Universiti Kuala Lumpur: Marks
Diunggah oleh
Robert Stevenson0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
18 tayangan6 halamanJudul Asli
Cover_Page_PW_1.doc
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
18 tayangan6 halamanUniversiti Kuala Lumpur: Marks
Diunggah oleh
Robert StevensonHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
UNIVERSITI KUALA LUMPUR
MALAYSIA FRANCE INSTITUTE
REFRIGERATION FUNDAMENTALS AND TOOLS
FRD 10103
ASSIGNMENT 1
Refrigeratio !it Perfor"a#e
Pre$are% &'(
Na"e St!%et) ID Re"ar*)
NA+ARUL +IKREY &IN
NAS,O&UDIN
-010.31.03.
MU,AMMAD I/&AL &IN &ADRUL
,IS,AM
-010.31.130
MU,AMMAD FARIS AKMAL &IN
A&DUL RA,MAN
-010.31.10.
MU,AMMAD D+A,IRUDDIN &IN
ILYAS
-010.31.120
MU,AMMAD ,ILMI &IN MO,D
K,AIRI
-010.31.1-2
MARKS
Date(
Pre$are% For( Lo*e"a ,a")ir
2 | P a g e
Ta34e of Cotet
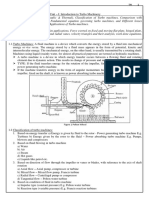
1.0 Refrigeration workshop Unit 2
1.1 Unit Description and schematic diagram
2.0 Major component and accessories
2.1 Type and Function
Result of Activity !
".0 Measuring data taken from the Refrigeration unit and ca#cu#ation $
".1 Mo##ier chart
".2 %sychrometric chart
&.0 'onc#usion 10
!.0 References 1
3 | P a g e
R(')%R*'+T),- '*M%R(..*R
+ reciprocating compressor is a positi/e disp#acement compressor that uses
pistons dri/en 0y a crankshaft to de#i/er gases at high pressure.
The intake gas enters the suction manifo#d1 then f#ows into the compression
cy#inder where it gets compressed 0y a piston dri/en in a reciprocating motion /ia
a crankshaft1 and is then discharged. +pp#ications inc#ude oi# refineries1 gas
pipe#ines and refrigeration p#ants. The app#ication is the 0#owing of p#astic 0ott#es
made of po#yethy#ene terephth#ate 2%(T3.
)n the ionic #i4uid piston compressor many sea#s and 0earings were remo/ed in the
design as the ionic #i4uid does not mi5 with the gas. .er/ice #ife is a0out 10 times
#onger than a regu#ar diaphragm compressor with reduced maintenance during use1
energy costs are reduced 0y as much as 206. The heat e5changers that are used in
a norma# piston compressor are remo/ed as the heat is remo/ed in the cy#inder
itse#f where it is generated. +#most 1006 of the energy going into the process is
0eing used with #itt#e energy wasted as reject heat.
7"8
4 | P a g e
'(,TR)FU-+9 '*M%R(..*R
Centrifugal compressors1 sometimes termed radial compressors1 are a su0:c#ass
of dynamic a5isymmetric work:a0sor0ing tur0omachinery.
718
The idea#i;ed compressi/e dynamic tur0o:machine achie/es a pressure rise 0y
adding kinetic energy</e#ocity to a continuous f#ow of f#uid through the rotor
orimpe##er. This kinetic energy is then con/erted to an increase in potentia#
energy<static pressure 0y s#owing the f#ow through a diffuser. The pressure rise in
impe##er is in most cases a#most e4ua# to the rise in the diffuser section.
Scroll Compressors:
The scro## compressor comprises of two inter#ea/ed scro##s of which one is fi5ed
and the other or0its eccentrica##y without rotating. During its motion sma## gaps are
created 0etween the scro##s where the refrigerant gets compressed. The scro##s can
ha/e different shapes #ike in/o#ute1 +rchimedean spira# or hy0rid cur/e. )n another
arrangement 0oth the scro##s may 0e rotating eccentrica##y to produce the
compression.
