WorksheetDokumen11 halamanChapter 2 - WorksheetHenokBelum ada peringkat
- Problem SetDokumen4 halamanProblem SetCalcifer da DemonBelum ada peringkat
- ME101 Endsem 2018 Final PDFDokumen2 halamanME101 Endsem 2018 Final PDFt sBelum ada peringkat
- M1 Specimen Paper and Mark SchemeDokumen9 halamanM1 Specimen Paper and Mark Schemejayesh1997Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanics PartDokumen2 halamanMechanics PartPetros JereBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Apc Practice Problems 03 - 2d Motion - SolutionsDokumen15 halaman05 Apc Practice Problems 03 - 2d Motion - Solutionshunderas19Belum ada peringkat
- PHYF 115 Tutorial QuestionsDokumen25 halamanPHYF 115 Tutorial QuestionsSattishZeeBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises: Theory of MachinesDokumen4 halamanExercises: Theory of Machinesgangadharan tharumarBelum ada peringkat
- MENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsDokumen3 halamanMENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsMidnight_dreamerBelum ada peringkat
- MME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking SchemeDokumen18 halamanMME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking Schemecharles ondiekiBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Chapter 12 (Chapter 1 & 2 Mac 2017)Dokumen8 halamanTutorial Chapter 12 (Chapter 1 & 2 Mac 2017)Firdaus AriffBelum ada peringkat
- MCG3130 Midterm 2010Dokumen2 halamanMCG3130 Midterm 2010Brian Pham VuBelum ada peringkat
- Math May 2006 Exam M1Dokumen8 halamanMath May 2006 Exam M1dylandonBelum ada peringkat
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDokumen6 halamanWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematic Particle Problems SolvedDokumen4 halamanKinematic Particle Problems SolvedMohamad HasyimiBelum ada peringkat
- Practice ProblemsDokumen4 halamanPractice Problemsska dooshBelum ada peringkat
- Solomon Press M1KDokumen5 halamanSolomon Press M1KnmanBelum ada peringkat
- MEK453-Assignment 1 - (Oct 23-Feb 24)Dokumen2 halamanMEK453-Assignment 1 - (Oct 23-Feb 24)Espresso LatteBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial - 6 ME-101, Division III (2017-2018 Semester-II) Feb-23, 2018 Time: 8-00 To 8-55.am Q1Dokumen2 halamanTutorial - 6 ME-101, Division III (2017-2018 Semester-II) Feb-23, 2018 Time: 8-00 To 8-55.am Q1Ashish FugareBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating velocities, accelerations and forces for moving objectsDokumen3 halamanCalculating velocities, accelerations and forces for moving objectssara MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- TUTORIAL+CHAPTER+4 SolutionDokumen13 halamanTUTORIAL+CHAPTER+4 SolutionNoOna MieyraBelum ada peringkat
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDokumen8 halaman9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Lec. 2 1Dokumen5 halamanLec. 2 1easesaymichael02Belum ada peringkat
- LESSON 1 LINEAR MOTIONDokumen14 halamanLESSON 1 LINEAR MOTIONIzawati AmatBelum ada peringkat
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Dokumen4 halamanUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Vivin MathewBelum ada peringkat
- June2015 6ExamTimetable18.03.16 PDFDokumen4 halamanJune2015 6ExamTimetable18.03.16 PDFkwejkbaBelum ada peringkat
- This Paper Contains Four Questions. You Are To Attempt Any ThreeDokumen4 halamanThis Paper Contains Four Questions. You Are To Attempt Any ThreekwejkbaBelum ada peringkat
- June2012.3 Exam TimetableDokumen3 halamanJune2012.3 Exam TimetablekwejkbaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 2Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 2kwejkbaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic FittingDokumen124 halamanHydraulic FittingDhanraj PatilBelum ada peringkat
- M100-10 (M-MA Meters) - V3 - 2.11.19 - 1Dokumen28 halamanM100-10 (M-MA Meters) - V3 - 2.11.19 - 1ronald mudimuBelum ada peringkat
- Final Copy Specific Heat Capacity ExperimentDokumen3 halamanFinal Copy Specific Heat Capacity Experimentjoevic torrecampoBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 4Dokumen13 halamanTarea 4Isidro MedranoBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnositc Trouble Codes and Possible CausesDokumen6 halamanDiagnositc Trouble Codes and Possible CausesJuan Carlos Sequeira Robles100% (1)
- Diesel Tiller ManualDokumen77 halamanDiesel Tiller ManualRickson Viahul Rayan C100% (3)
- DowelDokumen3 halamanDowelganeshl08Belum ada peringkat
- Laporan Harian WS 34 Dan 15 2021Dokumen2 halamanLaporan Harian WS 34 Dan 15 2021tyok sajaBelum ada peringkat
- Kershaw 12-12BridgeCraneDokumen3 halamanKershaw 12-12BridgeCranecamelia_pirjan5776Belum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Analysis On Lateral Torsional BucklDokumen5 halamanFinite Element Analysis On Lateral Torsional BucklPraneeth VenkatBelum ada peringkat
- Cebora Bravo MIG2235 ManualDokumen5 halamanCebora Bravo MIG2235 Manualradu_3g6573100% (1)
- Entropy: Reference: J.M. Smith, H.C. Van Ness, M.M. Abbott. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics7 EditionDokumen34 halamanEntropy: Reference: J.M. Smith, H.C. Van Ness, M.M. Abbott. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics7 EditionNelsonBelum ada peringkat
- ThermodymanicsDokumen5 halamanThermodymanicsnavy.aulakh11Belum ada peringkat
- Heat Load-KitchenDokumen1 halamanHeat Load-Kitchenrinko447459Belum ada peringkat
- 6 Rolled BeamsDokumen3 halaman6 Rolled BeamsBCXC LLAMBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Drawing 3906 Slip Form Concrete Barrier F Shape Installation and ConstructionDokumen1 halamanStandard Drawing 3906 Slip Form Concrete Barrier F Shape Installation and Constructiondannychacon27Belum ada peringkat
- Single Multi Stage CompressorsDokumen7 halamanSingle Multi Stage CompressorsV.m. ChenthilBelum ada peringkat
- Jgeen 22 00051Dokumen35 halamanJgeen 22 00051d_diasol38Belum ada peringkat
- Flyer C600sport c650gt-1 PDFDokumen19 halamanFlyer C600sport c650gt-1 PDFYogi Ari PurnaBelum ada peringkat
- MC 10168039 0001 PDFDokumen12 halamanMC 10168039 0001 PDFLuis Pirry MejíaBelum ada peringkat