Single Transistor LED Flasher
Diunggah oleh
Soumitra PaulHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Single Transistor LED Flasher
Diunggah oleh
Soumitra PaulHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
How to Make a Single Transistor LED Flasher at Home
Posted by hitman
Can you imagine of making a formidable little LED flasher or blinker using just a single transistor and
a couple of other passive parts.
That looks too good to be tue, hoever the folloing diagram ill simply prove that it!s really
possible to create a legal LED blinker using just one general purpose transistor as the main
component.
" came across this phenomena some eight years ago, accidentally, hile trying to make a smallest
possible motorcycle side indicator flasher, and as really ama#ed.
$oever, then " did have not any idea that it as happening due to the negative resistance
characteristics of the transistor.
The circuit actually e%ploits the negative resistance factor in transistors to produce the blinking effect.
"!ll be soon riting a comprehensive article on this and e!ll see there ho the concept can be
modified in many different ays.
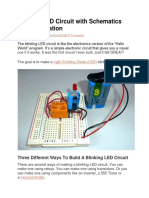
Parts List for the proposed single transistor LED flasher circuit
&' ( )*+,
&) ( ',, -hms,
T' ( .C /0+,
C' ( ',, u1 to 0+, u1
LED ( 2ny Type, any color
Simplest LED Flasher Circuit
This may be the simplest LED flasher circuit you can build, ith the notable e%clusion of LED!s ith
integrated flashing circuits
This might be a good replacement for the L345,5 in some applications.
In action.
Take a close look. Only the emitter and collector leads of the
2N2222 are connected.
The base lead was cut off. The LED is from a string of Christmas
lights and it has an integrated !! Ohm resistor.
1ind updates at .projects.cappels.org
As simple as it gets and still works
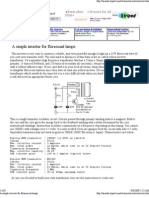
This LED flasher occurred to me hile reading about negative resistance in transistors. "t as reported
that Leona Esaki, ho as at 6ony at the time, had been surprised to see a negative resistance region
hile investigating production defects in transistors hich lead to his thesis ork on the Esaki or
Tunnel Diode in '5/+, hich eventually lead to his receiving the 7obel Pri#e in '5+).
The ""! uf ca#acitor is #artially discharged through
the transistor$ LED$ and current limiting resistor.
"n this implementation, a common 7P7 transistor is used. "n the circuit, a 'k resistor charged the 44,
uf capacitor until the voltage became large enough to get the emitter8base junction to avalanche. "n the
oscilloscope image, it can be seen that the peak voltage 9yello trace: as a little bit less than 5 volts.
2t this point transistor turned on ;uickly and partially discharged the 44, uf capacitor through the
LED and the ',, -hm current limiting resistor. The current avform, hich is the voltage drop across
the ',, -hm resistor, is shon in the blue trace on the scope image. Peak current as )< milliamps,
and the transistor continued to discharge the capacitor until conduction suddenly ceased at < milliamps
93any thanks to Luke in 2ustralia for pointing out the correct current:. 2fter the transistor stopped
conducting, the capacitor began charging again, thus starting a ne cycle.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Troubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundDari EverandTroubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple and Cheap Dark-Detecting LED Circuit - Evil Mad Scientist LaboratoriesDokumen22 halamanA Simple and Cheap Dark-Detecting LED Circuit - Evil Mad Scientist LaboratoriesnoufutanurBelum ada peringkat
- Share What You MakeDokumen16 halamanShare What You MakeSameer ChakoleBelum ada peringkat
- Three Simple Ways to Blink an LEDDokumen9 halamanThree Simple Ways to Blink an LEDDada AlbertBelum ada peringkat
- Save and build over 100 transistor circuits with this free eBookDokumen133 halamanSave and build over 100 transistor circuits with this free eBookEugenio NanniBelum ada peringkat
- 1 100TransistorCircuits PDFDokumen133 halaman1 100TransistorCircuits PDFAnonymous mqsR6k1q6Belum ada peringkat
