Addie Model
Diunggah oleh
ASMAHAN0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
509 tayangan2 halamanAddie Model
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAddie Model
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
509 tayangan2 halamanAddie Model
Diunggah oleh
ASMAHANAddie Model
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
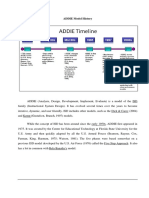
ADDIE Model
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The ADDIE model is the generic process traditionally used by instructional designers and
training developers. The five phases—Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and
Evaluation—represent a dynamic, flexible guideline for building effective training and
performance support tools.
It is an Instructional Systems Design (ISD) model. Most of the current instructional design
models are spin-offs or variations of the ADDIE model; other models include the Dick & Carey
and Kemp ISD models. One commonly accepted improvement to this model is the use of rapid
prototyping. This is the idea of receiving continual or formative feedback while instructional
materials are being created. This model attempts to save time and money by catching problems
while they are still easy to fix. For example, the ADDIE model was used in the framework for
helping create new research topics in learning technology (Liu, 2008).
Instructional theories also play an important role in the design of instructional materials.
Theories such as behaviorism, constructivism, social learning and cognitivism help shape and
define the outcome of instructional materials.
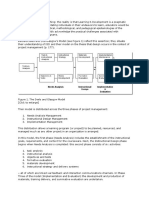
In the ADDIE concept, each step has an outcome that bleeds into the subsequent step.
Analysis > Design > Development > Implementation > Evaluation
[edit] Analysis Phase
In the analysis phase, the instructional problem is clarified, the instructional goals and objectives
are established and the learning environment and learner's existing knowledge and skills are
identified. Below are some of the questions that are addressed during the analysis phase:
[edit] Design Phase
The design phase deals with learning objectives, assessment instruments, exercises, content,
subject matter analysis, lesson planning and media selection. The design phase should be
systematic and specific. Systematic means a logical, orderly method of identifying, developing
and evaluating a set of planned strategies targeted for attaining the project's goals. Specific
means each element of the instructional design plan needs to be executed with attention to
details.
[edit] Development Phase
The development phase is where instructional designers and developers create and assemble the
content assets that were blueprinted in the design phase. In this phase, storyboards and graphics
are designed. If elearning is involved, programmers develop and/or integrate technologies.
Testers perform debugging procedures. The project is reviewed and revised according to the
feedback received.
[edit] Implementation Phase
During the implementation phase, a procedure for training the facilitators and the learners is
developed. The facilitators' training should cover the course curriculum, learning outcomes,
method of delivery, and testing procedures. Preparation of the learners includes training them on
new tools (software or hardware) and student registration.
This is also the phase where the project manager ensures that the books, hands-on equipment,
tools, CD-ROMs and software are in place, and that the learning application or website is
functional.
[edit] Evaluation Phase
The evaluation phase consists of two parts: formative and summative. Formative evaluation is
present in each stage of the ADDIE process. Summative evaluation consists of tests designed for
domain specific criterion-related referenced items and providing opportunities for feedback from
the users which were identified
[edit] References
• Liu, G. Z. (2008). Innovating research topics in learning technology: Where are the new
blue oceans?.British Journal of Educational Technology, 39(4), 738-747.
• Molenda, M. (2003). In search of the elusive addie model. Performance improvement,
42(5), 34.
