LCRQ Meter by BRT
Diunggah oleh
ritesh120543111008Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
LCRQ Meter by BRT
Diunggah oleh
ritesh120543111008Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Electronics Measurements & Instrumentation
Branch : Electronics & Communication
Semester : 5TH
EXPERIMENT NO:-9- Measurement Using LCRQ Meter.
AIM: Measurement using LCRQ Meter.
APPARATUS:
1.
2.
3.
4.
6018 LCRQ Meter.
Capacitors.
Resistors.
Inductors.
THEORY:
The LCR Q Bridge measures inductance, capacitance, resistance and Q factor by using
two circuit arrangement i.e. series and parallel. As we know the basic property of RLC circuit
called as Resonance LCR Q bridge use that property to measure capacitance, resistance,
inductance and Q factor. Lets see how that works first we calculate capacitance and inductance.
As we know
Resonance frequency fr = 1/2LC
Now test frequency is known value here and if the value of either component is measured by
the circuit by using above formula.
Q Meter measure the quality factor Q of a coil. Quality factor of a radio frequency coil
is the ratio of its reactance XL = 2f0L at the radio frequency and its effective resistance R.
Q=
As shown in figure a series resonant circuit is connected to the variable frequency source E.
If the frequency of the source is varied and adjusted such that there is resonance, then
Q=
Now IXL cannot be measured because the resistance and the reactance of the coil cannot be
separated. But at resonance, IXL = IXC so IXC at resonance can be measured and Q factor can be
known.
Q=
Because, IXL = IXC and IR = E.
VTVM or transistor voltmeter is connected across the capacitor. If F is maintained constant,
EC is proportional to Q.
Also Q = 1/D
Where D is Dissipation factor of Capacitor and it is given by,
D = CxRx ,
Where = 2f
DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Electronics Measurements & Instrumentation
Branch : Electronics & Communication
Semester : 5TH
EXPERIMENT NO:-9- Measurement Using LCRQ Meter.
FRONT PANEL CONTROLS:
1. POWER.
2. DIGITAL DISPLAY.
3. LC/R : By this P.B. the instrument determines whether the reactive or resistive component of
the value measured is being displayed. If 1st LED lit then it measure L or C and if 2nd LED lit
then it measure resistance.
4. 100 Hz/1 kHz: with the help of this button we can select the frequency at which measurement
is to be made.
5. SER/PAR: the equivalent circuit of a component under test can be pressed either in terms of its
series or parallel equivalent value at the given frequency.
6. HOLD: The HOLD button disable auto range to measure large quantity of components within
particular range.
7. Q : when Q button is selected meter displays Q factor of component.
8. BIAS: Internal 2V DC or external 50V DC for electrolyte capacitor.
9. RANGE LED Indicator: the units, in which the measured value is being displayed, are
indicated on the range indication LEDS.
10. TEST CONNECTORS: The component under test can be directly connected on to banana
terminal.
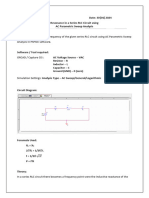
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
COIL UNDER
TEST
Rsh
VTVM
Figure-1 Internal Circuit diagram of LCRQ Meter.
DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Electronics Measurements & Instrumentation
Branch : Electronics & Communication
Semester : 5TH
EXPERIMENT NO:-9- Measurement Using LCRQ Meter.
PROCEDURE:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Connect the power supply cord to the LCR Q Meter.
Connect a Component like resistor, inductor, capacitor at the test terminals.
Switch on the Power Supply and note the reading of meter for the component.
Calculate Q factor and D theoretically.
OBSERVATIN TABLE:
Sr.
No.
