ICT - 0418 - Y07 - SW - T05 (Data Types (22Kb) )
Diunggah oleh
Yenny TigaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ICT - 0418 - Y07 - SW - T05 (Data Types (22Kb) )
Diunggah oleh
Yenny TigaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SECTION 5 Data Types
Recommended Prior Knowledge Students should have completed Practical Unit 3
Context This section should be the fifth studied by the students. It builds on the knowledge obtained from studying all the previous sections.
Outline This section describes the theory of data structure and types.
section Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities Online Resources Other resources
5a Identify different data types: Use appropriate database software e.g. http://www.supersir.co.uk/data_ty (Walmsley, et. al., 2004,
• logical/Boolean, Microsoft Access, to demonstrate the pes.htm Chapter 5)
• alphanumeric/text, different data types
• numeric (real and integer) http://www.theteacher99.btinterne (Leadbetter, & Wainwright,
• date. t.co.uk/theteacher/gcse/newgcse/ 2004, 12.5)
module1/task1.htm
5b Select appropriate data types for a given Create a simple flat file database setting http://www.supersir.co.uk/data_ty (Walmsley, et. al., 2004, Chpts
set of data: all data types to ‘text’. Then discuss with pes.htm 5 & 13)
• logical/Boolean, students which data type would be most
• alphanumeric/text, suitable for each field. Ensure you have http://www.theteacher99.btinterne (Leadbetter, & Wainwright,
• numeric fields which will match each data type. t.co.uk/theteacher/gcse/newgcse/ 2004, 12.6)
• date. module1/task1.htm
5c Describe what is meant by the terms Use a table of data from, say, a http://www.theteacher99.btinterne (Walmsley, et. al., 2004,
• file, geography text book. Equate the table to a t.co.uk/theteacher/gcse/newgcse/ Chapter 5)
• record, file, a row to a record and a column to a module5/task1.htm
• field, field. Show them a typical computer (Leadbetter, & Wainwright,
• key field. database and go through each of the http://www.supersir.co.uk/Databa 2004, 12.4)
terms. se_design.htm
http://www.jegsworks.com/Lesso
ns/lesson1-2/lesson2-
4database.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcs
ebitesize/ict/databases/2databas
esrev2.shtml
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Practical Entity Framework: Database Access for Enterprise ApplicationsDari EverandPractical Entity Framework: Database Access for Enterprise ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- ICT - 0418 - Y07 - SW - T04 (Computer Networks (46Kb) )Dokumen3 halamanICT - 0418 - Y07 - SW - T04 (Computer Networks (46Kb) )Yenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Tle/Tvl - : Activity Sheet - Quarter 3 - MELC 5-6Dokumen6 halamanTle/Tvl - : Activity Sheet - Quarter 3 - MELC 5-6Mikasa AckermannBelum ada peringkat
- (Department of Computer Science) WarningDokumen6 halaman(Department of Computer Science) WarningAurang ZaibBelum ada peringkat
- IT21103 Lab ExercisewA - Answer SchemeFinalDokumen13 halamanIT21103 Lab ExercisewA - Answer SchemeFinalsitiBelum ada peringkat
- IAL IT Scheme-Of-Work For Unit 4 011019Dokumen34 halamanIAL IT Scheme-Of-Work For Unit 4 011019Anumi JayasingheBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Modern Database Management 11tDokumen29 halamanSolution Manual For Modern Database Management 11taimee_jc90% (10)
- DOKUMEN 3.2: Maklumat Terperinci Setiap Mata PelajaranDokumen7 halamanDOKUMEN 3.2: Maklumat Terperinci Setiap Mata PelajaranhoongchengBelum ada peringkat
- Cape Notes Unit 2 Database ManagementDokumen3 halamanCape Notes Unit 2 Database ManagementPratimaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Database: Learning PointsDokumen25 halamanIntroduction To Database: Learning PointsHoàng Vũ NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages and Disadvantages of A Computerized Database Advantages DisadvantagesDokumen6 halamanAdvantages and Disadvantages of A Computerized Database Advantages DisadvantagesOumotiaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Databases and Database UsersDokumen26 halamanChapter 1: Databases and Database Userssirheed77Belum ada peringkat
- Slides1 Introduction-MergedDokumen96 halamanSlides1 Introduction-MergedKiều TrinhBelum ada peringkat
- Dbms Lab ManualDokumen48 halamanDbms Lab ManualSai kiran BiradarBelum ada peringkat
- CIS-612 Advanced Visual BasicDokumen4 halamanCIS-612 Advanced Visual BasicPra SetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 DBMS Concepts and Architecture Introduction of DBMSDokumen16 halamanLecture 1 DBMS Concepts and Architecture Introduction of DBMSPOOJA SHARMABelum ada peringkat