• Strickland, A.W. (2006). ADDIE. Idaho State University College of Education Science,
Math & Technology Education. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
أحد نماذج التصميمم التعليمي التي تعتمد في إنشائها علي خمس-: الترجمه
التطوير-3 التصمي-2 التحلي-1 مراحل وهى
4-التقويم-5 التطبيق
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ad DieDokumen3 halamanAd DieJeffrey DanielsBelum ada peringkat
- Addie Model LABONIDokumen4 halamanAddie Model LABONILaboni patraBelum ada peringkat
- Addie ModelDokumen2 halamanAddie ModelPutra AftusBelum ada peringkat
- ADDIEDokumen3 halamanADDIEつづ くBelum ada peringkat
- Allyvensia Binti Dohiuil 65385Dokumen4 halamanAllyvensia Binti Dohiuil 65385ALLYVENSIA DOHIUILBelum ada peringkat
- ICT3Dokumen19 halamanICT3p_kritsanasak4992Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 - The ADDIE ModelDokumen4 halamanLesson 1 - The ADDIE ModelJustine Jerk BadanaBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design Models - Kelly MossDokumen19 halamanInstructional Design Models - Kelly MossrereanggreiniBelum ada peringkat
- Nstructional Design ModelsDokumen10 halamanNstructional Design ModelsMary Florilyn ReclaBelum ada peringkat
- Addie ModelDokumen7 halamanAddie ModelgrmetalrockBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design Models and MethodsDokumen8 halamanInstructional Design Models and MethodsJoshua Rosenbaum100% (1)
- Instructional Design TheoriesDokumen17 halamanInstructional Design TheoriesmysticblissBelum ada peringkat
- Addie Model AssignmentDokumen13 halamanAddie Model AssignmentMia mooreBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design Models: Tonia A. DousayDokumen29 halamanInstructional Design Models: Tonia A. DousayAhmad SyarifBelum ada peringkat
- ADDIE Model Report Word FileDokumen3 halamanADDIE Model Report Word Fileconz12Belum ada peringkat
- Addie ModelDokumen2 halamanAddie ModelAnurag JainBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design in Online Course Development - Mary Roween C. RodriguezDokumen15 halamanInstructional Design in Online Course Development - Mary Roween C. RodriguezRoden RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 3.design - InstructionDokumen20 halamanChap 3.design - Instructionbluebird2112Belum ada peringkat
- Addie Vs AssureDokumen10 halamanAddie Vs AssureCML78100% (1)
- Instructional Design For Active LearningDokumen35 halamanInstructional Design For Active LearningAzhagesvaran Tamilselvam100% (1)
- Addie ModelDokumen3 halamanAddie ModelmysticblissBelum ada peringkat
- AddieModel VoicenotesDokumen45 halamanAddieModel VoicenotesJunel Lapinid100% (1)
- ADDIE Model: Analysis PhaseDokumen2 halamanADDIE Model: Analysis PhaseNimSha NimzzBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional DesignDokumen6 halamanInstructional Designapi-254210572Belum ada peringkat
- White Paper - Introduction To The ADDIE ISD ModelDokumen17 halamanWhite Paper - Introduction To The ADDIE ISD ModelShahzad HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan 1 Abu Ubaidah Amir Bin Abdul Aziz (2021.2.edu02.0002) April 2021 0187029086Dokumen13 halamanSoalan 1 Abu Ubaidah Amir Bin Abdul Aziz (2021.2.edu02.0002) April 2021 0187029086Abu UbaidahBelum ada peringkat
- Addie Model: Adala, Wahdah M. Dagalea, Xylene B. Estrada, Jerome Fajardo, Ina Ih, Joyce Christian Lucaylucay, Eden FaithDokumen16 halamanAddie Model: Adala, Wahdah M. Dagalea, Xylene B. Estrada, Jerome Fajardo, Ina Ih, Joyce Christian Lucaylucay, Eden FaithJerry SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Stewartk Edid6503-Assign 3Dokumen10 halamanStewartk Edid6503-Assign 3api-432098444Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 (Instructional Design)Dokumen20 halamanAssignment 2 (Instructional Design)zoulzz0903Belum ada peringkat
- Analysis of ModelsDokumen9 halamanAnalysis of ModelsTakeshi YukataBelum ada peringkat