Q
Measured
by meter
Q
D
Obtained Measured
by
by meter
calculations
D
Obtained by
calculations
1
2
CALCULATIONS:
CONCLUSION:
________
GRADE
_______________________
SIGNATURE OF STAFF
3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ford Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - PowertrainDokumen62 halamanFord Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - Powertraininfocarsservice.deBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus 2012 Singing 20190122Dokumen91 halamanSyllabus 2012 Singing 20190122suzypienaarBelum ada peringkat
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Dari EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Belum ada peringkat
- Frigga Haug - Beyond Female Masochism. Memory-Work and Politics (1992, Verso) PDFDokumen275 halamanFrigga Haug - Beyond Female Masochism. Memory-Work and Politics (1992, Verso) PDFKalindaMarínBelum ada peringkat
- Instrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualDari EverandInstrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualDokumen148 halamanMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab Manualsramiz_1987100% (1)
- Ledger - Problems and SolutionsDokumen1 halamanLedger - Problems and SolutionsDjamal SalimBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Seminar Agenda and Generator System OverviewDokumen86 halamanTechnical Seminar Agenda and Generator System OverviewKenneth100% (1)
- Technical Data Speedmaster SM 102: Printing Stock Blanket CylinderDokumen1 halamanTechnical Data Speedmaster SM 102: Printing Stock Blanket CylinderAHMED MALALBelum ada peringkat
- Models of Collaboration Between Education and ServicesDokumen17 halamanModels of Collaboration Between Education and ServicesSimran Josan100% (3)
- ASTM 3950 Testing Methods For Strapping Versie 2007 211007 PDFDokumen7 halamanASTM 3950 Testing Methods For Strapping Versie 2007 211007 PDFNestor CzerwackiBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT LABDokumen23 halamanELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT LABDhinakarrajBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageDari EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Modeling Interview Questions AnsweredDokumen6 halamanFinancial Modeling Interview Questions AnsweredBHAVEN ASHOK SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of RLC &Q Using LCR-Q MeterDokumen6 halamanMeasurement of RLC &Q Using LCR-Q MeterKshitiz Panwar50% (2)
- 8 Hints For Successful Impedance MeasuremDokumen12 halaman8 Hints For Successful Impedance MeasuremJesús MartínezBelum ada peringkat
- UIET Lab Manual Basic ElectronicsDokumen48 halamanUIET Lab Manual Basic ElectronicsHarry HarryBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2: AC Measurements-Capacitors and Inductors: Prerequisite Reference MaterialsDokumen10 halamanLab 2: AC Measurements-Capacitors and Inductors: Prerequisite Reference MaterialsLeandro ArvattiBelum ada peringkat
- LCR MeterDokumen6 halamanLCR MeterUmair GulBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Lab EquipmentDokumen5 halamanIntroduction To Lab EquipmentKashif Mujeeb Abdul MujeebBelum ada peringkat
- DC & AC Analysis of RL Circuit Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanDC & AC Analysis of RL Circuit Lab ReportUsairum MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- C-V Measurement Tips, Tricks, and Traps: Lee Stauffer Senior Staff Technologist Keithley Instruments, IncDokumen14 halamanC-V Measurement Tips, Tricks, and Traps: Lee Stauffer Senior Staff Technologist Keithley Instruments, IncJoshua SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Project ProposalDokumen6 halamanProject ProposalishakubalamiBelum ada peringkat
- ENA - Lab - Manual (Update 17-4-2019) PDFDokumen76 halamanENA - Lab - Manual (Update 17-4-2019) PDFMuhammad SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCDokumen5 halamanLab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCAbdul QudoosBelum ada peringkat
- 283 - EEM LAb Manual-MadhabDokumen27 halaman283 - EEM LAb Manual-MadhabECE DepartmentBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Circuits and SimulationDokumen64 halamanElectrical Circuits and SimulationNaveen Yallapu0% (1)
