Capital Structure
Diunggah oleh
tekleyHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Capital Structure
Diunggah oleh
tekleyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Capital Structure
Capital Structure is referred to as the ratio of different kinds of securities raised by a firm as
long-term finance. The capital structure involves two decisions-
a) Type of securities to be issued are equity shares, preference shares and long term
borrowings (Debentures).
b) Relative ratio of securities can be determined by process of capital gearing. On this basis,
the companies are divided into two-
i. Highly geared companies - Those companies whose proportion of equity
capitalization is small.
ii. Low geared companies - Those companies whose equity capital dominates total
capitalization.
Essential features of sound capital Mix
A sound or an appropriate Capital mix/structure should have the following essential features:
1. Highest possible use of leverage
2. Capital structure should be flexible
3. To avoid undue financial/business risk with the increase of debt
4. The use of debt should be within the capacity of a firm. The firm should be in a position
to meet its obligations in paying the loan and interest charges as and when due.
5. It should involve smallest amount of possible risk of loss of control
6. It must avoid undue restrictions in agreement of debt.
Factors Determining Capital Structure
1. Trading on Equity- The word equity denotes the ownership of the company. Trading
on equity means taking advantage of equity share capital to borrowed funds on
reasonable basis. It refers to additional profits that equity shareholders earn because of
issuance of debentures and preference shares. It is based on the thought that if the rate of
dividend on preference capital and the rate of interest on borrowed capital is lower than
the general rate of companys earnings, equity shareholders are at advantage which
means a company should go for a judicious blend of preference shares, equity shares as
well as debentures. Trading on equity becomes more important when expectations of
shareholders are high.
2. Degree of control- In a company, it is the directors who are so called elected
representatives of equity shareholders. These members have got maximum voting rights
in a concern as compared to the preference shareholders and debenture holders.
Preference shareholders have reasonably less voting rights while debenture holders have
no voting rights. If the companys management policies are such that they want to retain
their voting rights in their hands, the capital structure consists of debenture holders and
loans rather than equity shares.
3. Flexibility of financial plan- In an enterprise, the capital structure should be such that
there is both contractions as well as relaxation in plans. Debentures and loans can be
refunded back as the time requires. While equity capital cannot be refunded at any point
which provides rigidity to plans. Therefore, in order to make the capital structure
possible, the company should go for issue of debentures and other loans.
4. Choice of investors- The companys policy generally is to have different categories of
investors for securities. Therefore, a capital structure should give enough choice to all
kind of investors to invest. Bold and adventurous investors generally go for equity shares
and loans and debentures are generally raised keeping into mind conscious investors.
5. Capital market condition- In the lifetime of the company, the market price of the shares
has got an important influence. During the depression period, the companys capital
structure generally consists of debentures and loans. While in period of boons and
inflation, the companys capital should consist of share capital generally equity shares.
6. Period of financing- When company wants to raise finance for short period, it goes for
loans from banks and other institutions; while for long period it goes for issue of shares
and debentures.
7. Cost of financing- In a capital structure, the company has to look to the factor of cost
when securities are raised. It is seen that debentures at the time of profit earning of
company prove to be a cheaper source of finance as compared to equity shares where
equity shareholders demand an extra share in profits.
8. Stability of sales- An established business which has a growing market and high sales
turnover, the company is in position to meet fixed commitments. Interest on debentures
has to be paid regardless of profit. Therefore, when sales are high, thereby the profits are
high and company is in better position to meet such fixed commitments like interest on
debentures and dividends on preference shares. If company is having unstable sales, then
the company is not in position to meet fixed obligations. So, equity capital proves to be
safe in such cases.
9. Sizes of a company- Small size business firms capital structure generally consists of
loans from banks and retained profits. While on the other hand, big companies having
goodwill, stability and an established profit can easily go for issuance of shares and
debentures as well as loans and borrowings from financial institutions. The bigger the
size, the wider is total capitalization.
Components of Cost Of Capital
The term cost of capital refers to the maximum rate of return a firm must earn on its investment
so that the market value of companys equity shares does not fall.
