Inter Connected Power System - Combined
Diunggah oleh
Palak AriwalaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Inter Connected Power System - Combined
Diunggah oleh
Palak AriwalaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
Seat No.: _____ Enrolment No.______
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
B. E. VII
th
SemesterExamination Nov- 2011
Subject code: 170901
Subject Name: Inter Connected Power System
Date:19/11/2011 Time: 10:30 am 01:00 pm
Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 (a) Derive the expression for B-coefficients in case of two generating plants
connected to an arbitrary number of loads through a transmission network.
07
(b) Discuss the procedure for solving the swing equation using point by point
method.
07
Q.2 (a) Compare the GS and NR methods of load flow study. 07
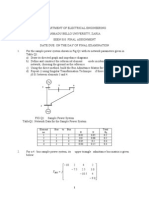
(b) The following figure shows a simple 4-bus system.
1 2
3 4
0.05+j0.15
0.05+j0.15
0.15+j0.45
Line G, pu B, pu
1-2 2.0 6.0
1-3 1.0 3.0
2-3 0.666 2.0
2-4 1.0 3.0
3-4 2.0 6.0
The shunt admittances at all the buses are assumed negligible.
1) Find Y
BUS
assuming that the line shown dotted is not connected.
2) What modifications need to be carried out in Y
BUS
if the line shown dotted
is connected?
07
OR
(b) A system consists of four identical 400 MVA generating units feeding a total load
of 1016 MW. The inertia constant of each unit is 5 on 400 MVA base. The load
changes by 1.5% for a 1% change in frequency. When there is sudden drop in
load by 16 MW, obtain the power system time constant (T
p
) with constants H and
D expressed on 1600 MVA base.
07
Q.3 (a) A power system has two generating plants and power is being dispatched
economically with P
1
= 150 MW and P
2
= 275 MW.
The loss coefficients are:
2 1
11
2 1
12
2 1
22
0.10 10 MW
0.10 10 MW
0.13 10 MW
B
B
B
=
=
=
08
2
To raise the total load on the system by 1 MW, an additional cost of 200 Rs./hour
will be incurred. Find;
a) The penalty factor of plant:1
b) The additional cost per hour to increase the output of plant:1 by 1 MW.
(b) Give reasons:
1) One of the buses is taken as slack bus in load flow studies.
2) Bus admittance matrix is a spare matrix.
3) An acceleration factor is commonly used in load flow studies using GS
method.
06
OR
Q.3 (a) Give the algorithm with flow chart for a fast decoupled load flow solution. 07
(b) Write a short note on Load Dispatch Centre. 07
Q.4 (a) What is power system islanding? Why it is needed? What is ideal procedure to
restore the grid? Discuss the effects of islanding.
07
(b) Derive a mathematical model of turbine speed governing system. 07
OR
Q.4 (a) A 100 MVA, 50 Hz synchronous generator having inertia constant of the machine
as 5 kW-sec per kVA. The load suddenly increases by 50 MW. Due to delay in
governor action there is a delay of 0.6 seconds in opening of steam valve. Find the
frequency deviation.
07
(b) Distinguish between steady state, dynamic and transient stability. Derive power
angle equation sin
e m
P P = . State the assumptions made.
07
Q.5 (a) A single area consists of two generating units, rated at 400 and 800 MVA, with
speed regulation of 4% and 5% on their respective ratings. The units are operating
in parallel, sharing 700 MW. Unit 1 supplies 200 MW and unit 2 supplies 500
MW at 1.0 per unit (50 Hz) frequency. The load is increased by 130 MW.
Assume there is no frequency-dependent load. Find the steady-state frequency
deviation and the new generation on each unit.
07
(b) Explain the following:
1) Bus incidence matrix
2) Primitive network
07
OR
Q.5 (a) A 50 Hz generator of reactance of 1.2 pu is connected to an infinite bus bar
through a line reactance of 0.6 pu. |E| = 1.2 pu and |V| = 1.0 pu. The inertia
constant is 4 MW-sec per MVA. The generator is loaded to 50% of its maximum
power limit. Find the frequency of natural oscillations.
