English Reviewer
Diunggah oleh
Ina Ardan0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
308 tayangan6 halamanenglish
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inienglish
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
308 tayangan6 halamanEnglish Reviewer
Diunggah oleh
Ina Ardanenglish
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
The Rain Came Notes
Made by: Grace Ogot
Labong-o The father
Minya The Mother
Oganda The Daughter; her name means beans
Luo The tribe being cared by Labong-o
Ndithi The Medicine Man
Podho The Ancestor of the Luo
Nyabogo The messenger
Kech, the son of a neighboring clan elder, smaller
Dimo thought to be a cruel husband
Osinda The guy who Osinda Choose; saved her.
Karlamo Sacred Place
She turned southward to start her trek
The household assembled at the SIala Tree
Makato and The Cowrie Shell
Made By: Supanee Khanchanathiti
Makato Orphan soon to be King; 12 years of age when he met the King; Picked One Cowrie
Shell; Became the ruler of the City of Mon
Sukhotai The Land where Makato wished to go
Pra Ruang King of Sukhotai
City of Mon Where Makato came from
Kun Wang Most important person in the Kings Court; given to Makato
Irony
There are 3 types of Irony
Verbal
Situational
Dramatic
Verbal Irony
Verbal Irony has two types:
Overstatement exaggerates
Understatement underestimate
- Verbal Irony is the use of words to mean something different from what a person actually
says.
Examples of verbal irony include:
Thanks for the ticket officer you just made my day!
I cant wait to read the seven hundred page report.
The above examples show how irony is used to show someones frustration or disappointment.
Sarcasm and Irony *croo croo*
Most of the time, sarcasm and verbal irony are used interchangeably. There is however a clear
distinction between the two.
In most cases, sarcasm is used to insult or to cause harm.
A statement like Great, someone stained my new dress. is ironic, while You call this a work
of art? is sarcastic.
While verbal irony implies a different meaning to what is actually said, sarcasm is mainly used
as a sharp and direct utterance designed to cause pain.
Dramatic Irony
This type of irony is popular in works of art such as movies, books, poems and plays.
Example of a Dramatic Irony:
An example of dramatic irony is in a movie where a detective does not know that the criminal
responsible for the crimes in the city is his partner. The audience however is already aware of
this fact and waits anxiously to know what will happen once the character finds out what they
already know.
Stages of Dramatic Irony
Installation audience is informed of something the character does not know about
Exploitation using this information to develop curiosity among the audience
Resolution what happens when the character finally finds out what is going on?
A special category of dramatic irony is tragic irony.
Tragic irony occurs when a character in a play does or says something that communicates a
meaning unknown to her but recognized by the audience
An example of tragic irony is when a character orders poisoned food that is supposed to kill
him or her and the audience already knows that the character is destined to die from food
poisoning.
Tragic irony was common in plays that depicted the lives of legends in ancient Greece.
The audience already knew the fate of the characters before they watched the play.
Situational Irony
It involves a discrepancy between what is expected to happen and what actually happens.
Example of a Situational Irony
An example would be when someone buys a gun to protect himself, but the same gun is used
by another individual to injure him. One would expect that the gun would keep him safe, but it
has actually caused him injury.
There is however a difference between situation irony and coincidence or bad luck.
When someone washes his car and it rains, that is just bad luck; nothing led him or her to think
that it would not rain. However, when a TV weather presenter gets caught in an unexpected
storm, it is ironic because he or she is expected to know the exact weather changes.
For situation irony to occur there has to be something that leads a person to think that a
particular event or situation is unlikely happen.
TYPES OF LITERARY CONFLICTS
1) Man Vs. Himself 2) Man Vs. Man 3) Man Vs. Society 4) Man Vs. Nature
Coordinating Conjunctions- join 2 words or phrases that are grammatically alike
FANBOYS
1) For- presents an explanation
2) And- presents non-contrasting ideas
3) Nor- presents non-contrasting negative ideas
4) But- presents contrast or exception
5) Or- presents alteration of ideas
6) Yet- presents contrast or excpetion
7) So- presents the effect
ENGLISH
ELEMENTS OF A SHORT STORY
1. Setting
-The setting refers to place, time, weather condition, social condition, and even mood or
atmosphere. To recognize the setting of the story, you may ask these questions:
Where is the action taking place?
Where is the story taking place? Is it during the day, night, what year, what period?
What is the weather condition? Is it sunny, rainy, and stormy?
What is the daily life of the character? What are his customs and status in life?
What is the feeling created at the beginning of the story? Is it bright, cheerful, dark or
frightening?
