Eco Analyses (Impacts) : Impacts of Global Trade Flows
Diunggah oleh
imadebest0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
30 tayangan7 halamanImpact of global trade fows resources in economy will shift towards increasing the production of the good or service that is experiencing increased demand. Rapid and large shifts in the value of exchange rates have more signi%cant to %nancial marets than to the real economy.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
analyses.doc
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniImpact of global trade fows resources in economy will shift towards increasing the production of the good or service that is experiencing increased demand. Rapid and large shifts in the value of exchange rates have more signi%cant to %nancial marets than to the real economy.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
30 tayangan7 halamanEco Analyses (Impacts) : Impacts of Global Trade Flows
Diunggah oleh
imadebestImpact of global trade fows resources in economy will shift towards increasing the production of the good or service that is experiencing increased demand. Rapid and large shifts in the value of exchange rates have more signi%cant to %nancial marets than to the real economy.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
Impacts of global trade fows
Resources in economy will shift towards increasing the production of the
good or service that is experiencing increased demand e.g. mining boom
Decline in overseas demand for good or service or if imports tae a higher
proportion of the domestic maret! producers may cease production and
economy will shift production away from that item e.g. vehicle
manufacturing
"rends in the direction of trade can also have impact e.g. increasing
priority on relationship with #hina therefore $"As etc.
Impacts of global fnancial fows
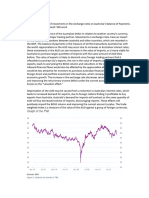
Rapid and large shifts in the value of exchange rates have more
signi%cant to %nancial marets than to the real economy short term but in
the medium to longer term can have substantial e&ect.
A&ects con%dence. "o some extent! the value of currency is seen as
indication of overseas con%dence in the economy's future. (hen money
)owing out and exchange rate falling! can weaen domestic con%dence
and slow rate of economic growth. *igher interest rates may help stabilise
%nancial )ows short term but liely to reduce level of real economic
activity in the medium term.
(hen large currency movements occur! %nancial marets can become
destabilised. +enders may be reluctant to loan further funds unless
borrowers pay higher interest rates.
Factors that STRENGTHEN the
international business cycle
"rade )ows
Investment )ows and investor
sentiments
"ransnational corporations
$inancial )ows
"echnology
,lobal interest rates
International organisations
Factors that WEAKEN the
international business cycle
Domestic interest rates
,overnment %scal policies
-ther domestic economic policies
Exchange rates
.tructural factors
Regional factors
Advantages of free trade
Allows countries to obtain goods and services that they cannot produce
themselves
Allows specialisation to improve e/ciency. "his leads to better allocation
of resources and increased production.
Encourages the e/cient allocation of resources because countries have a
comparative advantage.
Economies of scale lowers average costs of production.
International competitiveness will improve as domestic businesses face
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
greater competitive pressures from foreign producers.
Encourages innovation and spread of new technology and production
processes.
*igher living standards as a result of lower prices! increased production
and increased consumer choice.
Disadvantages of free trade
Increase in short term unemployment may occur as some domestic
businesses may %nd it hard to compete with imports. In the long term! as
the domestic economy redirects resources to areas of production in which
it has comparative advantage! the rise in unemployment should correct
itself.
0ew industries may %nd it more di/cult to establish themselves.
1roduction surpluses from some countries may be 2dumped' (sold at
unrealistically low prices) on the domestic maret which may hurt e/cient
domestic industries.
Impact of globalisation
*igh income and newly industrialised economies have gained from fast
economic growth and closer relationships built on increased trade and
investment )ows.
Expected convergence of economic performance but last decade has
actually shown a divergence of growth trends.
$oreign indebtedness (Africa)! exchange rate volatility (+atin America) and
%nancial integration (in)exibility of the common euro currency) may
destabilise or constrain economic growth.
Impacts on economic development mainly via economic growth3 lift in
economic growth rate raises income levels and provides more resources
for education and health care! and for programs to clean up the
environment but also causes income ine4uality to increase and causes
damage to natural environment.
Consequences of High CAD
,rowth of foreign liabilities so lenders might become more reluctant to
lend to or invest in Australia.