- 1 100TransistorCircuitsDokumen133 halaman1 100TransistorCircuitscengiz doğanBelum ada peringkat
- Talking Electronics Led TorchDokumen27 halamanTalking Electronics Led TorchKalFowleBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Night Light Project DocumentationDokumen5 halamanAutomatic Night Light Project DocumentationArnel Langomez Remedios100% (1)
- Detecting DarknessDokumen23 halamanDetecting DarknessGADGETMALLBelum ada peringkat
- ZVS OriginalDokumen9 halamanZVS OriginaldllabarreBelum ada peringkat
- Build your own 10X oscilloscope probes for under $10 using household itemsDokumen18 halamanBuild your own 10X oscilloscope probes for under $10 using household itemsswshantha100% (1)
- ESR Capacitor Meter ProjectDokumen22 halamanESR Capacitor Meter ProjectmisiracBelum ada peringkat
- Infrared Emitter From CMOS 555 Robot RoomDokumen6 halamanInfrared Emitter From CMOS 555 Robot RoomnkimlevnBelum ada peringkat
- 20 Electronics Beginner Led Projects Electronic Technology Simple Circuit and ProjectsDokumen58 halaman20 Electronics Beginner Led Projects Electronic Technology Simple Circuit and Projectsdavid reyesBelum ada peringkat
- Tesla Coil Final Year ProjectDokumen12 halamanTesla Coil Final Year ProjectPeerzada Wahid100% (2)
- Varun Bansal: Revised Edition 1Dokumen18 halamanVarun Bansal: Revised Edition 1YogeshgreatBelum ada peringkat
- Joule Thief 0 6 PDFDokumen5 halamanJoule Thief 0 6 PDFKlein Marrion Delino100% (1)
- Blue Ring TesterDokumen8 halamanBlue Ring Testers12originalBelum ada peringkat
- R - 11 - Robots Page 11Dokumen5 halamanR - 11 - Robots Page 11straf238Belum ada peringkat
- Electronics Project Book PDFDokumen70 halamanElectronics Project Book PDFMadalina Croitoru Ristea100% (3)
- Reibot - Easy High Voltage - ReiBotDokumen6 halamanReibot - Easy High Voltage - ReiBotGilberto ManhattanBelum ada peringkat
- Pulse Boost White LEDDokumen9 halamanPulse Boost White LEDsinghadkBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Detector RevisedDokumen10 halamanMetal Detector RevisedMpu Wanto0% (1)
- Literature Review of Automatic Night LampDokumen5 halamanLiterature Review of Automatic Night Lampafmzvadopepwrb100% (1)
- PowerLabs Flyback Driver: A Simple High Voltage GeneratorDokumen8 halamanPowerLabs Flyback Driver: A Simple High Voltage GeneratorJayam SonaniBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Talkingelectronics Com Projects LEDTorchCircuits LEDTorchCircuits P1 HTML PDFDokumen20 halamanWWW Talkingelectronics Com Projects LEDTorchCircuits LEDTorchCircuits P1 HTML PDFgleand latuniBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Projects-DIYDokumen139 halamanElectronics Projects-DIYtara196688% (8)
- VNA Hfst3 CapacitorDokumen8 halamanVNA Hfst3 CapacitorAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics For Absolute BeginnersDokumen17 halamanElectronics For Absolute Beginnersvladadj_1603Belum ada peringkat
- Spez KR C4 Compact enDokumen65 halamanSpez KR C4 Compact enNuno MonteiroBelum ada peringkat
- Arc Reactor: Written By: Eric WeinhofferDokumen7 halamanArc Reactor: Written By: Eric WeinhofferCharles Louie LibronBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Chap3bDokumen24 halaman5 - Chap3bgustav_goodstuff8176Belum ada peringkat
- An Electronic 90V PlateDokumen71 halamanAn Electronic 90V PlateNur Fifi AssilaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronics Chapter Summaries and QuizDokumen73 halamanBasic Electronics Chapter Summaries and QuizBluff FlersBelum ada peringkat
- DimmerDokumen39 halamanDimmerWahyumithali HamelianiBelum ada peringkat
- The Transistor Amplifier: TopicsDokumen65 halamanThe Transistor Amplifier: TopicsShaksham Inc.Belum ada peringkat
- The Electrolytic Cap ESR Problem, and This MeterDokumen5 halamanThe Electrolytic Cap ESR Problem, and This Meterrichardp3Belum ada peringkat
- Tesla Coil ConstructionDokumen4 halamanTesla Coil Constructiondllabarre100% (2)
- LCD Monitor RepairingDokumen8 halamanLCD Monitor Repairingshrink2008Belum ada peringkat
- Oxygen Sensor Simulator - JumperDokumen7 halamanOxygen Sensor Simulator - JumperBrianssrt4100% (2)