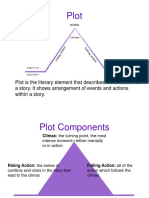
2. Plot
- It is the sequence of events in a story or play. The plot is a planned, logical series of events
having a beginning, middle and end. The short story usually has one plot, and it could be
read in one sitting .There are five essential parts of a plot :
a. Exposition/Introduction
-In the introduction, the setting and the characters are revealed.
b. Rising Action
-This is where the events in the story become complicated and the conflict in the story is
revealed .This is where events between introduction and climax take place.
c. Climax
It is the turning point of the story and the highest point of interest. It is where the reader asks
what will happen next. Will the conflict be resolved or not?
d. Falling Action
- The problems and complications begin to be resolved.
e. Denouement
- This is the final outcome or untangling of events in the story.
3. Conflict
-It is the opposition of forces which ties one incident to another and makes the plot move .
There are two types of conflict:
External refers to outside forces that may cause conflict, like another human being,
circumstances, environment, etc.
Internal - refers a struggle within oneself. The character maybe debating inside himself about
what to do.
4. Character
there are two meanings for the word character: the person in a work of fiction and the
characteristics of a person. He may be the protagonist, the good-natured character, or the
antagonist, the opponent of the main character.
5. Point of View
- the angle from which the story is told
6. Theme
- it is the controlling idea or value in a piece of fiction. The theme maybe the author s idea
about a topic or view of human nature.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Types of IronyDokumen30 halamanTypes of IronyNOXIOUSBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of FictionDokumen6 halamanElements of FictionCzarina Pauline CunananBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 Creative Non FictionDokumen2 halamanModule 4 Creative Non FictionArnel BoholstBelum ada peringkat
- Stylistic Devices: Baena, Julie Ann Tecson, Rose Mae Ojario, Mae Villegas, Christian JayDokumen46 halamanStylistic Devices: Baena, Julie Ann Tecson, Rose Mae Ojario, Mae Villegas, Christian JayRose Mae TecsonBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of A StoryDokumen17 halamanElements of A StoryhBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8. Types of IronyDokumen22 halamanGrade 8. Types of IronyEll ParaisoBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of Prose and Drama - EL115Dokumen11 halamanCharacteristics of Prose and Drama - EL115Ivy YbanezBelum ada peringkat
- SETTING - The Time and Location in Which A Story Takes Place Is Called The Setting. ForDokumen6 halamanSETTING - The Time and Location in Which A Story Takes Place Is Called The Setting. ForJoymeeBelum ada peringkat
- CNF Week4 Analyzing Fictional ElementsDokumen67 halamanCNF Week4 Analyzing Fictional ElementsROSELYN LAZALITABelum ada peringkat
- Literary Elements - Definitions and ExamplesDokumen9 halamanLiterary Elements - Definitions and Examplesapi-339254566Belum ada peringkat
- Elemets of FictionDokumen4 halamanElemets of FictionLaura Sophia BondocBelum ada peringkat
- Literary Elements HandoutDokumen7 halamanLiterary Elements HandoutSusana Dalmao100% (1)
- Grade 12 Creative Non FictionDokumen6 halamanGrade 12 Creative Non FictionbetingleaBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Class 2-3Dokumen5 halamanPractical Class 2-3Jahan NepesowaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Irony PDFDokumen3 halamanTypes of Irony PDFIffah NadhirahBelum ada peringkat
- Writing - Unit 5 - STCDokumen14 halamanWriting - Unit 5 - STCElizavetaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Activity: Unitii:Fiction WritingDokumen9 halamanPractice Activity: Unitii:Fiction WritingJM SilerioBelum ada peringkat
- Storyelements 2Dokumen96 halamanStoryelements 2hanna.luna378Belum ada peringkat
- Descriptive EssayDokumen58 halamanDescriptive EssayMehala Mohan50% (2)
- Introduction To Literature MidtermDokumen46 halamanIntroduction To Literature MidtermAlharbi SiBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of ProseDokumen38 halamanElements of Proseapi-264812155100% (2)
- Elements of ProseDokumen40 halamanElements of Prosekate villanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- The Lady or The Tiger Study Guide PDFDokumen8 halamanThe Lady or The Tiger Study Guide PDFA. A. Suleiman100% (1)
- Cnf-Q3-Week 6Dokumen11 halamanCnf-Q3-Week 6guiaBelum ada peringkat
- English ModuleDokumen29 halamanEnglish ModuleMichie BantiloBelum ada peringkat
