Infections in Pregnancy
Diunggah oleh
KathleenZunigaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Infections in Pregnancy
Diunggah oleh
KathleenZunigaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INFECTIONS IN
PREGNANCY
IRMA A. LEE, MD, MHPEd
October 3, 2011
Goals in pregnancy
! Reduce risk of congenital structural
abnormalities/deformities
! Optimize health care to minimize
effects of vertical transmission
! Avoidance of horizontal transmission to
health care providers
! Prevention
! T- oxoplasma
! O- thers (Varicella zoster virus, Hepatitis,
Parvovirus, HIV
Group B Streptococcus)
! R-ubella
! C-ytomegalo virus
! H-erpes virus
TOXOPLASMOSIS
! Acute toxoplasmosis during pregnancy is
rare
! Acquired through ingestion of encysted
organisms in raw or undercooked
meat or through contact with infected
cat feces or contaminated soil
! Overall risk of having affected child
! 2% - 1
st
trimester
! 10% - 28 weeks
! 4% - at term
DIAGNOSIS
! Maternal Signs/Symptoms
! Non-tender posterior cervical adenopathy
and flu-like symptoms
! Serologic Test for Immunoglobulin G
and M antibodies
! IgG appears 1-2 weeks of infection and
peaks between 6-8 weeks
! IgM appears within 1
st
week of infection
then declines over several months
and may persist for years
DIAGNOSIS
! PCR testing of amniotic fluid
most accurate method to test for fetal
infection
done on 2
nd
trimester or 4 weeks after
an acute maternal infection
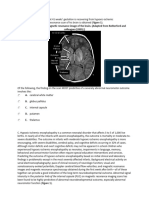
CONGENITAL
TOXOPLASMOSIS
! Sonographic abnormalities:
- Ventricular dilation (75%)
- Intracranial calcifications (18%)
- Increased placental thickness (32%)
- Hepatosplenomegaly (14%)
- Fetal ascites (15%)
- Pericardial or pleural effusions
- Microcephaly (5%)
CONGENITAL
TOXOPLASMOSIS
! At birth- maculopapular rash,
hepatosplenomegaly, seizures,
convulsions
! Blindness, deafness, mental retardation
TREATMENT
! Spiramycin (3-4 g/day)
- concentrates in the placenta
- given once maternal infection is confirmed
until delivery
! Pyrimethamine (25-100mg PO QID) and
Sulfadiazine (1-1.5g PO QID) and
Folinic acid 10-25mcg
- given once fetal infection is confirmed
- both are folic acid antagonists and cross the
placenta and penetrate the fetal brain and
cerebrospinal fluid
RUBELLA
! A mild viral illness with 30% of mothers
being asymptomatic or with a mild 3-
day rash with potential auricular
adenopathy
! Transmission: Airborne
! Diagnosis: Serologic testing of IgM or IgG
antibody titer which becomes positive
4 weeks after exposure
CONGENITAL RUBELLA
! Risk of major fetal damage varies with the
time of maternal infection:
! 80-90%- first 3 months
! 10%- 4
th
month
! 6%- 5
th
month
! no risk thereafter
! congenital heart (patent ductus arteriosus)
cataract, deafness
microcephaly
mental retardation
PREVENTION
! MMR - children 12-15 months of age and
at school age
- non- pregnant women and
women at reproductive age
group
! No treatment
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS
! Most common cause of viral intrauterine
infection affecting 0.5-2.5% of all
neonates
! Infection can occur in-utero, intrapartum and
through breastmilk
! Transmission: Contact with body fluids or
sexual contact
! 40% of pregnant women with primary
infection! congenital CMV
! 1-2% of newborns are CMV infected from
primary maternal CMV or reactivation of
prior infection
CONGENITAL CMV
! 85-90% of infected are asymptomatic at
birth
! 5-10% unilateral/bilateral hearing
impairment
! Blueberry muffin baby
! Other symptoms/ signs:
! Jaundice, thrombocytopenia,
hepatosplenomegaly, chorioretinitis, deafness,
microcephaly, mental retardation or death due
to DIC and sepsis
CMV INFECTION
! 4-8 weeks incubation period