07
(b) Write a short note on Automatic Voltage Control. 07
*************
1
Seat No.: ________ Enrolment No.______________
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
BE- VII
th
SEMESTEREXAMINATION MAY/JUNE- 2012
Subject code: 170901 Date: 24/05/2012
Subject Name: Inter Connected Power System
Time: 02:30 pm 05:00 pm Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1
(a) Derive static load flow equations. Hence explain classification of buses . (7)
(b) Derive the criterion for economic distribution of load between different (7)
units of a plant when transmission losses are neglected.
Q.2
(a) Discuss dynamics of synchronous machine and derive the swing equation (7)
(b) A 50Hz, 4-pole turbo alternator rated 20,000 kVA, 13.2 kV has an inertia (7)
constant of 9 kW-sec/kVA. Find the K.E. stored in the rotor at synchronous
speed. Find the accelerating torque if the shaft input is 26,800 hp (metric) and
the electric power developed is 16,000 kW. If the acceleration is maintained
constant for a period of 15 cycles, determine the change in torque angle in that
period and the rpm at the end of 15 cycles
OR
(b) A synchronous generator feeds 1.0 pu power to an infinite bus through a (7)
transmission system (double circuit line). A fault occurs on one line which
reduces the maximum power transfer to 0.5 pu, whereas before the fault this
power was 2.0 pu and after the clearance of fault is 1.5 pu. By the use of
equal area criteria determine the critical clearing angle. The losses in the
system may be neglected.
Q.3
(a) The following is the system data for a load flow solution (9)
Bus code Admittance
1-2 2-j8
1-3 1-j4
2-3 0.666-j2.664
2-4 1-j4
3-4 2-j8
Bus Pg Qg Pd Qd Bus voltage
1 ? ? 0 0 1.06
2 0 0 0.5 0.2 ?(PQ)
3 0 0 0.4 0.3 ?(PQ)
4 0 0 0.3 0.1 ?(PQ)
Find the bus voltages V
2
and V
3
at the end of first iteration using GS method.
Use acceleration factor = 1.6
(b) Compare GS and NR method of load flow (5)
OR
2
Q.3
(a) With the help of a neat diagram explain turbine speed governing mechanism (7)
(b) Explain tie line load bias method of frequency control (7)
Q.4
(a) Derive the expression for B-coefficients in case of two generating plants (9)
connected to an arbitrary number of loads through a transmission network.
(b) A system having two generating units connected through a line has the (5)
following loss co-efficients
B
11
= 0.110
-2
MW
-1
, B
12
= -0.0110
-2
MW
-1
and B
22
= 0.1310
-2
MW
-1
Power is being dispatched economically with P
1
=120 MW and P
2
= 200 MW.
To raise the system load by 1 MW costs an additional Rs. 40 per hour. Find
the penalty factor of plant 1 and the additional cost per hour to increase the
output of plant 1 by 1 MW
OR
Q.4
(a) Explain point by point method of stability. State the assumptions made (9)
(b) Prove that synchronizing co-efficient of a machine should be positive for (5)
system stability
Q.5
(a) Discuss Z
BUS
building algorithm. Explain all types of modifications when (9)
transmission lines are added between the buses.
(b) Obtain Z
BUS
using Z
BUS
building algorithm for the system whose data (5)
is given below
Line no Bus code Impedance
1 R-1 0.6
2 R-2 0.5
3 1-3 0.25
4 2-3 0.5
Assume bus R as the reference bus
OR
Q.5
(a) Explain formulation of Y
BUS
using singular transformation. (7)
(b) Explain cascade tripping and network islanding in brief. (7)
**********
1
Seat No.: ________ Enrolment No.______________
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
B. E. - SEMESTER VII EXAMINATION WINTER 2012
Subject code: 170901 Date: 26/12/2012
Subject Name: Inter Connected Power System
Time: 10.30 am - 01.00 pm Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt any five questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 (a) I. Discuss various methods to improve steady state stability.
II. Explain terms: Cascading (blackouts), Islanding
04
03
(b) Form the Y
BUS
by using singular transformation method for the
network shown in Fig 1 including the generator buses.
Figure 1
07
Q.2 (a) Discuss advantages and limitations of Gauss-Siedel and Newton-
Raphson methods. Of the two, which method is generally
preferred for solving load flow problem?
06
(b) Discuss the algorithm of load flow solution using Newton-
Raphson method for all type of buses.