Increased servicing costs could lead to 2debt trap' (borrowing money
simply to service existing foreign liabilities)
Increased volatility for exchange rates as high #AD may undermine the
con%dence of overseas investors in the Australian economy! reducing
demand for A5D. .hort term worsen #AD problem as prices of imports
increase.
#onstraint on future economic growth also nown as balance of payments
constraint.
6ore contractionary economic policy however in short to medium term!
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
the combination of tighter macroeconomic policies and accelerated
microeconomic reform is liely to slow down economic growth and raise
unemployment.
.udden loss of international investor con%dence could trigger a ma7or
crisis e.g. ,reece.
Appreciation of echange rate
!ositive e"ects
Increased 2purchasing power'
Decreases the interest servicing
cost on Australia's foreign debt
Reduce the value of foreign debt
that has been borrowed in foreign
currency
In)ationary pressures reduced
due to imports becoming cheaper
#egative e"ects
Exports more expensive
Encourages import spending and
worsens the #AD
+ower %nancial in)ows because
more expensive unless expects
A5D to continue rising
Reduces value of foreign income
earned on Australia's investments
abroad as well as foreign assets
(nown as 2valuation e&ect')
Depreciation of echange rates
!ositive e"ects
Exports become cheaper
therefore more competitive!
leading to an increase in export
income and improve #AD in
medium term
Discourages import spending
Increases value of foreign income
earned on investments abroad
and foreign assets
,reater %nancial in)ows unless
investors expect currency to
continue falling
#egative e"ects
Reduced 2purchasing power'
Increases interest servicing cost
on foreign debt
Raise dollar value of foreign debt
borrowed in foreign currency
In)ationary pressures will
increase as imports more
expensive
Implications of reduction in protection levels on FI$%&
+ess competitive individual %rms in marginal! import8competing industries
will shrin
.ectors of economy may die out e.g. vehicle manufacturing and
manufacturing in general because relatively low silled labour is re4uired
and we can't compete with the lower wage costs of industrialising
economies e.g. #hina.
Restructuring their operations with aim of staying in business or focus on
one particular aspect of production
.purs innovation and productivity growth through increased competitive
pressure
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
+ower input costs for many %rms! maing export %rms more
internationally competitive
,lobal resources boom in recent years has seen Australia shift bac to a
heavily commodity8focused export base
.ubstantial overall growth in export volumes
Implications of reduction in protection levels on I#DI'ID(A)&
,ains and losses distributed unevenly
#an experience substantial dislocation! particularly through increase in
unemployment associated with restructuring of industries and cuts in local
production
Import8competing industries are concentrated in particular regions so
unemployment in these areas climbed dramatically9 also relatively low8
silled 7obs so structural unemployment
+onger term! the lost employment opportunities should be more than
recouped by the growth experience by sectors that are e/cient and
internationally competitive
Improved living standards3 greater variety! higher 4uality
Implications of reduction in protection levels on *+',$#%,#-&
Reduction in government revenue
6ay a&ect levels of government spending because has to assist the
structural ad7ustment process and provide %nancial support
1olitical conse4uences because generally unpopular with wider
community due to short term e&ects
"herefore better to phase out
Impact of international protection levels on Australia
Australian exports less competitive and will struggle to penetrate foreign
marets
1articular disadvantage as result of protectionist policies of other nations
and trading blocs e.g. E5 has heavily subsidised agricultural production
6ining and resources sector more liely to face export restrictions to
secure energy supplies for domestic economy
$or manufacturing industries! there are non8tari& barriers e.g. technical
restrictions and licensing act that are disguised barriers
.ervice industries arguably face the most prohibitive barriers but are
simply natural barriers caused by geography! language and cultural
di&erences etc. Also regulations or foreign ownership restrictions!
licensing laws and rules relating to government procurement
Impacts of unemployment
Economy's resources are not being used to full capacity therefore
operating below production possibility frontier and total output is below
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
what it could be therefore lower household income and expenditure! lower
sales and pro%ts! higher unemployment levels! reduced business
investment! production and employment
0ot contributing to production process so reduction in economy's living
standards
Decline in labour maret sills for long term unemployed. In this way
cyclical or short term unemployment can turn into long term structural
employment! nown as hysteresis.