! Viremia between 3-12 months
! Infected fetus shed virus up to 6 years
! Viral transmission via primary or
recurrent maternal infection
! Rate of transmission increases with
gestational age, highest at 3
rd
trimester
! Severity of disease is inversely proportional
to gestational age
! Neonatal CMV through breast milk does not
lead to visceral or neurological sequelae
Primary Maternal Infection
(CMV IgM + or PCR +)
30-40% fetal infection (CMV PCR + in AF)
90% Asymptomatic at birth 10% Symptomatic at birth
10-15% develop
abnormalities
85-90% develop
abnormalities
RECURRENT INFECTION
Occur with immunosuppression and during
pregnancy
Recurrent infection during pregnancy are often
asymptomatic and primarily caused by
reactivation of the endogenous virus or low
grade chronic infection or reinfection by a
different strain of CMV
Risk of vertical transmission is 0.5-2%
Risk of CMV congenital infection is only 0.5%
Neonates infected from recurrent infection has
<8% risk of hearing loss and chorioretinitis
DIAGNOSIS
Usually asymptomatic or with
mononucleosis- like or flu-like
symptoms
Presence of symptoms or abnormal
laboratories highly suggestive of
primary infection
CMV screening not routinely
recommended
IgM and IgG screening at 8-12 weeks
AFP PCR for CMV to detect in-utero
infection
MATERNAL CMV INFECTION
IgM is 75% sensitive and persist for 4-8
months. Repeat at 18-20 weeks and 30-32
weeks
IgG + and IgM - with high IgG avidity
index = no risk of primary infection
IgG CMV offers good protection in
recurrent infection with 0.5-1% of fetal
infection
NEONATAL CMV INFECTION
CMV virus in AF by PCR at 21 weeks at
6 weeks interval
Ultrasound findings:
- Ventriculomegaly
- Oligohydramnios
- Echogenic bowel
- Choroid plexus cyst
- Pleural effusion
- Brain/liver calcifications
ROLE OF CMV SPECIFIC
HYPERIMMUNE GLOBULIN
For mothers with primary CMV ! to
reduce maternal systemic or placental viral
loads
Reduce placental and fetal inflammation in
infected fetuses ! increase fetal blood
flow with enhanced fetal nutrition and
oxygenation
PREVENTION
Hygiene avoid direct contact with
children, frequent hand washing, glove
use
Live-attenuated CMV vaccine
Glycoprotein B construct vaccine
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS
! Recurrent STD caused by
! HSV-1 90% oral
10% genital
! HSV-2 10% oral
90% genital
! Ulceration in genitalia with severe local pain,
dysuria, sacral paresthesia, tender inguinal
lymph nodes, fever, malaise
PRIMARY FIRST EPISODE
HSV confirmed in a person without
prior HSV-1 or HSV-2 antibodies
2-4% of IgG negative women
seroconvert (acquire) to HSV-1 or
HSV-2 during pregnancy
No fetal consequences unless
convert shortly before labor
and delivery
NON-PRIMARY FIRST EPISODE
HSV-2 confirmed with prior findings of
HSV-1 antibodies or vice-versa
1.5-2% of HSV-1 IgG + women
seroconvert to HSV-2
Risk of conversion from HSV-2 IgG +
to HSV-1 + <1%
Symptoms milder
RECURRENT GENITAL
HERPES
Caused by reactivation of latent HSV usually
HSV-2
20-30% of pregnant women are IgG + for
HSV-2 with intermittent shedding from
vaginal mucosa
Virions travel from the skin or mucosa to the
sensory dorsal root ganglion where latency is
established. Viral replication ! recurrent
clinical outbreaks
Trauma, UV radiation, extreme temperature,
stress, hormonal fluctuations, immuno-
suppression
RISK OF FETAL
TRANSMISSION
Maternal-fetal transmission of HSV via
contact with infected genital secretions
40-50% neonatal HSV infection if delivery
occurs during primary infection
0-3% neonatal HSV-infection occurs during
recurrent infection
Sites of intrapartum viral entry are the fetal
eyes,nasopharynx or break in the skin
NEONATAL HSV INFECTION
First episode primary infection !