08
OR
(b) Figure 2 shows the one line diagram of simple three bus power
system with generator at buses 1 & 3. The magnitude of voltage
at bus 1 is adjusted to 1.05 pu. Voltage magnitude at bus 3 is
fixed at 1.04 pu with real power generation of 200 MW. A load
consisting of 400 MW and 250 Mvar is taken from bus 2. Line
impedances are marked in pu on 100 MVA base, and line
charging susceptances are neglected. Obtain Gauss-siedel power
flow solution for 2 iteration.
08
2
Figure 2 [PTO]
Q.3 (a) Discuss procedure for solving the swing equation using point by
point method.
07
(b) A 100 MVA, 2 pole, 60 Hz generator has a moment of inertia
50x10 kg.m
3
. (a) What is energy stored in the rotor at rated
speed? (b) What is the corresponding angular momentum? (c)
Determine the inertia constant H. (d) If the input to the generator
is suddenly increased by 25 MW, determine the rotor
acceleration.
07
OR
Q.3 (a) How can the transient stability of a system be improved? Discuss
the traditional as well as new approaches to the problem.
07
(b) A synchronous motor is receiving 35% of the power that it is
capable of receiving from an infinite bus. If the load on the motor
is doubled, determine the maximum value of load angle during
the swinging of motor around its new equilibrium position using
equal area criteria.
07
Q.4 (a) Show that when number of generating units are operating in
parallel and supplying power into a transmission network, the
most economical scheduling of load is obtained when their
incremental cost of received power are equal. Derive an equation
coordinating the incremental cost of production, the incremental
transmission loss and the incremental cost of received power.
07
(b) Incremental fuel costs in dollars per megawatthour for a plant
consisting of two units are given by
= 0.008 + 8.0 = 0.0096 + 6.4
Assume that both units are operating at all times, that total load
varies from 250 to1250 MW, and that maximum and minimum
loads on each unit are to be 625 and 100 MW, respectively. Find
the incremental fuel cost of the plant and the allocation of load
between units for the minimum cost of various total loads.
07
OR
Q.4 (a) Write short note on unit commitment. 07
3
*************
Q.4 (b) A two bus system is shown in figure 3. If 100 MW is transmitted
form plant 1 to the load, a transmission loss of 10 MW is
incurred. Find the required generation for each plant and the
power received by the load when the system is Rs 25/MWh.
= 0.02 +16.0 Rs/MWh, = 0.04 + 20.00 Rs/MWh
Figure 3
07
Q.5 (a) Describe speed governing system for controlling real power flow
in the system.
07
(b) Explain automatic load dispatch in power system. 07
OR [PTO]
Q.5 (a) Explain fully the flat frequency control method and selective
frequency control methods used for controlling frequency in
single/two area power system.
07
(b) Explain methods used for voltage control in power systems. 07
Plant 1
P
G1
P
G2
Load P
D2
Plant 2
1
Seat No.: ________ Enrolment No.___________
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
BE - SEMESTERVII EXAMINATION WINTER 2013
Subject Code: 170901 Date: 26-11-2013
Subject Name: Interconnected Power Systems
Time: 10:30 TO 01:00 Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 (a) Write a short note on how black out occurs in a large size power system. 07
(b) Give a list of methods to improve transient stability of a large size power system. 07
Q.2 (a) Describe the advantages of interconnections of power systems in details. 07
(b) Give comparison of GS method and NR method used for load flow studies of power
systems.
07
OR
(b) Write a short note on islanding of part of power system. 07
Q.3 (a) Discuss the algorithm of load flow solution using Newton-Raphson method for all
type of buses.
10
(b) Describe the concept of steady state stability in brief. 04
OR
Q.3 (a) State the assumptions made for load flow studies and applications of load flow
studies.
07
(b) Table given below gives the information of a four bus transmission network with line
impedances. The shunt admittance at all the buses is assumed negligible. Form a
suitable graph and find primitive admittance matrix and bus incidence matrix of the
network. Find Ybus of the system using these matrices.
