DC Bus Voltage Regulation
Diunggah oleh
HasRasfa0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
110 tayangan2 halamanThis document discusses controlling the voltage of a DC bus for DC distribution systems using a three-phase bidirectional inverter and converter. The bidirectional inverter and converter allow power to flow between the DC bus and AC grid while regulating the DC bus voltage within a certain range. This control method prevents wide swings in DC bus voltage and improves the reliability of DC distribution systems without increasing the size of DC bus capacitors. The objectives are to control DC bus voltage, allow bidirectional power flow with power factor correction, and enhance the reliability of DC distribution systems. Benefits over existing systems include continuous DC voltage regulation, controlled output voltage, high power conversion capability, and support for both rectification and grid connection modes.
Deskripsi Asli:
DC Bus Voltage Regulation
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses controlling the voltage of a DC bus for DC distribution systems using a three-phase bidirectional inverter and converter. The bidirectional inverter and converter allow power to flow between the DC bus and AC grid while regulating the DC bus voltage within a certain range. This control method prevents wide swings in DC bus voltage and improves the reliability of DC distribution systems without increasing the size of DC bus capacitors. The objectives are to control DC bus voltage, allow bidirectional power flow with power factor correction, and enhance the reliability of DC distribution systems. Benefits over existing systems include continuous DC voltage regulation, controlled output voltage, high power conversion capability, and support for both rectification and grid connection modes.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
110 tayangan2 halamanDC Bus Voltage Regulation
Diunggah oleh
HasRasfaThis document discusses controlling the voltage of a DC bus for DC distribution systems using a three-phase bidirectional inverter and converter. The bidirectional inverter and converter allow power to flow between the DC bus and AC grid while regulating the DC bus voltage within a certain range. This control method prevents wide swings in DC bus voltage and improves the reliability of DC distribution systems without increasing the size of DC bus capacitors. The objectives are to control DC bus voltage, allow bidirectional power flow with power factor correction, and enhance the reliability of DC distribution systems. Benefits over existing systems include continuous DC voltage regulation, controlled output voltage, high power conversion capability, and support for both rectification and grid connection modes.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
DC-Bus Voltage Control with a Three-
Phase Bidirectional Inverter and
converter for DC Distribution Systems
ABSTRACT
Renewable power generation systems grow rapidly. By nature, renewable power
is not continuous and reliable. It will be converted into dc form and buffered with energy
storage elements. This brings dc-driving opportunities for electric appliance and
equipment which are mostly supplied with dc voltage sources. However, the distributed
generation systems require bidirectional inverters to control the power flow between dc
bus and ac grid, and to regulate the dc bus to a certain range of voltages. This paper
presents dc-bus voltage control with a three-phase bidirectional inverter for dc
distribution systems. The bidirectional inverter can fulfill both grid connection and
rectification modes with power factor correction approaches. hen the system is
operated in grid-connection mode, it needs a higher dc-bus voltage to prevent dramatic
voltage drop below the lower bound due to a step dc load increase. !nd the system
requires a lower dc-bus voltage to e"tend the range of voltage swing in rectification
mode. In the literature, there are some power flow controls for dc distribution system
with constant-power loads, such as general dc#dc converters. The bidirectional inverter
can fulfill both grid connection and rectification with power factor correction. This
method can prevent dc-bus voltage from wide variation and improve the availability of
the dc distribution systems without increasing dc-bus capacitance.
Objectives
To prevent dc-bus voltage from wide variation and improve the availability of the
dc distribution systems without increasing dc-bus capacitance.
To control the dc-bus voltage with a three-phase bidirectional inverter and
bidirectional converter for dc distribution systems.
To ma$e the bidirectional inverter to perform as both grid connection and
rectification modes with power factor correction.
To ma$e the bidirectional converter to perform as both grid connection and
rectification modes with power factor correction.
To improve the availability of the dc distribution system without increasing dc-
bus capacitance.