- Ee45 Lab ReportsDokumen9 halamanEe45 Lab ReportschrizzdMBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Electronics - I by P.K.PaulDokumen9 halamanAnalog Electronics - I by P.K.PaulRohitBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Report: Characterizing Resonant Series RLC Circuits Using LabviewDokumen15 halamanExperiment Report: Characterizing Resonant Series RLC Circuits Using LabviewPortia ShilengeBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2 - Vector Network Analyzer MeasurementDokumen25 halamanExperiment 2 - Vector Network Analyzer MeasurementBadut234Belum ada peringkat
- CA Solved Lab Manual (TC-19069)Dokumen50 halamanCA Solved Lab Manual (TC-19069)Sohaib Waseem100% (2)
- Experiment No1Dokumen11 halamanExperiment No1Farzi IDBelum ada peringkat
- A Novel Method For Digital Signal Conditioning Using Resistive and Capacitive Sensor - EditedDokumen5 halamanA Novel Method For Digital Signal Conditioning Using Resistive and Capacitive Sensor - EditedManjusha SreedharanBelum ada peringkat
- Measurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353Dokumen145 halamanMeasurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353NishaKamarajBelum ada peringkat
- High Speed Multichannel Impedance Measuring System: Acta ImekoDokumen6 halamanHigh Speed Multichannel Impedance Measuring System: Acta ImekoGoran MiljkovicBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment ManualDokumen17 halamanExperiment ManualKavita BishtBelum ada peringkat
- CT Testing TheoryDokumen15 halamanCT Testing TheoryClyde CauchiBelum ada peringkat
- RC and RL Circuit AnalysisDokumen8 halamanRC and RL Circuit AnalysisMagdalena SimicBelum ada peringkat
- Q MeterDokumen2 halamanQ MeterhafizrahimmitBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 9Dokumen13 halamanLab 9Abu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- LCR Meter Project ReportDokumen12 halamanLCR Meter Project ReportDarshan Sonawane100% (1)
- Lab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitDokumen4 halamanLab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitAly HuzmurBelum ada peringkat
- Preamble:: Laboratory Manual Electrical MeasurmentDokumen57 halamanPreamble:: Laboratory Manual Electrical MeasurmentRoopa ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFDokumen71 halamanLinear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFHaris -Belum ada peringkat
- Circuit and Network Theory Lab ReportDokumen8 halamanCircuit and Network Theory Lab Reportpeaceissa695Belum ada peringkat
- I2ZDokumen11 halamanI2ZdaveadeBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Multimeter Measurements GuideDokumen12 halamanDigital Multimeter Measurements GuideMahadevBelum ada peringkat
- Measure Inductance Using AC Hay's BridgeDokumen53 halamanMeasure Inductance Using AC Hay's BridgeKeshav Kumar Pushpam100% (1)
- RC Circuits: J H U, P ADokumen6 halamanRC Circuits: J H U, P APavan PatelBelum ada peringkat
- A Method of Measuring RLC Components For Microcontroller Systems - 15470Dokumen4 halamanA Method of Measuring RLC Components For Microcontroller Systems - 154701004 NAGAJOTHI PBelum ada peringkat
- Measurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353: List of ExperimentsDokumen144 halamanMeasurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353: List of ExperimentsVijayapriya RamachandranBelum ada peringkat
- Method High Order Harmonic Measurement and Analysis: New ofDokumen4 halamanMethod High Order Harmonic Measurement and Analysis: New ofLawsay AlqurainyBelum ada peringkat
- The RC Circuit Charging and DischargingDokumen8 halamanThe RC Circuit Charging and DischargingMd. Sazidul Haque SazzadBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3Dokumen9 halamanExperiment 3SANJAY NILAVAN .S.76Belum ada peringkat
- Effective Multi-Tap TransformerDokumen8 halamanEffective Multi-Tap Transformer15101980Belum ada peringkat
- Lab - 8 - Common Emitter Amplifiers-IIDokumen5 halamanLab - 8 - Common Emitter Amplifiers-IIAhmed ChBelum ada peringkat
- Elvis and Bode PlotsDokumen7 halamanElvis and Bode PlotsKashif AmjadBelum ada peringkat
- Ee8511 Control and Instrumentation Laboratory PMCDokumen73 halamanEe8511 Control and Instrumentation Laboratory PMCILYAS BASHA100% (1)
- Experiment 4 AC Measurents RC A RL Ckts 210330Dokumen7 halamanExperiment 4 AC Measurents RC A RL Ckts 210330MK MillyBelum ada peringkat