microcephaly, ventriculomegaly,
spasticity, echogenic bowel,
hepatosplenomegaly, flexed
extremities
30% of infants die
40% neurogenic sequelae
DIAGNOSIS
History
Maternal signs and symptoms
HSV culture 48-72 hours at appearance of
lesions
Serologic testing
PCR assay of genital lesions
Tzanck smear multinucleated giant cells and
viral inclusions
PREVENTION
Avoid sexual contact with
infected individuals
Condoms
Suppression decreases recurrent
genital lesions at term, and viral
shedding
ANTIVIRAL DRUGS
Acyclovir (Zovirax) inhibits viral
thymidine kinase; crosses placenta
but safe
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) prodrug of
acyclovir; better absorption; longer
half-life; decrease shedding
Fanciclovir prodrug of Penciclovir;
no specific studies in pregnancy
MANAGEMENT
1. Primary HSV
Analgesia
Hygiene
Antiviral - Acyclovir 400 mg PO TID 7-14
days
Valacyclovir 1g PO 7-14 days
Suppression - Acyclovir 400mg PO BID
or
Valacyclovir 500mg PO OD at
36 weeks to delivery
MANAGEMENT
2. First episode within 6-12 weeks
of delivery
IV Acyclovir intrapartum to both
mother and neonate
Daily Acyclovir or Valacyclovir from 36
weeks until delivery
MANAGEMENT
3.Complicated CMV infection
! IV Acyclovir 5-10mg/kg /BW q 8 hours until improved
followed by oral antiviral drug x 10 days
4. Recurrent HSV
! Analgesia
! Hygiene
! Antiviral
! Suppression therapy
MODE OF DELIVERY
With active lesions at term ! CS
PPROM remote from term ! Expectant
Cesarean delivery should not be offered
solely for a history of HSV
VARICELLA-ZOSTER
! A double-stranded DNA Herpes virus
acquired in childhood
! Primary infection manifests as Varicella
(Chickenpox)
! Herpes Zoster (Shingles) is an eruption
from reactivation of latent HSV
infection of dorsal root ganglia
! Transmission: Direct contact and
respiratory droplet
DIAGNOSIS
Varicella Maculopapular vesicular
pruritic lesions
Herpes Zoster Painful lesions over
sensory nerve root
distributions
Laboratory diagnosis:
ELISA VZV IgG titer
Tissue culture
Tzanck smear
Direct fluorescent antibody test
Nucleic acid amplification test
MATERNAL PRIMARY
VARICELLA
Pneumonitis
Bacterial superinfection (cellulitis,
abscess formation)
CONGENITAL VARICELLA
SYNDROME
Occurs in 2% when mothers have the
infection <20 weeks
Varicella Embryopathy (cutaneous
scar, denuded skin, limb hypoplasia,
muscle atrophy, rudimentary digits,
microcephaly, intracranial calcification,
cortical atrophy, cataracts,
chorioretinitis, microphthalmia,
psychomotor retardation)
NEONATAL VZV INFECTION
Fetal exposure just before or during
delivery result in 25-50% of cases
Varicella-Zoster Immune globulin
to neonates whose mother developed
Varicella 5 days before to up to 2 days
post-delivery
TREATMENT
Supportive care
Acyclovir 500mg q 8 hours for
complicated varicella or immuno-
compromised
Varicella Zoster Immune globulin
up to 96 hours post exposure
PREVENTION
Varivax not recommended
to pregnant women
HEPATITIS A
! Caused by RNA virus transmitted by
fecal-oral route
! Average incubation period is 28 days with
symptoms lasting 2 to 6 months
! Children are usually asymptomatic in
contrast to adults who are always
symptomatic
! Prevalent in areas with poor sanitation
and closed living conditions
! Occurs in " 1 : 1,000 pregnancies
RISKS OF ACQUIRING HAV
! Travel to prevalent countries
! Homosexuals
! IV drug users
! Working with non-human primates
! Chronic liver disease
MANAGEMENT IN PREGNANCY
! Supportive
! No perinatal transmission
! Anti-HAV IgM- diagnostic
criterion for acute Hepatitis A
HEPATITIS B
! Most common form of viral hepatitis in
pregnancy
! Caused by DNA virus transmitted
parenterally and sexual contact
! Acute hepatitis occurs 1-2 : 1,000
pregnancies in U.S.
