Principle of Transformers
Diunggah oleh
Izzat AzmanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Principle of Transformers
Diunggah oleh
Izzat AzmanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
JJ102 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
CASE STUDY 1
MUHAMAD FAIZ BIN RAJAB 01DKM13F1034
MUHAMMAD SYAHRIN BIN AZMI 01DKM13F1032
MUHAMMAD ZULKIFLI BIN SHAFIEE 01DKM13F1028
Principle of Transformers
A transformer is a device that changes (transforms) and alternating potential
difference (voltage) from one value to another value be it smaller or greater
using the principle of electromagnetic induction.
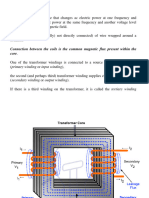
A transformer consists of a soft iron coil with two coils wound around it which
are not connected to one another. These coils can be wound either on
separate limbs of the iron core or be arranged on top of each other.
The coil to which the alternating voltage is supplied is called the primary coil or
primary winding. When
an alternating potential difference is supplied the resulting alternating current
in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic field around it. This changing
field induces an alternating current in the secondary coil. The size of the
induced voltage resulting from the induced current in the secondary coil
depends on the number of turns in the secondary coil.
The relationship between the voltage and the number of turns in each coil is
given by:
If the primary winding is higher than the secondary winding, then
the current at the primary is higher than the current at secondary.
Automatically the primary voltage also higher compare to the
secondary voltage.
While if the secondary winding is higher than the primary winding,
the current at the secondary winding is higher than the current at
primary winding. This will ensure that the secondary voltage also
higher compare to the primary voltage.
Step-up Transformer
On a step-up transformer there are more turns on the secondary coil than the
primary coil. The induced voltage across the secondary coil is greater than the
applied voltage across the primary coil or in other words the voltage has been
stepped-up.
Step-down Transformer
A step down transformer has less turns on the secondary coil that the primary
coil. The induced voltage across the secondary coil is less the applied voltage
across the primary coil or in other words the voltage is stepped-down.
Transformers are very efficient. If it is assumed that a transformer is 100%
efficient (and this is a safe assumption as transformers may be up to 99%
efficient) then the power in the primary coil has to be equal to the power in
the secondary coil, as per the law of conservation of energy.
Power in primary coil = Power in secondary coil
Remember, power = potential difference x current
Thus,
Primary coil p.d. x primary coil current = Secondary coil p.d. x secondary coil
current
V
P
x I
P
= V
S
x I
S
So if the potential difference is stepped up by a transformer then the current is
stepped down by roughly the same ratio. In the case of the potential being
stepped down by the transformer then the current is stepped up by the same
ratio.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Principle of TransformersDokumen2 halamanPrinciple of Transformersismun nadhifahBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDari EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Principle of TransformersDokumen2 halamanPrinciple of TransformersJovit SamaniegoBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Basics and Transformer Principles of OperationDokumen14 halamanTransformer Basics and Transformer Principles of Operationengsamir296Belum ada peringkat
- Transformer BasicsDokumen10 halamanTransformer BasicsRaja DesinguBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Basics A Typical Voltage TraDokumen13 halamanTransformer Basics A Typical Voltage Trarotimi olalekan fataiBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Basics and Principles of OperationDokumen6 halamanTransformer Basics and Principles of Operationmkeen85Belum ada peringkat
- Transformer Basics: Register To Download Premium Content!Dokumen12 halamanTransformer Basics: Register To Download Premium Content!Venkatesh PeruthambiBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer BasicsDokumen14 halamanTransformer BasicsJohn Brix BalisterosBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Transformer?: Mutual InductionDokumen3 halamanWhat Is A Transformer?: Mutual InductionYaser QadeerBelum ada peringkat
- Working Principle of TransformerDokumen16 halamanWorking Principle of TransformerSunil100% (1)
- Assignment Be&e TransformerDokumen17 halamanAssignment Be&e TransformerAbbyBelum ada peringkat
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: TrasformersDokumen13 halamanFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Trasformersrambabu_09cp037Belum ada peringkat
- Me 2Dokumen7 halamanMe 2shayma ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To TransformersDokumen186 halamanIntroduction To TransformerscaplukBelum ada peringkat