+ess tax revenue and more transfer payments as well as funding training
and labour maret programs so decreases government revenue
Excess of supply of labour so slower wage growth
Increased ine4uality because tends to occur more fre4uently among lower
income earners
#rime! social isolation! debt! homelessness! family tensions and
breadown! boredom! loss of sills! self esteem! poor health! psychological
disorders. 6ore resources directed towards dealing with these social
problems.
,"ects of infation
6ain constraint on economic growth
Distorts economic decision maing because producers and consumers
change spending and investment decisions to minimise e&ect on
themselves therefore low in)ation is better because it removes distortion
to investment and savings decisions
*igher in)ation also distort consumers' decisions to spend or save
disposable income
0ominal wage demands during high in)ation due to eroded purchasing
power therefore wage8price in)ationary spiral
0et wealth decline
*igher levels of in)ation result in more contractionary %scal and monetary
policies therefore slower economic growth and higher unemployment
*igher in)ation results in increased prices for exports! reducing
international competitiveness and 4uantity of exports
*igh in)ation cases currency to depreciate over time
.ustained low in)ation may foster greater international con%dence in
economy! strengthening value of dollar
+ower in)ation normally brings about reductions in nominal interest rates
since they are based on real rate of returns plus in)ation. *igher in)ation
usually results in higher interest rates as R:A tries to reduce demand
pressures
,conomic e"ects of inequality
.enefts
6ainly derived from incentive
Costs
Reduces overall utility
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
e&ects
Encourages increased education
and sill levels
(or longer and harder
6ore e/cient allocation of
resources due to higher mobility
Entrepreneurs accept riss more
readily
1otential for higher savings and
capital formation
(satisfaction)
Reduce economic growth
Reduces consumption and
investment
2conspicuous consumption' i.e.
higher income earners buy
expensive stu& for displaying
wealth
1overty and social problems
Increases cost of welfare support
&ocial e"ects of inequality
.enefts
*igher levels of saving or
productivity
Encourages hard wor! ris8taing
and social mobility
Costs
Ine4uality of opportunity
.ocial class divisions
poverty
Conficts in government policy ob/ectives
simultaneous reduction in unemployment and in)ation
achieving economic growth and external balance i.e. balance of
payments constraint which refers to limitation on rate of growth from
impact of high growth on #AD
environmental damage and greater ine4uality in income distribution
policies aimed at long term goals often involve signi%cant structural
change and substantial costs in shorter term e.g. higher unemployment
so often focus on shorter term due to political considerations
Impacts of fscal policy
Economic activity3
8 Expansionary3 increase level of activity through reduction in taxation
revenue and;or increase in government expenditure to stimulate
aggregate demand and multiplied increase in consumption and
investment
8 #ontractionary3 decrease activity through increase in taxation
revenue and;or decrease in government expenditure to dampen
aggregate demand and multiplied decrease in consumption and
investment
8 0eutral3 maintain gap between revenue and spending at same level
as previous year! no e&ect
Resource use3
8 ,ovt. spending in particular area of economy where marets will not
provide resources 4uicly enough without government intervention
e.g. natural disaster9 or public good.
Eco Analyses (Impacts)
8 .peci%c taxing and spending policies e.g. to discourage consumption
of products without banning e.g. tobacco
Income distribution3
8 "axing e.g. if reduce tax rates at upper end of income scale or
increase rate of ,."! less progressive
8 Reductions in spending on community services or transfer payments
also widen ine4uality
.avings and #AD3
8 :udget de%cit decreases national savings! therefore upward pressure
on interest rates and private sector investment will be 2crowded out'
8 "win de%cits theorem i.e. budget de%cit means more in)ow of funds
from overseas for investment and to %nance investment which
increase the si<e of foreign debt! increase debits on income
component of current account therefore increased #AD
Impact of changes in interest rates
#hanges demand for credit
6onetary policy3
8 "ighten3 upward pressure on interest rates! dampen consumer and
investment spending! lower economic activity! lower in)ation!
