Muscular System
Diunggah oleh
Chris_Barber09100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
322 tayangan1 halamanMuscular System
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniMuscular System
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
322 tayangan1 halamanMuscular System
Diunggah oleh
Chris_Barber09Muscular System
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
Human Anatomy - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
09: Axial and Appendicular Musculature
Key Terms
Axial Muscles: the muscles of the pectoral and pelvic
girdles, as well as the muscles of the upper and lower
extremities, will be covered first.
Appendicular Muscles: the muscles of the head and neck,
vertebral column, and the muscles of the perineum and
pelvic region.
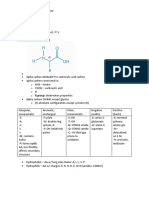
Muscles that Move the Hand: (1) Muscles that act at the
elbow, (2) pronators and supinators, and (3) muscles that
act at the wrist.
Quadriceps Muscles: The muscles that extend the knee
are the rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis,
and vastus medialis. These muscles form the quadriceps
muscles. These muscles cover the anterior and lateral
aspects of the femur. These are powerful extensor muscles
of the knee, which are attached to the patella through the
quadriceps tendon.
Fascia: Fascia is a fibrous layer that permeates different
regions of the body. This fibrous sheet that courses through
the arms and legs separates tissue into compartments. The
fascia in the thigh forms the following compartments: (1)
anterior compartment, (2) medial compartment, and (3)
posterior compartment.
Extra-ocular Muscles: There are six extra-ocular muscles
that position the eye, and are located on the surface of the
orbit. The extra-ocular muscles are the: medial rectus,
lateral rectus, inferior rectus, superior rectus, inferior
oblique and the superior oblique muscles.
Mastication: To masticate, or chew your food, the
mandible and temporomandibular joint must be moved. The
muscles of mastication that perform these movements are
the: masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, and the lateral
pterygoid muscle.
Muscles of the Tongue: All the muscles of the tongue end
in the word glossus, which is the root word for tongue.
These muscles position the tongue for chewing, drinking,
swallowing and speech production.
Muscles of the Perineum and Pelvic Diaphragm: The
muscles of the perineum and the pelvic diaphragm function
to (1) support the organs of the pelvic cavity, (2) control
the movements of material through the urethra and the
anus, and (3) flex the joints of the sacrum and coccyx.
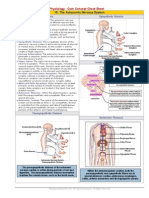
Muscles that Move the Hand and Forearm
Head and Neck Muscles
Extra-Ocular Muscles
There are six extra-ocular muscles that position the
eye, and are located on the surface of the orbit. The
extra-ocular muscles are the: medial rectus, lateral
rectus, inferior rectus, superior rectus, inferior oblique
and the superior oblique muscles.
Oblique and Rectus Musculature
The muscles that move the hand can be organized
by groups: (1) Muscles that act at the elbow, (2)
pronators and supinators, and (3) muscles that act
at the wrist.
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then rewrite it out on
a blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Urinary SystemDokumen1 halamanUrinary SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Human Physiology IntroductionDokumen1 halamanHuman Physiology IntroductionChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDokumen1 halamanAutonomic Nervous SystemChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen1 halamanPeripheral Nervous SystemChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- ProteinsDokumen1 halamanProteinsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology IntroductionDokumen1 halamanCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDokumen1 halamanChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen6 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- VirusesDokumen1 halamanVirusesChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Molecular Cell Biology MasterDokumen6 halamanMolecular Cell Biology Masterdealt100% (5)
- Rate Law GraphsDokumen2 halamanRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen1 halamanMitosis and MeiosisChris_Barber09100% (1)
- MCAT Hormones and EnzymesDokumen2 halamanMCAT Hormones and EnzymesDevie Saha100% (3)
- Bio Cheat Sheet MasterDokumen7 halamanBio Cheat Sheet MasterChris_Barber0986% (7)
- MCAT MetabolismDokumen4 halamanMCAT MetabolismNawledge9308100% (1)
- 01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsDokumen1 halaman01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsBlaine Rogalski100% (2)
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDokumen8 halamanMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology MasterDokumen13 halamanMicrobiology MasterDelixae Phoinix100% (6)
- ImmunologyDokumen1 halamanImmunologyChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Biotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentDokumen40 halamanBiotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentnescafeforeverBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDokumen16 halamanMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideDokumen22 halamanMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211Belum ada peringkat
- Biology: Anterior Pituitary HormonesDokumen12 halamanBiology: Anterior Pituitary Hormoneserika12767% (3)