Drawbacks of existing system
%ow efficiency.
&ore components are required.
High losses during power conversion
High cost
Advantages of proposed system
'ontinuous regulation of dc bus voltage
'ontrolled output voltage
High power conversion can possible
Both the rectification and as well as grid connected mode can possible
'ontrolled output voltage.
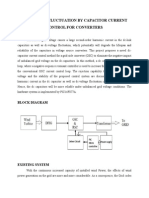
B%(') *I!+R!&
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Single Phase To Three Phase SystemDokumen57 halamanSingle Phase To Three Phase SystemASK projectsBelum ada peringkat
- Antilock Brakes PDFDokumen117 halamanAntilock Brakes PDFZak Carrigan100% (1)
- High-Efficiency Hybrid Resonant Converter for Wide PV Input RegulationDokumen76 halamanHigh-Efficiency Hybrid Resonant Converter for Wide PV Input RegulationVINAYBelum ada peringkat
- High Voltage DC Transmission: Presented byDokumen75 halamanHigh Voltage DC Transmission: Presented bySahnavaz Saiyyed100% (1)
- Grid Interface of Wind PowerDokumen34 halamanGrid Interface of Wind PowerM Paul PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- LCC HVDCDokumen7 halamanLCC HVDCSubbu ChBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC TechnologyDokumen48 halamanHVDC TechnologyIsrajuddinBelum ada peringkat
- ECE Capstone Design Project on Renewable Energy DC-DC Converter ControlDokumen19 halamanECE Capstone Design Project on Renewable Energy DC-DC Converter ControlSabir VeBelum ada peringkat
- Backup PolicyDokumen2 halamanBackup PolicyEdwin SemiraBelum ada peringkat
- DC Bus RegulationDokumen1 halamanDC Bus RegulationG Vignesh GvsBelum ada peringkat
- Isolated Bidirectional Grid-Tied Three-Phase Ac-Dc Power Conversion Using Series Resonant Converter Modules and A Three-Phase UnfolderDokumen26 halamanIsolated Bidirectional Grid-Tied Three-Phase Ac-Dc Power Conversion Using Series Resonant Converter Modules and A Three-Phase UnfolderTajudeen TajuBelum ada peringkat
- DC-Bus Voltage Regulation For DC Distributio N System: With Controllable DC LoadDokumen4 halamanDC-Bus Voltage Regulation For DC Distributio N System: With Controllable DC LoadPidikiti Surendra BabuBelum ada peringkat
- DC-Bus Voltage Regulation and Power Compensation With Bi-Directional Inverter in DC-Microgrid ApplicationsDokumen8 halamanDC-Bus Voltage Regulation and Power Compensation With Bi-Directional Inverter in DC-Microgrid ApplicationsAbi Yusuf AuliaBelum ada peringkat
- DC Voltage Fluctuation Control for ConvertersDokumen13 halamanDC Voltage Fluctuation Control for ConvertersVigneshInfotechBelum ada peringkat
- SSR HVDCDokumen8 halamanSSR HVDCsajedarefinBelum ada peringkat
- DC Voltage Controller For Asymmetric-Twin-Converter-Topology-Based High-Power StatcomDokumen4 halamanDC Voltage Controller For Asymmetric-Twin-Converter-Topology-Based High-Power StatcomRajasekar PanneerselvamBelum ada peringkat
- A DC-DC Converter With High Voltage Gain and Two Input Boost StagesDokumen5 halamanA DC-DC Converter With High Voltage Gain and Two Input Boost StagespandiBelum ada peringkat
- D StatcomDokumen11 halamanD Statcomdorababu2007Belum ada peringkat
- Bi-Directional Battery Management SystemDokumen28 halamanBi-Directional Battery Management SystemAjit NarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics 08 00774Dokumen15 halamanElectronics 08 00774Bruno HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- An Electromagnetic Transient Simulation Model ForDokumen4 halamanAn Electromagnetic Transient Simulation Model ForMohit Kumar ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges Faced in HVDC SystemsDokumen12 halamanChallenges Faced in HVDC SystemsPKBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Dokumen9 halamanHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)oeric2kBelum ada peringkat