possibly higher unemployment
8 +oosen3 downward pressure on interest rates! boost consumer and
investment spending! higher level of economic activity! falling
unemployment! increased in)ation
Impacts of microeconomic reform
.hort term costs3 7ob cuts! subsidies withdrawn! ine/cient industries
closed down
+ifted productivity growth due to greater )exibility and incentives to
improve production processes and business management
,reater economic activity and lower unemployment! higher living
standards
+ower in)ation because of the greater competitive pressures
.enefts
,reater e/ciency and
productivity growth
0ew business and 7ob
opportunities
*igher economic growth and
living standards
+ower in)ation
Costs
*igher unemployment in short
term
#losure of ine/cient businesses
,reater wor intensity
+ess e4ual distribution of
income
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Measuring and Types of UnemploymentDokumen14 halamanMeasuring and Types of UnemploymentAnderson MaradzaBelum ada peringkat
- Remedies For Balance of Payments DeficitDokumen4 halamanRemedies For Balance of Payments DeficitAmjad Rashid BhattiBelum ada peringkat
- Macro Economics: An Essay-Centric GuideDokumen14 halamanMacro Economics: An Essay-Centric GuidezachBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9Dokumen8 halamanChapter 9LanaBelum ada peringkat
- Exports Impact On EconomyDokumen4 halamanExports Impact On EconomyjainchanchalBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Driving Economic GrowthDokumen5 halamanFactors Driving Economic GrowthKevin Nguyen100% (1)
- International BusinessDokumen4 halamanInternational BusinessajeetandsrkBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled DocumentDokumen2 halamanUntitled Documentbsma.tenoriorcBelum ada peringkat
- Nazeer Trade Barriers AsgnmntsDokumen8 halamanNazeer Trade Barriers AsgnmntsNazeeruddin MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Protection in AustraliaDokumen4 halamanProtection in AustraliaAnkita SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Changes in Economic GrowthDokumen6 halamanChanges in Economic GrowthMmapontsho TshabalalaBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 H2 Economics CSQ2 AnswerDokumen4 halaman2021 H2 Economics CSQ2 AnswerDurai Manickam NizanthBelum ada peringkat
- MarshallDokumen9 halamanMarshallSam CatlinBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge International As and A Level EDokumen5 halamanCambridge International As and A Level ERoddricBelum ada peringkat
- Difference Between Economic Growth and Development Difference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanDifference Between Economic Growth and Development Difference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentGian Georgette SalcedoBelum ada peringkat
- Harambee University Faculty of Business and Economics Master of Business Administration (MBA)Dokumen9 halamanHarambee University Faculty of Business and Economics Master of Business Administration (MBA)Getu WeyessaBelum ada peringkat
- C) The Balance of PaymentsDokumen7 halamanC) The Balance of Paymentsressejames24Belum ada peringkat
- EconsDokumen13 halamanEconsmysourlemonsBelum ada peringkat
- II. Exchange Rates - Macroeconomic Effects of Currency FluctuationsDokumen6 halamanII. Exchange Rates - Macroeconomic Effects of Currency FluctuationsKent Lawrence A. CalunsagBelum ada peringkat
- $economic GrowthDokumen28 halaman$economic GrowthAishath Aala AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND ITS DETERMINANTSDokumen20 halamanAGGREGATE DEMAND AND ITS DETERMINANTSsanchit12334556Belum ada peringkat
- International EconomicsDokumen20 halamanInternational EconomicsMonika BansalBelum ada peringkat
- The World Economic Recovery Continues, More or Less As PredictedDokumen52 halamanThe World Economic Recovery Continues, More or Less As PredictedSaloni PuriBelum ada peringkat
- AJC Prelims 2015 Q6 ECONS WEEK 7Dokumen10 halamanAJC Prelims 2015 Q6 ECONS WEEK 7glenda chiaBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen5 halamanReportmAmei DiwataBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of A High CAD EssayDokumen2 halamanEffects of A High CAD EssayfahoutBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 7 - Govt Macro Intervention Part IDokumen16 halamanTopic 7 - Govt Macro Intervention Part Ideveshsoukharee234dbis97zxc4Belum ada peringkat
