Instrumentation Lab 07
Diunggah oleh
Fakhar AbbasHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Instrumentation Lab 07
Diunggah oleh
Fakhar AbbasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF COMPUTER AND EMERGING SCIENCES, ISLAMABAD
Prepared by: Engr.Fakhar Abbas, Version: 2.0
Last Edited by: Engr. Fakhar Abbss, 20
th
October , 14
Verified by: Dr. Ata Ul Aziz Ikram Updated: Fall 2014
Instrumentation and Measurement
(EL-220)
LABORATORY MANUAL
Engr. Fakhar Abbas
Introduction to Operational Amplifier LM 741
(LAB # 07)
Student Name: ______________________________________________
Roll No: ________________ Section: ____
Date performed: _____________, 2014
Manual Submission Date: _____________, 2014
MARKS AWARDED: ________ / 100
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 2 of 15
Lab # 07: Introduction to Operational Amplifier LM 741
Learning Objectives:
1. To understand principle, working and applications of OP-Amps.
2. Implement Op-Amp as Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifier on Bread Board as well as on
MultiSim
3. Implement Op-Amp as Summing and Difference Amplifiers on Bread Board as well as on
MultiSim
4. Implement Instrumentation Amplifier on Bread Board as well as on MultiSim
Equipment Required:
1. Digital Multimeter (DMM)
2. Breadboard
3. LM 741 ICs
4. DC Power Supply
5. Function Generator
6. Oscilloscope and Probes
7. Resistors (as required)
8. Connecting Wires
Introduction:
OP- AMP Basics:-
The Pin diagram of LM 741 is shown as
Operational amplifiers are convenient building blocks
that can be used to build amplifiers, filters, and even an
analogue computer. Op-amps are integrated circuits
composed of many transistors & resistors such that the
resulting circuit follows a certain set of rules.
The most common type of op-amp is the voltage
feedback type and that's what we'll use
The schematic representation of an op-amp is shown above.
There are two input pins (non-inverting and inverting), an output pin, and two power pins. The
ideal Op-Amp has infinite gain. It amplifies the voltage difference between the two inputs and that
voltage appears at the output. Without feedback this op-amp would act like a comparator (i.e.
when the non-inverting input is at a higher voltage than the inverting Input the output will be high;
when the inputs are reversed the output will be low).
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 3 of 15
Two rules will let you figure out what most simple op-amp circuits do:
1. No current flows into the input pins (i.e. infinite input impedance)
2. The output voltage will adjust to try and bring the input pins to the same voltage (this rule is
Valid for the circuits shown below)
Inverting Amplifier:-
The inverting Op-Amp is shown as, the output
voltage
= - (R2/R1)
and Voltage Gain
= -R2/R1
Take R1= 1 K and R2 = 5K, +Vcc= 12V and
Vcc = -12V, Generate a sinusoidal signal of
frequency 1 KHz and 1V (peak to peak) on
Oscilloscope.
a) Measurements:-
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Calculate Voltage Gain= ________________
Measured Voltage Gain = ___________________
Compare the measured and calculated values? Why does measured value deviate from calculated
value?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
b) Now replace R1=5K, see the results again, now compare calculated and measured values
again?
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Calculate Voltage Gain= ________________
Measured Voltage Gain = ___________________
Conclusion:-
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 4 of 15
c) Software Part: - MultiSim Implementation of Inverting Amplifier
Implement the inverting amplifier circuit in MultiSim, paste snapshot of schematic diagram as
well as oscilloscope output. Oscilloscope must show two waveforms, also use Measurement
Probes for verification of voltages/currents in schematic diagram.
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 5 of 15
Non-Inverting Amplifier:-
The non-inverting Op-Amp is shown as, the output
voltage
= (1+R2/R1)
and Voltage Gain
=
1+R2/R1
Take R1= 1 K and R2 = 5K, +Vcc= 12V and Vcc =
-12V, Generate a sinusoidal signal of frequency 1 KHz
and 1V (peak to peak) on Oscilloscope.
a) Measurements:-
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Calculate Voltage Gain= ________________
Measured Voltage Gain = ___________________
Compare the measured and calculated values? Why does measured value deviate from calculated
value?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
b) Now replace R1=5K, see the results again, now compare calculated and measured values
again?