Line, bus to bus R in pu X in pu Line, bus to bus R in pu X in pu
1-2 0.05 0.15 2-4 0.1 0.3
1-3 0.1 0.3 3-4 0.05 0.15
2-3 0.15 0.45
07
Q.4 (a) Describe unit commitment in detail. 07
(b) Derive the expression for B-coefficients in case of two generating plants connected to
an arbitrary number of loads through a transmission network.
07
OR
Q.4 (a) Explain the functions of load dispatch centre in detail. 07
(b) Describe the methods of voltage control adopted for large size power system in detail. 07
Q.5 (a) Describe flat frequency control and selective frequency control used for controlling
frequency in power system.
07
(b) In a two-bus system, two power plants are connected by a transmission line. If 100
MW is transferred from plant 1 to the load connected at bus 2, a transmission loss of
10 MW is incurred. Find the required generation for each plant and the power
received by load when the system is Rs 250/MWh. The incremental fuel costs of the
two plants are given below:
07
= 0.02
+ 16.0
= 0.04
+ 20.0
OR
2
Q.5 (a) Discuss procedure for solving the swing equation using point by point method. 07
(b) A synchronous generator of reactance 1.2 pu is connected to an infinite bus bar (|V| =
1.0 pu) through transformers and a line of total reactance of 0.06 pu. The generator no
load voltage is 1.2 pu and its inertia constant is H=4 MW-s/MVA. The resistance and
machine damping may be assumed negligible. The system frequency is 50 Hz.
Calculate the frequency of natural oscillations if the generator is loaded to (i) 50 %
and (ii) 80 % of its maximum power limit.
07
*************
Seat No.: ________ Enrolment No.___________
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
BE - SEMESTERVII EXAMINATION SUMMER 2014
Subject Code: 170901 Date: 22-05-2014
Subject Name: Interconnected Power Systems
Time: 02:30 pm - 05:00 pm Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 (a) Prove that in a Y
BUS
matrix, the off diagonal elements are negative of the transfer (7)
admittance connected between the two buses, while the diagonal elements are sum
of all admittances connected to that bus
(b) What is power angle curve? Draw power angle for synchronous generator and motor (7)
Also define steady state, transient and dynamic stability.
Q.2 (a) Explain cascade tripping and network islanding in brief (7)
(b) What is penalty factor? Discuss the criteria for economic dispatch when losses of (7)
of the system are considered
OR
(b) With the help of neat diagram explain turbine speed governing system (7)
Q.3 (a) A synchronous machine having a voltage of 0.910
0
is and having reactance of (6)
j0.3 pu is connected to an infinite bus having a voltage of 1 0
0
. Determine whether
synchronous machine
(i) is working as a generator or motor?
(ii) is absorbing active power or delivering active power to the bus?
(iii) is absorbing reactive power or delivering reactive power to the bus?
(iv) is working at leading p.f. or lagging p.f.?
Support your answer with valid reasons
(b) Discuss the dynamics of synchronous machine and hence derive the swing equation (8)
OR
Q.3 (a) Explain equal area criteria of stability (6)
(b) A power deficient area receives 50 MW over a tie line from another area. The (8)
maximum steady state capacity of the line is 100 MW. Find the allowable sudden
load that can be switched on without the loss of stability
Q.4 (a) Obtain Y
BUS
matrix for the system shown in figure (7)
(b) Compare NR and GS method of load flow (7)
OR
Q.4 (a) A constant load of 300 MW is supplied by two 200 MW generators 1 and 2 for (4)
which the respective fuel costs in Rs/hr are
dF
1
/dP
1
= 0.10P
1
+20; dF
2
/dP
2
= 0.12P
2
+ 15
Determine (i) the most economical division of load (ii) the savings in Rs/day
thereby obtained as compared to equal load sharing between the machines
(b) Figure shows a system having two plants 1 and 2 connected to buses 1 and 2. There (10)
two loads and a network of four branches. The branch currents and impedances are
I
1
= 4 j1 pu, I
2
= 3.2 j0.8 pu, I
3
= 7.2 j1.8 pu I
4
= 2 j0.5 pu,
Z
1
= 0.02 + j0.08 pu, Z
2
= 0.02+ j0.08 pu, Z
3
= 0.01 + j0.04 pu, Z
4
= 0.01 + j0.04 pu.
Calculate the loss coefficients of the system in pu.
