Reservoirs - Ch. 1 - Introduction
Diunggah oleh
timsykiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Reservoirs - Ch. 1 - Introduction
Diunggah oleh
timsykiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
Reservoirs - General description
1.1 Introduction
Concrete is a porous material and as such not completely liquid and gas tight. However, under certain
conditions a concrete structure may behave liquid tight, or guarantee an adequate tightness. In this respect, the following aspects are important:
Composition of the concrete mixture
Structural design
Control of crack formation
Construction execution
It should be clear that the aspect of liquid tightness requires a lot of attention. In most codes, not
much attention is paid to liquid-tight structural design. But due to the increasing attention for the protection of ground and ground water against pollutants, a strong stimulus has been created for the production of liquid-tight structures. The theme liquid tightness will be discussed intensively in Chapter 2.
1.2 Design
The shape of structures for the storage of liquid of gas is determined by a number of factors:
Capacity
Process engineering considerations
Design considerations
Aesthetics
Soil conditions
The following shapes are imaginable and feasible (Fig. 1.1):
Rectangular (single or multiple)
Cylindrical
Conical (for example water towers)
Egg-shaped (for example sludge fermentation tanks)
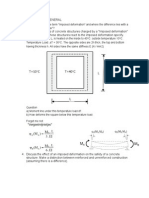
Drop-shaped or spherical (often in steel, drinking water storage)
Base moments
Horizontal moments
spheroid
Fig. 1.1: Possible reservoir designs: drop-shaped, rectangular and cylindrical.
The structural difference between the above mentioned types is enormous. For the drop-shaped or
spherical tanks the membrane action is predominant, while for the rectangular reservoir the bending and
shear actions are most important (also see Fig. 1.1). In most cases, combinations of several loading
cases have to be analysed.
In these notes attention will be paid to reservoirs of rectangular and cylindrical shape that are made
from reinforced or prestressed concrete (also see Fig. 1.2). Further, a distinction can be made between
in-situ concrete and precast concrete structures.
1-1
Fig. 1.2: Tall aeration tank: situation during construction.
1.3 Function of reservoirs
Reservoirs may have a permanent or temporary function. Next to the storage function, for some structures the transport function is dominant. In the case of storage of environmentally hazardous fluids, the
protective function may be the most important one. Except the capability of storage, the structure must
also be able to resist extreme loads such as impacts, explosions and fires without loosing its retaining
function. Depending on the relevant conditions and load configurations, the structure has to maintain it
liquid retaining function on a permanent or temporary basis. Retaining liquid does not necessarily mean
that the structure is 100% liquid tight.
Reservoirs are very important from a strategic point of view. This is not only the case for industrialised
societies, but also for developing countries. It often concerns the storage of liquids, gases, bulk products, energy carriers, etc., the availability of which is crucial for the functioning of society. Consequently, these structures have to be operational reliable. As far as the structural aspect is concerned, the
main responsibility lies with the designer. Proper understanding of the force transmission and distribution, smart detailing and good construction is of essential importance to come to a good and reliable
product.
1-2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 7 Hardening ConcreteDokumen43 halamanChapter 7 Hardening ConcretetimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Multidimensional Linear Regression Examples 2015Dokumen8 halamanMultidimensional Linear Regression Examples 2015timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Report 4Dokumen21 halamanReport 4timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5Dokumen21 halamanLecture 5timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Prestressed Cylindrical Reservoir: Dundation Angth of Piles Ross-Section Piles Earing CapacityDokumen1 halamanPrestressed Cylindrical Reservoir: Dundation Angth of Piles Ross-Section Piles Earing CapacitytimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- ISCHP13 ProceedingsDokumen368 halamanISCHP13 ProceedingstimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionsDokumen7 halamanQuestionstimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Mult LA Exercise1 2015Dokumen3 halamanSolution Mult LA Exercise1 2015timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Cylindrical Reservoirs: Case Study CIE5130Dokumen1 halamanDesign of Cylindrical Reservoirs: Case Study CIE5130timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Multidimensional Linear Regression Examples Error Propagation Rev3Dokumen8 halaman2015 Multidimensional Linear Regression Examples Error Propagation Rev3timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Imposed Deformations - ApplicationsDokumen19 halamanChapter 8 Imposed Deformations - ApplicationstimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Introduction Transport Engineering and Logistics Technique November 7 2013 AnswersDokumen4 halamanExam Introduction Transport Engineering and Logistics Technique November 7 2013 AnswerstimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Solution Exercises MLR Error PropagationDokumen8 halaman2015 Solution Exercises MLR Error PropagationtimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Reservoirs - Ch. 5 - PrefabricationDokumen27 halamanReservoirs - Ch. 5 - PrefabricationtimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Introduction To Offshore Engineering Oe4606 Complete Lecture 1 16Dokumen102 halamanSummary Introduction To Offshore Engineering Oe4606 Complete Lecture 1 16timsyki100% (1)
- MATLAB LA Intro 2015 Rev1Dokumen39 halamanMATLAB LA Intro 2015 Rev1timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Spring 2014 Question Hour: Learning Units 5-8 + Exam: - Consequentialism Deontological Ethics Virtue Ethics Care EthicsDokumen3 halamanSpring 2014 Question Hour: Learning Units 5-8 + Exam: - Consequentialism Deontological Ethics Virtue Ethics Care EthicstimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Introduction Transport and Logistic Engineering Lecture 2 4Dokumen9 halamanSummary Introduction Transport and Logistic Engineering Lecture 2 4timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Examination Wb3420 November 2013 Question 4Dokumen1 halamanAnswer Examination Wb3420 November 2013 Question 4timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook To Learn MatlabDokumen79 halamanHandbook To Learn MatlabtimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Lecture 1 6 Plus FormulasDokumen13 halamanSummary Lecture 1 6 Plus FormulastimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Introduction Transport and Logistic Engineering Lecture 2 4Dokumen9 halamanSummary Introduction Transport and Logistic Engineering Lecture 2 4timsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Building Structure ReadingDokumen7 halamanBuilding Structure ReadingtimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Verification and Implementation of Strut-And-Tie Model inDokumen281 halamanVerification and Implementation of Strut-And-Tie Model inrpatel5509Belum ada peringkat
- Prestressing Layout For Cylindrical ReservoirDokumen2 halamanPrestressing Layout For Cylindrical ReservoirtimsykiBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)