- C. Studies Handout - Economic ClimateDokumen5 halamanC. Studies Handout - Economic ClimateChrisana LawrenceBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Economic Development and GrowthDokumen74 halamanFactors Affecting Economic Development and GrowthAnonymous MPVl949TgBelum ada peringkat
- Ch6 F1 ACCA BPPDokumen35 halamanCh6 F1 ACCA BPPIskandar BudionoBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Growth ExplainedDokumen5 halamanEconomic Growth ExplainedSalma HaythemBelum ada peringkat
- Macro EconomicesDokumen82 halamanMacro Economicessougata2384Belum ada peringkat
- InflationDokumen42 halamanInflationAman SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Growth vs DevelopmentDokumen27 halamanEconomic Growth vs DevelopmentSam Rae LimBelum ada peringkat
- Submitted By: Shagun Vishwanath Ballb (Semester 3) 1020202148Dokumen23 halamanSubmitted By: Shagun Vishwanath Ballb (Semester 3) 1020202148Shagun VishwanathBelum ada peringkat
- Indicators of Macro EnvironmentDokumen61 halamanIndicators of Macro Environmentgolapa007Belum ada peringkat
- Economic Performance: GDP and Circular Flow GDP and Business CycleDokumen26 halamanEconomic Performance: GDP and Circular Flow GDP and Business CycleSohel MozidBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Task 1 School DraftDokumen5 halamanEconomics Task 1 School Draftjaya.nadsBelum ada peringkat
- RecessionDokumen3 halamanRecessionBharathi SivaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On Trade DeficitDokumen7 halamanResearch Paper On Trade Deficittcwqbmrif100% (1)
- Effects of Globalisation On The UK EconomyDokumen2 halamanEffects of Globalisation On The UK EconomyBang VutheBelum ada peringkat
- Justifications For Protectionism EssayDokumen3 halamanJustifications For Protectionism EssayCharles TetleyBelum ada peringkat
- Economic GrowthDokumen13 halamanEconomic Growthwayandragon247Belum ada peringkat
- Economy Global WorstDokumen1 halamanEconomy Global WorstLadyGaizeBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of MNCs on Host CountriesDokumen2 halamanImpact of MNCs on Host Countriespoojaarora_10_juneBelum ada peringkat
- Macroeconomic and Industry AnalysisDokumen4 halamanMacroeconomic and Industry AnalysisFajar TaufiqBelum ada peringkat
- Economics of PakistanDokumen26 halamanEconomics of PakistanMUHAMMAD NAZARBelum ada peringkat
- NJC 2009 Question Analysis TradeDokumen7 halamanNJC 2009 Question Analysis TradedavidbohBelum ada peringkat
- UK Current Account Deficit Widens to Record HighDokumen31 halamanUK Current Account Deficit Widens to Record Highmks93Belum ada peringkat
- Causes For Foreign Currency Liquidity Gap: A Situation Analysis of The Ethiopian EconomyDokumen6 halamanCauses For Foreign Currency Liquidity Gap: A Situation Analysis of The Ethiopian Economyketema simeBelum ada peringkat
- ConversationDokumen4 halamanConversationDương HạnhBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Economic Concepts and Government InterventionDokumen19 halamanUnderstanding Economic Concepts and Government InterventionBandu SamaranayakeBelum ada peringkat
- MessageDokumen1 halamanMessage204917Belum ada peringkat
- Economics Term 2 NotesDokumen6 halamanEconomics Term 2 NotesJay JiaBelum ada peringkat
- Impacts of AUD depreciationDokumen2 halamanImpacts of AUD depreciationWwil DuBelum ada peringkat
- Muhammad Danish Dar (9182024) (BBA-4C Evening) (Assignment 2)Dokumen8 halamanMuhammad Danish Dar (9182024) (BBA-4C Evening) (Assignment 2)Danish DarBelum ada peringkat
- Government Trade Policy Statement: DownloadDokumen18 halamanGovernment Trade Policy Statement: DownloadKarun Kiran PolimetlaBelum ada peringkat
- The Sector Strategist: Using New Asset Allocation Techniques to Reduce Risk and Improve Investment ReturnsDari EverandThe Sector Strategist: Using New Asset Allocation Techniques to Reduce Risk and Improve Investment ReturnsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Smooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1Dari EverandSmooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1Belum ada peringkat
