MCAT Physics Equation List
Diunggah oleh
Chris_Barber09Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MCAT Physics Equation List
Diunggah oleh
Chris_Barber09Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MCAT Physics Equation List (Formulas)
2/24/12 12:43 PM
Go to: Gold Standard MCAT | MCAT Organic Chemistry
MCAT Physics Equation Lists (Formulas)
alpha: a
mu:
delta:
If you don't see the Greek symbols above then the equations below will not make
sense; thus adjust fonts on your browser to Unicode.
Memorize These!
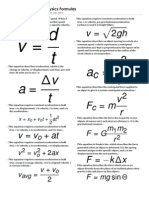
Translational motion
x = x 0 + v 0 t + 1/2at2
V = Vo + at
Frictional force
f max =
k < s always
Uniform circular motion
Fc = mac = mv2 /r
ac= v2 /r
Momentum, Impulse
I = F t = M
M = mv
Work, Power
W = F d cos
P = W/t
Energy (conservation)
ET = Ek + Ep
E = mc2
Spring Force, Work
F = -kx
W = kx2 /2
Continuity (fluids)
A v = const.
Av = const.
Current and Resistance
I = Q/t
R = l/A
Resistors (series, par.)
Req = R1 + R2 . . .
1/ Req = 1/ R1 +1/ R2
Sound
dB = 10 log 10 (I/I0 )
beats = f
Kirchoff's Laws
i = 0 at a junction
V = 0 in a loop
Thermodynamics
Q = mc T (MCAT !)
Q = mL
http://www.goldstandard-mcat.com/physics-equation-lists/
Page 1 of 5
MCAT Physics Equation List (Formulas)
2/24/12 12:43 PM
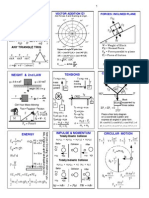
Torque forces
L1 = F1 r1 (CCW + ve)
L2 = F2 r2 (CW -ve)
Torque force at EQ
Fx = 0 and Fy = 0
L = 0
Refraction
( sin 1 )/(sin 2 ) = v1 /v2 = n2 /n1 = 1 /2
n = c/v
Memorize as Pairs
F = ma
F = qE
Similar Form
F = KG ( m 1 m 2 / r 2 )
F = k ( q1 q2 / r2 )
V = IR
P = IV
Paired Use
vav = d / t
aav = v / t
(avg vel, acc)
v=f
E = hf
(f = 1/T)
Ek = 1/2 mv2
Ep = mgh
(kin, pot E)
= F/A
= gh
(pressure )
SG = substance / water
= 1 g/cm3 = 103 kg/m3
(Spec Grav)
= mass / volume
Fb = Vg = mg
(buoyant F)
Irms = Imax / 2
Vrms = Vmax / 2
Root Mean Sq
1/ i + 1/ o = 1/ f = 2/r = Power
M = magnification = - i/o
Optics
Note: Specific gravity (SG) is equivalent to the fraction of the height of a buoyant object below the surface of the
fluid.
http://www.goldstandard-mcat.com/physics-equation-lists/
Page 2 of 5
MCAT Physics Equation List (Formulas)
2/24/12 12:43 PM
Don't Memorize, Know How to Use...
+ gh + 1/2 v2 = constant
Bernouilli's Equation
Fluids in Motion
L = L0 (1 + T )
Linear Expansion
Solids, Temp
A = A0(1 + T )
Area Expansion
V = V0(1 + T )
Volume Expansion
fo = fs (V vo )/( V vs )
Doppler Effect: when d is decreasing use + vo and vs
V = Ed for a parallel plate capacitor
d = the distance between the plates
dF = dq v(B sin ) = I dl(B sin )
Laplace's Law
RH rule
1/ Ceq = 1/ C1 + 1/ C2 + 1/ C3 . . .
Capacitors in Ser. and Par.
Ceq = C1 + C2 . .
.
Potential Energy ( PE ) = W = 1/2
QV
Work in Electricity
W = 1/2 CV2
G = H - TS
Gibbs Free Energy
G = -RTln Keq
=3
Atomic Physics
1) alpha () particle = 2He4 (helium nucleus);
2) beta () particle = -1e0 (an electron);
3) a positron +1e0 (same mass as an electron but opposite charge);
4) gamma () ray = no mass, no charge, just electromagnetic energy;
5) m / t = rate of decay where m = change in mass, t = change in time.
http://www.goldstandard-mcat.com/physics-equation-lists/
Page 3 of 5
MCAT Physics Equation List (Formulas)
2/24/12 12:43 PM
5) m / t = rate of decay where m = change in mass, t = change in time.
