Economics, Goods, Utility, Opportunity Cost and PPC
Diunggah oleh
Betty Bavorová100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
152 tayangan7 halamanIB notes for economics
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniIB notes for economics
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
152 tayangan7 halamanEconomics, Goods, Utility, Opportunity Cost and PPC
Diunggah oleh
Betty BavorováIB notes for economics
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Economics, goods, utility, opportunity
cost and PPC
What is economics?
Economics is a science about how wants are satisfied with resources.
Human needs and wants are infinite.
Resources are scarce.
Social science is a field of science studying people in society.
Economics
o Robinson Crusoe Economics is economics without other people or money
o Catalaxy talks about a society with more people, money,
scarcity is the main concept in economics
o If we cannot economize it, it is scarce
Economics is a science studying human behaviour as a relationship between their needs/wants and
limited resources.
Homo oeconomicus:
A fully rational person
knows his options and possibilities
can compare these
can choose between them, so that
o consumer he maximizes utility
o firm it maximizes profit
Positive and normative
Positive economics focuses on statements answerable by yes or no; can be evaluated as true or
false. (The price of beer IS around 30CZK.)
Normative economics focuses on evaluative statements. (The price of beer SHOULD be zero. The
price of beer is TOO HIGH.)
Basic economic problem
We have scarce resources.
What should we produce?
How much?
How should we produce it?
Who should it be produced for?
Which system works better in order to allocate our scarce resources to the ends we have?
Micro and macro
Microeconomics is the study of individual business decisions, individual markets and businesses.
Macroeconomics is the study of large-scale economies, such as national, regional or global
economies.
Economic models
Ceteris paribus all other things will be equal; an economic way of having controlled variables
Not perfect, just trying to represent a phenomenon independently.
Three economic systems
1. FREE MARKET ECONOMY
capitalism, laissez-faire, anarchy, voluntaryism, private enterprise economy
prices determined by demand/supply only
2. PLANNED ECONOMY
socialism, communism, cybersocialism, national socialism
central planning committee, government, planned allocation for prices etc.
3. MIXED ECONOMY
social democracies
most common (in West)
Simple categorization of goods
A good is everything you might want to buy; everything for which there is a supply and demand.
The opposite of a good is a bad.
1. FREE GOODS
are not scarce
i.e. air
2. PRIVATE GOODS
scarce
i.e. clothes, houses
3. PUBLIC GOODS
scarce
Are non-rival and non-excludable.
rival goods: if one person uses it, nobody else can use it at the same time (so
i.e. not pavements)
excludable goods: a person can be forbidden from using a good
i.e. infrastructure
Factors of production
land
labour (L)
o The people
o The labourer owns the labour and sells it to the company for his wage.
capital (K)
o human (the skills and know-how of the person)
o physical (machinery, buildings, vehicles, computing systems,)
o social (networking, contacts,)
o religious (investing into the afterlife)
entrepreneurship
Different technologies are described as different combinations of labour and capital:
T
1
-> 2K + 3L = Q
T
2
-> 2K x 3L = Q
(Q stands for quantity)
Economic growth
Nominal national income the value of all the goods and services produced in an economy in a
given time period (1 yr); can be measured
1. by looking at the value of the output of the goods and services
2. by the expenditure on the goods and services
3. by total incomes of the households for letting the firms use their factors of production
Real national income - The actual quantity of goods and services produced. The standard of living
depends very much on the quantities of goods and services produced. Immeasurable.
Markets
1. OUTPUT (PRODUCT) MARKETS
goods and services are exchanged
2. INPUT MARKETS
resources (labour, capital, land) are exchanged
Physical places (goods and services exchanged for money) X online markets (credit cards or money
transfer)
1. PRODUCT MARKET
goods and services are bought and sold
2. FACTOR MARKET / LABOUR MARKET
the factors of production are bought and sold
3. FINANCIAL MARKET
foreign exchange market, where international currencies are traded
4. STOCK MARKET
shares in companies are bought and sold
Utility
Utility is a measure of pleasure and has no unit. It is perfectly subjective.
1. TOTAL UTILITY
total pleasure from consuming a bundle of sth
2. MARGINAL UTILITY
extra utility gained by consuming a unit of sth
It is rational to buy the highest amount of a good where marginal utility > marginal cost.