- Single Phase T'MerDokumen4 halamanSingle Phase T'Merjay shahBelum ada peringkat
- InductorDokumen9 halamanInductorhabtemariam mollaBelum ada peringkat
- HHHHHHHHHDokumen21 halamanHHHHHHHHHjameswovelee7Belum ada peringkat
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Panchmahal: Topic:-Transformer Prepared By: - Guided By: - Mr.v. D. PadoleDokumen15 halamanJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Panchmahal: Topic:-Transformer Prepared By: - Guided By: - Mr.v. D. PadoleArpit PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Investigatory Report 2023-24-3Dokumen21 halamanPhysics Investigatory Report 2023-24-3mohammedzuhairabdulkareemBelum ada peringkat
- EE352 Chapter #4 Ideal Transformers and Real Equivalent CircuitsDokumen31 halamanEE352 Chapter #4 Ideal Transformers and Real Equivalent CircuitsCan ARABACIBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power Transformer. Theory, ProtectionDokumen109 halamanElectrical Power Transformer. Theory, ProtectionAdeel ZafarBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Single Phase Transformers IdealDokumen13 halaman3 Single Phase Transformers Idealrjaymigrins30Belum ada peringkat
- Pysics InvestigatoryDokumen8 halamanPysics InvestigatoryAyush XI-ABelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen21 halamanReporthrishikesh anvekarBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSFORMERS LectureDokumen9 halamanTRANSFORMERS LectureDarylBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power Transformer - Definition and Types of TransformerDokumen6 halamanElectrical Power Transformer - Definition and Types of Transformersampath kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV TransformerDokumen31 halamanUnit IV TransformerParikshit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- EEE101 Ch8Dokumen22 halamanEEE101 Ch8SERHAT YILDIRIMBelum ada peringkat
- Mutual Induction ExperimentDokumen11 halamanMutual Induction ExperimentAnil Tandon71% (35)
- Group 4 TransformerDokumen43 halamanGroup 4 TransformerNelgine GepuitBelum ada peringkat
- SrabanDokumen10 halamanSrabanTenz WastonBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution Transformer Center-Tapped United States Split-Phase Grounded ConductorDokumen13 halamanDistribution Transformer Center-Tapped United States Split-Phase Grounded ConductorMani KapurBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of TransformerDokumen51 halamanBasics of TransformerNeil LachicaBelum ada peringkat
- Transformers: Electrical Energy Circuit Inductively Coupled Electrical Conductors CurrentDokumen16 halamanTransformers: Electrical Energy Circuit Inductively Coupled Electrical Conductors CurrenttalhawasimBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer:: Date:02-04-2019 Power Distribution Lab Assignment No:01Dokumen9 halamanTransformer:: Date:02-04-2019 Power Distribution Lab Assignment No:01Rasheed ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer 8405239 PowerpointDokumen13 halamanTransformer 8405239 PowerpointVijjawal GanorkarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen40 halamanChapter 5Ali AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- Ideal Transformer:: S P S PDokumen9 halamanIdeal Transformer:: S P S Ptitubd0% (1)
- Transformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen32 halamanTransformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaParvezKhanBelum ada peringkat
- TransformersDokumen24 halamanTransformersMonique ReidBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSFORMERSDokumen24 halamanTRANSFORMERStmmbonelaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machine & Control SystemsDokumen36 halamanElectrical Machine & Control SystemsHatem DheerBelum ada peringkat
- Eee118 Ch2 MidDokumen40 halamanEee118 Ch2 MidalareeqiBelum ada peringkat
- TransformersDokumen77 halamanTransformersAvik PoudelBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer: Component CoreDokumen4 halamanTransformer: Component CoreSameer SabirBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDokumen22 halamanBasic Electrical EngineeringLipi SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Transformers PDFDokumen23 halamanTransformers PDFVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra SwamyBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic InductionDokumen14 halamanElectromagnetic InductionHaziq KhanBelum ada peringkat
- University Physics Lab Report (UWI)Dokumen10 halamanUniversity Physics Lab Report (UWI)VanoiMariaStylesWilkinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Project On "Transformers"Dokumen17 halamanPhysics Project On "Transformers"Jaÿ Üx100% (1)
- Single Phase Transformer Construction and WorkingDokumen11 halamanSingle Phase Transformer Construction and Workingmanthan NaikBelum ada peringkat
- 325 04 TransformersDokumen31 halaman325 04 TransformersNurullah MertelBelum ada peringkat