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Calculate Voltage Gain= ________________
Measured Voltage Gain = ___________________
Conclusion:-
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 6 of 15
c) Software Part: - MultiSim Implementation of Non-Inverting Amplifier
Implement the non-inverting amplifier circuit in MultiSim, paste snapshot of schematic diagram as
well as oscilloscope output. Oscilloscope must show two waveforms, also use Measurement
Probes for verification of voltages/currents in schematic diagram.
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 7 of 15
Summing Amplifier:-
The Summing Op-Amp is shown as, the output voltage
= - [(R4/R1)
+(R4/R2)
+(R4/R3)
] and Voltage Gain
= - R4 [1/R1 + 1/R2 +1/R3] for
Take R1= 1 K , R2 = 2.2K, R3= 3K, and R4= 5K
+Vcc= 12V and Vcc = -12V, Generate a sinusoidal signal of
frequency 1 KHz and 1V (peak to peak) for all 3 input voltages
on Oscilloscope.
a) Measurements:-
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Calculate Voltage Gain= ________________
Measured Voltage Gain = ___________________
Compare the measured and calculated values?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 8 of 15
b) Software Part: - MultiSim Implementation of Summing Amplifier
Implement the summing amplifier circuit in MultiSim, paste snapshot of schematic diagram as
well as oscilloscope output. Oscilloscope must show two waveforms, also use Measurement
Probes for verification of voltages/currents in schematic diagram.
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 9 of 15
Difference Amplifier:-
The circuit for the difference amplifier is shown as:
a) Write down the equation of output voltage?
= ___________________________
b) Take R1= 1 K , R2 = 5K, +Vcc= 12V and
Vcc = -12V, Generate a sinusoidal signal of
frequency 1 KHz and 1V (peak to peak) for all
input voltages on Oscilloscope.
Calculate
= __________________
Measured
= _________________
Compare calculated and measured value?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 10 of 15
c) Software Part: - MultiSim Implementation of Difference Amplifier
Implement the difference amplifier circuit in MultiSim, paste snapshot of schematic diagram as
well as oscilloscope output. Oscilloscope must show two waveforms, also use Measurement
Probes for verification of voltages/currents in schematic diagram.
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 11 of 15
Instrumentation Amplifier (IA):-
Figure 7.6: Instrumentation Amplifier
Instrumentation amplifier is a kind of differential amplifier with additional input buffer stages. The
addition of input buffer stages makes it easy to match (impedance matching) the amplifier with the
preceding stage. Instrumentation is commonly used in industrial test and measurement application.
The instrumentation amplifier also has some useful features like low offset voltage, high CMRR
(Common mode rejection ratio), high input resistance, high gain etc. The circuit diagram of a
typical instrumentation amplifier using op-amp is shown figure 7.6.
In the circuit diagram, op-amps labeled A1 and A2 are the input buffers. Anyway the gain of these
buffer stages is not unity because of the presence of R
1
and R
Gain
. Op amp labeled A3 is wired as a
standard differential amplifier. R
3
connected from the output of A3 to its non- inverting input is
the feedback resistor. R
2
is the input resistor. The voltage gain of the instrumentation amplifier can
be expressed by using the equation below.
If its needed to vary the gain of the instrumentation amplifier then the resistance R
Gain
is replaced
by a suitable potentiometer.
The above Gain of Stage 1 can be derived as follows
Gain through Stage 2 = R3/R
2
, Differential input Resistance= 2R
2
+ R
3,
Common Mode Gain = 0,
CMRR = Very High, Gain= Unity Gain, Voltage = V
1
, V
2
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 12 of 15
Current through R
1
= (V
1
V
2
)/R
gain
Voltage across R
1
= R
1
(V
1
V
2
)/R
gain
Voltage across Nodes
)
So, Gain of Stage 1 will be
= (
)
Formula applied:
The voltage gain of the complete circuit
Where
is the voltage gain of stage 1 and
is the stage 2 gain.