- VSC HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source ConvertersDokumen9 halamanVSC HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source ConvertersKantipudi RajasekharBelum ada peringkat
- Multi LVL DC DC BoostDokumen9 halamanMulti LVL DC DC BoostDurga PrathibhaBelum ada peringkat
- Tapping Small Power from Composite AC-DC Transmission LinesDokumen84 halamanTapping Small Power from Composite AC-DC Transmission LinesRamkiran RishiBelum ada peringkat
- Efficiency Optimization Method For Cascaded Two-Stage Boost ConverterDokumen11 halamanEfficiency Optimization Method For Cascaded Two-Stage Boost ConverterragulkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Vehicle Charging Station With An Energy Storage Stage For Split-Dc Bus Voltage BalancingDokumen3 halamanElectric Vehicle Charging Station With An Energy Storage Stage For Split-Dc Bus Voltage BalancingJohn AjishBelum ada peringkat
- An Advanced Two Level Double Dual Boost ConverterDokumen5 halamanAn Advanced Two Level Double Dual Boost ConverterGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Dokumen10 halamanHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)kanthbcBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractDokumen8 halamanHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractVelu SamyBelum ada peringkat
- DC Hybrid Marine Electrical Distribution: Its Benefits and Other Technical CondsiderationsDokumen27 halamanDC Hybrid Marine Electrical Distribution: Its Benefits and Other Technical CondsiderationsAMARGEETH P MBelum ada peringkat
- Ijset 2014 201Dokumen7 halamanIjset 2014 201Innovative Research PublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Achieving Flexible Power Distribution with ABB's Onboard DC GridDokumen6 halamanAchieving Flexible Power Distribution with ABB's Onboard DC Gridashishdce7643Belum ada peringkat
- Dc-Voltage Fluctuation by Capacitor Current Control For ConvertersDokumen3 halamanDc-Voltage Fluctuation by Capacitor Current Control For ConvertersVigneshInfotechBelum ada peringkat
- A Literature Review On High Gain DC-DC Boost ConverterDokumen8 halamanA Literature Review On High Gain DC-DC Boost ConverterVidvek InfoTechBelum ada peringkat
- Apec 2017 7931118Dokumen6 halamanApec 2017 7931118saddlepointtechBelum ada peringkat
- Batch 10Dokumen68 halamanBatch 10Pidikiti Surendra BabuBelum ada peringkat
- A DC - DC Multilevel Boost Converter: J.C. Rosas-Caro J.M. Ramirez F.Z. Peng A. ValderrabanoDokumen9 halamanA DC - DC Multilevel Boost Converter: J.C. Rosas-Caro J.M. Ramirez F.Z. Peng A. ValderrabanoahmedBelum ada peringkat
- A DC - DC Multilevel Boost Converter: J.C. Rosas-Caro J.M. Ramirez F.Z. Peng A. ValderrabanoDokumen9 halamanA DC - DC Multilevel Boost Converter: J.C. Rosas-Caro J.M. Ramirez F.Z. Peng A. ValderrabanoahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Three Phase Current Controlled Voltage Source Rectifier For Battery Charging ApplicationDokumen13 halamanThree Phase Current Controlled Voltage Source Rectifier For Battery Charging ApplicationPriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemsDokumen33 halamanPower Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemssrilakshmisiriBelum ada peringkat
- Control of Three-Phase Inverter For AC Motor Drive With Small DC-Link Capacitor Fed by Single-Phase AC SourceDokumen8 halamanControl of Three-Phase Inverter For AC Motor Drive With Small DC-Link Capacitor Fed by Single-Phase AC SourceAnand KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Bidirectional Power Flow Control in DC Microgrid Through Switched-Capacitor Cell Using Hybrid DC-DC ConverterDokumen16 halamanBidirectional Power Flow Control in DC Microgrid Through Switched-Capacitor Cell Using Hybrid DC-DC ConverterKarthik SDBelum ada peringkat
- What Is HVDC TransmissionDokumen8 halamanWhat Is HVDC Transmissionajay deoBelum ada peringkat
- A Common Ground Switched-Quasizsource Bidirectional DC-DC Converter With Wide-Voltage-Gain Range For Evs With Hybrid Energy SourcesDokumen4 halamanA Common Ground Switched-Quasizsource Bidirectional DC-DC Converter With Wide-Voltage-Gain Range For Evs With Hybrid Energy SourcesBrightworld ProjectsBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC 3Dokumen16 halamanHVDC 3Avnish Kumar TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- HVDC SlidesDokumen25 halamanHVDC SlidesAreeb ZulkifleBelum ada peringkat
- DC-DC High-Voltage-Gain Converters With Low Count of Switches and Common GroundDokumen22 halamanDC-DC High-Voltage-Gain Converters With Low Count of Switches and Common GroundSzymon FBelum ada peringkat
- Power ElectronicsDokumen2 halamanPower ElectronicsG VigneshBelum ada peringkat
- Bi-Directional DC-to-DC Converter For Solar Applications With Battery BackupDokumen5 halamanBi-Directional DC-to-DC Converter For Solar Applications With Battery BackupPaulius BruneikaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Grid-Connected PV-Wind-Battery Based Multi-Input Transformer Coupled Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterDokumen10 halamanAnalysis of Grid-Connected PV-Wind-Battery Based Multi-Input Transformer Coupled Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterMagpie 2023Belum ada peringkat
- HVDC Transmission System: NeristDokumen25 halamanHVDC Transmission System: NeristKaran SinghaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Control of PV Array Based Distributed GeneratorDokumen9 halamanControl of PV Array Based Distributed GeneratorShareef KhanBelum ada peringkat
- PendahuluanDokumen10 halamanPendahuluanZoneoTakan Berpling DrimhuBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Phase Inverter ProposalDokumen4 halaman3 Phase Inverter ProposalAlan Walker100% (1)
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246Dokumen1 halamanSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246mydearteacherBelum ada peringkat
- Three-Phase, Power Quality Improvement ACDC Converters A ReviewDokumen27 halamanThree-Phase, Power Quality Improvement ACDC Converters A ReviewDr. Nitin LangerBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2 Part BDokumen6 halamanUnit-2 Part BMr. R. Jagan EEEBelum ada peringkat
- DC/DC Converter For Hevs and Resonant Active Clamping TechniqueDokumen6 halamanDC/DC Converter For Hevs and Resonant Active Clamping TechniqueMile BericBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Dokumen84 halamanAdvanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Aryesh Vasudevan NamboodiriBelum ada peringkat
- India's 2012 Blackouts Impacted Over 600 Million PeopleDokumen2 halamanIndia's 2012 Blackouts Impacted Over 600 Million PeopleHasRasfaBelum ada peringkat
- Regulation of DC VoltageDokumen6 halamanRegulation of DC VoltageHasRasfaBelum ada peringkat
- DC Bus VoltageDokumen12 halamanDC Bus VoltageHasRasfaBelum ada peringkat
- Regulation of DC BusDokumen2 halamanRegulation of DC BusHasRasfaBelum ada peringkat
- GSM BSNLDokumen23 halamanGSM BSNLAshok Kumar JBelum ada peringkat