- A Silent Song and Other Stories Edited by Godwin Siundu : Volume One: A Guide to Reading A Silent Song and Other Stories ed. by Godwin Siundu, #1Dari EverandA Silent Song and Other Stories Edited by Godwin Siundu : Volume One: A Guide to Reading A Silent Song and Other Stories ed. by Godwin Siundu, #1Belum ada peringkat
- Techniques and Literary DevicesDokumen39 halamanTechniques and Literary DevicesHerlou C Lualhati100% (1)
- Eng4u Elements Devices Active ReadingDokumen8 halamanEng4u Elements Devices Active ReadingΑθηνουλα Αθηνα100% (1)
- Grade 9 Twenty Literary DevicesDokumen8 halamanGrade 9 Twenty Literary DevicesEllen RyooBelum ada peringkat
- My-Elements of The StoryDokumen100 halamanMy-Elements of The StoryRonald MwewaBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Fiction - JHS DemonstrationDokumen41 halamanElements of Fiction - JHS DemonstrationArnel NavalesBelum ada peringkat
- GED11 - 14. DramaDokumen6 halamanGED11 - 14. DramaKyle CepilloBelum ada peringkat
- ÔN DẪN LUẬNDokumen42 halamanÔN DẪN LUẬNNgọc ThơmBelum ada peringkat
- Literature: Ms. Reynosa B. RimoroDokumen79 halamanLiterature: Ms. Reynosa B. RimoroDexter Carl Bolinto JrBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Out For 1st QuarterDokumen2 halamanHand Out For 1st QuarterTam FerrolBelum ada peringkat
- Verbal Irony ThesisDokumen5 halamanVerbal Irony Thesiscaseyhudsonwashington100% (1)
- Creative Nonfiction WorksheetDokumen6 halamanCreative Nonfiction WorksheetGershom Perez AcaboBelum ada peringkat
- Hog10m1 M3Dokumen4 halamanHog10m1 M3Verna Jane NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- The Oracle Given To King Acrisius Will Be Fulfilled by His GrandsonDokumen2 halamanThe Oracle Given To King Acrisius Will Be Fulfilled by His GrandsonAva BarramedaBelum ada peringkat
- Title: Literature: The Seventh Man (Answer Key)Dokumen26 halamanTitle: Literature: The Seventh Man (Answer Key)jana75% (4)
- Elements Techniques and Literary Devices in Drama 1Dokumen5 halamanElements Techniques and Literary Devices in Drama 1Zekenari CiBelum ada peringkat
- Irony Thesis ExamplesDokumen7 halamanIrony Thesis Exampleshmnxivief100% (2)
- SN 3.1 Literary DevicesDokumen3 halamanSN 3.1 Literary DevicesHeleina De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Figures of Speech and Other Literary TechniquesDokumen35 halamanFigures of Speech and Other Literary TechniquesDonna MenesesBelum ada peringkat
- Figure of SpeechDokumen4 halamanFigure of Speechmcheche12Belum ada peringkat
- Welcome To Creative Non FictionDokumen27 halamanWelcome To Creative Non FictionErica Atienza - DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Creative NonfictionDokumen50 halamanElements of Creative NonfictionKen Donal100% (1)
- Short StoryDokumen2 halamanShort StoryAmanda MojarBelum ada peringkat
- A Short Story Is A Brief Work of 2Dokumen10 halamanA Short Story Is A Brief Work of 2airagarcia_18Belum ada peringkat
- Elements of Short Story: Plot Setting Characters Theme Point of View Good WritingDokumen8 halamanElements of Short Story: Plot Setting Characters Theme Point of View Good Writingyuvita prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Conflict, POV, FF, ThemeDokumen20 halamanConflict, POV, FF, ThemeMarion Giana AdezaBelum ada peringkat
- Comedic Devices PDFDokumen20 halamanComedic Devices PDFridhimaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 (CNF)Dokumen2 halamanModule 2 (CNF)NashimahBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of A Short StoryDokumen19 halamanElements of A Short StoryJohn Briane CapiliBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of The Short StoryDokumen3 halamanElements of The Short StoryRiver Lincoln HargreevesBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of NarrativeDokumen34 halamanElements of NarrativeAnne Cadiz100% (2)
- Short Story PlotDokumen4 halamanShort Story PlotcaseyBelum ada peringkat
- Movie Review: InsiangDokumen3 halamanMovie Review: InsiangIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Project ProposalDokumen2 halamanProject ProposalIna Ardan0% (1)
- Latent Heat of Fusion: AbstractDokumen6 halamanLatent Heat of Fusion: AbstractIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal ConductivityDokumen1 halamanThermal ConductivityIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Huma AssignmentDokumen1 halamanHuma AssignmentIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- ARDAN - Bank Inquiries and Data From PSEDokumen24 halamanARDAN - Bank Inquiries and Data From PSEIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- World, / Have Mercy On UsDokumen1 halamanWorld, / Have Mercy On UsIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Piano Carol of The BellsDokumen3 halamanPiano Carol of The BellsLomberto CroisereBelum ada peringkat