The overall voltage gain can be controlled by adjustment of
. The common mode signal
attenuation for the instrumentation amplifier is that provided by the difference amplifier. This can
be maximized by making resistor R
3
adjustable. The dc output voltage level can be controlled if R
2
is
connected to an adjustable bias voltage of being directly grounded.
Task:
Design an instrumentation amplifier to have an overall voltage gain of 100. The input signal
amplitude is varied till the op-amps are saturated (LM 741 op-amps are to be used) and the supply
voltage is 12V.
Hint:-
You can assume:
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 13 of 15
Theoretical Calculation of Output Voltage and Gain
Procedure
Step1: Set up the circuit as shown in the figure.
Step2: Measure the output voltage obtained and note down the Gain
Step3: Compare with the theoretically obtained value.
Step4: Vary the input subsequently and note down the output voltage. Calculate the gain.
Tabulation
Input
Voltage
Output
Voltage
(Measured)
Gain
(Measured)
Output
Voltage
(Calculated)
Gain
(Calculated)
Difference
between
Calculated
and
Measured
Practically
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 14 of 15
Software Part: - MultiSim Implementation of Instrumentation Amplifier
Implement the Instrumentation amplifier circuit in MultiSim, paste snapshot of schematic diagram
as well as oscilloscope output. Oscilloscope must show two waveforms, also use Measurement
Probes for verification of voltages/currents i
Instrumentation &
Measurement Lab
National University
of Computer and Emerging Sciences
Islamabad
Roll No: __________
L
a
b
#
07
(EL220) Fall 2014
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 15 of 15
Student's feedback: Purpose of feedback is to know the strengths and weaknesses of the system
for future improvements. This feedback is for the 'current lab session'. Circle your choice:
[-3 = Extremely Poor, -2 = Very Poor, -1 = Poor, 0 = Average, 1 = Good, 2 = Very Good, 3 =
Excellent]:
The following table should describe your experience with:
S# Field Rating Describe your experience in words
1 Overall
Session
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
2 Lab Instructor
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
3 Lab Staff
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
4 Equipment
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
5 Atmosphere
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
Any other valuable feedback: ______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
M
A
R
K
S
A
W
A
R
D
E
D
A
t
t
i
t
u
d
e
N
e
a
t
n
e
s
s
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
n
e
s
s
o
f
r
e
s
u
l
t
s
I
n
i
t
i
a
t
i
v
e
L
a
b
T
a
s
k
#
1
L
a
b
T
a
s
k
#
2
L
a
b
T
a
s
k
#
3
L
a
b
T
a
s
k
#
4
L
a
b
T
a
s
k
#
5
T
O
T
A
L
TOTAL
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 20 100
EARNED
Student's Signature: _________________________________
Lab Instructor's Comments:________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Lab Instructor's Signature: _________________________
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Time and Work Problems: A. B. C. DDokumen2 halamanTime and Work Problems: A. B. C. DFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- A Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsDokumen5 halamanA Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDokumen2 halamanA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDokumen2 halamanA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasDokumen13 halamanPerformance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Multi-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysDokumen6 halamanMulti-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- On The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsDokumen5 halamanOn The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Group Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryDokumen5 halamanGroup Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Antenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsDokumen14 halamanAntenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Duality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemDokumen2 halamanDuality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Massive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignDokumen16 halamanMassive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
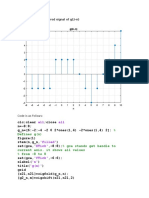
- Heaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffDokumen2 halamanHeaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Using Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueDokumen5 halamanUsing Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsDokumen8 halamanEngineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersDokumen15 halamanPerformance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Level 2 Analytical ReasonigDokumen30 halamanLevel 2 Analytical ReasonigFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Challan FormDokumen1 halamanChallan FormFakhar Abbas100% (1)
- Shifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IDokumen2 halamanShifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IFakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- SNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Dokumen1 halamanSNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Fakhar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- MC44817Dokumen8 halamanMC44817felipefreeBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 - Operational AmplifierDokumen90 halamanBab 3 - Operational AmplifierAryu MitaBelum ada peringkat
- Slup 094Dokumen16 halamanSlup 094L30N1Belum ada peringkat
- 4 / Digit, BCD Output, A/D Converter Features: Data Sheet August 28, 2007Dokumen15 halaman4 / Digit, BCD Output, A/D Converter Features: Data Sheet August 28, 2007Erasmo Franco SBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Switching Power Module Based On SKHI 10/17 DriverDokumen5 halamanDevelopment of Switching Power Module Based On SKHI 10/17 DriverLullaby summerBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3. Single Stage BJT Amplifiers: Names: 1. Buse YILBAŞ - 2376119 2. Elif CABRİ - 2374668 Section: 10Dokumen5 halamanExperiment 3. Single Stage BJT Amplifiers: Names: 1. Buse YILBAŞ - 2376119 2. Elif CABRİ - 2374668 Section: 10Buse YılbaşBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Discovery 2 Reference ManualDokumen58 halamanAnalog Discovery 2 Reference ManualAntonio Madueño LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Buffer Texas InstrumentsDokumen5 halamanBuffer Texas InstrumentsGabriel AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- 74AUP1T34: 1. General DescriptionDokumen22 halaman74AUP1T34: 1. General DescriptioncicBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifiers: What Is An Operational Amplifier?Dokumen10 halamanOperational Amplifiers: What Is An Operational Amplifier?Ali MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- EE 230 Lab Design Project ReportDokumen7 halamanEE 230 Lab Design Project Reportapi-490772627Belum ada peringkat
- Op AmpDokumen74 halamanOp AmpACSVBelum ada peringkat
- AD694-Circuito Transmisor de 4-20ma, 0-10VDokumen17 halamanAD694-Circuito Transmisor de 4-20ma, 0-10VNolan Alexis Rosales SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Silego SLG8LP465 PLL DatasheetDokumen27 halamanSilego SLG8LP465 PLL DatasheetewolwentaBelum ada peringkat
- Increase Op Amp Output With Discrete BufferDokumen2 halamanIncrease Op Amp Output With Discrete BuffertomritchBelum ada peringkat
- vm5n MeDokumen74 halamanvm5n MeGajanan Patil.Belum ada peringkat
- 74HC540 74HCT540: 1. General DescriptionDokumen17 halaman74HC540 74HCT540: 1. General DescriptionMohamed AlsapaghBelum ada peringkat
- TPS65150 Low Input Voltage, Compact LCD Bias IC With VCOM BufferDokumen48 halamanTPS65150 Low Input Voltage, Compact LCD Bias IC With VCOM BufferNurudeen KaikaiBelum ada peringkat
- OverdriveDokumen2 halamanOverdrivetransilvanpopBelum ada peringkat
- Flex PDFDokumen30 halamanFlex PDFRolando d'HellemmesBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 03Dokumen15 halamanLab 03Zekeri ZekkerriyyaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Architecture I: Digital Design: CPU Registers Register Transfer and MicrooperationsDokumen46 halamanComputer Architecture I: Digital Design: CPU Registers Register Transfer and MicrooperationsSaumenRoyBelum ada peringkat
- HIGH Frequency and Low Out (Ut Impedance BufferDokumen4 halamanHIGH Frequency and Low Out (Ut Impedance BufferDeepak BishtBelum ada peringkat
- M XrutytDokumen12 halamanM XrutytDistribuidorIBoolPedregalDeSantoDomingo100% (1)
- EC8073 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS - 1 BY UmwDokumen95 halamanEC8073 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS - 1 BY UmwMaheswaran UmaiyorupaganBelum ada peringkat
- Batch Weighing Machine: A Report OnDokumen20 halamanBatch Weighing Machine: A Report Onanshit gargBelum ada peringkat
- WAGO Power Supplies and WAGO System Modules 60397415Dokumen48 halamanWAGO Power Supplies and WAGO System Modules 60397415teo2005Belum ada peringkat
- Support Information OnlyDokumen7 halamanSupport Information OnlytermmmBelum ada peringkat
- Alpine mrv-f345 SMDokumen39 halamanAlpine mrv-f345 SMCarlos MunozBelum ada peringkat
- KLIPSCH Computer Speaker Service ManualDokumen21 halamanKLIPSCH Computer Speaker Service ManualEric CreechBelum ada peringkat