EE220 Lecture 5
Diunggah oleh
uplbseles0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan21 halamanUnit Commitment (EE220)
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniUnit Commitment (EE220)
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan21 halamanEE220 Lecture 5
Diunggah oleh
uplbselesUnit Commitment (EE220)
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 21
EE 220
Lecture 5: Introduction to Power System Control
Power System Control
Power system control involves the use of various
technology and methodology in maintaining certain
dynamic performance of a power system
Power system control is closely related to power
system stability
EE 220
Power System Stability
Main purpose:
Ability to maintain equilibrium
Divided into two main types
Angle Stability
Voltage Stability
Torque Balance of synchronous machine
Ability to maintain steady voltage
Disturbance disrupts equilibrium
EE 220
i.e. Faults
Power System Stability
Practical power system network is highly meshed
with different interconnected equipment, loads and
generators
Under ideal condition, the power system operates at
desired frequency i.e. 60 Hz
However power system is imperfect, load variation
occurs and generators vary its load as well
Electrical power output of generator is dependent on
the rotational performance of synchronous machine
Machine must maintain its synchronous speed for
normal operation
EE 220
Transient Stability
Ability of the power system to maintain synchronism
when subjected to a severe transient disturbance,
such as a short circuit on transmission line
A power system is transiently stable for a particular
steady-state operating condition and for a particular
(large) disturbance or sequence of disturbances if,
following that (or sequence of) disturbance(s) it
reaches an acceptable steady-state operating
condition.
EE 220
first swing
instability
stabl
e
Voltage stability ability of a power system to
maintain steady acceptable voltages at all buses of
the system after being subjected to a disturbance
from a given initial operating condition.
Voltage collapse the process by which the
sequence of events accompanying voltage instability
leads to a blackout or abnormally low voltages in a
significant part of the power system.
Frequency stability the ability of a power system
to maintain steady frequency following a severe
system upset resulting in a significant imbalance
between generation and load.
Philippines
60 Hz
Overfrequency = excess generation
Underfrequency = deficiency in generation
Voltage Control
Voltage on power system is primarily dependent on
reactive power or MVAR
Sources
Generator
Capacitor/Reactor
EE 220
Generator Control
Synchronous Generators are the common generator
in a power system
The reactive power of a generator is dependent on
its excitation system
EE 220
Generator Excitation system
Main function
Provide DC current to field winding
The field winding is primary responsible in maintaining
proper voltage at generator terminal
Generator exciter can be quickly modified for voltage
regulation
However MVAR production of generators depends on its
capability and availabiliy
EE 220
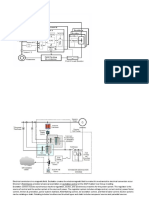
Elements of an Excitation System
EE 220
Elements of an Excitation System
Exciter provides DC
power to generator field
winding
EE 220
Elements of an Excitation System
Process or amplifies input
control signal for exciter
control (feedback
amplifier)
EE 220
Elements of an Excitation System
Provides additional input
signal to the regulator to
damp power system
oscillation
EE 220
Elements of an Excitation System
Ensure that the capability
limits of the exciter is
met and protected
EE 220
Frequency Control
Frequency is controlled by balancing supply and
demand
Governor system in generators senses any change
in rotational speed to adjust its mechanical input
power
EE 220
Governor Modes of Operation
Droop Mode
Decrease in speed due to increase in load
If the frequency decreases (droops), the governor will
respond by increasing fuel output until reference speed is
attained
Droop mode ensures that the increase in fuel position is
enough to prevent over-speeding when the system
returns to normal
In a meshed network with several generators need to
adjust its speed at a single reference to ensure that each
generator will adjust to demand proportional to its
capacity
EE 220
Governor Modes of Operation
Isochronous Mode
Fixed frequency regardless of load
Governor will maintain its frequency setting of the
generator despite load variation
Usually used on isolated system
EE 220
Generator Power Generation and
Control Blocks
EE 220
Reporting
FACTS Devices
21
Static VAR Compensator (SVC)
Static Compensator (STATCOM)
Universal Power Flow Controllers (UPFC)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- 17th International Conference On Electrical, Electronics and Systems Engineering December 21 - 22, 2015 Istanbul, TurkeyDokumen47 halaman17th International Conference On Electrical, Electronics and Systems Engineering December 21 - 22, 2015 Istanbul, TurkeyPraveen Nayak BhukyaBelum ada peringkat
- ExcitationDokumen12 halamanExcitationDdumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Small Signal Stability AnalysisDokumen71 halamanSmall Signal Stability AnalysisRick Leon VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Power System StabilityDokumen31 halamanAnalysis of Power System Stabilitytarnedo1100% (1)