Everything, where marginal utility/value > marginal cost is consumer surplus.
Opportunity cost (OC)
The next best alternative forgone
The opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone, in a situation in which
a choice needs to be made between several mutually exclusive alternatives given limited resources.
Profit is denoted as . It equals the revenue (R) minus the cost.
Economic profit: OC
OC is what you give up to get an opportunity.
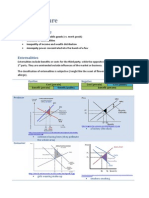
Production Possibility Curve / Frontier (PPC/PPF)
(http://cramster-image.s3.amazonaws.com/definitions/economics-14-img-1.png)
It is only possible to produce a certain amount of a good A (butter) while producing a certain amount
of good B (guns). The OC grows for every successive butter/gun.
Growth Development
whole PPC moving outwards
increased resources
o labour force
o change in labour force
participation
o change in labour/leisure decision
improved technology (innovation)
expansion of capital stock
an improvement in the rules (laws,
institutions and policies) of the economy
moving along the curve
decision to produce more of product X
Circular flow diagram
Output
markets
Households
Input
markets
Firms
GOODS
MONEY
Individual demand
1. THE INCOME EFFECT
Consumer buys less at a higher price, because the money he has does not pay for the
original quantity.
2. THE SUBSTITUTION EFFECT
Consumer substitutes good with higher price with a good with lower price.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- J Butler - Revisiting Bodies and PleasuresDokumen10 halamanJ Butler - Revisiting Bodies and PleasuresDiego Madias100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Indian Constitution MCQDokumen17 halamanIndian Constitution MCQJohn100% (1)
- Diokno 0001Dokumen1 halamanDiokno 0001Angela Bau0% (4)
- FBI Files: Clarence 13x Smith (Part 2)Dokumen36 halamanFBI Files: Clarence 13x Smith (Part 2)☥ The Drop Squad Public Library ☥100% (1)
- ElasticityDokumen4 halamanElasticityBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Public Versus Private GoodsDokumen2 halamanPublic Versus Private GoodsBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- IB SL Trigonometric FunctionsDokumen2 halamanIB SL Trigonometric FunctionsBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Ch2 FunctionsDokumen6 halamanCh2 FunctionsBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Ch3 Chemistry of LifeDokumen24 halamanCh3 Chemistry of LifeBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Atomic StructureDokumen13 halamanChapter 2 Atomic StructureBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic NomenclatureDokumen4 halamanInorganic NomenclatureBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 PeriodicityDokumen13 halamanCH 3 PeriodicityBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Public Choice (Not Only Politics!) : Median Voter ModelDokumen2 halamanPublic Choice (Not Only Politics!) : Median Voter ModelBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Cells: Assesment Statements From Pearson Baccalaureate HL BiologyDokumen16 halamanCells: Assesment Statements From Pearson Baccalaureate HL BiologyBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Cells: Assesment Statements From Pearson Baccalaureate HL BiologyDokumen16 halamanCells: Assesment Statements From Pearson Baccalaureate HL BiologyBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Quantitative ChemistryDokumen7 halamanChapter 1 Quantitative ChemistryBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Market FailureDokumen2 halamanMarket FailureBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Government InterventionDokumen2 halamanGovernment InterventionBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Checking Progress in IB ChemistryDokumen3 halamanChecking Progress in IB ChemistryBetty Bavorová100% (1)
