Necessary of Compensation
Diunggah oleh
Nishiya VijayanDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Necessary of Compensation
Diunggah oleh
Nishiya VijayanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Necessary of Compensation
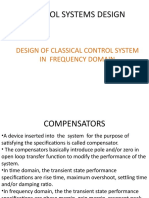
In order to obtain the desired performance of the system, we use compensating networks.
Compensating networks are applied to the system in the form of feed forward path gain
adjustment.
Compensate a unstable system to make it stable.
A compensating network is used to minimize overshoot.
These compensating networks increase the steady state accuracy of the system. An
important point to be noted here is that the increase in the steady state accuracy brings
instability to the system.
Compensating networks also introduces poles and zeros in the system thereby causes
changes in the transfer function of the system. Due to this, performance specifications of
the system change.
Effects of Lead Compensator
Lead compensator adds a dominant pole and zero. This increases the damping of the
closed loop system.
This increased damping means less overshoot, less rise time, less settling time. Thus there
is an improvement in transient response.
It improves phase margin of the closed loop system
It increases bandwidth of the closed loop system. More bandwidth faster is the response.
Steady state error doesnt get affected
Limitations of Lead compensation
Maximum lead angle available from a lead network is 60
o
.Thus if a lead of 70 to 90 is
required multiple lead compensators are required.
Lead compensation requires additional gain to offset the attenuation in lead network.
More bandwidth sometimes makes the system susceptible to noise
Effects of Lag Compensator
It improves steady state performance.
The attenuation due to lag compensator shifts the gain crossover frequency to a lower
frequency point. Thus bandwidth of the system gets reduced.
The system becomes more sensitive to parameter variations
This makes system less stable
Reduced bandwidth means slower response
Effects of Lag-Lead Compensator
Lag lead compensator is used when both fast response and good accuracy is required
Increases low frequency gain which improves the steady state
It increases bandwidth and thereby speed of response
Since it has larger bandwidth settling and rise time are low
MODULE 5
Drawbacks of transfer function
Transfer function defined under zero initial conditions
Only applicable to LTI system
Restricted to single input single output system
Doesnt provide any information regarding internal state of the system
Advantages of state variable analysis
Applicable to any type of system
Can be applied to MIMO systems
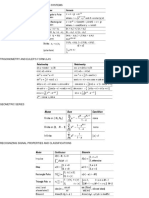
Properties of state transition matrix ((t)=
)
(t)=
,then (0)=
=I
-1
(t)=
= (-t)
(t
1
+t
2
) = (t
1
)* (t
2
)
= (t
1
)* (t
2
)
(t
1-
t
2
)* (t
2-
t
3
) = (t
1-
t
3
)
= (t
1-
t
3
)
Characteristics equation
Asymptotically stable system
A system which produces zero output for zero input irrespective of initial conditions.
An asymptotically stable system is also BIBO stable, but not vice versa
No. BIBO Asymptotically stable
1 Zero state stabilty Zero input stability
2 External stability Internal stability
3 All poles of G(s) on Left
Half Plane
All eigen values of A are in
LHP
4 Bounded output for
bounded input
Output=0 for zero input
5 Necessary and sufficient
condition
Impulse response should
be bounded
All eigen values of A are in
LHP
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Harnessing Bistable Structural Dynamics: For Vibration Control, Energy Harvesting and SensingDari EverandHarnessing Bistable Structural Dynamics: For Vibration Control, Energy Harvesting and SensingBelum ada peringkat
- EEE 324 - Lecture Note 4Dokumen5 halamanEEE 324 - Lecture Note 4Jerry MashmanBelum ada peringkat
- Control System Last Minute RevisionDokumen34 halamanControl System Last Minute RevisionAnshul YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 1. Compensator Design Using Bode Plot: Points To RememberDokumen10 halamanUnit 5 1. Compensator Design Using Bode Plot: Points To RememberRajasekhar AtlaBelum ada peringkat
- K Flop ManualDokumen306 halamanK Flop Manualhappydude7632Belum ada peringkat
- System and Automatic Control Lab (EC-218) : Experiment No. 4 ObjectDokumen5 halamanSystem and Automatic Control Lab (EC-218) : Experiment No. 4 Objectarjunv_14Belum ada peringkat
- Compensation in Control SystemDokumen10 halamanCompensation in Control Systemshouvikchaudhuri0% (1)
- Lag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemDokumen11 halamanLag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemShah Jay100% (1)
- A Novel Approach For Tuning Power System Stabilizer (SMIB System) Using Genetic Local Search TechniqueDokumen11 halamanA Novel Approach For Tuning Power System Stabilizer (SMIB System) Using Genetic Local Search TechniqueShraddha VardikarBelum ada peringkat