Rotary Compressors:
The rotary compressors ha/e two rotating e#ements1 #ike gears1 0etween which the
refrigerant is compressed. These compressors can pump the refrigerant to #ower or
moderate condensing pressures. .ince they can hand#e sma## /o#ume of the gas and
produce #esser pressure1 they are used in fewer app#ications.
5 | P a g e
6 | P a g e
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseDari EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideDari EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuidePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (8)
- To Study The Characteristic Curve of Centrifugal Compressor.Dokumen19 halamanTo Study The Characteristic Curve of Centrifugal Compressor.mustapai2250% (2)
- Service Manual MIH Series Condensing Units Heat Pump: 1.5 Tons To 5 TonsDokumen30 halamanService Manual MIH Series Condensing Units Heat Pump: 1.5 Tons To 5 TonsHenry Javier RíosBelum ada peringkat
- Full Lab Report ThermoDokumen42 halamanFull Lab Report Thermoatiqah75% (4)
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDokumen9 halamanKhulna University of Engineering & Technology17044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1 Midterm de MesaDokumen7 halamanActivity 1 Midterm de MesaEmmanuelle De MesaBelum ada peringkat
- AbstractDokumen11 halamanAbstractSibasish Singh SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- EjectorsDokumen2 halamanEjectorsaqsa.noureen715Belum ada peringkat
- Non Conventional IC EngineDokumen8 halamanNon Conventional IC EngineKiran KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 1 Forced Draft Fan Basiano FINALDokumen9 halamanExperiment No. 1 Forced Draft Fan Basiano FINALRYNANDREW BASIANOBelum ada peringkat
- A Project On Pneumatic ViceDokumen13 halamanA Project On Pneumatic ViceKumar Gk50% (2)
- Compressed Air Supply: Training NotesDokumen22 halamanCompressed Air Supply: Training NotesardianalimBelum ada peringkat
- D.J College of Engg.& Tech.: Presented To:-Presented ByDokumen35 halamanD.J College of Engg.& Tech.: Presented To:-Presented Byshakti sindhuBelum ada peringkat
- Selecting The Right Preheater Fan and Drive: TumellDokumen12 halamanSelecting The Right Preheater Fan and Drive: TumellNguyen Dang Binh ThanhBelum ada peringkat
- Design & Fabrication of Air Driven Engine: Sanketh S, Harsha R N, Manunath MVDokumen10 halamanDesign & Fabrication of Air Driven Engine: Sanketh S, Harsha R N, Manunath MVretechBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering PI Q&ADokumen93 halamanMechanical Engineering PI Q&AsdBelum ada peringkat
- Air CompressorDokumen31 halamanAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare33% (3)
- Automatic Pneumatic Vice and JackDokumen33 halamanAutomatic Pneumatic Vice and JackTechnico Technocrats100% (2)
- Project ReportDokumen29 halamanProject Reportgeetikag_23Belum ada peringkat
- Sys A CDokumen40 halamanSys A Cdnageshm4n244Belum ada peringkat
- Volumetric EfficiencyDokumen7 halamanVolumetric EfficiencyDumithJayathilaka100% (1)
- LAB 3 Air Compressor System AuditDokumen7 halamanLAB 3 Air Compressor System AuditAmirulAminBelum ada peringkat
- HelenDokumen15 halamanHelenhelenBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Compressors RecentDokumen34 halamanCentrifugal Compressors RecentMOAB FIFA mobileBelum ada peringkat
- U3 Reciprocating Air Compressor: TitleDokumen14 halamanU3 Reciprocating Air Compressor: TitleShahir Afif Islam0% (1)
- Marine Gas Turbine PDFDokumen14 halamanMarine Gas Turbine PDFSaint JoaquinBelum ada peringkat