- MIM Advanced Databases OutlineDokumen4 halamanMIM Advanced Databases Outlinebrittain markaleBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 DSDokumen48 halamanWeek 1 DSRajachandra VoodigaBelum ada peringkat
- Databases and Database Management Systems (DBMS)Dokumen12 halamanDatabases and Database Management Systems (DBMS)sagardeshmukh4Belum ada peringkat
- Data Basics MCQ's - T4TutorialsDokumen5 halamanData Basics MCQ's - T4TutorialsGashaw MekonnenBelum ada peringkat
- Data Structures: Model Course Syllabi andDokumen16 halamanData Structures: Model Course Syllabi andAftab AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- CSCE 156/156H/RAIK 184H Assignment 4 - Project Phase III Database DesignDokumen4 halamanCSCE 156/156H/RAIK 184H Assignment 4 - Project Phase III Database Designs_gamal15Belum ada peringkat
- Course Coordinatoi: DR.: SubjectDokumen8 halamanCourse Coordinatoi: DR.: Subjectmgrstudio100Belum ada peringkat
- Fall 2006: LIS 505 Information Systems and Technology SyllabusDokumen7 halamanFall 2006: LIS 505 Information Systems and Technology SyllabushongcuiBelum ada peringkat
- 06 BT-45 Basics of Computer ApplicationsDokumen9 halaman06 BT-45 Basics of Computer ApplicationsRaazia MirBelum ada peringkat
- Structural XML Query ProcessingDokumen41 halamanStructural XML Query ProcessingatifchaudhryBelum ada peringkat
- Data Structure and Algorithm COMP 202Dokumen53 halamanData Structure and Algorithm COMP 202lunaBelum ada peringkat
- CC4057NI - Introduction To Information Systems S21 (1st Sit) - CW2 QPDokumen5 halamanCC4057NI - Introduction To Information Systems S21 (1st Sit) - CW2 QPAshish GhishingBelum ada peringkat
- QALD-4 Open Challenge: Question Answering Over Linked DataDokumen17 halamanQALD-4 Open Challenge: Question Answering Over Linked DataMeo Meo ConBelum ada peringkat
- Cor Jesu College: Course SyllabiDokumen2 halamanCor Jesu College: Course Syllabirnave1120Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan DatabaseDokumen2 halamanLesson Plan DatabaseMuthu Muhammad NachiarBelum ada peringkat
- CG-Math031 SY2022-23 - HybridDokumen5 halamanCG-Math031 SY2022-23 - HybridJohn Emmanuel FormenteraBelum ada peringkat
- CS208 Principles of Data Base DesignDokumen3 halamanCS208 Principles of Data Base Designrichard miniBelum ada peringkat
- C Se 487 Course Outline Jan 28Dokumen4 halamanC Se 487 Course Outline Jan 28MonicaP18Belum ada peringkat
- Big Data Technologies: Course Code Level ProgramDokumen3 halamanBig Data Technologies: Course Code Level ProgramSubodh dhungelBelum ada peringkat
- Outline 2017Dokumen15 halamanOutline 2017Gladys Gladys MakBelum ada peringkat
- Course OutlineDokumen3 halamanCourse Outlinedejenedagime999Belum ada peringkat
- Operate Database Application Power PonitDokumen19 halamanOperate Database Application Power PonitAnonymous dLIq7U3DKzBelum ada peringkat
- Database Development Based On MFC Application in MDokumen9 halamanDatabase Development Based On MFC Application in MKhalil TemmarBelum ada peringkat
- EnsembleDokumen12 halamanEnsembleMahesh RamalingamBelum ada peringkat
- Is HDB Content ListDokumen2 halamanIs HDB Content ListcosideskBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Outcomes:: 4.7.1. Explain What A Database Is and How It Is Organised and OperatedDokumen15 halamanLearning Outcomes:: 4.7.1. Explain What A Database Is and How It Is Organised and OperatedVallenshia Vaezera UaatjoBelum ada peringkat
- Illustrated Microsoft Office 365 and Access 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Friedrichsen Solutions Manual 1Dokumen36 halamanIllustrated Microsoft Office 365 and Access 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Friedrichsen Solutions Manual 1heidihoffmankpqearxdwi100% (23)
- Illustrated Microsoft Office 365 and Access 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Friedrichsen Solutions Manual 1Dokumen8 halamanIllustrated Microsoft Office 365 and Access 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Friedrichsen Solutions Manual 1gloria100% (38)
- Unit 2.4: Bioinformatics and DatabasesDokumen55 halamanUnit 2.4: Bioinformatics and DatabasesBala SubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- Web Based Programming 1 Syllabus TemplateDokumen5 halamanWeb Based Programming 1 Syllabus TemplateHanz Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Data Mining and Warehousing LabDokumen4 halamanData Mining and Warehousing LabPhamThi ThietBelum ada peringkat