- Physic Practical Project - TransformerDokumen18 halamanPhysic Practical Project - Transformerkrishnakantpsharma2342005Belum ada peringkat
- ContentDokumen12 halamanContentHarishBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer DetailsDokumen26 halamanTransformer DetailsMadhu Mathi ErBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10Dokumen6 halamanTransformer: Mahindra École Centrale EE101: Basic Electrical Engineering (Fall 2015) Experiment 10nirmalaBelum ada peringkat
- Sarthak PhysicsDokumen10 halamanSarthak PhysicsPriyanshu GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On TransformerDokumen80 halamanPresentation On TransformerGodlisten NyariBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 6 ReportDokumen27 halamanLab 6 ReportIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- SchaaassDokumen2 halamanSchaaassIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Front Page PDFDokumen1 halamanFront Page PDFIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1Dokumen6 halamanAssignment 1Nur AfiqahBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Analysis: Circuit Problems #2 Engr. 179 - Engineering Problem SolvingDokumen2 halamanTransient Analysis: Circuit Problems #2 Engr. 179 - Engineering Problem SolvingIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- EEE228 Chapter 1Dokumen25 halamanEEE228 Chapter 1Izzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- ReferencesDokumen35 halamanReferencesIzzat Azman100% (1)
- Quiz 2Dokumen4 halamanQuiz 2Izzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- JJ513 Engineering Design: Procedure of Bearing SelectionDokumen14 halamanJJ513 Engineering Design: Procedure of Bearing SelectionIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- JJ513 Engineering Design: Procedure of Bearing SelectionDokumen14 halamanJJ513 Engineering Design: Procedure of Bearing SelectionIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment T2-4: Lagging EfficiencyDokumen5 halamanExperiment T2-4: Lagging EfficiencyIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Application of GearDokumen3 halamanApplication of GearIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- JJ 618 Engineering Plant TechnologyDokumen1 halamanJJ 618 Engineering Plant TechnologyIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- CVDokumen1 halamanCVIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Questionnaire Topic: A Research On The Facilities in The Library of Ungku Omar PolytechnicDokumen4 halamanQuestionnaire Topic: A Research On The Facilities in The Library of Ungku Omar PolytechnicIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- OralDokumen1 halamanOralIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Muka Depan Lab Print SkaliDokumen2 halamanMuka Depan Lab Print SkaliIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Feedwater HeaterDokumen6 halamanFeedwater HeaterIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Plant EngDokumen4 halamanPlant EngIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline (DKM2A) BA201 DEC 2013Dokumen4 halamanCourse Outline (DKM2A) BA201 DEC 2013Izzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Front PageDokumen3 halamanFront PageIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Tool BitDokumen2 halamanTool BitIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Hello SkribDokumen1 halamanHello SkribIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- CopyrightsadDokumen1 halamanCopyrightsadIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cum Activezi Autocad 2014Dokumen1 halamanCum Activezi Autocad 2014Alexys100% (1)
- Gas Front Welding Report - 2Dokumen2 halamanGas Front Welding Report - 2Izzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Content: 1-2 Objective 3 Manufacturing Process 4-8 Conclusion 9 Appendix 10 Reference 11Dokumen1 halamanContent: 1-2 Objective 3 Manufacturing Process 4-8 Conclusion 9 Appendix 10 Reference 11Izzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Politeknik Premier Ungku Omar: Steam Dryness Fraction Lab ReportDokumen2 halamanPoliteknik Premier Ungku Omar: Steam Dryness Fraction Lab ReportIzzat Azman100% (1)
- Front PageDokumen3 halamanFront PageIzzat AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Radiation GeometryDokumen62 halamanSolar Radiation GeometrySai ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Richtekusainc Rt906950gb Datasheets 6616Dokumen15 halamanRichtekusainc Rt906950gb Datasheets 6616JayR VillaBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Lab 1Dokumen9 halamanMachine Lab 1مالك المجيديBelum ada peringkat
- 100-9 0Dokumen104 halaman100-9 0jhierryBelum ada peringkat
- Panasonic sd698s - RPHDokumen40 halamanPanasonic sd698s - RPHAnonymous 2iQ1B59100% (1)
- MT-1706 3-5/6 True-RMS Digital Multimeter: DC1000V20A-AC750V-60MOHM-BUZZDokumen19 halamanMT-1706 3-5/6 True-RMS Digital Multimeter: DC1000V20A-AC750V-60MOHM-BUZZKhalid FarhatBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2: Superposition Theorem: To Verify Current Flow and Voltage Drop Using Superposition TheoremDokumen10 halamanLab 2: Superposition Theorem: To Verify Current Flow and Voltage Drop Using Superposition TheoremDesmond GohBelum ada peringkat