6) If the number of half-lifes n are known we can calculate the percentage of a pure radioactive sample left after
undergoing decay since the fraction remaining = (1/2) n .
Nelectrons = 2 n2 , where Nelectrons designates the number of electrons in shell n .
The state of each electron is determined by the four quantum numbers:
principal quantum number n determines the number of shells, possible values are: 1 (K), 2 (L), 3 (M), etc...
angular momentum quantum number l, determines the subshell, possible values are: 0 (s), 1 (p), 2 (d), 3 (f),
n-1, etc...
magnetic momentum quantum number ml , possible values are: l , ... , 0
spin quantum number ms ,determines the direction of rotation of the electron, possible values are: 1/2.
The Basics
sin = opp/hyp
cos = adj/hyp
tan =opp/adj
= sin -1 x
arcsec = sec-1
r2 = x2 + y2
angle may be given in radians (R) where 1 revolution = 2R = 360
estimate square root 3 as 1.7 and root 2 as 1.4
cross-sectional area of a tube = area of a circle = r2 where can be estimated as 3.14 and r is the radius of
the circle; circumference = 2r
Some Units to Memorize
Both work and energy are measured in joules where 1 joule (J) = 1 N 1 m . {Imperial units: the footpound , CGS units: the dyne-centimeter or erg }
The SI unit for power is the watt (W) which equals one joule per second (J/s) = volts amperes .
Current is measured in amperes = coulombs/sec. The units of resistance are ohms, symbolized by
(omega), where 1 ohm = 1 volt/ampere.
The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (1 Pa = 1 N/m2 ). Other units are: 1.00 atm = 1.01 105 Pa = 1.01
bar = 760 mmHg = 760 torr.
The SI unit for the magnetic induction vector B is the tesla where 1 T = 1 N/(A)(m) = 104 gauss.
http://www.goldstandard-mcat.com/physics-equation-lists/
Page 4 of 5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- MCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDari EverandMCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuidePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (3)
- Formulas For The MCAT: General ChemistryDokumen1 halamanFormulas For The MCAT: General Chemistrymissee728Belum ada peringkat
- Sterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsDari EverandSterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Physics ReviewDokumen57 halamanMCAT Physics ReviewrinieroxBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDari EverandMCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- AAMC7 RSolutionsDokumen40 halamanAAMC7 RSolutionsharmit12Belum ada peringkat
- Don's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesDari EverandDon's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDokumen3 halamanMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- MCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideDari EverandMCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Jack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsDokumen6 halamanJack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsLoraBelum ada peringkat
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDari EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsBelum ada peringkat
- FREE MCAT ResourcesDokumen16 halamanFREE MCAT ResourcesDivjot KaranBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsDari EverandMCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsDokumen14 halamanGeneral Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsCodie SimoneauxBelum ada peringkat
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDari EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsBelum ada peringkat
- P-S KA Notes in Q&A Format (Created From 100 PG Version)Dokumen158 halamanP-S KA Notes in Q&A Format (Created From 100 PG Version)medmedBelum ada peringkat
- Sterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDari EverandSterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsBelum ada peringkat
- A Amc 7 SolutionsDokumen30 halamanA Amc 7 SolutionsTravanL.HurstBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills Review 2024-2025: Online + BookDari EverandMCAT Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills Review 2024-2025: Online + BookBelum ada peringkat
- McatDokumen6 halamanMcatapi-383289428100% (1)
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsDari EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT VocabDokumen101 halamanMCAT VocabUsman Ali Akbar100% (1)
- College Chemistry: Complete General Chemistry ReviewDari EverandCollege Chemistry: Complete General Chemistry ReviewPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- MCAT Physics Reference NotesDokumen16 halamanMCAT Physics Reference NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- OAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewDari EverandOAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- 5R Mcat PrepDokumen73 halaman5R Mcat Preprajatgoyal2050% (2)
- MCAT Physics and Math Review 2024-2025: Online + BookDari EverandMCAT Physics and Math Review 2024-2025: Online + BookPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- MCAT Sample Questions Template 1Dokumen42 halamanMCAT Sample Questions Template 1gendut_novri0% (1)
- AnswerDokumen290 halamanAnswerAnonymous y7dnrafdu100% (1)
- MCAT Full Length3Dokumen75 halamanMCAT Full Length3AliBelum ada peringkat
- Next-Step MCAT OutlineDokumen24 halamanNext-Step MCAT OutlineSage NorrieBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Test For AkuDokumen12 halamanMCAT Test For AkuKamran ParvezBelum ada peringkat