- 18EC36 - Module5 - Transducer, Programmable Logic ControllerDokumen33 halaman18EC36 - Module5 - Transducer, Programmable Logic ControllerINDIAN LEGENDSBelum ada peringkat
- Measure AC Signals with CRODokumen57 halamanMeasure AC Signals with CRODhamu DharanBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Measurement Lab ManualDokumen57 halamanElectrical Measurement Lab Manualckrishna625100% (1)
- Exp 8Dokumen12 halamanExp 8esumshunBelum ada peringkat
- Ee6511 Control and Instrumentation Laboratory PDFDokumen73 halamanEe6511 Control and Instrumentation Laboratory PDFDhivya BBelum ada peringkat
- Verification of circuit theorems and principles using breadboard experimentsDokumen23 halamanVerification of circuit theorems and principles using breadboard experimentsEngr. AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Print ElectricalDokumen13 halamanPrint ElectricalLiaquat AliBelum ada peringkat
- EE8511-Control and Instrumentation LaboratoryDokumen140 halamanEE8511-Control and Instrumentation Laboratorygangsh50% (2)
- (1-4) DESIGN OF LC METER USING ARDUINO-formatDokumen4 halaman(1-4) DESIGN OF LC METER USING ARDUINO-formatMika RasoanaivoBelum ada peringkat
- 130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDokumen2 halaman130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaBelum ada peringkat
- InviDokumen1 halamanInviritesh120543111008Belum ada peringkat
- 2011 RemDokumen2 halaman2011 RemHet PatelBelum ada peringkat
- I DX ExampleDokumen4 halamanI DX ExampleJoão VieiraBelum ada peringkat
- Business Research Chapter 1Dokumen27 halamanBusiness Research Chapter 1Toto H. Ali100% (2)
- Big Bang TheoryDokumen9 halamanBig Bang TheoryLoo DrBradBelum ada peringkat
- Metaswitch Datasheet Network Transformation OverviewDokumen5 halamanMetaswitch Datasheet Network Transformation OverviewblitoBelum ada peringkat
- EC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryDokumen38 halamanEC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryAbhay AmbuleBelum ada peringkat
- ICJ Judgment on Philippines' Bid to Intervene in Indonesia-Malaysia Maritime Boundary CaseDokumen8 halamanICJ Judgment on Philippines' Bid to Intervene in Indonesia-Malaysia Maritime Boundary CaseZayd Iskandar Dzolkarnain Al-Hadrami100% (1)
- MicrotoxOmni Software Version 4Dokumen12 halamanMicrotoxOmni Software Version 4Louise Veronica JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Renold Transmission Chain Catalogue ENG 0112Dokumen94 halamanRenold Transmission Chain Catalogue ENG 0112nataliaBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Aceh MedikaDokumen10 halamanJurnal Aceh MedikaJessica SiraitBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Sanjeev Nanda - Devoted Son and GrandsonDokumen1 halamanMr. Sanjeev Nanda - Devoted Son and GrandsonSanjeev NandaBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and Operating Instructions Gen-Key: Energy DivisionDokumen22 halamanInstallation and Operating Instructions Gen-Key: Energy DivisionAnonymous RcxX0FcBelum ada peringkat
- Gee1-Lp1 2022-2023Dokumen18 halamanGee1-Lp1 2022-2023Sherrizah AlidoBelum ada peringkat
- Dada and Buddhist Thought - Sung-Won Ko PDFDokumen24 halamanDada and Buddhist Thought - Sung-Won Ko PDFJuan Manuel Gomez GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 SyllabusDokumen23 halamanGrade 9 SyllabusClopzBelum ada peringkat
- Orbeez Sorting and Patterns Learning ExperienceDokumen5 halamanOrbeez Sorting and Patterns Learning Experienceapi-349800041Belum ada peringkat
- Performance of Filler Material in GabionsDokumen4 halamanPerformance of Filler Material in GabionsPreetham N KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MARS Motor Cross Reference InformationDokumen60 halamanMARS Motor Cross Reference InformationLee MausBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Deck de BosBoerderij - Dec2023Dokumen32 halamanConcept Deck de BosBoerderij - Dec2023Bruna San RomanBelum ada peringkat
- Anuj Singh ResumeDokumen4 halamanAnuj Singh ResumeAnuj BaghelBelum ada peringkat
- Sexual ExtacyDokumen18 halamanSexual ExtacyChal JhonnyBelum ada peringkat
- Kiribati, Gilbertese BibleDokumen973 halamanKiribati, Gilbertese BibleAsia BiblesBelum ada peringkat
- MELCs Briefer On SPJDokumen27 halamanMELCs Briefer On SPJKleyr QuijanoBelum ada peringkat