- A Framework For Metadata Creation ToolsDokumen12 halamanA Framework For Metadata Creation Toolsruxandra28Belum ada peringkat
- Databases: DSIC. Academic Year 2010-2011Dokumen19 halamanDatabases: DSIC. Academic Year 2010-2011Youkie MarsBelum ada peringkat
- Field Tech Manuals (GIS, GPS, RS) GIS Database ConceptsDokumen22 halamanField Tech Manuals (GIS, GPS, RS) GIS Database ConceptsKamil UsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Database Management Systems: IV SemesterDokumen2 halamanDatabase Management Systems: IV SemesterRamu SitaBelum ada peringkat
- PM LabDokumen93 halamanPM Labtejaavirneni1315Belum ada peringkat
- ISD IISEM ME-v1 PDFDokumen220 halamanISD IISEM ME-v1 PDFnvrsaynoBelum ada peringkat
- Baeza Yates 2003Dokumen8 halamanBaeza Yates 2003api-3803202Belum ada peringkat
- Dbms MANUALDokumen98 halamanDbms MANUALYogita GhumareBelum ada peringkat
- DbmsDokumen60 halamanDbmsneerajsingh30101994Belum ada peringkat
- 63.271: Data Structures Syllabus: Catalog DescriptionDokumen3 halaman63.271: Data Structures Syllabus: Catalog DescriptionWizzman LastBelum ada peringkat
- NetworkingDokumen12 halamanNetworkingcaseyfarmerBelum ada peringkat
- 72552Dokumen8 halaman72552Andres GuevaraBelum ada peringkat
- RG - Computer Science-SSC - After IRC On 29 Mar 2019 PDFDokumen9 halamanRG - Computer Science-SSC - After IRC On 29 Mar 2019 PDFediealiBelum ada peringkat
- Decay EquationsDokumen1 halamanDecay EquationsYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatic NotesDokumen9 halamanElectrostatic NotesYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise: Use The Table Above As A Guide To Answer The Following QuestionsDokumen1 halamanExercise: Use The Table Above As A Guide To Answer The Following QuestionsYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- TransformersDokumen2 halamanTransformersYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 ThermometerDokumen1 halaman2011 ThermometerYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Notes - Radiation Related TermsDokumen7 halamanNotes - Radiation Related TermsYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Presentation - Haadi & AqilDokumen11 halamanPhysics Presentation - Haadi & AqilYenny Tiga100% (1)
- Cie o Level Physics Syllabus For Year 2012Dokumen46 halamanCie o Level Physics Syllabus For Year 2012Sakib Ex-rccBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALDokumen24 halamanRevision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALYenny Tiga100% (3)
- Work Energy Cartoon DiscussionDokumen2 halamanWork Energy Cartoon DiscussionYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Additional Results Reporting June 20101Dokumen4 halamanA Guide To Additional Results Reporting June 20101Mohsin SadiqBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics, VectorDokumen1 halamanKinematics, VectorYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Examiner Tips For O Level Physics 5054Dokumen10 halamanExaminer Tips For O Level Physics 5054muzaahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter: Work, Energy & Power Work: Case Description Work Done? ExplanationDokumen1 halamanChapter: Work, Energy & Power Work: Case Description Work Done? ExplanationYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
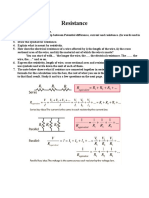
- ResistanceDokumen1 halamanResistanceYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure ExerciseDokumen2 halamanPressure ExerciseYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer 1Dokumen1 halamanTransformer 1Yenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- TransformerDokumen3 halamanTransformerYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsDokumen9 halamanMaths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Resistance ExDokumen1 halamanPhysics Resistance ExYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Uses of RadioactivityDokumen2 halamanUses of RadioactivityYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conversion and ConservationDokumen4 halamanEnergy Conversion and ConservationYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Index of Refraction& Snells WorksheetDokumen1 halamanIndex of Refraction& Snells WorksheetYenny Tiga0% (1)
- Travel and Tourism SOW - Front Page (Word 97-2003)Dokumen38 halamanTravel and Tourism SOW - Front Page (Word 97-2003)Yenny Tiga100% (3)