- 16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsDokumen1 halaman16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsBlaine RogalskiBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Organic Summary SheetDokumen6 halamanMCAT Organic Summary SheetSpencer Thomas100% (2)
- Biology OutlinesDokumen21 halamanBiology OutlinesKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Cells Cheat SheetDokumen2 halamanCells Cheat SheetUlka Sutar100% (2)
- MCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetDokumen6 halamanMCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry y Lecture 1 1 - Atoms, Molecules S and Quan Ntum Mec HanicsDokumen3 halamanChemistry y Lecture 1 1 - Atoms, Molecules S and Quan Ntum Mec HanicsChethranBelum ada peringkat
- MCAT Biology Complete OutlinesDokumen34 halamanMCAT Biology Complete OutlinesJacob Mikhail90% (10)
- Preliminary Instructions: Cu Ni CR Fe FeDokumen4 halamanPreliminary Instructions: Cu Ni CR Fe FeEmmanuel Ryan100% (1)
- MCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Dokumen74 halamanMCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Examkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsDokumen3 halamanExamkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsAyodejiES1Belum ada peringkat
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Dokumen5 halamanBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT ChemistryDokumen3 halamanMCAT ChemistryDurvPatelBelum ada peringkat
- A. Continuity at A Point: FC C F FX FX FCDokumen4 halamanA. Continuity at A Point: FC C F FX FX FCSage NorrieBelum ada peringkat
- Review Sheet McatDokumen16 halamanReview Sheet McatCal GoBelum ada peringkat
- Master AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsDokumen30 halamanMaster AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsSukhvir AujlaBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen6 halamanBiochemistryBlaine Rogalski100% (14)
- Organic Reactions Summary SheetDokumen2 halamanOrganic Reactions Summary Sheetthacheee64% (11)
- College PhysicsDokumen6 halamanCollege PhysicsDelixae Phoinix100% (1)
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDokumen1 halamanMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Cheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Dokumen1 halamanCheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Norma Leticia Ramos33% (3)
- MCAT ReviewDokumen114 halamanMCAT Reviewjustinwendel100% (4)
- MCAT - Organic Chemistry OverviewDokumen20 halamanMCAT - Organic Chemistry Overviewrvar839100% (2)
- MCAT Mnemonic SDokumen17 halamanMCAT Mnemonic STasneem MahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 1: Amino AcidsDokumen4 halamanCh. 1: Amino AcidsNicole Ann LimBelum ada peringkat
- OChem MasterDokumen6 halamanOChem MasterDelixae PhoinixBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas For The MCAT: General ChemistryDokumen1 halamanFormulas For The MCAT: General Chemistrymissee728Belum ada peringkat
- Cell CommunicationDokumen25 halamanCell Communicationprehealthhelp100% (12)
- Mcat Mnemonics 2017Dokumen57 halamanMcat Mnemonics 2017Blinka199100% (2)
- Intro To Diagnostic Imaging - 2 - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERDokumen37 halamanIntro To Diagnostic Imaging - 2 - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERAly MssreBelum ada peringkat
- The Neck: Overview and Objectives of This DissectionDokumen5 halamanThe Neck: Overview and Objectives of This Dissectionapi-61200414Belum ada peringkat
- Muscle - System ANATOMYDokumen54 halamanMuscle - System ANATOMYfatimamuzammil406Belum ada peringkat
- Periodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftDokumen10 halamanPeriodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftCassandra ColigadoBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyAbdomenandPelvisPosteriorAbdominalWallNerves StatPearls NCBIBookshelfDokumen11 halamanAnatomyAbdomenandPelvisPosteriorAbdominalWallNerves StatPearls NCBIBookshelfKavya KavyasujathaBelum ada peringkat
- Myology: Gansheng-Wei Department of AnatomyDokumen46 halamanMyology: Gansheng-Wei Department of Anatomyprasun_vBelum ada peringkat
- IntroductionDokumen64 halamanIntroductionkarokamil243Belum ada peringkat
- Myology: P By: M .HDokumen60 halamanMyology: P By: M .HAklilu AbrhaBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Dr. Fouad Heikel.: Subject: Hip JointDokumen6 halamanProf. Dr. Fouad Heikel.: Subject: Hip JointHashim OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Notes PDFDokumen2 halamanHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDokumen3 halamanProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Reproductive System NotesDokumen3 halamanReproductive System NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Macromolecules PDFDokumen11 halamanMacromolecules PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Digestive System PDFDokumen3 halamanDigestive System PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiovasculary System PDFDokumen5 halamanCardiovasculary System PDFChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Nucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Dokumen4 halamanNucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Leaving GroupsDokumen1 halamanLeaving GroupsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 4Dokumen6 halamanPhysics Rules 4Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Rate Law GraphsDokumen2 halamanRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Notes CarbohydratesDokumen21 halamanNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Notes RNA and DNADokumen23 halamanNotes RNA and DNAChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Dokumen5 halamanBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDokumen1 halamanMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Notes CarbohydratesDokumen3 halamanNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- CARBSDokumen24 halamanCARBSGulus CfBelum ada peringkat