- MATLAB-Simulink Based Analysis ofDokumen4 halamanMATLAB-Simulink Based Analysis ofAmare KassawBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power System 5 Lecture NoteDokumen123 halamanElectrical Power System 5 Lecture NoteAduma JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Static Excitation SystemDokumen36 halamanStatic Excitation Systemlrpatra100% (1)
- Lec 1Dokumen28 halamanLec 1ahmedibrahim4260Belum ada peringkat
- Modeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation SystemsDokumen7 halamanModeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation Systemsni60Belum ada peringkat
- Reactive Power ControlDokumen73 halamanReactive Power Controlمحمد سليمانBelum ada peringkat
- Monthly Progress Report 20 May 20Dokumen25 halamanMonthly Progress Report 20 May 20SBILALAHMEDBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Flow of Power in AC System and ConventionalDokumen22 halaman1 - Flow of Power in AC System and ConventionalchintanpBelum ada peringkat
- Static Excitation System - Stage-2Dokumen38 halamanStatic Excitation System - Stage-2raghavendran raghuBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation SystemDokumen38 halamanExcitation SystemRaja Ramachandran100% (1)
- General Excitation SystemDokumen58 halamanGeneral Excitation SystemReza GhasemiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 19-20 OnlineDokumen73 halamanUnit 2 19-20 Onlinehabte gebreial shrashrBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Stability-Chapter 3Dokumen84 halamanPower System Stability-Chapter 3Du TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- Generator Excitation SystemDokumen34 halamanGenerator Excitation Systemwas00266100% (1)
- Avr LFC GB BDDokumen53 halamanAvr LFC GB BDBetelhem DerejeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen14 halamanUnit 1Yogesh KarlekarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter TwoDokumen85 halamanChapter Twohabte gebreial shrashrBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage and Reactive Power Control: Rolly E. BalayboaDokumen17 halamanVoltage and Reactive Power Control: Rolly E. BalayboaGeva GarradoBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyDokumen12 halamanExcitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyAmeer Hamza100% (1)
- Psoc Unit 1Dokumen10 halamanPsoc Unit 1Dhivya B100% (1)
- 3.2 - Excitation SystemsDokumen18 halaman3.2 - Excitation SystemsEliyanto E BudiartoBelum ada peringkat
- Suresh Main Project of ExcitationDokumen68 halamanSuresh Main Project of Excitationvenkeyharish0% (1)
- Vocational Training Reort of NTPC SipatDokumen22 halamanVocational Training Reort of NTPC Sipatmuskan sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDokumen31 halamanExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentSudar WadiBelum ada peringkat
- AVR Automatic Voltage RegulatorDokumen2 halamanAVR Automatic Voltage RegulatorLithleuxay Philavong50% (2)
- Generator Excitation SystemDokumen21 halamanGenerator Excitation SystemHammad Malik100% (1)
- Excitation System of Synchronous GeneratorDokumen7 halamanExcitation System of Synchronous GeneratorMOHSIN_IIUIBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation CourseDokumen31 halamanExcitation CourseFarhanBaqiBelum ada peringkat
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDokumen31 halaman02-2 Excitation CourseFulki Kautsar S100% (1)
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDokumen31 halaman02-2 Excitation CourseAnonymous xU9ZHqBelum ada peringkat
- 197 - EE8702, EE6603 Power System Operation and Control - NotesDokumen85 halaman197 - EE8702, EE6603 Power System Operation and Control - Notessimali.varma.elect.2021Belum ada peringkat
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDokumen31 halaman02-2 Excitation CoursejaikolangaraparambilBelum ada peringkat
- M.A.M College of Engineering: Department of Electrical and Electronics EnggDokumen16 halamanM.A.M College of Engineering: Department of Electrical and Electronics EnggsathishneBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Power Generation and Excitation SystemDokumen20 halamanElectric Power Generation and Excitation SystemMansen NsubugaBelum ada peringkat
- BEE047 PSOC NotesDokumen90 halamanBEE047 PSOC NotesCharles RobiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Voltage Captions RegulatorDokumen10 halamanAutomatic Voltage Captions RegulatorJohn SagarBelum ada peringkat
- Power System TransientsDokumen11 halamanPower System TransientsKhairul AshrafBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation Systems: Raman JainDokumen15 halamanExcitation Systems: Raman JainrohitctppBelum ada peringkat
- Stability Performance of New Static Excitation System With Boost-Buck ConverterDokumen8 halamanStability Performance of New Static Excitation System With Boost-Buck ConverterMartua MarioBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Lab-3: Electrical Power System Protection EE-182, EE-183, EE-196, EE-202 Section: FDokumen2 halamanPre Lab-3: Electrical Power System Protection EE-182, EE-183, EE-196, EE-202 Section: FMaaz HussainBelum ada peringkat
- EEU801 Power System Stability: Dr. Kawita D. Thakur Government College of Engineering, AmravatiDokumen20 halamanEEU801 Power System Stability: Dr. Kawita D. Thakur Government College of Engineering, AmravatiSominath HarneBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Various Excitation Systems For Diesel GeneratorDokumen8 halamanComparison of Various Excitation Systems For Diesel GeneratorbehroozBelum ada peringkat