! Chronic carrier state occurs in 6-10 :
1,000 pregnancies
! Incubation period is 60 to 90 days
RISK FACTORS
! Perinatal transmission- highest of risk
chronic HBV infection
! Sexual contact
! IV drug users
! STDs
! Multiple sexual partners
! House contacts
! Mental institutions/ Prisons
! Acupuncture
! HBV infected patients at high risk of HIV and
HCV infections
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
! Incubation period depends on viral
exposure than laboratory changes
! Antigens
! S Surface - Infected if present > 6
months
Chronic HBV infection
! c - Core
! e Infectious
! Antibodies
! S Immune
! C covers window period, usually
precedes HBsAb conversion
Table 29.1 Interpretation of the Hepatitis B Panel
Test Results Interpretation Vertical Transmission
HBsAg Negative Susceptible 0%
Anti-HBc Negative
Anti-HBs Negative
HBsAg Negative Immune due to natural Infection 0%
Anti-HBc Positive
Anti-HBs Positive
HBsAg Negative Immune due to Hepatitis B vaccination 0%
Anti-HBc Negative
Anti-HBs Positive
HBsAg Positive Acutely Infected First trimester: 10%
Third trimester: 80-90%
HBeAg - : 10-20%
HBeAg + : 90%
Anti-HBc Positive
Anti-HBc IgM Positive
Anti-HBs Negative
HBsAg Positive Chronically Infected First trimester: 10%
Third trimester: 80-90%
HBeAg - : 10-20%
HBeAg + : 90%
Anti-HBc Positive
Anti-HBc IgM Negative
Anti-HBs Negative
HBsAg Negative Four Interpretations possible:
1. May be recovering from acute HBV infection
2. May be distantly immune and test is not sensitive enough to
detect very low level of anti-HBs in serum
3. May be susceptible with false positive anti-HBc
4. May be an undetectable level of HBsAg present in the serum
and the person is actually a carrier
0%
Anti-HBc Positive
Anti-HBs Negative
DIAGNOSIS
! Hepatitis B panel
! Screen for HBV by HBsAg
! HBV DNA by quantitative PCR
! Liver Biopsy
PREGNANCY CONSIDERATIONS
! Vertical transmission is high when
laboratory is as follows:
HBsAg + 10-20%
HBsAg + HBeAg+ 80-90%
! Vertical transmission is trimester related
! 10%- first trimester
! 80-90%- third trimester
! Only 10% transmission is transplacental,
hematogenous or thru breastfeeding
MAIN INTERVENTION
THERAPIES
! HBV vaccine- 3 IM injections over 6 months
period
! 95% seroconversion and immune rate safe in
pregnancy and neonate
1. Recombivax within 12 hours of delivery
with:
! Maternal HBeAg + = 5 or
! Maternal HBeAg = 2.5 give as ffs:
" 20 years old = 10 mg (1mL)
" 11-19 years old = 5 mg (0.5mL)
" < 11 years old = 2.5 mg (0.25 mL)
MAIN INTERVENTION
THERAPIES
2. Engerix B within 12 hours of delivery
with:
! Maternal HBeAg + = 10 or
! Maternal HBeAg = 10
" > 20 yrs old = 20 mg (1mL)
" 11-19 yrs old = 20 mg (1mL)
" < 11 yrs old = 10 mg (0.5 mL)
! HBIg
! Adult 0.5 mL/kg IM
! Neonate 0.13 mL/kg
ACUTE HEPATITIS B IN
PREGNANCY
! Document conversion of HBsAg to +
! Outpatient supportive therapy
! If with co-morbidities like bilirubin >
15mg/dL
! Vit. K 10mg/IM q8 hrs x 3 doses
! Consider Interferon
EXPOSURE TO HB DURING
PREGNANCY
! If HBsAg and HBsAb HBIg
and HB vaccine (prevents >5% of
transmission)
! HBIg must be given within 14 days of
exposure
VERTICAL TRANSMISSION
PREVENTION
! All newborns of mothers HBsAg +
should receive HBIg and
HB vaccine within 12hrs of birth
! 95% prevention of neonatal HBV
HEPATITIS C
! Caused by RNA virus acquired via
infected blood, sexual contact or
mother-to-infant (vertical
transmission)
! Incubation period 30-60days
! Complications: Cirrhosis and
Hepatocellular carcinoma
DEFINITION OF TYPES OF
HCV INFECTION
! HCV: HCVAb +
! Chronic HCV: HCVAb + and
HCV RNA +
! Chronic Active HCV: HCVAb +
and HCV RNA + and LFTs
RISK FACTORS FOR HCV
INFECTION
! BT or exposure to blood products
! IV drug users
! Multiple sexually transmitted diseases
! HIV Infection
! Multiple sexual partners
! History of body piercing/ tattooing
! Organ transplant - Berone 1992
! Unexplained elevated transaminases
! Patient or staff involved in chronic dialysis