- Braking Unit Yaskawa - CDBR - 4045BDokumen54 halamanBraking Unit Yaskawa - CDBR - 4045BAnoop KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary Side Synchronous Rectification Control: Implementation and SR Features For Flyback Tomáš TichýDokumen62 halamanSecondary Side Synchronous Rectification Control: Implementation and SR Features For Flyback Tomáš TichýLeonardo OrtizBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Engines 4Dokumen19 halamanHeat Engines 4member1000Belum ada peringkat
- SEL-751 Settings Report: Global Group 1Dokumen10 halamanSEL-751 Settings Report: Global Group 1Diego Alejandro Vera SuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry WorksheetDokumen3 halamanStoichiometry WorksheetPiiNkiE ChongBelum ada peringkat
- Friction Sample Question AnswersDokumen7 halamanFriction Sample Question AnswersIbrahim HossainBelum ada peringkat
- ResonanceDokumen48 halamanResonancePrakash Nik79% (92)
- Siemens 8da10 SWG CatalogueDokumen64 halamanSiemens 8da10 SWG CatalogueGilberto Mejía100% (1)
- RM3048XE 3.0kW 48V DC Modular Rectifiers v1.0Dokumen2 halamanRM3048XE 3.0kW 48V DC Modular Rectifiers v1.0pakojidastavimBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem II Exam 1 Ans Key VA f08Dokumen5 halamanGen Chem II Exam 1 Ans Key VA f08ASaad117100% (1)
- Chapter 01 PDFDokumen27 halamanChapter 01 PDFRahayu Riandika PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsDokumen20 halamanLab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsChris Ang76% (21)
- Dry Gas GradientDokumen4 halamanDry Gas Gradientlutfi awnBelum ada peringkat
- Propuestas E2 MsDokumen3 halamanPropuestas E2 MsPedro OlivoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 33 Optical Absorption in Semiconductors PDFDokumen44 halamanLesson 33 Optical Absorption in Semiconductors PDFBobbette BobbertBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 24 - Electric PotentialDokumen12 halamanChapter 24 - Electric PotentialVV CepheiBelum ada peringkat
- Revision 3 (Differentiation)Dokumen2 halamanRevision 3 (Differentiation)Tan Chin HuatBelum ada peringkat
- Ohmite Component Selector: Catalog 4000KDokumen205 halamanOhmite Component Selector: Catalog 4000Klem abesamisBelum ada peringkat
- Panasonic VF0 InvertersDokumen4 halamanPanasonic VF0 InvertersTecnico 1 EmbarbaBelum ada peringkat
- SKF Bearing SelectDokumen3 halamanSKF Bearing Selectmechanical09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 3 Electric FieldDokumen22 halamanPhysics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 3 Electric FieldDilini WijesinghBelum ada peringkat
- TD RWG Ewg Poti enDokumen3 halamanTD RWG Ewg Poti enJanko PekoljBelum ada peringkat
- L4 Laboratory MathematicsDokumen5 halamanL4 Laboratory MathematicsZeian Jacob BaylaBelum ada peringkat
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDari EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDari EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (22)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDari EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Abrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingDari EverandAbrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingBelum ada peringkat
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDari EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Machine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsDari EverandMachine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesDari EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Casing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationDari EverandCasing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesDari EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityDari EverandAdvanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Well Testing Project Management: Onshore and Offshore OperationsDari EverandWell Testing Project Management: Onshore and Offshore OperationsBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsDari EverandFundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsBelum ada peringkat
- Guide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesDari EverandGuide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable OperationsDari EverandThe Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable OperationsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (5)
- Heat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsDari EverandHeat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Advanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationDari EverandAdvanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (4)
- Heavy and Extra-heavy Oil Upgrading TechnologiesDari EverandHeavy and Extra-heavy Oil Upgrading TechnologiesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsDari EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)