- Extra Chirality ProblemsDokumen21 halamanExtra Chirality ProblemsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Amino Acid NotesDokumen15 halamanAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDokumen6 halamanAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Physics Rules 2Dokumen4 halamanPhysics Rules 2Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 5Dokumen10 halamanPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- Chapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionDokumen2 halamanChapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsDokumen3 halamanRegents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- 107 Rules in PhysicsDokumen2 halaman107 Rules in PhysicsChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- AAMC 11 Essay 2Dokumen5 halamanAAMC 11 Essay 2Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Equation SheetDokumen2 halamanPhysics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Rules 1Dokumen2 halamanPhysics Rules 1Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewDokumen9 halamanAdvanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- MCAT Physics Equation SheetDokumen6 halamanMCAT Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- AAMC 11 Essay 1Dokumen6 halamanAAMC 11 Essay 1Chris_Barber09Belum ada peringkat
- Shoulder Complex Special TestsDokumen30 halamanShoulder Complex Special TestspeawbaBelum ada peringkat
- GTU 104.2015 Teaching Timetable and Assessment ScheduleDokumen9 halamanGTU 104.2015 Teaching Timetable and Assessment ScheduleJebatAl-KelantaniBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Anatomy of Vertebrate SkeletonDokumen53 halamanComparative Anatomy of Vertebrate SkeletonYlane Lee100% (1)
- Importance of Strengthening Your Core MusclesDokumen6 halamanImportance of Strengthening Your Core Musclesallan_apduaBelum ada peringkat
- Lunge or Anjana's Pose: NjaneyasanaDokumen13 halamanLunge or Anjana's Pose: NjaneyasanaLomombBelum ada peringkat
- Range of MotionDokumen17 halamanRange of MotionJim Cariaga100% (2)
- 3B Scientific Medical Education 2017 USDokumen232 halaman3B Scientific Medical Education 2017 USJuan Javier Apaza PillcoBelum ada peringkat
- Krav Maga El Sistema Oficial de Autodefensa IsraeliDokumen10 halamanKrav Maga El Sistema Oficial de Autodefensa IsraeliAdd GarBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesDokumen32 halamanMuscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesMaria Celina Lomboy SerapioBelum ada peringkat
- Standing Post ExercisesDokumen11 halamanStanding Post Exercisesrappa84100% (2)
- Extract From Anatomy Course LectureDokumen5 halamanExtract From Anatomy Course LectureMumuh Moe' MuhtadinBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of The BodyDokumen2 halamanParts of The BodyKru EkachaiBelum ada peringkat
- Mcqs PDFDokumen12 halamanMcqs PDFAmrit63% (8)
- Abdominal WorkoutDokumen16 halamanAbdominal Workoutvjeevan5Belum ada peringkat
- Evijas To DO LIST: Rotational Dynamic Warm-Up: Low To High ChopDokumen19 halamanEvijas To DO LIST: Rotational Dynamic Warm-Up: Low To High ChopArtūrs GrīnbergsBelum ada peringkat
- Chair Based Strength Exercises No Equipment AllActive Information GuideDokumen24 halamanChair Based Strength Exercises No Equipment AllActive Information GuideAyuy Welliss Medusa100% (1)
- Newborn AssessmentDokumen6 halamanNewborn AssessmentAyuni Salleh100% (1)
- 2019 Jerrold The Extraction of Teeth Part 1 Considerations Regarding Which Teeth To Extract Seminars in OrthodonticsDokumen5 halaman2019 Jerrold The Extraction of Teeth Part 1 Considerations Regarding Which Teeth To Extract Seminars in Orthodonticsplayer osama100% (1)
- 16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbDokumen27 halaman16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbAlapati Vinod KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Miracle7 (Tiger Moves) John Peterson PDFDokumen9 halamanMiracle7 (Tiger Moves) John Peterson PDFstarks33_2001100% (2)
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckDokumen36 halaman6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyThe Vertebral ColumnDokumen70 halamanAnatomyThe Vertebral ColumnJardee DatsimaBelum ada peringkat
- Reflexology ChartDokumen1 halamanReflexology ChartEng. Sam100% (2)
- The Elbow ComplexDokumen12 halamanThe Elbow ComplextafelaBelum ada peringkat
- Chestionar F. Stom. A. I Sem. I ENGL. 2013Dokumen5 halamanChestionar F. Stom. A. I Sem. I ENGL. 2013Cristina caimacBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Ex MusclesDokumen18 halamanUpper Ex MusclesKatreena VillarenteBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Anatomy and Fascia of The Neck Surface Anatomy of The NeckDokumen3 halamanSurface Anatomy and Fascia of The Neck Surface Anatomy of The Neckفراس الموسويBelum ada peringkat
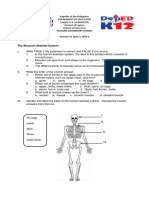
- Science 6 Quiz 1 & 2, QTR 2Dokumen2 halamanScience 6 Quiz 1 & 2, QTR 2Reymart B Tiosan100% (1)
- FTU CountDokumen1 halamanFTU CountOliver QBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System PowerpointDokumen40 halamanSkeletal System PowerpointLee KaiYangBelum ada peringkat