CPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering Drugs
Diunggah oleh
AinahMahaniJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering Drugs
Diunggah oleh
AinahMahaniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DIABETES AND LIPID LOWERING DRUGS
DIABETES
DIABETES AND LIPID LOWERING DRUGS
STANDARD TREATMENT VS INTENSIVE TREATMENT
DIABETES
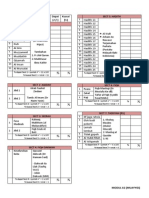
INSULIN
RAPID
Aspart
SHORT
Soluble insulin
INTERMEDIATE
Isophane insulin
(NPH)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
To mimic prandial (mealtime) insulin.
Aspart must be consumed right before meal or up to 15mins
after meal whereas soluble insulin 15mins prior meal or
immediately after.
Subcutaneously
Delayed absorption from its conjugation with protamine,
forming less soluble complex. SubC
Standard treatment involves injection of insulin twice daily. In
contrast intensive treatment involves more frequent
injections.
ADA recommend target mean blood glucose levels of Hba1c
of 7% or less or 154mg/dL
INDICATION
In emergency e.g. DKA given IV
subC in regular basis usually given with
LA
All type of diabetes except DKA
Use for basal control and usually given
with rapid or short acting insulin for
mealtime control
ADVERSE EFFECTS
Headache
Anxiety
Tachycardia
Confusion
Vertigo
Diaphoresis
Lipodystrophy
Hypersensitivity
DIABETES AND LIPID LOWERING DRUGS
LONG
Glargine
Isoelectric point of insulin glargine is lower than that of human
insulin, leading to precipitation at the injection site and
extending its action.
Stimulate insulin release from -cells by blocking the ATP
+
sensitive K channel
Reduce hepatic glucose production
Increase peripheral insulin sensitivity
Pharmacokinetics
Extensively metabolised by CYP 450 enzymes in the liver
Excreted via liver and kidney
To be used with caution in patients with renal or hepatic
insufficiency
1. Reduction of hepatic glucose output (inhibits gluconeogenesis)
2. Slows intestinal absorption of sugars
3. Improves peripheral glucose uptake and utilisation (especially
in muscle cells)
4. Reduces hyperlipidemia
Pharmacokinetics
Not metabolised, cleared from the body by active tubular
secretion, excreted unchanged in the urine
To be used with caution in patients with renal insufficiency or
those predisposed to metabolic acidosis
Given subC
Slower onset than NPH, and has flat,
prolonged hypoglycaemic effect with no
peak
TZDS/GLI
TAZONE
BIGUANIDES
SULPHONYLUREAS
GLICLAZIDE
METFORMIN
PIOGLITAZONE
Suitable for pt with DM2 that cannot be
controlled with only diet
Activate the transcription factor PPAR, which affects adipose
cell differentiation and lipid metabolism
Metabolised in the liver by CYP 450 enzymes, metabolites are
eliminated mainly in bile
useful in overweight people with
diabetes
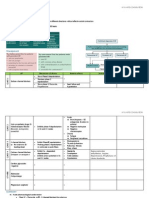
HYPOGLYCAEMIA
6.
Clinical Features
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
AUTONOMIC
Anxiety
Sweating
Hunger
Tremor
Palpitations
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
NEUROGLYCOPENIC
Confusion
Vertigo
Drowsy
Visual trouble seizures
Coma
Can suppress appetite
and causes less weight
gain than sulphonylureas
Largely gastrointestinal
including anorexia,
diarrhoea, nausea and
abdominal discomfort
May cause lactic acidosis
Weight gain
Fluid retention
Heart failure
Bladder cancer?