programs
! Participant in in-vitro fertilization program
from anonymous donors
MOTHER TO INFANT
TRANSMISSION
! HCV RNA + for 2 occasions 3-4
months apart, when infant is 2
mos old OR
! Anti-HCV detected after the infant is
18mos old
! Co-infection with HIV and high
maternal viral load associated
with high transmission risk
PREVENTION
! Avoid risk factors
! Prevent complications by avoiding
alcohol and hepatotoxic
medicine and foods
EFFECT OF PREGNANCY ON
HEPATITIS C
! Pregnancy does not affect the clinical
course of acute or chronic
Hepatitis C
! Linear increase in HCV viremia
throughout pregnancy
EFFECT OF HEPATITIS C ON
PREGNANCY
! Chronic Hepatitis C associated
with preterm delivery and
IUGR
! Long term effects cirrhosis, cancer,
death
THERAPY
! No approved treatment of HCV
infection during pregnancy
! No HCV vaccine or Ig
! Pegylated Interferon ! and ribavirin
eradicate virus >50% in
non- pregnant women
HEPATITIS D
! Caused by RNA virus that depends
upon co-infection with hepatitis B
for replication
! Epidemiology similar to Hepatitis A
! Perinatal transmission is possible if
Hep B occur simultaneously
HEPATITIS E
! Caused by RNA virus
! Similar to Hep A
! Endemic in developing countries
! Associated with high maternal mortality
! No perinatal transmission
HUMAN
IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS
! Infects T lymphocytes that express
the CD4 antigen! Progressive
loss and impairment of cellular
immunity ! Opportunistic
infection and malignancies
RISK OF PERINATAL
TRANSMISSIONS
! Closely related to viral load at the
time of delivery
! Low CD 4 and T- lymphocyte count
! Lack of antiretroviral therapy
! Biological phenotype of the virus
RISK OF PERINATAL
TRANSMISSIONS
! Substance abuse
! Rupture of membranes > 4 hours
! Hepatitis C Co-infection
! STIs
! Preterm delivery
! Chorioamnionitis
PERINATAL EFFECTS
! IUGR
! Stillbirth
! Low Apgar Score
GOAL OF HIV TREATMENT
IN PREGNANCY
! Prevent vertical transmission by
reducing maternal viral load to
< 1000 copies/ml or below the limit
of detection of the assay
PREGNANCY MANAGEMENT
! Screening with ELISA ! Western blot
! Multidisciplinary approach
! Counselling
! Antiretroviral combination-
Azidothymidine; Zidovudine
! Continue monitoring CD 4 count and
HIV-RNA levels
! Women with VL >1,000 copies/ml benefit
from cesarean delivery
PARVOVIRUS
! Human parvovirus B19 is a single stranded
DNA virus
! 3-4 % incidence in pregnant women
! Highest infection rate with school teachers,
day care workers or women with
school-age children
! Transmitted by respiratory droplets
MATERNAL INFECTION
! Usually asymptomatic
! May have flu-like symptoms,
arthralgias, adenopathy
NEONATAL INFECTION
! 25-33 % of fetus of mothers with
primary Parvovirus B19 become
infected by vertical transmission
! 90% no sequelae
! 10% fetal anemia! myocarditis!
fetal hydrops
DIAGNOSIS
! IgM or Ig G seroconversion
! PCR
! Electron microscopy
! MS AFP
! Fetal Ultrasound
GROUP B STREPTOCOCCUS
INFECTION
! Streptococcus agalactiae or Lancefield
group B streptococcus (GBS) is bacterial
infection involving the pregnant woman
and her newborn
! Asymptomatic GBS anovaginal colonization
in preterm women is 20 %
! Major cause of postpartum infection and
most common cause of neonatal sepsis
NEONATAL INFECTION DUE
TO GBS
! Neonates acquire infection via vertical
transmission in-utero from maternal
genital tract or at delivery
! Early onset- illness in the newborn within
24 hours of life
! Late onset- occurs 3-4 weeks of age or
between 7 days to 3 months of age
NEONATAL SEQUELAE
! Sepsis
! Pneumonia
! Meningitis
! Focal infection such as osteomyelitis,
septic arthritis
RISK FACTORS
! Prolonged rupture of membranes > 18
hours
! Preterm delivery
! Temperature > 38 C
! Maternal chorioamnionitis
! Young maternal age
! African-american race
! Hispanic ehtnicity
! GBS bacteriuria in pregnancy
DIAGNOSIS
! Anovaginal swab at 35- 37 weeks !