- Developer Android Com 4Dokumen3 halamanDeveloper Android Com 4Mohammed MushtahaBelum ada peringkat
- Control & Monitoring ROTORKDokumen20 halamanControl & Monitoring ROTORKdiuska13Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorials For STM32F103RB: Nicolas BarbotDokumen13 halamanTutorials For STM32F103RB: Nicolas BarbotcarBelum ada peringkat
- D3D Workstations Dec22jan23Dokumen40 halamanD3D Workstations Dec22jan23gyuregabiBelum ada peringkat
- Acer Aspire 1670Dokumen66 halamanAcer Aspire 1670Roberto CanBelum ada peringkat
- Steps For Handling Page Fault - Easy NotesDokumen4 halamanSteps For Handling Page Fault - Easy NotesanuBelum ada peringkat
- ASUS G750JX-IB71 17.3Dokumen2 halamanASUS G750JX-IB71 17.3Mihai ZamfirBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco ME 3400 Series Ethernet Access Switches Technical OverviewDokumen105 halamanCisco ME 3400 Series Ethernet Access Switches Technical OverviewLephu ANBelum ada peringkat
- Picoblaze ManualDokumen75 halamanPicoblaze ManualmarcelinyBelum ada peringkat
- ORECK Weather Station ManualDokumen16 halamanORECK Weather Station ManualMR XBelum ada peringkat
- Installation & Operation Instructions: Mark II Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllersDokumen25 halamanInstallation & Operation Instructions: Mark II Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllersMUHAMMAD USMANBelum ada peringkat
- Data Protection and Management Participant Guide 1 PDFDokumen610 halamanData Protection and Management Participant Guide 1 PDFKevin YuBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de PhotoModelerDokumen5 halamanManual de PhotoModelerLuis Enrique Cotrina LeyvaBelum ada peringkat
- (G02!00!989) - FCC FO Clamps 8-14 - DC Clamps 22-32mm - Revision BDokumen1 halaman(G02!00!989) - FCC FO Clamps 8-14 - DC Clamps 22-32mm - Revision BChusé Antón Burillo ArbejBelum ada peringkat
- Types of I/O Commands & Techniques in Computer ArchitectureDokumen9 halamanTypes of I/O Commands & Techniques in Computer ArchitectureANUJ TIWARIBelum ada peringkat
- Sacombank Success Story Dcc3354 SacomBank CS v4Dokumen2 halamanSacombank Success Story Dcc3354 SacomBank CS v4thanh-truong-8011Belum ada peringkat
- Ospf StatesDokumen9 halamanOspf StatesnextinnovationBelum ada peringkat
- 3M 9700IPB ManualDokumen38 halaman3M 9700IPB ManualErich MagdzikBelum ada peringkat
- The Complexity of Theorem-Proving ProceduresDokumen8 halamanThe Complexity of Theorem-Proving ProceduresSrijit SanyalBelum ada peringkat
- DataSheet SWC515 Pinmount WM en 111001Dokumen6 halamanDataSheet SWC515 Pinmount WM en 111001GOW_23Belum ada peringkat
- OSS ReferenceDokumen336 halamanOSS ReferenceMonish R Nath50% (2)
- Sony Brochure of Cinealta VeniceDokumen52 halamanSony Brochure of Cinealta VeniceTodorBelum ada peringkat
- 74HC151Dokumen11 halaman74HC151jnax101Belum ada peringkat
- Anvyl ™ FPGA Board Reference Manual: Revised April 11, 2016 This Manual Applies To The Anvyl Rev. BDokumen16 halamanAnvyl ™ FPGA Board Reference Manual: Revised April 11, 2016 This Manual Applies To The Anvyl Rev. Bshivanand_shettennavBelum ada peringkat
- APGuide 2006Dokumen16 halamanAPGuide 2006Biblioteca Brasil AviationBelum ada peringkat
- TSR ProgrammingDokumen19 halamanTSR ProgrammingBen AvrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Active Directory: Troubleshooting: WorkshopplusDokumen2 halamanActive Directory: Troubleshooting: WorkshopplusMailbox 4allworkBelum ada peringkat
- Most Common Blue Screen ErrorsDokumen8 halamanMost Common Blue Screen ErrorsVinod_DELLBelum ada peringkat