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2011Dokumen6 halamanMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2011Yenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsDokumen9 halamanMaths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Dokumen3 halamanMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Yenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Introduction CoverDokumen1 halamanMaths Introduction CoverYenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Dokumen6 halamanMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny Tiga100% (2)
- Maths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Dokumen3 halamanMaths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Yenny TigaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study - EducationDokumen1 halamanCase Study - EducationA. B. M Ishtiaque AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Bishnoi Community Born Out of Environmental Compulsion and ConvictionDokumen2 halamanBishnoi Community Born Out of Environmental Compulsion and ConvictionAyush ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- RecommendationDokumen5 halamanRecommendationitsezBelum ada peringkat
- Years: University of The PhilippinesDokumen24 halamanYears: University of The PhilippinesAfricaEdnaBelum ada peringkat
- My Map: Step 1. I Will Review The Principles of Learning On Pp. 21-25 ofDokumen26 halamanMy Map: Step 1. I Will Review The Principles of Learning On Pp. 21-25 offitz zamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurvedic Case RecordingDokumen75 halamanAyurvedic Case Recordingnilesh_manakikarBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Design For CONTEXTUALIZED MATERIALSDokumen3 halamanActivity Design For CONTEXTUALIZED MATERIALSJhon Mark Minggito BanhawBelum ada peringkat
- Promotion Policy 11 January WAPDADokumen28 halamanPromotion Policy 11 January WAPDANigah Hussain100% (1)
- Equivalent Record Form: Department of Education MIMAROPA RegionDokumen1 halamanEquivalent Record Form: Department of Education MIMAROPA RegionEnerita AllegoBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Dokumen36 halamanGrade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Mariyah QPBelum ada peringkat
- Repertoire Spring 2016Dokumen19 halamanRepertoire Spring 2016Connor McMillan100% (1)
- Policy Changes: Offered in The Morning or Is Clashing With Another Core Course Then They May Take Core Course in TheDokumen1 halamanPolicy Changes: Offered in The Morning or Is Clashing With Another Core Course Then They May Take Core Course in ThesirfanalizaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Idea 2 TemplateDokumen2 halamanLesson Idea 2 Templateapi-689669314Belum ada peringkat
- Accomplishment Report in District PopDev 2023Dokumen2 halamanAccomplishment Report in District PopDev 2023ジーニー ベイブス100% (1)
- Infection-Prevention-Control HDFDokumen15 halamanInfection-Prevention-Control HDFArlene AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Order of ProcessionDokumen3 halamanOrder of ProcessionTrisha Ma Louisse RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Choral Pedagogy and Vocal HealthDokumen7 halamanChoral Pedagogy and Vocal Healthradamir100% (1)
- Leveled Readers in EnglishDokumen88 halamanLeveled Readers in EnglishKristine NatanawanBelum ada peringkat
- T.S. Eliot BiographyDokumen2 halamanT.S. Eliot BiographyWeber LiuBelum ada peringkat
- Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan in Music 6 - For C.ODokumen4 halamanSemi - Detailed Lesson Plan in Music 6 - For C.OZai92% (13)
- Prediction As A Reading StrategyDokumen93 halamanPrediction As A Reading StrategySouhil BenaskeurBelum ada peringkat
- Z Fuller 16343229 102091 Drama2b 1h 2016 Assessment 2Dokumen26 halamanZ Fuller 16343229 102091 Drama2b 1h 2016 Assessment 2api-305377750Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1: The Nature of AccountingDokumen6 halamanFundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1: The Nature of AccountingMylen Noel Elgincolin ManlapazBelum ada peringkat
- S3B The Brain Parts and FunctionDokumen1 halamanS3B The Brain Parts and FunctionNSABIMANA JANVIERBelum ada peringkat
- Lyric Shame - Gillian WhiteDokumen361 halamanLyric Shame - Gillian WhiteXaverius MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation RubricsDokumen7 halamanEvaluation RubricsopositionsBelum ada peringkat
- Flip Certification GuidlinesDokumen10 halamanFlip Certification GuidlinesSingh AbBelum ada peringkat
- Tcs 3Dokumen2 halamanTcs 3learn2hackBelum ada peringkat
- FMF Program Officer 2 Position DescriptionDokumen1 halamanFMF Program Officer 2 Position DescriptionmeronBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Nursing Judgment 1Dokumen5 halamanClinical Nursing Judgment 1api-601489653Belum ada peringkat