- Stanley Meyer ExplainedDokumen14 halamanStanley Meyer ExplainedFer CebBelum ada peringkat
- Fun Circuit Experiments With Light and Soundsrev2Dokumen43 halamanFun Circuit Experiments With Light and Soundsrev2vjeran bachBelum ada peringkat
- POWERLABS' High Voltage Solid State Flyback DriverDokumen11 halamanPOWERLABS' High Voltage Solid State Flyback DriverArnab Acharya50% (2)
- Lessons Learned During A Uv Lamp Debugging: GurugramDokumen6 halamanLessons Learned During A Uv Lamp Debugging: GurugramNarendra AsharBelum ada peringkat
- True bypass relay pedal circuitDokumen8 halamanTrue bypass relay pedal circuitnanodocl5099Belum ada peringkat
- Power Supply RepairDokumen4 halamanPower Supply RepairterezkiBelum ada peringkat
- Valve Curve TracerDokumen7 halamanValve Curve TracerIsa Campos100% (1)
- Stereo VU MeterDokumen7 halamanStereo VU MeterVlatko KrstevskiBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Less Power Supply For MicrocontrollersDokumen11 halamanTransformer Less Power Supply For MicrocontrollersSentimental SagBelum ada peringkat
- Diode As A Switch WorkingDokumen4 halamanDiode As A Switch Workingbantu1210% (1)
- Automatic Night Lamp Construction Guide - Build a Self-Lighting LampDokumen10 halamanAutomatic Night Lamp Construction Guide - Build a Self-Lighting Lampmekm09Belum ada peringkat
- A Perpetual LightDokumen7 halamanA Perpetual Lightsuherlan endanBelum ada peringkat
- SunSeeker ProjectDokumen35 halamanSunSeeker ProjectBien MorfeBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Inverter For Flour..Dokumen8 halamanA Simple Inverter For Flour..Daniel Vladimir MaciucaBelum ada peringkat
- Cold Electricity Circuit Diagram With Capacitors - by UFOpolitics - Tír Na Saor Land of The FreeDokumen6 halamanCold Electricity Circuit Diagram With Capacitors - by UFOpolitics - Tír Na Saor Land of The FreeSadegh Simorgh100% (4)
- Build your own 15Hz zapper in 9 daysDokumen5 halamanBuild your own 15Hz zapper in 9 daysgoransamardziski7225Belum ada peringkat
- Arduino Based Pulse Induction Detector - LC-Trap - 3 StepsDokumen6 halamanArduino Based Pulse Induction Detector - LC-Trap - 3 StepsMaribel Caricari ZuritaBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware Tutor: Crescent SoftwareDokumen32 halamanHardware Tutor: Crescent SoftwareZephir AWTBelum ada peringkat
- Health Products ITGIDokumen1 halamanHealth Products ITGISoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To GurmukhiDokumen4 halamanAn Introduction To Gurmukhiami1577Belum ada peringkat
- Sarvakashata Nivarna Stotram PDFDokumen9 halamanSarvakashata Nivarna Stotram PDFSoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Mswlogo Abréviations - Abbreviations: WWW - Algo.Be/Logo - HTMLDokumen1 halamanMswlogo Abréviations - Abbreviations: WWW - Algo.Be/Logo - HTMLLong TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- Swayamvara Parvati MantraDokumen13 halamanSwayamvara Parvati MantraPraveenkumar Cr100% (2)
- Toroidal Ferrite Core TutorialsDokumen12 halamanToroidal Ferrite Core TutorialsSoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Tree Cutting Permit Application GuideDokumen20 halamanTree Cutting Permit Application GuideSoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- SB 7Dokumen1 halamanSB 7pacificBelum ada peringkat
- Specialty Lubricants: Molykote HP-500 GreaseDokumen2 halamanSpecialty Lubricants: Molykote HP-500 GreaseSoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Ashampoo LicensesDokumen1 halamanAshampoo LicensesSoumitra PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Cartridge Failures EngDokumen2 halamanCartridge Failures Engedijhon5815Belum ada peringkat
- Soaps and Detergents PDFDokumen16 halamanSoaps and Detergents PDFsachinsaboo3Belum ada peringkat
- Gallbladder Natural Therapy PDFDokumen14 halamanGallbladder Natural Therapy PDFSoumitra Paul100% (1)
- Speedball Screen Printing InstructionsDokumen12 halamanSpeedball Screen Printing InstructionsantcaraBelum ada peringkat
- Ecdis-W: Warship Electronic Chart Display and Information SystemDokumen2 halamanEcdis-W: Warship Electronic Chart Display and Information SystemEngr Muhammad SalmanBelum ada peringkat