- Master AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsDokumen30 halamanMaster AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsSukhvir AujlaBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Physics FormulasDokumen6 halamanMCAT Physics Formulasjetone472100% (2)
- MCAT Practice PsDokumen4 halamanMCAT Practice PsStephen CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT BiologyDokumen410 halamanMCAT BiologyKevin Jiang100% (10)
- MCAT Full Length5Dokumen81 halamanMCAT Full Length5Ali100% (1)
- MCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Dokumen30 halamanMCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Chris_Barber09100% (2)
- The Princeton Review MCAT Verbal ReasoningDokumen4 halamanThe Princeton Review MCAT Verbal ReasoningAyodejiES1Belum ada peringkat
- Pre-Med Guide 3Dokumen15 halamanPre-Med Guide 3api-521535528100% (1)
- Preparation For MCAT Verbal ReasoningDokumen88 halamanPreparation For MCAT Verbal ReasoningAishwarya Balasubramaniyan100% (3)
- MCAT Physics Review 1Dokumen46 halamanMCAT Physics Review 1dana milstein100% (1)
- Explanations For Every Single Question For Every Userful Resource For The MCATDokumen643 halamanExplanations For Every Single Question For Every Userful Resource For The MCATBaoz Ping0% (10)
- Nova BiologyDokumen410 halamanNova Biologysupherao150% (2)
- Breaking Down CARS Passages HandoutDokumen15 halamanBreaking Down CARS Passages HandoutShumeng YangBelum ada peringkat
- Bio MCAT NotesDokumen2 halamanBio MCAT NotesJuan DeSantosBelum ada peringkat
- Mcat Mnemonics 2017Dokumen57 halamanMcat Mnemonics 2017Blinka199100% (2)
- MCAT Practice Solutions 8RDokumen41 halamanMCAT Practice Solutions 8RcynthiazorBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Essentials 2016 - FinalDokumen42 halamanMCAT Essentials 2016 - FinalBenjamin PhuaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 1: Amino AcidsDokumen4 halamanCh. 1: Amino AcidsNicole Ann LimBelum ada peringkat
- Aamc Mcat5Dokumen0 halamanAamc Mcat5Britanny Nelson100% (1)
- P/S McatDokumen28 halamanP/S McatMahdeeHaqueSyed100% (2)
- MCAT BootcampDokumen7 halamanMCAT BootcampAyah HamzaBelum ada peringkat
- KTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFDokumen24 halamanKTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFAmisha Vastani100% (6)
- Practice Test 8Dokumen58 halamanPractice Test 8The LightBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Sciences: Time: 100 Minutes Questions 1-77Dokumen79 halamanPhysical Sciences: Time: 100 Minutes Questions 1-77mattyg35Belum ada peringkat
- How To Prepare For MCAT (Study Schedule)Dokumen28 halamanHow To Prepare For MCAT (Study Schedule)Maria SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Mcat 2Dokumen62 halamanMcat 2Jacques Diambra OdiBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDokumen16 halamanMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT Full Length4Dokumen77 halamanMCAT Full Length4Ali100% (1)
- Reproductive System NotesDokumen3 halamanReproductive System NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiovasculary System PDFDokumen5 halamanCardiovasculary System PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDokumen3 halamanProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Macromolecules PDFDokumen11 halamanMacromolecules PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Digestive System PDFDokumen3 halamanDigestive System PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Dokumen5 halamanBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Heart Notes PDFDokumen2 halamanHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Nucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Dokumen4 halamanNucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Notes CarbohydratesDokumen3 halamanNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Notes CarbohydratesDokumen21 halamanNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Notes RNA and DNADokumen23 halamanNotes RNA and DNAChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Rate Law GraphsDokumen2 halamanRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Leaving GroupsDokumen1 halamanLeaving GroupsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDokumen1 halamanMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Amino Acid NotesDokumen15 halamanAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 5Dokumen10 halamanPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDokumen6 halamanAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Extra Chirality ProblemsDokumen21 halamanExtra Chirality ProblemsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- CARBSDokumen24 halamanCARBSGulus CfBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionDokumen2 halamanChapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 1Dokumen2 halamanPhysics Rules 1Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 4Dokumen6 halamanPhysics Rules 4Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsDokumen3 halamanRegents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Equation SheetDokumen2 halamanPhysics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- 107 Rules in PhysicsDokumen2 halaman107 Rules in PhysicsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 2Dokumen4 halamanPhysics Rules 2Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT Physics Equation SheetDokumen6 halamanMCAT Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewDokumen9 halamanAdvanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- AAMC 11 Essay 2Dokumen5 halamanAAMC 11 Essay 2Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- AAMC 11 Essay 1Dokumen6 halamanAAMC 11 Essay 1Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Experiment No 6Dokumen4 halamanExperiment No 6LJ IDANE ARANASBelum ada peringkat