The individual cost of each source of financing is called component of cost of capital. The
component of cost of capital is also known as the specific cost of capital which includes the
individual cost of debt, preference shares, ordinary shares and retained earnings. Such
components of cost of capital have been presented below
A. Cost of Debt
* Cost of perpetual or irredeemable debt
* Cost of non-perpetual or redeemable debt
* Debt issued at par
* Debt issued at premium or discount
B. Cost Of Preference Share
* Cost of perpetual preference Share
* Cost of redeemable preference Share
C. Cost of ordinary/equity shares or common stock
D. Cost of retained earnings.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Accounting and BookkeepingDokumen37 halamanAccounting and BookkeepingtekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Transitions: Set A Transition For An Individual or Group of SlidesDokumen2 halamanSlide Transitions: Set A Transition For An Individual or Group of SlidestekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Equation (A L + SE) Accounting Cycle Accounting ConceptsDokumen23 halamanAccounting Equation (A L + SE) Accounting Cycle Accounting ConceptstekleyBelum ada peringkat
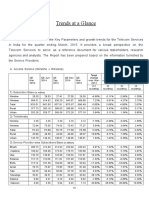
- Trends at A Glance: A. Access Service (Wireline + Wireless)Dokumen4 halamanTrends at A Glance: A. Access Service (Wireline + Wireless)tekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Sources of FinanceDokumen16 halamanSources of FinancetekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Charging Section of CSTDokumen13 halamanCharging Section of CSTtekleyBelum ada peringkat
- MSAccess Database Management SystemDokumen13 halamanMSAccess Database Management SystemtekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Air PollutionDokumen3 halamanAir PollutiontekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Edit Data: Access 2007 Databases Hold The Actual Data Records Inside Tables. You Can Add, Edit, and DeleteDokumen10 halamanEdit Data: Access 2007 Databases Hold The Actual Data Records Inside Tables. You Can Add, Edit, and DeletetekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of BrandingDokumen7 halamanDefinition of BrandingtekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Psychoanalytic TheoryDokumen10 halamanPsychoanalytic TheorytekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Marketing FunctionsDokumen7 halamanModern Marketing FunctionstekleyBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Ati - Atihan Term PlanDokumen9 halamanAti - Atihan Term PlanKay VirreyBelum ada peringkat
- Running Wild Lyrics: Album: "Demo" (1981)Dokumen6 halamanRunning Wild Lyrics: Album: "Demo" (1981)Czink TiberiuBelum ada peringkat
- XZNMDokumen26 halamanXZNMKinza ZebBelum ada peringkat
- Cartographie Startups Françaises - RHDokumen2 halamanCartographie Startups Françaises - RHSandraBelum ada peringkat
- 12.2 ModulesDokumen7 halaman12.2 ModulesKrishna KiranBelum ada peringkat
- Prayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriDokumen1 halamanPrayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriJulian ChackoBelum ada peringkat
- General Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionDokumen15 halamanGeneral Nursing Council of Zambia: Summary of Results For Each School December 2019 Qualifying Examinations SessionAndrew LukupwaBelum ada peringkat
- Options TraderDokumen2 halamanOptions TraderSoumava PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Lectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDokumen10 halamanLectio Decima Septima: de Ablativo AbsoluteDomina Nostra FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- (Mr. Nigel West, Oleg Tsarev) TRIPLEX Secrets Fro (B-Ok - Xyz)Dokumen377 halaman(Mr. Nigel West, Oleg Tsarev) TRIPLEX Secrets Fro (B-Ok - Xyz)conbeBelum ada peringkat
- Climate Change and Mitigation Programs in Davao CityDokumen64 halamanClimate Change and Mitigation Programs in Davao CityChona BurgosBelum ada peringkat
- Henry IV Part 1 Study GuideDokumen21 halamanHenry IV Part 1 Study GuideawtshfhdBelum ada peringkat
- Things Fall ApartDokumen4 halamanThings Fall ApartJack ConnollyBelum ada peringkat
- WN On LTC Rules 2023 SBDokumen4 halamanWN On LTC Rules 2023 SBpankajpandey1Belum ada peringkat
- Linking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationDokumen2 halamanLinking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationAlexa GandioncoBelum ada peringkat
- Top Notch 1 Unit 9 AssessmentDokumen6 halamanTop Notch 1 Unit 9 AssessmentMa Camila Ramírez50% (6)
- Implementation of Brigada EskwelaDokumen9 halamanImplementation of Brigada EskwelaJerel John Calanao90% (10)
- Specific Relief Act, 1963Dokumen23 halamanSpecific Relief Act, 1963Saahiel Sharrma0% (1)
- Achieving Rapid Internationalization of Sub Saharan Africa - 2020 - Journal of BDokumen11 halamanAchieving Rapid Internationalization of Sub Saharan Africa - 2020 - Journal of BErnaBelum ada peringkat
- Merger and Acquisition Review 2012Dokumen2 halamanMerger and Acquisition Review 2012Putri Rizky DwisumartiBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ADokumen7 halaman10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ANico FalzoneBelum ada peringkat
- Executive Summary: College of EngineeringDokumen17 halamanExecutive Summary: College of Engineeringjoel c. herreraBelum ada peringkat
- About Debenhams Company - Google SearchDokumen1 halamanAbout Debenhams Company - Google SearchPratyush AnuragBelum ada peringkat
- 13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDokumen1 halaman13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDove LogahBelum ada peringkat
- Final Report Class V - SLAS 15-16 PDFDokumen87 halamanFinal Report Class V - SLAS 15-16 PDFbhairav ghimireBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Engineering Project TopicsDokumen5 halamanComputer Engineering Project Topicskelvin carterBelum ada peringkat
- Breterg RSGR: Prohibition Against CarnalityDokumen5 halamanBreterg RSGR: Prohibition Against CarnalityemasokBelum ada peringkat
- Romanian Architectural Wooden Cultural Heritage - TheDokumen6 halamanRomanian Architectural Wooden Cultural Heritage - ThewoodcultherBelum ada peringkat
- Vayutel Case StudyDokumen10 halamanVayutel Case StudyRenault RoorkeeBelum ada peringkat
- Agile Scrum MCQDokumen6 halamanAgile Scrum MCQHarshith InjamBelum ada peringkat