Q.5 (a) Discuss the algorithm for formulating Z
BUS
matrix of system (10)
(b) In the equation Y
BUS
= A
T
YA, what are matrices Y and A? Also mention their (4)
dimensions
OR
Q.5 (a) Explain point by point method of stability in detail (10)
(b) A 100 MVA synchronous generator operates on full load at a frequency of 50 Hz (4)
A 40 MW load is suddenly removed from the system. Due to time lag in the
governor system, the steam valve begins to close after 0.5 seconds. Determine
the change in frequency that occurs in this time. Assume H = 5 MJ/MVA
*************
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 171011-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFDokumen2 halaman171011-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDokumen2 halamanInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksAmit PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDokumen2 halamanInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- 171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFDokumen3 halaman171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Methods in Power SystemsDokumen7 halamanComputer Methods in Power SystemssuhrudkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Power System AnalysisDokumen5 halamanPower System AnalysisVidyavihar ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Merged DocumentDokumen25 halamanMerged DocumentAshokAbiBelum ada peringkat
- ICPS Gtu PaperDokumen7 halamanICPS Gtu PaperHrushikesh DalichaBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksDokumen2 halamanSubject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksVinod KohliBelum ada peringkat
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDokumen4 halaman9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- Model Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationDokumen5 halamanModel Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationVinod KohliBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityHImanshu JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Be Winter 2020Dokumen2 halamanBe Winter 2020Rushikesh PandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Dokumen2 halamanSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Psa All Questions and AnswersDokumen8 halamanPsa All Questions and AnswersMODERN TELUGAMMAYIBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty of EngineeringDokumen2 halamanFaculty of Engineeringavinashavi93Belum ada peringkat
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Dokumen3 halamanWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Anonymous MYbA037ikBelum ada peringkat
- Power SystemDokumen3 halamanPower SystemMogaka LucasBelum ada peringkat
- Eeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Dokumen5 halamanEeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Kabir MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Dokumen2 halamanSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- EE75 August 2014Dokumen2 halamanEE75 August 2014MSGBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Nithiya MaharajanBelum ada peringkat
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDokumen4 halamanPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemestermahesBelum ada peringkat
- Ee2404 Set1Dokumen121 halamanEe2404 Set1Sachin Samy0% (1)
- Eee Iii Year 2017-2018Dokumen48 halamanEee Iii Year 2017-2018J JulietBelum ada peringkat
- PS7101 AdvancedPowerSystemAnalysisDokumen20 halamanPS7101 AdvancedPowerSystemAnalysismadhes14Belum ada peringkat
- Ee306 ADokumen3 halamanEe306 AAparna JoseBelum ada peringkat
- L-4rr-2/EEE 28/3/2022: DateDokumen39 halamanL-4rr-2/EEE 28/3/2022: DateSanjid ElahiBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankDokumen3 halaman2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankJeril joseBelum ada peringkat
- R05410204-Power System Operation and ControlDokumen6 halamanR05410204-Power System Operation and ControlSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- 117 GQ 052018Dokumen3 halaman117 GQ 052018Bala Raju ReddyboyaBelum ada peringkat
- May 2010Dokumen8 halamanMay 2010Viswa ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- NR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsDokumen6 halamanNR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- Psa Solved May 2019Dokumen18 halamanPsa Solved May 2019Bestowal Infotechs 2018Belum ada peringkat
- PSOC Assignment2015-2016 StudentsDokumen2 halamanPSOC Assignment2015-2016 StudentsVijaya Aditya TadepalliBelum ada peringkat