- EIB Investment Report 2018/2019: Retooling Europe's economyDari EverandEIB Investment Report 2018/2019: Retooling Europe's economyBelum ada peringkat
- Ce QuizDokumen2 halamanCe QuizCidro Jake TyronBelum ada peringkat
- The Names & Atributes of Allah - Abdulillah LahmamiDokumen65 halamanThe Names & Atributes of Allah - Abdulillah LahmamiPanthera_Belum ada peringkat
- 100 Commonly Asked Interview QuestionsDokumen6 halaman100 Commonly Asked Interview QuestionsRaluca SanduBelum ada peringkat
- Semester 3 SyllabusDokumen12 halamanSemester 3 SyllabusFuggi JaanBelum ada peringkat
- Council Of Architecture Scale Of ChargesDokumen4 halamanCouncil Of Architecture Scale Of ChargesAshwin RajendranBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment - Lesson 1Dokumen12 halamanAssessment - Lesson 1Charlynjoy AbañasBelum ada peringkat
- SOP For Storage of Temperature Sensitive Raw MaterialsDokumen3 halamanSOP For Storage of Temperature Sensitive Raw MaterialsSolomonBelum ada peringkat
- All India Ticket Restaurant Meal Vouchers DirectoryDokumen1.389 halamanAll India Ticket Restaurant Meal Vouchers DirectoryShauvik HaldarBelum ada peringkat
- HIstory of PerfumeDokumen3 halamanHIstory of PerfumebetselevenBelum ada peringkat
- Whipping Cream PowderDokumen2 halamanWhipping Cream PowderSALCON ConsultancyBelum ada peringkat
- Budget Planner Floral Style-A5Dokumen17 halamanBudget Planner Floral Style-A5Santi WidyaninggarBelum ada peringkat
- Tentative Quotation For Corporate Video (5 Minutes)Dokumen2 halamanTentative Quotation For Corporate Video (5 Minutes)Lekha JauhariBelum ada peringkat
- CPB145 CVTDokumen1 halamanCPB145 CVTDantiancBelum ada peringkat
- Plants Promoting Happiness: The Effect of Indoor Plants on MoodDokumen11 halamanPlants Promoting Happiness: The Effect of Indoor Plants on MoodWil UfanaBelum ada peringkat
- G.R. No. 190583 - People vs FrontrerasDokumen12 halamanG.R. No. 190583 - People vs FrontrerasKaren Faye TorrecampoBelum ada peringkat
- Igbo Traditional Security System: A Panacea To Nigeria Security QuagmireDokumen17 halamanIgbo Traditional Security System: A Panacea To Nigeria Security QuagmireChukwukadibia E. Nwafor100% (1)
- Ict Lesson 2 Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanIct Lesson 2 Lesson Planapi-279616721Belum ada peringkat
- Unit Test 1: Vocabulary & GrammarDokumen2 halamanUnit Test 1: Vocabulary & GrammarAlexandraMariaGheorgheBelum ada peringkat
- Repeaters XE PDFDokumen12 halamanRepeaters XE PDFenzzo molinariBelum ada peringkat
- Commissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCDokumen17 halamanCommissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCelif maghfirohBelum ada peringkat
- 1888 Speth Ars Quatuor Coronatorum v1Dokumen280 halaman1888 Speth Ars Quatuor Coronatorum v1Paulo Sequeira Rebelo100% (2)
- Quantitative Techniques For Business DecisionsDokumen8 halamanQuantitative Techniques For Business DecisionsArumairaja0% (1)
- Solutions Manual For Corporate Finance, 6e Jonathan BerkDokumen7 halamanSolutions Manual For Corporate Finance, 6e Jonathan Berksobiakhan52292Belum ada peringkat
- Brother LS2300 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDokumen96 halamanBrother LS2300 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Practice Questions on Bonding and Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDokumen26 halamanAdditional Practice Questions on Bonding and Mechanical Properties of MaterialsYeo JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Einstein Quotes On SpiritualityDokumen2 halamanEinstein Quotes On Spiritualitybob jamesBelum ada peringkat
- Kinds of Variables and Their UsesDokumen22 halamanKinds of Variables and Their UsesJulie Ann Baltazar Gonzales100% (1)
- Ys 1.7 Convergence PramanaDokumen1 halamanYs 1.7 Convergence PramanaLuiza ValioBelum ada peringkat
- Munslow, A. What History IsDokumen2 halamanMunslow, A. What History IsGoshai DaianBelum ada peringkat
- Work-Life Balance: Before ReadingDokumen5 halamanWork-Life Balance: Before ReadingJulianna AvilaBelum ada peringkat