- 1 - Bohr Atom, Electron Configuration and Quantum TheoryDokumen7 halaman1 - Bohr Atom, Electron Configuration and Quantum TheoryBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Fim Theory HLDokumen2 halamanFim Theory HLBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Demand, Supply and Market EquilibriaDokumen5 halamanDemand, Supply and Market EquilibriaBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2.2 The Mass SpectrometerDokumen1 halamanChapter 2.2 The Mass SpectrometerBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Elasticity: Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)Dokumen2 halamanElasticity: Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)Betty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2.1 The AtomDokumen2 halamanChapter 2.1 The AtomBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1.1 The Mole ConceptDokumen1 halamanChapter 1.1 The Mole ConceptBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2.3 Eukaryotic CellsDokumen3 halamanChapter 2.3 Eukaryotic CellsBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2.2 Prokaryotic CellsDokumen1 halamanChapter 2.2 Prokaryotic CellsBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- IB Bio SL: Cell TheoryDokumen3 halamanIB Bio SL: Cell TheoryBetty BavorováBelum ada peringkat
- SK Reso For Appointment of SK SecretaryDokumen3 halamanSK Reso For Appointment of SK SecretaryTAU GOLDEN HARVESTBelum ada peringkat
- Religious Aspects of La ViolenciaDokumen25 halamanReligious Aspects of La ViolenciaDavidBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On The "Cry" of August 1896Dokumen27 halamanNotes On The "Cry" of August 1896Chelsea EspirituBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper Susan B AnthonyDokumen8 halamanResearch Paper Susan B Anthonyntjjkmrhf100% (1)
- Gender Spectrum - My Gender JourneyDokumen3 halamanGender Spectrum - My Gender JourneyGender SpectrumBelum ada peringkat
- Lexington GOP Elects Chair Who Denies 2020 Election Results - The StateDokumen9 halamanLexington GOP Elects Chair Who Denies 2020 Election Results - The Staterepmgreen5709Belum ada peringkat
- Apache-Nde-NneéWorking Group Shadow Report / UN CERD 88th Session: Review of The Holy SeeDokumen135 halamanApache-Nde-NneéWorking Group Shadow Report / UN CERD 88th Session: Review of The Holy SeeInternational Organization for Self-Determination and Equality (IOSDE)Belum ada peringkat
- Sarias - To Understand A Scandal Watergate Beyond NixonDokumen7 halamanSarias - To Understand A Scandal Watergate Beyond NixonLanceCaugheyBelum ada peringkat
- Amin S Empire and MultitudeDokumen13 halamanAmin S Empire and MultitudeMatt IskraBelum ada peringkat
- Thinking About Nuclear Power in Post-Saddam Iraq Pub979Dokumen83 halamanThinking About Nuclear Power in Post-Saddam Iraq Pub979scparcoBelum ada peringkat
- Samson OptionDokumen5 halamanSamson OptionRubén PobleteBelum ada peringkat
- Provoc ADokumen42 halamanProvoc AScooterKatBelum ada peringkat
- TangentsDokumen36 halamanTangentsJBSfanBelum ada peringkat
- Government of Andhra Pradesh Boilers Department: Application ID: BEC1800264Dokumen2 halamanGovernment of Andhra Pradesh Boilers Department: Application ID: BEC1800264Bharath NadimpalliBelum ada peringkat
- Unprecedented E4 - Middle Finger To GodDokumen12 halamanUnprecedented E4 - Middle Finger To Godwamu885100% (1)
- Air and Space LawDokumen10 halamanAir and Space Lawinderpreet sumanBelum ada peringkat
- Umland PHD Dissertation6BritshspellingDokumen243 halamanUmland PHD Dissertation6Britshspellingprevisetrazite100% (1)
- No. Amendments Enforced Since Objectives: Amendments To The Constitution of IndiaDokumen8 halamanNo. Amendments Enforced Since Objectives: Amendments To The Constitution of IndiaPrashant SuryawanshiBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Law IDokumen132 halamanLabor Law ICeledonio ManubagBelum ada peringkat
- Commonwealth of Nations: OriginsDokumen2 halamanCommonwealth of Nations: OriginsAndaVacarBelum ada peringkat
- HR Assistant Manager OpeningDokumen6 halamanHR Assistant Manager OpeningPraneet TBelum ada peringkat
- Youth Pledge Day Marks Birth of Indonesian NationDokumen6 halamanYouth Pledge Day Marks Birth of Indonesian NationisnadewayantiBelum ada peringkat
- PPP EnglishDokumen8 halamanPPP Englishសុគន្ធី កែវBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 Board - of - Director Posting FINAL PDFDokumen1 halaman2013 Board - of - Director Posting FINAL PDFlindsaywilliam9Belum ada peringkat
- Wa'AnkaDokumen367 halamanWa'AnkaAsarBelum ada peringkat
- UNDP Starter Kit All AboutDokumen29 halamanUNDP Starter Kit All AboutSafeer UllahBelum ada peringkat