- QP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocDokumen8 halamanQP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocMohammed AlhakeemiBelum ada peringkat
- Nr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlDokumen8 halamanNr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Operation and ControlDokumen8 halamanPower System Operation and Controlrajaniram100% (2)
- PSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFDokumen10 halamanPSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFsagar R Rao0% (1)
- Faculty of EngineeringDokumen2 halamanFaculty of EngineeringAvĩńăśĥBůņņÿBelum ada peringkat
- Btech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Dokumen2 halamanBtech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Raj KamalBelum ada peringkat
- 209 Power System - 3Dokumen4 halaman209 Power System - 3sukirajBelum ada peringkat
- Psa ModelDokumen2 halamanPsa ModelSyed MeerBelum ada peringkat
- X10407EE8702 WatermarkDokumen4 halamanX10407EE8702 WatermarkP.Barani Tharan -EEEBelum ada peringkat
- C F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksDokumen3 halamanC F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksPranav R KrishBelum ada peringkat
- 1792Dokumen7 halaman1792Mohd AliBelum ada peringkat
- Seventh Sem 2015 BDokumen3 halamanSeventh Sem 2015 BMonisha S.Belum ada peringkat
- Rr310205 Electromechanics IIIDokumen8 halamanRr310205 Electromechanics IIISRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- Faculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsDokumen5 halamanFaculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsLibraryBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityTBelum ada peringkat
- Aishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailDokumen3 halamanAishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailSujesh ChittarikkalBelum ada peringkat
- R5410204-Power System Operation and ControlDokumen4 halamanR5410204-Power System Operation and ControlShakthi BoseBelum ada peringkat
- Eel301 2022Dokumen2 halamanEel301 2022rraj09102002Belum ada peringkat
- Eee Sem 7 Ee2404lmDokumen36 halamanEee Sem 7 Ee2404lmAnonymous gAVMpR0aBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Simulation Lab - QuestionsDokumen13 halamanPower System Simulation Lab - QuestionsMATHANKUMAR.SBelum ada peringkat
- QP End Term PS II 2021Dokumen2 halamanQP End Term PS II 2021Lovely Sarkar19UEE004Belum ada peringkat
- Power System - IDokumen8 halamanPower System - Isatya_vanapalli3422Belum ada peringkat
- CapsaDokumen4 halamanCapsasumikannuBelum ada peringkat
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDari EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Dari EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Belum ada peringkat
- Gujarati Grammer 4 PDFDokumen17 halamanGujarati Grammer 4 PDFJennifer CarlsonBelum ada peringkat
- Tie Up Hospital Esic SuratDokumen4 halamanTie Up Hospital Esic SuratPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- 47 March 2018 GyanparabDokumen30 halaman47 March 2018 GyanparabPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- HTTP 164.100.129.99 Mts Pdfprint VerifyprintDokumen2 halamanHTTP 164.100.129.99 Mts Pdfprint VerifyprintPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Fig: 1 Different SectorDokumen2 halamanFig: 1 Different SectorPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Bank Po PaperDokumen10 halamanBank Po Paperzipsy53Belum ada peringkat
- Rudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiDokumen389 halamanRudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiHarshad Ashodiya Interior Designer57% (14)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentsDokumen3 halamanCommissioning of Electrical EquipmentsPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 04Dokumen61 halamanLecture 04gurutheboss1100% (3)
- RRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Dokumen53 halamanRRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Palak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- RRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Dokumen53 halamanRRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Palak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank of English Vii Mani - Ram TezpurDokumen68 halamanQuestion Bank of English Vii Mani - Ram TezpurAparna Kalla MendirattaBelum ada peringkat
- 180904Dokumen2 halaman180904Palak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen1 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen1 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- P UtilizationDokumen1 halamanP UtilizationPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Practice and DesignDokumen1 halamanPower System Practice and DesignMeet Joshi50% (2)
