Differential Equations Note Card.4
Diunggah oleh
Nicholas ManiaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Differential Equations Note Card.4
Diunggah oleh
Nicholas ManiaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
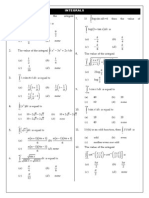
( )
( )}
{ (
)}
DE
{ ( )}
{ ( )}
{ ( )}
()
( )
(
(
)
|
{ ( )
( )
( )}
Tran in s
( )}
()
Tran in t
{ (
)}
Hipster form
{ () (
Inverse
{ ( )
( )
( )
(
(
)
)
( )
{ ( )}
}
( )
{ (
)}
{ ( )}|
( )
[(
) (
]
( )
( )
( )
st
( )
( )
)
2.)Solve Auxiliary equation and generate
yc based off cases
3.) Solve as var par only if ( )
originally, otherwise y is yc
Differential Operator
or-
( ( ))
( ))
[
(
Ex.)
( )
1.) Distinct real roots:
( )
[
( )
Exact:
2.) Repeating real:
3.) Distinct complex:
4.) Repeating complex:
Sub for Y and solve like 1 order linear
Cauchy_Euler Equation
)
)]
Bernoullis Equation (sub):
( )
Multiply and continue as Exact
Cauchy-Euler Cases
( )
( )
Separation of var
4: repeating complex
Simplest Annihilator:
Non Exact
2: repeating real
3: distinct complex
( )
Cases for m
1: distinct real
( )
Gamma
Linear Sub:
( )
)}
)}
( )
( )
{ ( )|
) (
Separation of var
( )
5.) compare the function in step 4 and yc to get a form
of yp
6.)solve for coefficients in yp
7.) general solution is
Fourier Series:
()
Inverse
{ (
( )
( )|
)
)
)
( )
( )
)( )
( )
( )]
Use Annihilator to solve DE:
)
)
(
( )
Tip: After step 3 check. It should be the product rule
4.) Integrate Ratios
Inverse:
[ ( )]}
[ ( )]
( ) (
)
{ } { } ( )( )
( )
{ ( ) }
)(
2.) Find yc ; yc=c1 y1+c2 y2+
3.) calculate the following determinates (Kramers rule)
( )
1.) Change lead coefficient to 1 if needed
( )
( )
Int:
{
(
(
( )
( )
( )}
( )
Var. Par.
Derivatives:
)
(
()
( )
)(
( )
{ }
{ ( )}
Differential op.
(
( ))
( ))]
(
( ))]
( )
( )
( )}
( )
Mixture of Two Solutions:
th
( )
( )
() ( )
)
()
q z
)
)C
)T G S
Homogenous DE (sub):
1.) see if all the same degree
2.) use one of the following subs
( )
( )
Solve n order lin. Homo. DE
( )
( )
( ) ( )
( )}
Def.
( )
( )}
Linear 1 Order DE (Integrating Factor)
()
Newtons Law of Cooling/Warming:
st
Rate Problems: Growth & Decay:
1. separate 2. integrate
3. solve for dependent var if possible
Exact
{ }
{ }
Separation of variables
() ()
{ }
Reduc. Of Order
( )
( )
( )
1.) one of the solutions is given y 1
( ) ( )
3.) sub back in to DE
4.) solve for u, a w may be needed
Nonlinear DE
)
)
( ) Dep var miss.
( ) Indie var miss.
2.) sub & solve
Nonlinear DE
( )
( )
( )
)
)
)
Solving System of Linear DE by Elimination
Ex.)
1.) Re-write Using D ex.)
2.) Move all dep. var. to one side; line up like var.
Ex.)
3.) Eliminate one var. then solve DE.
(
may be need)
4.) Solve for other var. by using the initial relationship if
app. Ex)
Solving DEs using POWAHR! Seriesses ex.)
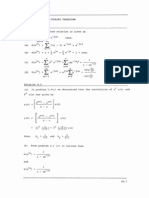
Check If Linear Independent
(
(
(
(
)
)
(
(
)
)
(
(
)
|
|
( )
) (
(
)
(
(
)
( )
( )
( )
2.)sub back into DE.