- Isolated Sloped Footing SpreadsheetDokumen283 halamanIsolated Sloped Footing Spreadsheetarif_rubin100% (3)
- Chapter 6 Powerpoint IIDokumen34 halamanChapter 6 Powerpoint IIhdavey100% (1)
- 905 Series Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps & CompressorsDokumen4 halaman905 Series Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps & CompressorsCristina FerrarBelum ada peringkat
- Enen 619-03 Final Research ProjectDokumen26 halamanEnen 619-03 Final Research ProjectSalman NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Geo-Synthetics: Specifications For Railway SectorDokumen51 halamanGeo-Synthetics: Specifications For Railway SectorVISHWAJITBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Heat Capacity Lab Report2Dokumen6 halamanSpecific Heat Capacity Lab Report2milayosores100% (2)
- Analysis of Helical Coil Heat Exchangers: by V.Swapna Priya Guide R S MauryaDokumen23 halamanAnalysis of Helical Coil Heat Exchangers: by V.Swapna Priya Guide R S MauryaSwapna Priya VattemBelum ada peringkat
- EDTA Titration of Calcium and MagnesiumDokumen3 halamanEDTA Titration of Calcium and MagnesiumAnonymous NxpnI6jC67% (3)
- TE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 5 - Thermodyn Propertis of Moist AirDokumen48 halamanTE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 5 - Thermodyn Propertis of Moist AirAkshay ChandoleBelum ada peringkat
- Science Water Cycle HydrosphereDokumen3 halamanScience Water Cycle Hydrosphereapi-254658342Belum ada peringkat
- 00s6. UI SS Lecture 6 Clastic Classification 1002Dokumen33 halaman00s6. UI SS Lecture 6 Clastic Classification 1002MuzzammilAlMackyBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 15Dokumen17 halamanGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 15Katrine Visitacion Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 HIgh Cycle and Low Cycle FatigueDokumen21 halamanModule 4 HIgh Cycle and Low Cycle FatiguerohanBelum ada peringkat
- Sem1 CompileDokumen13 halamanSem1 Compilescc_12Belum ada peringkat
- Rasa Rat Nasa Muc ChayaDokumen8 halamanRasa Rat Nasa Muc ChayatemmBelum ada peringkat
- NFL BathindaDokumen26 halamanNFL BathindaSukhman ChahalBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Uk PDFDokumen293 halamanGates Uk PDFZMCONTROLBelum ada peringkat
- P-ToLUENESULFONIC ANHYDRIDE Ts2O From TsOH P2O5 Kieselguhr Then DCE Extraction EtcDokumen3 halamanP-ToLUENESULFONIC ANHYDRIDE Ts2O From TsOH P2O5 Kieselguhr Then DCE Extraction Etcfchem11Belum ada peringkat
- APA Tech Bulletin On FormadehydeDokumen4 halamanAPA Tech Bulletin On Formadehydeca_alzuBelum ada peringkat
- Scaling of MosfetDokumen40 halamanScaling of MosfetSaumitra TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Peroxide DecompositionDokumen17 halamanHydrogen Peroxide DecompositionTan Xin YuBelum ada peringkat
- (777577664) Numerical Problem 3Dokumen5 halaman(777577664) Numerical Problem 3Axel0% (1)
- StovesDokumen5 halamanStovesElsa LaminBelum ada peringkat
- Radiative Heat Transfer in Participating Media A ReviewDokumen20 halamanRadiative Heat Transfer in Participating Media A ReviewSanjeevan Lakra0% (1)
- Viva QuestionDokumen4 halamanViva QuestionBarathkannan Lakshmi PalanichamyBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Syntheses Collective Volume 6Dokumen1.299 halamanOrganic Syntheses Collective Volume 6caltexas100% (2)
- Lecture 2 - Origin of Elements, ClassificationDokumen24 halamanLecture 2 - Origin of Elements, ClassificationMihatsu TakiBelum ada peringkat
- Sizing of LPG Air Mix System (24mmbtu 60B-40P, 50psig)Dokumen1 halamanSizing of LPG Air Mix System (24mmbtu 60B-40P, 50psig)ekabudiartiBelum ada peringkat
- Stack Effect in High Rise Buildings A ReviewDokumen13 halamanStack Effect in High Rise Buildings A ReviewAhmedBadrBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- Higgs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceDari EverandHiggs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpacePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (30)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDari EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniversePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDari EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and SciencePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDari EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDari EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyBelum ada peringkat
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDari EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1395)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDari EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDari EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (60)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDari EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (20)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDari EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (54)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (76)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDari EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDari EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (57)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDari EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (500)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (49)