- Creating Training and Development Programs: Using The ADDIE MethodDokumen5 halamanCreating Training and Development Programs: Using The ADDIE MethodYayan NadzriBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 03. Addie ModelDokumen4 halamanBab 03. Addie ModelChai Siaw YenBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Week 4 Lesson Addie ModelDokumen6 halamanMidterm Week 4 Lesson Addie ModelCecelien Salgado AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design Models - Instructional Design Central (IDC)Dokumen10 halamanInstructional Design Models - Instructional Design Central (IDC)Anggie Paola CaocBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional Design Models - Kelly MossDokumen19 halamanInstructional Design Models - Kelly MossncelpaBelum ada peringkat
- Addie ModelDokumen48 halamanAddie Modelmarkespino100% (3)
- ADDIE ModelDokumen4 halamanADDIE ModelFran Ko100% (1)
- Topic 4 - Instructional Design ModelsDokumen25 halamanTopic 4 - Instructional Design ModelsHamizah ZuhairahBelum ada peringkat
- Outcome-Based Education Model For Computer Science EducationDokumen6 halamanOutcome-Based Education Model For Computer Science EducationJonathan Japson PasteraBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Theory of 3 Instructional DesignsDokumen12 halamanComparative Theory of 3 Instructional DesignsVonne HeartfordBelum ada peringkat
- 9 14 1 SMDokumen13 halaman9 14 1 SMsyifachsnBelum ada peringkat
- HPGD3103 Etut 1Dokumen19 halamanHPGD3103 Etut 1HAFABelum ada peringkat
- 2 Instructional Design ModelsDokumen6 halaman2 Instructional Design ModelsguardadobearBelum ada peringkat
- HPGD3103 Etut 1Dokumen19 halamanHPGD3103 Etut 1Ihwanor AsrafBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional DesignDokumen15 halamanInstructional DesignTHONDYNALUBelum ada peringkat
- Addie Model AssignmentDokumen15 halamanAddie Model AssignmentHeamadavi SukumaranBelum ada peringkat
- Instructional DesignDokumen18 halamanInstructional DesignAshkira AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- Elt Curriculum and Materials Development PresentasiDokumen5 halamanElt Curriculum and Materials Development PresentasiJaiyah AtunBelum ada peringkat
- Model Ri 2Dokumen8 halamanModel Ri 2yuifauzianiBelum ada peringkat
- ADDIE MODEL - Instructional Design ModelDokumen9 halamanADDIE MODEL - Instructional Design ModelEnz OgnillaBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel 1 - Ni Putu Adis Cantika Dewi - The Implementation of Quizlet To Learn Vocabulary Towards Junior High School StudentsDokumen10 halamanArtikel 1 - Ni Putu Adis Cantika Dewi - The Implementation of Quizlet To Learn Vocabulary Towards Junior High School StudentsAdis CantikaBelum ada peringkat
- Model Addie 6Dokumen3 halamanModel Addie 6Egan-Ash ArijenanBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Curriculum DevelopmentDokumen16 halamanReport On Curriculum DevelopmentDivine Jessica Puyaoan CamiringBelum ada peringkat
- 4 AsDokumen6 halaman4 AsWeljunBelum ada peringkat
- Addie ModelDokumen5 halamanAddie Modelmansor201250% (4)
- Instructional Planning For The Mother Tongue: Lesson 8 Lesson 8 Instructional Planning Cycle Instructional Planning CycleDokumen8 halamanInstructional Planning For The Mother Tongue: Lesson 8 Lesson 8 Instructional Planning Cycle Instructional Planning CycleGrace Kelly Tabanda100% (1)
- The ADDIE Model Why Use ItDokumen4 halamanThe ADDIE Model Why Use ItMuhammad Arif IzzudinBelum ada peringkat
- Group Project Software Management: A Guide for University Students and InstructorsDari EverandGroup Project Software Management: A Guide for University Students and InstructorsBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering the Instructional Design Process: A Systematic ApproachDari EverandMastering the Instructional Design Process: A Systematic ApproachBelum ada peringkat