- Autocad 2010 Tutorial Series Autocad Mechanical 2010 Tutorial SeriesDokumen4 halamanAutocad 2010 Tutorial Series Autocad Mechanical 2010 Tutorial Seriesbdi_roBelum ada peringkat
- Francis Turbines PDFDokumen12 halamanFrancis Turbines PDFabbas bilal100% (1)
- Phaser3300MFP Firmware Upgrade Instructions CWISDokumen2 halamanPhaser3300MFP Firmware Upgrade Instructions CWISAlgenis De Leon RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- JIMCO Filter Catalog with Products and SpecificationsDokumen8 halamanJIMCO Filter Catalog with Products and SpecificationsDedy CjBelum ada peringkat
- Meshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number OneDokumen14 halamanMeshing Methods (ANSYS Meshing) - Everyone Is Number Oneicemage1991Belum ada peringkat
- SAFETY DATA SHEET TITLEDokumen8 halamanSAFETY DATA SHEET TITLESukanta ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Sika PDS E SikaRep SDokumen3 halamanSika PDS E SikaRep Slwin_oo2435Belum ada peringkat
- Adf Interview Questions and AnsewrsDokumen85 halamanAdf Interview Questions and Ansewrsleninbabus100% (2)
- CS20 Instruction Manual: Inverted Vertical Turning CellDokumen83 halamanCS20 Instruction Manual: Inverted Vertical Turning CellHenryBelum ada peringkat
- Notice No.8: Rules and Regulations For TheDokumen40 halamanNotice No.8: Rules and Regulations For TherickBelum ada peringkat
- DP TV Aver 15022 DriversDokumen94 halamanDP TV Aver 15022 DriversMohammed Tahver Farooqi QuadriBelum ada peringkat
- Standing Waves Worksheet SolutionsDokumen6 halamanStanding Waves Worksheet SolutionsMaher TrabelsiBelum ada peringkat
- Çimsa Eco White TDS (EN)Dokumen1 halamanÇimsa Eco White TDS (EN)Babu NysemereBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Card TechnologyDokumen37 halamanSmart Card TechnologyShailesh GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Air Sentry Guardian-BreathersDokumen14 halamanAir Sentry Guardian-BreathersNelson PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Tech.Dokumen31 halamanEnvironmental Tech.csyena28225Belum ada peringkat
- Evaporation: (I) Vapour PressureDokumen15 halamanEvaporation: (I) Vapour Pressurevenka07Belum ada peringkat
- Preparatory Year Program Computer Science (PYP 002)Dokumen34 halamanPreparatory Year Program Computer Science (PYP 002)Hassan AlfarisBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Crystallinity On Electrical Properties of ElectronDokumen4 halamanEffect of Crystallinity On Electrical Properties of Electronapi-3837841Belum ada peringkat
- Categoria ApiDokumen61 halamanCategoria ApiHector MARTINEZ DEL ANGELBelum ada peringkat
- Ehv Bladder AccumulatorsDokumen38 halamanEhv Bladder AccumulatorsFranki Hari MBelum ada peringkat
- Mohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressDokumen26 halamanMohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressNitishBelum ada peringkat
- J320 Maintenance Spare Parts ListDokumen1 halamanJ320 Maintenance Spare Parts ListKeith ChengBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS 42935Dokumen3 halamanMSDS 42935EliasBelum ada peringkat
- Specification Substation AutomationDokumen258 halamanSpecification Substation Automationmspd2003100% (1)
- 02 - Heat ExchangersDokumen88 halaman02 - Heat ExchangerssanjaysyBelum ada peringkat
- Manual WkhtmltopdfDokumen5 halamanManual WkhtmltopdfGeorge DiazBelum ada peringkat
- PV Elite (Construccion de Recipiente) MDMTDokumen8 halamanPV Elite (Construccion de Recipiente) MDMTAlejandro CanoBelum ada peringkat
- System ConfigurationDokumen13 halamanSystem ConfigurationEdlyn Estopa BuenoBelum ada peringkat
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptDari EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptDari EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoDari EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Best Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptDari EverandBest Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksBelum ada peringkat
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensDari EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensBelum ada peringkat