- PSD 5qDokumen85 halamanPSD 5qSeid EndrisBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDokumen31 halamanExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentSandeep SinghBelum ada peringkat
- By:-S.Shivaprasad N.Swathireddy T.Ramu RanjankumarDokumen36 halamanBy:-S.Shivaprasad N.Swathireddy T.Ramu RanjankumarShiva Prasad SankojuBelum ada peringkat
- Reactive Power ControlDokumen25 halamanReactive Power ControlDeepti GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Excitation SystemDokumen59 halamanExcitation SystemVenkat Cherukuri100% (2)
- Excitation SystemDokumen38 halamanExcitation Systemlrpatra50% (2)
- Automatic Voltage Regulator in GensetDokumen8 halamanAutomatic Voltage Regulator in GensetPravat Kumar BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Power OscillationsDokumen54 halamanPower OscillationsVijay RohillaBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Aircraft Electrical Systems BackgroundDokumen5 halamanReport On Aircraft Electrical Systems BackgroundRahul ChandranBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Collapse: M. H. SadeghiDokumen31 halamanVoltage Collapse: M. H. Sadeghiken84hnBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorDari EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorBelum ada peringkat
- Ground Fault Currents in Unit Generator-Transformer - Sultan2012Dokumen5 halamanGround Fault Currents in Unit Generator-Transformer - Sultan2012uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Harmonics Using Fluke Power AnalyzerDokumen13 halamanHarmonics Using Fluke Power AnalyzeruplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Grid Stability Study After The Integration of A Wind Farm - Amor2015Dokumen6 halamanGrid Stability Study After The Integration of A Wind Farm - Amor2015uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Procedures Manual For Power System Studies: Emerson Network Power Power System Engineer Electrical Reliability ServicesDokumen22 halamanProcedures Manual For Power System Studies: Emerson Network Power Power System Engineer Electrical Reliability Servicesuplbseles100% (1)
- Arc Flash Report Example 2015Dokumen110 halamanArc Flash Report Example 2015uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- PSE Training Manual - IntroDokumen41 halamanPSE Training Manual - IntrouplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- B - Symmetrical Components (Stevenson, APMagabo)Dokumen2 halamanB - Symmetrical Components (Stevenson, APMagabo)uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Peg 70 Kap 08Dokumen36 halamanPeg 70 Kap 08megamaster2010Belum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint Tobias Part 1 of 4Dokumen6 halamanPowerpoint Tobias Part 1 of 4uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- 0B - Per Unit Calcs (APMagabo)Dokumen4 halaman0B - Per Unit Calcs (APMagabo)uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- 01.4TB.047 X-R RatioDokumen1 halaman01.4TB.047 X-R RatioMuhammad Irfan ArdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Es17.0 (Arc Flash)Dokumen30 halamanEs17.0 (Arc Flash)uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Lecture Using EDSA-ETAP-PSSE-MatlabDokumen38 halamanShort Circuit Lecture Using EDSA-ETAP-PSSE-MatlabTed LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Ccomplex Numbers: Rectangular vs. Polar Form: A Real Component B Imaginary ComponentDokumen1 halamanCcomplex Numbers: Rectangular vs. Polar Form: A Real Component B Imaginary ComponentuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- MiProtectio - Management SystemDokumen8 halamanMiProtectio - Management SystemuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Artificial Neural NetworksDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Artificial Neural NetworksEdu Daryl MacerenBelum ada peringkat
- Power Savers Mar2010Dokumen4 halamanPower Savers Mar2010challapradyumna8Belum ada peringkat
- Smart Grid Concept and CharacteristicsDokumen3 halamanSmart Grid Concept and CharacteristicsuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Dispatch: Antonio J. Conejo 2002Dokumen67 halamanEconomic Dispatch: Antonio J. Conejo 2002anithaarumallaBelum ada peringkat
- AC PowerDokumen13 halamanAC PoweruplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- EE141 ExamDokumen9 halamanEE141 ExamuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- PART IV. Instrument TransformersDokumen30 halamanPART IV. Instrument TransformersuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Vectors - Math220Dokumen4 halamanVectors - Math220uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- EE220 Lecture 4 PDFDokumen29 halamanEE220 Lecture 4 PDFuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Analysis PDFDokumen16 halamanSymmetrical Fault Analysis PDFlimkokchiang809Belum ada peringkat
- EE220 Economic Operations Exam 2Dokumen2 halamanEE220 Economic Operations Exam 2uplbseles0% (1)
- EE220 Lecture 5Dokumen21 halamanEE220 Lecture 5uplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- EE220 Lecture 4 PDFDokumen29 halamanEE220 Lecture 4 PDFuplbselesBelum ada peringkat
- EE220 Lecture 5Dokumen21 halamanEE220 Lecture 5uplbselesBelum ada peringkat