- Advanced Power System IIDokumen2 halamanAdvanced Power System IIdurgesh_ahirBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machine Design IIDokumen1 halamanElectrical Machine Design IIMeet JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Regarding Departmental Elective.Dokumen1 halamanGuidelines Regarding Departmental Elective.Jay ThakarBelum ada peringkat
- Pessor and ControllersDokumen2 halamanPessor and ControllersPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen1 halamanGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Power System Questions Part3Dokumen1 halamanAdvanced Power System Questions Part3vagoliyoBelum ada peringkat
- 09 Teaching SchemeDokumen1 halaman09 Teaching SchemeRahul TilekarBelum ada peringkat
- P Electronics IIDokumen1 halamanP Electronics IIPalak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- 76953125005465Dokumen43 halaman76953125005465Palak AriwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Advance Java TechnologyDokumen2 halamanAdvance Java TechnologySagar LodhiyaBelum ada peringkat
- PAS Genap Daring V MathsDokumen3 halamanPAS Genap Daring V MathsAngel & Bryan SimanjuntakBelum ada peringkat
- Generation of Electric Power From Domestic Cooking PDFDokumen8 halamanGeneration of Electric Power From Domestic Cooking PDFnoumi diaBelum ada peringkat
- Mcqs On HeatDokumen13 halamanMcqs On HeatParshantKumarBajajBelum ada peringkat
- Power Transformer Testing FormatDokumen4 halamanPower Transformer Testing FormatSARAVANAN ABelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Panel Load Calculation (28!5!11)Dokumen28 halamanElectrical Panel Load Calculation (28!5!11)Kushtrim MalaBelum ada peringkat
- Series and Parellel Circuit: Madam Anati Syahirah Binti HedzirDokumen58 halamanSeries and Parellel Circuit: Madam Anati Syahirah Binti HedzirAnati Syahirah Binti HedzirBelum ada peringkat
- Ch5 - DC Motors - 2Dokumen101 halamanCh5 - DC Motors - 2abdullah1996Belum ada peringkat
- VLF-60KV 0.1Hz Ultra-Low Frequency High Voltage Generator (HV TANK)Dokumen19 halamanVLF-60KV 0.1Hz Ultra-Low Frequency High Voltage Generator (HV TANK)Horacio BerniBelum ada peringkat
- Time and DistanceDokumen43 halamanTime and Distancejubs100% (2)
- En 50438 2013-BSDokumen70 halamanEn 50438 2013-BSMario BreškiBelum ada peringkat
- Homework #03: A 1 ° 120 1 Turns 1Dokumen17 halamanHomework #03: A 1 ° 120 1 Turns 1Arturo Barradas0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Power Electronics - Unit 9 - Week 7 - DC-DC SWITCHED CONVERTERSDokumen3 halamanFundamentals of Power Electronics - Unit 9 - Week 7 - DC-DC SWITCHED CONVERTERSRakib BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics-A.K. MohantyDokumen548 halamanFluid Mechanics-A.K. MohantyMechpec Mech100% (1)
- PDFDokumen58 halamanPDFSyed MuneebBelum ada peringkat
- 2700-2790 ManualDokumen14 halaman2700-2790 ManualVaghela UttamBelum ada peringkat
- STD X Worksheets February 2022Dokumen12 halamanSTD X Worksheets February 2022Haresh Tripathy 2Belum ada peringkat
- Electric Machines - Ashfaq HusainDokumen642 halamanElectric Machines - Ashfaq Husainwocaja8645100% (1)
- Angular KinematicsDokumen42 halamanAngular KinematicsSaima JabbarBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 4Dokumen9 halamanPhysics 4Ronak JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 11-13 PDFDokumen106 halamanCHP 11-13 PDFLittle-psyco :30% (1)
- Physics Paper 1 TZ1 SLDokumen14 halamanPhysics Paper 1 TZ1 SLSurendraBelum ada peringkat
- Ensc26 Lecture02 PressureDokumen44 halamanEnsc26 Lecture02 PressureCassandra AyadBelum ada peringkat
- Balls On A StringDokumen53 halamanBalls On A StringQazi QaziBelum ada peringkat
- Phys1001 2010Dokumen2 halamanPhys1001 2010LUI MAN KITBelum ada peringkat
- Teja Question Paper On ForceDokumen6 halamanTeja Question Paper On ForceGamerithmsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 Thermal MeasurementsDokumen22 halamanChapter 11 Thermal MeasurementsGiovanni SlackBelum ada peringkat
- CIE O LEVEL SYLLABUS Physics 5054Dokumen40 halamanCIE O LEVEL SYLLABUS Physics 5054Sakib Ex-rccBelum ada peringkat
- Ivy A. Sanque Maria Nova D. Estacion S8FE-li-31 S8FE-li-33Dokumen3 halamanIvy A. Sanque Maria Nova D. Estacion S8FE-li-31 S8FE-li-33BENNY CALLOBelum ada peringkat
- The Laws of Physics Are UniversalDokumen41 halamanThe Laws of Physics Are UniversalHara DumbeloBelum ada peringkat
- Adjustable Passive Magnetic Constant Force ActuatorDokumen5 halamanAdjustable Passive Magnetic Constant Force ActuatormmcyoungBelum ada peringkat