- Ray DiagramsDokumen2 halamanRay DiagramsIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- PE Paper 2nd TermDokumen1 halamanPE Paper 2nd TermIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Reading and Writing Assignment Rhetorical Patterns 2nd TermDokumen1 halamanReading and Writing Assignment Rhetorical Patterns 2nd TermIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Aero PhonesDokumen4 halamanAero PhonesIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Ray DiagramsDokumen2 halamanRay DiagramsIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Nortons TheoremDokumen1 halamanQuiz Nortons TheoremIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- English ProjectDokumen3 halamanEnglish ProjectIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- The Twelve OlympiansDokumen27 halamanThe Twelve OlympiansIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Major and Minor ScalesDokumen1 halamanMajor and Minor ScalesIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- English ReviewerDokumen10 halamanEnglish ReviewerIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Diwa NG PaskoDokumen14 halamanDiwa NG PaskoIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Out of My LeagueDokumen5 halamanOut of My LeagueIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Microbial BiotechnologyDokumen75 halamanChapter 5 Microbial BiotechnologyIna Ardan50% (2)
- Acetyl BromideDokumen7 halamanAcetyl BromideIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Health ReviewerDokumen4 halamanHealth ReviewerIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To FictionDokumen32 halamanIntroduction To FictionAbraham Movalone100% (1)
- Literary DevicesDokumen11 halamanLiterary DevicesKevin Ceriño CubitaBelum ada peringkat
- Handout MasterDokumen4 halamanHandout Masterapi-449515183Belum ada peringkat
- Week 11 To 20: Creative Writing - Dane GammadDokumen38 halamanWeek 11 To 20: Creative Writing - Dane GammadRia BarisoBelum ada peringkat
- Shakespeare PresentationDokumen44 halamanShakespeare PresentationEduard-Mario IacobiniBelum ada peringkat
- Creative Writing Q2 Module 5Dokumen31 halamanCreative Writing Q2 Module 5Diana Silva Hernandez79% (14)
- The Boy in The Stripped Pijamas Lesson PlanDokumen14 halamanThe Boy in The Stripped Pijamas Lesson PlanChen QiuBelum ada peringkat
- English Poetry and Drama Terms For ShakespeareDokumen22 halamanEnglish Poetry and Drama Terms For ShakespeareChuii MuiiBelum ada peringkat
- Periodical TestDokumen7 halamanPeriodical TestHezekiah Kaddesh CadangBelum ada peringkat
- Conflict 2Dokumen8 halamanConflict 2api-164711099Belum ada peringkat
- Types of ConflictDokumen16 halamanTypes of Conflictjg.mariane102Belum ada peringkat
- Story WritingDokumen7 halamanStory WritingMugdhaBelum ada peringkat
- ProseDokumen34 halamanProselil GoshBelum ada peringkat
- Reading and Writing Skills MODULE WEEK 1Dokumen12 halamanReading and Writing Skills MODULE WEEK 1Hazel Mae HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanLesson PlanLilay Barambangan100% (4)
- Worksheet - Elements of Short StoryDokumen3 halamanWorksheet - Elements of Short Storymaureen mae mana-ay100% (1)
- PLOt and ConflictDokumen36 halamanPLOt and ConflictAbiekhay Camillee Unson LavastidaBelum ada peringkat
- One Act PlayDokumen4 halamanOne Act PlayAmina Shah100% (1)
- Elements of A StoryDokumen50 halamanElements of A StoryLeshlengg LanwangBelum ada peringkat
- English ReviewerDokumen6 halamanEnglish ReviewerIna ArdanBelum ada peringkat
- The Summer I Learned To BikeDokumen17 halamanThe Summer I Learned To BikeMay Comia67% (6)
- NCERT Class 9 English Main Course Book Unit 5 MysteryDokumen27 halamanNCERT Class 9 English Main Course Book Unit 5 Mysterymayank645321Belum ada peringkat
- 21st Module 5 SinigangDokumen4 halaman21st Module 5 Sinigangsan draBelum ada peringkat
- Most Dangerous Game Unit 2008Dokumen25 halamanMost Dangerous Game Unit 2008ThiriBelum ada peringkat
- Task 12 The Art of StorytellingDokumen3 halamanTask 12 The Art of StorytellingakumubrianBelum ada peringkat
- Ang KalupiDokumen19 halamanAng KalupiClarizza Joyce Hervas100% (2)
- The Bear BoyDokumen17 halamanThe Bear BoyAseel TobailBelum ada peringkat
- Plot StructureDokumen109 halamanPlot StructureMarilo CostaBelum ada peringkat
- Midterms Reviewer For Literatire of The PhilippinesDokumen20 halamanMidterms Reviewer For Literatire of The PhilippinesAllen Bryan C. Datu100% (3)
- Elements of DramaDokumen20 halamanElements of DramaCarlos TabangayBelum ada peringkat