- CS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3Dokumen88 halamanCS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3sushinkBelum ada peringkat
- 4th Unit CSDDokumen98 halaman4th Unit CSDYeswanth Manikanta MBelum ada peringkat
- Lead - Lag ControllerDokumen2 halamanLead - Lag Controllerharry_chemBelum ada peringkat
- Compensators PDFDokumen34 halamanCompensators PDFSri Harshitha KBelum ada peringkat
- Ch3 Feedback Control System Characteristics: Main ContentDokumen27 halamanCh3 Feedback Control System Characteristics: Main Contentnainesh goteBelum ada peringkat
- CompensationDokumen11 halamanCompensationCyprian Obota OtienoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 ControlDokumen44 halamanChapter 4 ControlFootball HDBelum ada peringkat
- ELE 4623: Control Systems: Faculty of Engineering TechnologyDokumen15 halamanELE 4623: Control Systems: Faculty of Engineering TechnologyMaitha SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- High Gain GBW and SR P 5mWDokumen8 halamanHigh Gain GBW and SR P 5mWLucas Compassi SeveroBelum ada peringkat
- 3-Module5 - CompensatorDokumen11 halaman3-Module5 - CompensatorShashankaBelum ada peringkat
- Gain & Phase Margin - Bode PlotDokumen28 halamanGain & Phase Margin - Bode PlotDeepthiBelum ada peringkat
- The Design of Feedback Control SystemsDokumen36 halamanThe Design of Feedback Control SystemsNirmal Kumar PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Control Lab ReportDokumen20 halamanControl Lab ReportRavi SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Simulink Basics TutorialDokumen143 halamanSimulink Basics TutorialHiếu HuỳnhBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Control BasedDokumen10 halamanDigital Signal Control BasedFaisal IlyasBelum ada peringkat
- Control System Engineering Lab: Avanish Niranjan 17104088 EEN 210Dokumen17 halamanControl System Engineering Lab: Avanish Niranjan 17104088 EEN 210Umang SoinBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Levitation SystemDokumen9 halamanMagnetic Levitation SystemArjun SreenivasBelum ada peringkat
- EEN-305 Advanced Control Systems Lab ReportDokumen16 halamanEEN-305 Advanced Control Systems Lab ReportRitik MathurBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 PID 1Dokumen36 halamanChapter 10 PID 1Taufiq GalangBelum ada peringkat
- Control SystemDokumen11 halamanControl Systembalaji1986Belum ada peringkat
- AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Study The Step Response and Frequency Response of A GivenDokumen3 halamanAIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Study The Step Response and Frequency Response of A Givenpriyatosh dashBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation SystemDokumen59 halamanExcitation SystemVenkat Cherukuri100% (2)
- Introduction To Control SystemDokumen11 halamanIntroduction To Control SystemAbhishek MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Arithmetic For Signals and SystemsDokumen4 halamanComplex Arithmetic For Signals and SystemsBách Gia DươngBelum ada peringkat
- AS3842Dokumen10 halamanAS3842kik020Belum ada peringkat
- Control Systems: Steady State ErrorDokumen44 halamanControl Systems: Steady State Errorpham tamBelum ada peringkat
- Exciter Notes ForDokumen9 halamanExciter Notes ForCaloy CeloyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Eight Root Locus Control Design: Figure 8.1: A Common Controller-Plant ConfigurationDokumen44 halamanChapter Eight Root Locus Control Design: Figure 8.1: A Common Controller-Plant ConfigurationVijay GargBelum ada peringkat
- Products Home Rapid Order Services The Company Contact Us My ThorlabsDokumen2 halamanProducts Home Rapid Order Services The Company Contact Us My Thorlabsअमरेश झाBelum ada peringkat
- Controller Design Using Frequency ResponseDokumen35 halamanController Design Using Frequency Responseiamketul6340Belum ada peringkat
- Adding Noise To Improve MeasurementDokumen8 halamanAdding Noise To Improve MeasurementMegha AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I NotesDokumen43 halamanUnit I Notesaravinth69601Belum ada peringkat
- ROOT LOCUS Control System DesignDokumen25 halamanROOT LOCUS Control System DesignJustin Watkins100% (1)
- Steady State ErrorsDokumen41 halamanSteady State ErrorsMuhammad Noman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Characteristics of LeadDokumen3 halamanBasic Characteristics of LeadsbhaleshBelum ada peringkat
- Control Engineering ME - 4012: Instructor Muhammad Rizwan SiddiquiDokumen27 halamanControl Engineering ME - 4012: Instructor Muhammad Rizwan SiddiquiTalha JalilBelum ada peringkat
- Tuning of Power System StabilizerDokumen31 halamanTuning of Power System StabilizerRajesh PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- SSP 286 New Data Bus SystemsDokumen30 halamanSSP 286 New Data Bus Systemsภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะBelum ada peringkat