3.)Change
to
th
4.)Evaluate the non-common ks and leave the common k terms generalized
5.) set eqqualt to zero and calculate therms
6.) solution
Simplify in terms of and
Ex.)
|
|
( )
)
)
( )
(
(
( )
Solve
( ) (ODE)
(
)
( )
1. Replace ( ) with 0
th
2. Solve for
as demonstrated in Solve n order lin. Homo. DE box
3. Find a form for
as listed in the cases for ( ), compare
and
and fix duplicates by multiplying by an
4. Set
( ), and solve for the coefficients.
Final solution:
Otherwise, repeat step 3 for other var.
(
(
(
|
|
ODE Cases
( )
Any constant
)
2.) sub & solve; another term of w
may be needed
Differential Equations Note Card
For: SUNY Orange
By: Nicholas Mania (Class 2012)
REV.4 July 2013
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetDokumen2 halamanME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetPhyo Wai Aung67% (9)
- Interpolation Filters For Oversampled Audio DACsDokumen23 halamanInterpolation Filters For Oversampled Audio DACsIvar Løkken100% (3)
- Panel Data Lecture NotesDokumen38 halamanPanel Data Lecture NotesSanam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- A. Christie - B.A. - ThesisDokumen43 halamanA. Christie - B.A. - ThesisDonato PaglionicoBelum ada peringkat
- Mcwhirter. Video Essays and Film CriticismDokumen9 halamanMcwhirter. Video Essays and Film CriticismJames MacDowellBelum ada peringkat
- Dee Brown (Writer) PDFDokumen4 halamanDee Brown (Writer) PDFdantevantesBelum ada peringkat
- Road To A Star FMDokumen14 halamanRoad To A Star FMSyafiq KayBelum ada peringkat
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDokumen12 halamanEigenvalues and EigenvectorsGalih Nugraha100% (1)
- GATE Mathematics Paper 2011Dokumen8 halamanGATE Mathematics Paper 2011RajkumarBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Chapter 3 Differentiation 5oktDokumen38 halaman03 Chapter 3 Differentiation 5oktMohd ShahidBelum ada peringkat
- Transform Analysis of LTI SystemsDokumen117 halamanTransform Analysis of LTI SystemsreneeshczBelum ada peringkat
- Differential and Difference EquationsDokumen31 halamanDifferential and Difference EquationscavanzasBelum ada peringkat
- FODE 4 LecturesDokumen32 halamanFODE 4 LecturesZaid PeroBelum ada peringkat
- $RM3GFU6Dokumen14 halaman$RM3GFU6bacchuskevin10Belum ada peringkat
- Uraian FourierDokumen91 halamanUraian FourierAgus Dian PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- New Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential EquationsDokumen6 halamanNew Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential EquationsresearchinventyBelum ada peringkat
- Stochastic Structural Dynamics Lecture-10: Random Vibrations of Sdof Systems-2Dokumen46 halamanStochastic Structural Dynamics Lecture-10: Random Vibrations of Sdof Systems-2Kajal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3Dokumen11 halamanAssignment 3Shawn DeolBelum ada peringkat
- Maulina Putri Lestari - M0220052 - Tugas 3Dokumen10 halamanMaulina Putri Lestari - M0220052 - Tugas 3Maulina Putri LestariBelum ada peringkat
- BM 503 Basic Mathematics For Biomedical Science W5Dokumen185 halamanBM 503 Basic Mathematics For Biomedical Science W5Yasin CoturBelum ada peringkat
- Concourse 18.03 - Lecture #9: MX CX KX X X XDokumen4 halamanConcourse 18.03 - Lecture #9: MX CX KX X X XAna Petrovic TomicBelum ada peringkat
- Lapplace TransformDokumen22 halamanLapplace TransformAnthony KwoBelum ada peringkat
- Differentialequations EC400 MT2013 PDFDokumen20 halamanDifferentialequations EC400 MT2013 PDFAvijit PuriBelum ada peringkat
- F (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereDokumen9 halamanF (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereAlbert WillyBelum ada peringkat