culture
! PCR
TREATMENT
! Penicillin 5 M units/IV then 2.5 M units/IV
q 4 hours until delivery
! Ampicillin 2 g/IV then 1 g/IV q 4 hours
until delivery
! For Penicillin-allergic:
! Cefazolin 2 g/IV then 1 g/IV q 8 hours until
delivery
! Clindamycin 900 mg/IV q 8 hours until
delivery
! Erythromycin 500 mg/IV q 6 hours until
delivery
THANK YOU!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- ErrorlogDokumen1 halamanErrorlogKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections A Practical Guide 2nd EditionDokumen72 halamanPrevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections A Practical Guide 2nd EditionAndreah YoungBelum ada peringkat
- "500 Days in Downtown L.A." Walking TourDokumen6 halaman"500 Days in Downtown L.A." Walking TourKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- First Aid For The Obstetrics & Gynecology ClerkshipDokumen253 halamanFirst Aid For The Obstetrics & Gynecology ClerkshipSimona Prodanoiu100% (17)
- ArtsDistrict Booklet LR PDFDokumen12 halamanArtsDistrict Booklet LR PDFKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- MLC Interns Review 2011 - Dra ColomaDokumen251 halamanMLC Interns Review 2011 - Dra ColomaKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Guidelines Hand Hygiene in Health CareDokumen270 halamanWHO Guidelines Hand Hygiene in Health CareÐr Salma100% (1)
- Dehydration Oral Rehydration Guideline PDFDokumen2 halamanDehydration Oral Rehydration Guideline PDFKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Management of Cervical MyelopathyDokumen16 halamanSurgical Management of Cervical MyelopathykenthepaBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Mangla Sood.35663752 PDFDokumen4 halaman14 Mangla Sood.35663752 PDFKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- OB Intern's Review - Dra LeeDokumen214 halamanOB Intern's Review - Dra LeeKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Mod III - Cardio-Neph Shifting Samplex '11-12Dokumen19 halamanMod III - Cardio-Neph Shifting Samplex '11-12KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Immune-Mediated Connective Tissue DiseasesDokumen68 halamanImmune-Mediated Connective Tissue DiseasesKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Diseases in Pregnancy 2011Dokumen4 halamanHeart Diseases in Pregnancy 2011KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- OB CT and RenalDokumen4 halamanOB CT and RenalKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy 2012Dokumen80 halamanThyroid Disorders in Pregnancy 2012KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic Sclerosis, Antiphospholipid SyndromeDokumen51 halamanConnective Tissue Disorders: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic Sclerosis, Antiphospholipid SyndromeKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes in PregnancyDokumen88 halamanDiabetes in PregnancyKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Disorders in Pregnancy 2012Dokumen4 halamanPulmonary Disorders in Pregnancy 2012KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Infections in PregnancyDokumen5 halamanInfections in PregnancyKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders - Dr. Navarro, 9-17-12 and 9-19-12Dokumen4 halamanMovement Disorders - Dr. Navarro, 9-17-12 and 9-19-12KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Revised CTD and RDDokumen68 halamanRevised CTD and RDKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Myasthenia Gravis - Dr. Lokin, Sept 3, 2012Dokumen4 halamanMyasthenia Gravis - Dr. Lokin, Sept 3, 2012KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive ObDokumen6 halamanHypertensive ObKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Other Myasthenic Syndromes - Dr. Lokin, Sept 5, 2012Dokumen3 halamanOther Myasthenic Syndromes - Dr. Lokin, Sept 5, 2012KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- NP - MyelofibrosisDokumen55 halamanNP - MyelofibrosisKathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Peripheral Neuropathy - Dra. David, 9-10-12 and 9-12-12Dokumen5 halamanPeripheral Neuropathy - Dra. David, 9-10-12 and 9-12-12KathleenZunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Bicycle Riding As A Cause For Erectile DysfunctionDokumen5 halamanBicycle Riding As A Cause For Erectile DysfunctionKat ZunigsBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- POGI Infection in Pregnancy 2022Dokumen93 halamanPOGI Infection in Pregnancy 2022SDM RSTIBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic-Guideline-for-Neonatal SepsisDokumen13 halamanAntibiotic-Guideline-for-Neonatal SepsisNada AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Tog 12091Dokumen4 halamanTog 12091princessmeleana6499Belum ada peringkat