- Cs-Module 1 NotesDokumen58 halamanCs-Module 1 NotesSuprithaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Controllers - Proportional Integral and Derivative Controllers - Electrical4UDokumen13 halamanTypes of Controllers - Proportional Integral and Derivative Controllers - Electrical4UHasan Qayyum ChohanBelum ada peringkat
- Control System Viva QuestionDokumen13 halamanControl System Viva QuestionMasudur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Controller Design Using Root Loci MethodDokumen34 halamanController Design Using Root Loci Methodiamketul6340Belum ada peringkat
- Expt 4 First Order SystemDokumen4 halamanExpt 4 First Order SystemAngelo Legarda De CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Bhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted byDokumen36 halamanBhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted bytarnedo1Belum ada peringkat
- Automated Control Unit III Part 1,2Dokumen13 halamanAutomated Control Unit III Part 1,2Rakgnar LodbrokBelum ada peringkat
- Open Loop and Close Loop Control SystemDokumen10 halamanOpen Loop and Close Loop Control SystemAmrit SinghaBelum ada peringkat
- Transient and Steady State Response AnalysisDokumen83 halamanTransient and Steady State Response AnalysisPramod RajBelum ada peringkat
- Classical Control 1 Sche A MeDokumen7 halamanClassical Control 1 Sche A MeEric Leo AsiamahBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Experiment 7: Introduction To Bode Plots, Phase and Gain MarginDokumen12 halamanLab Experiment 7: Introduction To Bode Plots, Phase and Gain MarginFahad AneebBelum ada peringkat
- Low Power Cmos VgaDokumen7 halamanLow Power Cmos VgaMohammad Ayatullah MaktoomBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016Dokumen71 halamanSyllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016sreedeepuBelum ada peringkat
- Introd Electronics Jan - 17 (1) - Ktu - Question PaperDokumen3 halamanIntrod Electronics Jan - 17 (1) - Ktu - Question PaperNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- EC202 Signals & SystemsDokumen2 halamanEC202 Signals & SystemsNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Module1 QuizzDokumen3 halamanModule1 QuizzNishiya Vijayan0% (1)
- Ec100 Basics of Electronics EngineeringDokumen3 halamanEc100 Basics of Electronics EngineeringNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- SYLLABUSDokumen4 halamanSYLLABUSNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- IEC June16Dokumen3 halamanIEC June16Nishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016Dokumen71 halamanSyllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016sreedeepuBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessors & Microcontrollers - Dec07Dokumen1 halamanMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers - Dec07Nishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionbankDokumen12 halamanQuestionbankNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- COMMNLABDokumen12 halamanCOMMNLABNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Org 0000HDokumen1 halamanOrg 0000HNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Class Test 2 Time: 50 Minute Max - Marks:20 Marks: Part ADokumen1 halamanClass Test 2 Time: 50 Minute Max - Marks:20 Marks: Part ANishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Previous Year QuestionsDokumen3 halamanPrevious Year QuestionsNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Signal Procesiing LabDokumen5 halamanSignal Procesiing LabNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- EceDokumen5 halamanEceDinesh Kumar A RBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Am and FMDokumen2 halamanComparison of Am and FMNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Control SystemDokumen3 halamanControl SystemNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To MatlabDokumen25 halamanIntroduction To MatlabNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Problems-Basic ElecroncisDokumen1 halamanProblems-Basic ElecroncisNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Compute 32 Point DFT XDokumen4 halamanCompute 32 Point DFT XNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- GSM PDFDokumen8 halamanGSM PDFNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Necessary of CompensationDokumen3 halamanNecessary of CompensationNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Transistors PDFDokumen14 halamanTransistors PDFNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- MECCE Communication EngineeringDokumen21 halamanMECCE Communication EngineeringrvgmecBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Am and FMDokumen2 halamanComparison of Am and FMNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- OpampDokumen12 halamanOpampNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Programming Experiments Using 8051 SimulatorDokumen4 halamanProgramming Experiments Using 8051 SimulatorNishiya VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- I B E S: RIS Iometrics FOR Mbedded YstemsDokumen15 halamanI B E S: RIS Iometrics FOR Mbedded YstemsNishiya Vijayan100% (1)