- Discovery: Pneumatic Metal Sheet Cutting MachineDokumen7 halamanDiscovery: Pneumatic Metal Sheet Cutting MachineStella RaphaelBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Gear Changer in Two Wheelers - Pneumatic Model. (Report)Dokumen69 halamanAutomatic Gear Changer in Two Wheelers - Pneumatic Model. (Report)tariq7633% (3)
- Chapter 7Dokumen62 halamanChapter 7birlieBelum ada peringkat
- Blower Manual PDFDokumen6 halamanBlower Manual PDFDatta DoifodeBelum ada peringkat
- British Pneumatic HandbookDokumen96 halamanBritish Pneumatic HandbookAliArababadiBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report ON: Center Jack For CarsDokumen10 halamanProject Report ON: Center Jack For CarsKmineyBelum ada peringkat
- Compressor Head Calculations Design GuideDokumen24 halamanCompressor Head Calculations Design Guidec_nghiaBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Air Compressor BasicsDokumen7 halamanCentrifugal Air Compressor BasicsCésarBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Inlet Air Temperature Effect On Gas Turbine Compressor PerfornanceDokumen9 halamanAnalysis of Inlet Air Temperature Effect On Gas Turbine Compressor PerfornanceRafraf Ezdine100% (1)
- MECH-Industrial PneumaticsDokumen30 halamanMECH-Industrial PneumaticsPrakash KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Manual - Air Conditioning Test RigDokumen5 halamanExperiment Manual - Air Conditioning Test RigAreez MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Turbine1Dokumen13 halamanGas Turbine1Saurabh BarangeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 15 Aircraft Propulsion AssignmentDokumen18 halamanUnit 15 Aircraft Propulsion AssignmentTerrence Owens50% (2)
- Centrifugal CompressorDokumen19 halamanCentrifugal CompressorMOAB FIFA mobileBelum ada peringkat
- Compressor DesignDokumen34 halamanCompressor Designramamurthy123Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering Encyclopedia: Saudi Aramco Desktop StandardsDokumen12 halamanEngineering Encyclopedia: Saudi Aramco Desktop StandardsFA Ay100% (1)
- Selecting Air Conditioners For EnclosureDokumen7 halamanSelecting Air Conditioners For EnclosureErdinc KlimaBelum ada peringkat
- Comp Air Design GuideDokumen23 halamanComp Air Design GuideSaurabh Singh100% (1)
- Fans in Power StationsDokumen39 halamanFans in Power StationsAkashKishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Control & Instrumentation Volume 2Dokumen119 halamanControl & Instrumentation Volume 2Ramachandran Marappan100% (1)
- Thermal Analysis of Gas Turbine BladeDokumen46 halamanThermal Analysis of Gas Turbine BladeManepalli HarshavardhananBelum ada peringkat
- Draught System: Gas Atm AtmDokumen5 halamanDraught System: Gas Atm AtmSattyaki BasuBelum ada peringkat
- Fan Power ConsumptionDokumen8 halamanFan Power Consumptionchilamkurti_sivasankararaoBelum ada peringkat
- Piston Air Compressor FunctionalityDokumen4 halamanPiston Air Compressor FunctionalityRadhe kumawatBelum ada peringkat
- TLT Industrial FansDokumen42 halamanTLT Industrial FansNguyen Thanh TrungBelum ada peringkat
- IBU Brochure 2011Dokumen12 halamanIBU Brochure 2011toon_naBelum ada peringkat
- Turbo Intercooler Cooling SystemDokumen8 halamanTurbo Intercooler Cooling SysteminventionjournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of OD Cooling System Parameters Based On Thermal Modeling of Power Transformer WindingDokumen12 halamanDetermination of OD Cooling System Parameters Based On Thermal Modeling of Power Transformer Windingmpu682Belum ada peringkat
- Air Compressors and Pneumatic Control SystemsDokumen7 halamanAir Compressors and Pneumatic Control SystemsBader Shrbaji100% (2)
- Turbo-Machinery (Meng3201) : Chapter-3Dokumen28 halamanTurbo-Machinery (Meng3201) : Chapter-3Asnake Bahiru100% (1)
- Thermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualDari EverandThermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Unit 1 Impact of JetDokumen16 halaman2 Unit 1 Impact of Jetmohit sonawaneBelum ada peringkat
- NozzleDokumen49 halamanNozzleShafayat AhmmedBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Centrifugal PumpDokumen5 halamanStudy of Centrifugal Pumpउमेश गावंडेBelum ada peringkat
- Turbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Dokumen25 halamanTurbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Vibhor JainBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 4 Centrifugal CompressorDokumen11 halamanExp 4 Centrifugal CompressorFaris HamirBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen6 halamanPDFJithin kvBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen23 halamanUnit 4eyobBelum ada peringkat
- Ebara GS Ibb April 2022 - 220404 - 200628Dokumen4 halamanEbara GS Ibb April 2022 - 220404 - 200628chandra atmaBelum ada peringkat
- Type of Fuel PumpsDokumen30 halamanType of Fuel PumpsPrem MauryaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic and Compressible FlowDokumen6 halamanHydraulic and Compressible FlowJaya D40% (5)
- Compresor HRH051 DanfossDokumen1 halamanCompresor HRH051 Danfossjohn fredyBelum ada peringkat
- Pompa Dan ValveDokumen4 halamanPompa Dan ValveIkhwan IdhamBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Gas Generator Illustrated Parts CatalogueDokumen14 halamanIndustrial Gas Generator Illustrated Parts CataloguejuanaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of PumpsDokumen18 halamanTypes of PumpsAhmed Adel Ibrahim100% (1)
- MAE 112 Propulsion FinalDokumen4 halamanMAE 112 Propulsion FinalTony StarkBelum ada peringkat
- A Presentation On PumpsDokumen34 halamanA Presentation On PumpsSajjad Rasool ChaudhryBelum ada peringkat
- FM APPROVALS - 3060688 - Horizontal End Suction TypeDokumen2 halamanFM APPROVALS - 3060688 - Horizontal End Suction TypeAhlan kpBelum ada peringkat
- API 617 6th Ed, Feb 1995 Centrifugal CompressorsDokumen3 halamanAPI 617 6th Ed, Feb 1995 Centrifugal CompressorszahoorBelum ada peringkat
- Nipcib 000030Dokumen703 halamanNipcib 000030AlfoFSBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Fuel Feed Pump With Fuel Prefilter, FunctionDokumen2 halamanManual Fuel Feed Pump With Fuel Prefilter, FunctionTamer MoustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Momentum TransferDokumen12 halamanMomentum TransfermohitreddyBelum ada peringkat
- EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL BLOWER WITH BACKWARD FORWARD AND RADIAL CURVED VANE Ijariie7400Dokumen10 halamanEXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL BLOWER WITH BACKWARD FORWARD AND RADIAL CURVED VANE Ijariie7400Mohammed Asif Kattimani MechanicalBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal PumpDokumen7 halamanCentrifugal PumptanalialayubiBelum ada peringkat
- List of Equipments ATDokumen1 halamanList of Equipments ATLa RocaBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler Feed Pump ManualDokumen42 halamanBoiler Feed Pump ManualДмитрий ЗинченкоBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Rotating Equipment PDFDokumen96 halamanOverview of Rotating Equipment PDFAiyappa Devraj100% (6)
- Pumps and Turbines Study MaterialsDokumen9 halamanPumps and Turbines Study MaterialsHARSHIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Primetech Priming EjectorDokumen3 halamanPrimetech Priming EjectorVikk SuriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogo - NM SPERONIDokumen67 halamanCatalogo - NM SPERONIVenk KisaragiBelum ada peringkat