Dizziness
Hypoglycaemia
Weight gain (as insulin
preferentially deposits
calories in adipose tissue
in Type 2 diabetics)
Hyperinsulinemia
DIABETES AND LIPID LOWERING DRUGS
Initial Management
if x swallow - 2550ml 50% glucose IV
(via larger vein with
0.9% saline flush to
prevent phlebitis)
OR
oral sugar or LA
starch (toast)
glucagon 1mg IM if
no IV access (SA so
repeat after 20min
and follow with oral
carbs)
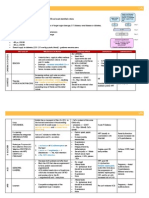
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
Clinical Features
Ketonaemia 3 mmol/L or significant ketonuria (++ on urine dipstick)
Blood glucose >11 mmol/L or known diabetes mellitus
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) <15 mmol/L and/or venous pH < 7.3
Intial Management
Fluid replacement
commence 0.9%
NaCl via infusion
pump + K+
replacement
STATIN
LIPID DIS.
SIMVASTATIN
IV insulin infusion
(0.1u/kg/hr)
MOA
Inhibit enzyme HMG
Co A reductase in
cholesterol synthesis
INDICATION
systolic <90mmHg 500ml NaCl/10-15min
systolic >90mmHg 1000ml/60mins
50u soluble insulin
(SA) made up to
50ml with 0.9%
NaCl solution
Primary Hyperlipidaemia
(Reduce LDL by 30% &
Raise HDL by 20%)
2 Hypercholesterolemia
CONTRAINDICATION
during pregnancy
and lactation
ADVERSE EFFECTS
Headache, nausea, rashes
Sleep disturbances
Rise in serum transaminase
Myositis & Rhabdomyolysis
Potassium
>5.5 - NIL
3.5 - 5.5 - 40mmol/L
<3.5 - senior review
INTERACTION
increased statin concentrations
e.g ciclosporin, clarithromycin,
calcium channel blockers,
antifungals
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Urinary IncontinenceDokumen1 halamanUrinary IncontinenceAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageDokumen1 halamanCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionDokumen3 halamanCSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)Dokumen1 halamanCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)AinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceDokumen4 halamanCsim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageDokumen4 halamanCsim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesDokumen2 halamanCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneDokumen7 halamanCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.92 - HypoventilationDokumen1 halamanCsim2.92 - HypoventilationAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseDokumen3 halamanCsim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Csim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaDokumen11 halamanCsim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionDokumen6 halamanCSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaDokumen1 halamanCSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen2 halamanCSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingDokumen1 halamanCPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersDokumen2 halamanCPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitDokumen3 halamanCPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Penilaian Bahan TamhidiDokumen3 halamanPenilaian Bahan TamhidiAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Penilaian Bahan MUAYYIDDokumen3 halamanPenilaian Bahan MUAYYIDAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsDokumen5 halamanCPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Infection and AntibioticsDokumen4 halamanInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - PainDokumen3 halamanCPTP - PainAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2Dokumen3 halamanCPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2AinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - EpilepsyDokumen4 halamanCPTP - EpilepsyAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationDokumen4 halamanCPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - HPT & HFDokumen4 halamanCPTP - HPT & HFAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- CPTP - Asthma & CopdDokumen5 halamanCPTP - Asthma & CopdAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Themed Week 7 - LIVERDokumen24 halamanThemed Week 7 - LIVERAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- Infection and AntibioticsDokumen4 halamanInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Funda Prof - Ad LMR AnswersDokumen35 halamanFunda Prof - Ad LMR AnswersFreeNursingNotesBelum ada peringkat