- Congenital SyphilisDokumen15 halamanCongenital SyphilisAlejandraSevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal SepsisDokumen87 halamanNeonatal Sepsisyhanne100% (129)
- Philhealth: Your Partner in HealthDokumen17 halamanPhilhealth: Your Partner in HealthElla Bint SaidBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatology Clinical Treatment Guidelines OTHER VERSIONDokumen94 halamanNeonatology Clinical Treatment Guidelines OTHER VERSIONAlexandraelsaBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Pneumonia in Developing Countries: Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal EdDokumen10 halamanNeonatal Pneumonia in Developing Countries: Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal EdadiBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Sepsis in Low Birth Weight Infants in Dr. Soetomo General HospitalDokumen4 halamanNeonatal Sepsis in Low Birth Weight Infants in Dr. Soetomo General HospitalMelati Nurul UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Sepsis: Progress Towards Improved Outcomes: Andi L. Shane, Barbara J. StollDokumen9 halamanNeonatal Sepsis: Progress Towards Improved Outcomes: Andi L. Shane, Barbara J. StollMarco Antonio Mendoza OjedaBelum ada peringkat
- 2024.sifilis CongenitaDokumen12 halaman2024.sifilis CongenitaWILLIAM ROSALES CLAUDIOBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study: Neonatal PneumoniaDokumen47 halamanCase Study: Neonatal PneumoniaJay Villasoto100% (1)
- Neonatal SepsisDokumen17 halamanNeonatal SepsisDhilla Feroh Kesuma TBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Sepsis: Prof DR Saima BatoolDokumen31 halamanNeonatal Sepsis: Prof DR Saima BatoolSAIMA BATOOLBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 109 Lec MidtermsDokumen8 halamanNCM 109 Lec MidtermsAngel Kim MalabananBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal InfectionsDokumen19 halamanNeonatal InfectionsA B Siddique RiponBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperbilirubinemia ManagementDokumen37 halamanHyperbilirubinemia ManagementkaerickaericBelum ada peringkat
- Ajp - 180544 EosDokumen9 halamanAjp - 180544 EosJeeBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Management of Pregnancy ComplicationsDokumen19 halamanClinical Management of Pregnancy ComplicationsooiziungieBelum ada peringkat
- Mrcog 2 Strat OgDokumen49 halamanMrcog 2 Strat OgHasan Dahamsheh100% (5)
- NeoPREP 2011Dokumen342 halamanNeoPREP 2011johnbarrow641Belum ada peringkat
- COVID-19 - Labor, Delivery, and Postpartum Issues and Care - UpToDateDokumen25 halamanCOVID-19 - Labor, Delivery, and Postpartum Issues and Care - UpToDateCamilo HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 06 Reducing Perinatal & Neonatal MortalityDokumen68 halaman06 Reducing Perinatal & Neonatal MortalityrositaBelum ada peringkat
- Guide Therapeutic Neonatal InfectionDokumen15 halamanGuide Therapeutic Neonatal InfectiongaasheBelum ada peringkat
- Sepsis Neonatorum PDFDokumen2 halamanSepsis Neonatorum PDFAri Julian SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Mid TermDokumen17 halamanMid TermTamoghna NaskarBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal InfectionDokumen56 halamanNeonatal InfectionAgust SalimBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal InfectionDokumen9 halamanNeonatal InfectionnishaBelum ada peringkat
- Genus CitrobacterDokumen8 halamanGenus CitrobacterAl Jay Mejos100% (1)
- Review of Neonatal Sepsis Causes, Risk Factors and ManagementDokumen9 halamanReview of Neonatal Sepsis Causes, Risk Factors and ManagementTiwi QiraBelum ada peringkat