- X X X DX: - 1 2 3 - Log Sin XDXDokumen6 halamanX X X DX: - 1 2 3 - Log Sin XDXJimmy SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Maths TestDokumen4 halamanMaths TestWang PengyuBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Dokumen9 halamanLecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)shinee_jayasila2080Belum ada peringkat
- 18.03 Study Guide and Practice Hour Exam II, March, 2006 I. Study GuideDokumen6 halaman18.03 Study Guide and Practice Hour Exam II, March, 2006 I. Study GuideemmyrovicBelum ada peringkat
- Eee2035F Exam Signals and Systems I: University of Cape Town Department of Electrical EngineeringDokumen3 halamanEee2035F Exam Signals and Systems I: University of Cape Town Department of Electrical EngineeringRubia IftikharBelum ada peringkat
- Summary (WS8-9)Dokumen2 halamanSummary (WS8-9)Mohammed KhalilBelum ada peringkat
- LADE18 Linear Constant Coeffient DEsDokumen18 halamanLADE18 Linear Constant Coeffient DEsRoumen GuhaBelum ada peringkat
- Crtanje Faznog PortretaDokumen7 halamanCrtanje Faznog Portretafeniks5Belum ada peringkat
- MMP AssignmntDokumen3 halamanMMP AssignmntNitasha HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Outline of Solutions To Homework 1Dokumen3 halamanOutline of Solutions To Homework 1Michel AndradeBelum ada peringkat
- Section A3.4: Power Series SolutionDokumen7 halamanSection A3.4: Power Series SolutionAdzar JumaaniBelum ada peringkat
- 10-1 and 13-1 Overheads (Landscape) PDFDokumen10 halaman10-1 and 13-1 Overheads (Landscape) PDFHabtamu GeremewBelum ada peringkat
- F616662GATE Mathematics Paper-2009Dokumen7 halamanF616662GATE Mathematics Paper-2009RajkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Green's Functions in Mathematical PhysicsDokumen10 halamanGreen's Functions in Mathematical PhysicsZow NiakBelum ada peringkat
- Ma 266 ReviewDokumen9 halamanMa 266 ReviewiiiiiiiBelum ada peringkat
- 1 To 3Dokumen14 halaman1 To 3needtoknowBelum ada peringkat
- Section 4.2: Homogeneous Equations With Constant CoefficientsDokumen2 halamanSection 4.2: Homogeneous Equations With Constant CoefficientsJuan AriasBelum ada peringkat
- Fourier Transform PairsDokumen1 halamanFourier Transform PairsNaggerpusBelum ada peringkat
- Multivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Dokumen5 halamanMultivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Belum ada peringkat
- Ordinary Differential EquationDokumen73 halamanOrdinary Differential EquationWahyu SutrisnoBelum ada peringkat
- 11 em One MarkDokumen20 halaman11 em One MarkR.SrinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture07 PDFDokumen3 halamanLecture07 PDFss_nainamohammedBelum ada peringkat
- HW1 AaDokumen2 halamanHW1 AaFatemeh NikraftarBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank M201Dokumen9 halamanQuestion Bank M201joydeep12Belum ada peringkat
- Numerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsDokumen14 halamanNumerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsMaz AmininBelum ada peringkat
- Finite DifferenceDokumen27 halamanFinite DifferencePhung NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- CE 809 - Lecture 2 - Free Vibration Response of SDF SystemsDokumen31 halamanCE 809 - Lecture 2 - Free Vibration Response of SDF SystemsArslan UmarBelum ada peringkat
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDokumen18 halamanOrdinary Differential EquationsNawar CullenBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency Responses For Sampled-Data SystemsDokumen9 halamanFrequency Responses For Sampled-Data SystemsrcloudtBelum ada peringkat
- 99ebook Com ErrataDokumen12 halaman99ebook Com ErrataghalzaiBelum ada peringkat
- K. K. Wagh Institute of Engineering Education & Research, Nashik-3 Open Book TestDokumen2 halamanK. K. Wagh Institute of Engineering Education & Research, Nashik-3 Open Book TestTaniyaBelum ada peringkat