- Peadiatric ECGDokumen54 halamanPeadiatric ECGsayedmBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Dian Kusumaningrum - PRESENTASI JCCA-ANTIBIOTIC DOSING IN CRITICALLY ILLDokumen31 halamanDr. Dian Kusumaningrum - PRESENTASI JCCA-ANTIBIOTIC DOSING IN CRITICALLY ILLRestu TriwulandaniBelum ada peringkat
- 18c. Lymphoma EditedDokumen36 halaman18c. Lymphoma EditedMUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRIBelum ada peringkat
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Breakthrough Pain PDFDokumen139 halamanThe Diagnosis and Treatment of Breakthrough Pain PDFSantiago HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- World Homeopathy Day-An Informative Article by - Dr.M.Rizwan Ali, Progressive Homeopathic Clinic, Gulbarga, Karnataka - IndiaDokumen2 halamanWorld Homeopathy Day-An Informative Article by - Dr.M.Rizwan Ali, Progressive Homeopathic Clinic, Gulbarga, Karnataka - IndiaDrRizwanAliBelum ada peringkat
- The Therapeutic Alliance in Couples and Family TherapyDokumen10 halamanThe Therapeutic Alliance in Couples and Family TherapySophiez0257Belum ada peringkat
- Mindfulness Interventions For Nursing Students: Application of Modelling and Role Modelling TheoryDokumen7 halamanMindfulness Interventions For Nursing Students: Application of Modelling and Role Modelling Theoryagnesia yusupBelum ada peringkat
- Swyer James MacLeod SyndromeDokumen12 halamanSwyer James MacLeod Syndromeflori.bBelum ada peringkat
- Entrelazamiento (Amir Aczel)Dokumen8 halamanEntrelazamiento (Amir Aczel)Memento MoriBelum ada peringkat
- Fasting Ramadan During PregnancyDokumen17 halamanFasting Ramadan During PregnancyHasiah Karim100% (1)
- Vol 9 ADokumen229 halamanVol 9 ADace SniedzeBelum ada peringkat
- One Man's Food Is Another Man's Poison - A Report On Metabolic Typing.Dokumen5 halamanOne Man's Food Is Another Man's Poison - A Report On Metabolic Typing.Dominik Reza Zaerin100% (1)
- CKD CHCRTDokumen28 halamanCKD CHCRTNurhidayati KeriyunBelum ada peringkat
- Letter To Stephen Muldrow USAFLM Re Dr. Asad Qamar May-12-2017Dokumen93 halamanLetter To Stephen Muldrow USAFLM Re Dr. Asad Qamar May-12-2017Neil GillespieBelum ada peringkat
- Night FeverDokumen5 halamanNight FeverdewioktaBelum ada peringkat
- POLK COUNTY - Goodrich ISD - 2008 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseDokumen48 halamanPOLK COUNTY - Goodrich ISD - 2008 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseTexas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseBelum ada peringkat
- Easy Health Insurance Claim Form PDFDokumen4 halamanEasy Health Insurance Claim Form PDFAnkithBelum ada peringkat
- Chap.30 Complications From Heart Disease WordDokumen6 halamanChap.30 Complications From Heart Disease WordcaisakiBelum ada peringkat
- BARC TrainingDokumen6 halamanBARC Trainingashfaqk100% (1)
- Xinnong Cheng - Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 1Dokumen282 halamanXinnong Cheng - Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 1Abrar Abizar100% (1)
- 3p7p Protocol For CosmodicDokumen3 halaman3p7p Protocol For CosmodicBacean Aurel Ioan100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDokumen7 halamanSchizophreniaMANOJ KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- History-Taking & Physical Examination by DR Samer Abu EidehDokumen48 halamanHistory-Taking & Physical Examination by DR Samer Abu EidehAbdullah MatarBelum ada peringkat
- Clasificare Carii Dentare Otr Cariologie An IIIDokumen79 halamanClasificare Carii Dentare Otr Cariologie An IIIStefana NanuBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For SchizoDokumen6 halamanNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEABelum ada peringkat
- Principles Involved in Bioassay by Different Methods A Minireview PDFDokumen18 halamanPrinciples Involved in Bioassay by Different Methods A Minireview PDFPankaj KushwahBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Pain NCPDokumen2 halamanAcute Pain NCPfbarlicosBelum ada peringkat
- CalgaryDokumen44 halamanCalgaryGifuGifuBelum ada peringkat
- Kyasanur Forest DiseaseDokumen2 halamanKyasanur Forest DiseaseGenoMacaraanBelum ada peringkat