- Y (N) U (N) : N+L N+LDokumen9 halamanY (N) U (N) : N+L N+Lapi-127299018Belum ada peringkat
- Laplace Transform of The Dirac Delta Function PDFDokumen6 halamanLaplace Transform of The Dirac Delta Function PDFmuchapeBelum ada peringkat
- 461 1698 1 PB PDFDokumen15 halaman461 1698 1 PB PDFSirtumnusFaunoBelum ada peringkat
- More On Functions 2 REDONE 2022Dokumen11 halamanMore On Functions 2 REDONE 2022Lazy BanditBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDari EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesDari EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- String-: By-Anushka GuptaDokumen4 halamanString-: By-Anushka GuptaNayanika AcharjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Subfiles by Michael CataliniDokumen508 halamanSubfiles by Michael Catalinignani123Belum ada peringkat
- Ravi Goyal ResumeDokumen4 halamanRavi Goyal Resumemanoj yadavBelum ada peringkat
- NoSQL Data Management1Dokumen32 halamanNoSQL Data Management1Aitha SankarBelum ada peringkat
- Minitab 16: ANOVA, Normality, Tukey, Control ChartsDokumen63 halamanMinitab 16: ANOVA, Normality, Tukey, Control Chartsciano654Belum ada peringkat
- Welcome To Excel VBA Eas1Dokumen115 halamanWelcome To Excel VBA Eas1Shailesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Zybo LinuxDokumen37 halamanZybo LinuxSyam SanalBelum ada peringkat
- Greer Citizen E-Edition 11.21.18Dokumen16 halamanGreer Citizen E-Edition 11.21.18greercitizenBelum ada peringkat
- How To Find If A Wage Type Is Taxable or Not - SAP Q&ADokumen4 halamanHow To Find If A Wage Type Is Taxable or Not - SAP Q&AMurali MohanBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Database 12c SQLPlus® Quick Reference PDFDokumen18 halamanOracle Database 12c SQLPlus® Quick Reference PDFBupBeChanhBelum ada peringkat
- Walther Von Der Vogelweide - PoemsDokumen197 halamanWalther Von Der Vogelweide - PoemsYvo YeomansBelum ada peringkat
- OFDMADokumen29 halamanOFDMAterryBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-7 OF TAW10-1 Working With Elementary Data ObjectsDokumen11 halamanUNIT-7 OF TAW10-1 Working With Elementary Data ObjectsSandeep AminBelum ada peringkat
- IBM DS3200 System Storage PDFDokumen144 halamanIBM DS3200 System Storage PDFelbaronrojo2008Belum ada peringkat
- Java Threading AssignmentDokumen32 halamanJava Threading Assignmentkumarharsh100% (2)
- How To Install Native Instruments Download Products (PC)Dokumen2 halamanHow To Install Native Instruments Download Products (PC)Jonathan BatesBelum ada peringkat
- Roboteics Lab ReportDokumen11 halamanRoboteics Lab ReportDoodee MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Data Normalization and StandardizationDokumen6 halamanData Normalization and StandardizationAllan SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 7 Introduction To Airbag FoldingDokumen12 halamanTutorial 7 Introduction To Airbag Foldingarthurs9792100% (1)
- Mikrotik Mpls y LPDDokumen4 halamanMikrotik Mpls y LPDMarco Antonio ChávarriBelum ada peringkat
- ICT Final Exam For Grade 9Dokumen4 halamanICT Final Exam For Grade 9YibeltalBelum ada peringkat
- Tukey 1980Dokumen4 halamanTukey 1980vakalaoBelum ada peringkat
- MultiplexersDokumen23 halamanMultiplexersAsim WarisBelum ada peringkat
- WEEK 6 Ctood PDFDokumen11 halamanWEEK 6 Ctood PDFDHARAM TEJ DBelum ada peringkat
- SQL Server 2000 To 2008 Upgrade White PaperDokumen41 halamanSQL Server 2000 To 2008 Upgrade White PaperdivandanBelum ada peringkat
- Lock Order DependenciesDokumen120 halamanLock Order DependenciesVũ Minh DũngBelum ada peringkat
- Big Data of Materials Science: Critical Role of The DescriptorDokumen5 halamanBig Data of Materials Science: Critical Role of The DescriptorDivyansh SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- CSeguro ResDokumen2 halamanCSeguro ResCatherine SeguroBelum ada peringkat