Cell Cycle Notes
Diunggah oleh
ShilpaDas0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
136 tayangan2 halamanHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
136 tayangan2 halamanCell Cycle Notes
Diunggah oleh
ShilpaDasHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Cell Cycle Notes
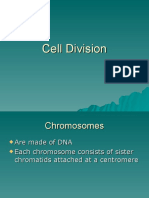
I. Chromosomes: thread-like structures of DNA and histones (protein)
forming a unit called a nucleosome
A. Chromatid: 2 sister chromatids make up a chromosome
B. Centromere: attaches 2 chromatids
C. Chromatin: unraveled DNA
D. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes = 46 total (diploid/2n)
II. The Cell Cycle:
A. somatic (body) cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form
2 identical daughter cells
Consists of 2 phases: Interphase (G1 S
G2) + Cell Division (M)
B. Interphase phase between mitosis, 90% of the time that elapses
Gap1 cell growth & assembly of carbs, lipids, and proteins
Synthesis DNA replication
G2 prep for mitosis
1. Proteins and organelles are made during all 3 stages
2. Nuclear envelope is well-defined
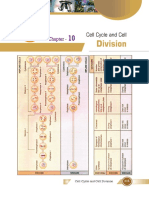
C. Cell Division (M) division of nucleus (mitosis) & cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
mitosis
Prophase: longest phase of M; chromosomes coil and become
visible while the nuclear membrane breaks down
centrioles: separate and move to opposite poles organizing
the mitotic spindle
spindle fibers: microtubules attach to centromere and move
sister chromatids at a site called the kinetochore
Metaphase: chromatids line up on the cell equator and centrioles are
at opposite poles
Anaphase: chromosomes move to opposite poles as spindles pull on
centromere
Telophase: 2 new nuclei form and nuclear membrane reforms
Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm
cleavage furrow cytoplasm in animal cell pinches inward
cell plate formation of new cell wall in plant cells during
telophase
III. Binary fission:
A. The copied prokaryotic DNA is attached to the plasma membrane at two
sites
B. the membrane grows in between the two attachment sites
C. Once the cell is almost double in size, the membrane pinches inward
and a cell wall forms
IV. Regulating the Cell Cycle
A. Uncontrolled Cell Growth
1.
Cancer - occurs when cells dont respond to growth signals
2.
Malignant tumors
i. cell mass that can damage the surrounding tissue
ii. metastasis - cells break loose from tumor spreading
throughout the body disrupting normal cell activities
3.
Causes of cancer
i. internal or external regulators are not working
ii. smoking, radiation exposure, viral infection
iii. defect in p53 and BRCA genes
B. Cell Cycle Regulators
1.
Cyclins
i. protein (kinase) found in cell during mitosis that forms
the spindle
ii. these regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotes
2.
internal regulators - proteins that respond to the events
inside the cell to make sure phases of division do not occur
too early
3.
external regulators
i. proteins that respond to the events outside the cell
which speed up or slow down the cell cycle
ii. growth factors most important regulators, especially
during embryonic development and healing
iii.molecules found on the surfaces of cells slow/stop cell
cycle of neighboring cells
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Krav Maga To Empower KidsDokumen7 halamanKrav Maga To Empower KidshectorhugoarBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Myocardial InfarctionDokumen23 halamanCase Study Myocardial InfarctionJester GalayBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division Note PDFDokumen12 halamanCell Division Note PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDokumen59 halamanCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaBelum ada peringkat
- Sheiko program training and FAQsDokumen34 halamanSheiko program training and FAQsGiovan Maria Catalan BelmonteBelum ada peringkat
- (90-55-3000) BIOLIS 50i - Operator's M - V5.7 PDFDokumen498 halaman(90-55-3000) BIOLIS 50i - Operator's M - V5.7 PDFMatrix100% (1)
- Burket's Oral Medicine 13th Ed Michael GlickDokumen1.139 halamanBurket's Oral Medicine 13th Ed Michael GlickMahima GoodwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division and the Cell Cycle ExplainedDokumen25 halamanCell Division and the Cell Cycle ExplainedZamantha Zaynn100% (1)
- Cell cycle checkpoints and regulationDokumen17 halamanCell cycle checkpoints and regulationKamaki RyuBelum ada peringkat
- Massive Transfusion ProtocolDokumen5 halamanMassive Transfusion ProtocolArlette Araceli Barbosa IbarraBelum ada peringkat
- Micronutrient Deficiency Among FilipinosDokumen20 halamanMicronutrient Deficiency Among FilipinosAlnyssa Cornell100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Division NotesDokumen5 halamanCell Cycle and Division NotesMicaela DavisBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen40 halamanCell DivisionMohamed NourBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Chapter 12 NotesDokumen3 halamanAP Bio Chapter 12 NotesBisesh100% (1)
- Cytogenetics 1Dokumen31 halamanCytogenetics 1mm3370350Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokumen4 halamanCell Cycle and Cell DivisionanuminiatureBelum ada peringkat
- The Phase of Growth and DNADokumen4 halamanThe Phase of Growth and DNARedBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDokumen22 halamanNew Microsoft PowerPoint Presentationsaramaktoof2Belum ada peringkat
- 03 Cell CycleDokumen11 halaman03 Cell CyclereyesconelBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes 1st Quarter 1Dokumen27 halamanBiology Notes 1st Quarter 1Janelle Grace OrdanizaBelum ada peringkat
- CycleDokumen7 halamanCycleAbbas TalibBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology of CellDokumen7 halamanPathology of CellamanuelBelum ada peringkat
- MitosisDokumen17 halamanMitosisadamahmad20007Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Bio AssignmentDokumen11 halamanCell Bio AssignmentPranay PatnaikBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Project:The Cell Cycle Group Number: 672: Name of MembersDokumen16 halamanBiology Project:The Cell Cycle Group Number: 672: Name of MembersNadhirah MohamadBelum ada peringkat
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter OutlineDokumen7 halamanMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outlineapi-455371000Belum ada peringkat
- MustakDokumen3 halamanMustakMh Mari HereBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokumen3 halamanCell Cycle and Cell DivisionRRBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle Checkpoints and PhasesDokumen6 halamanCell Cycle Checkpoints and PhasesJoyce NoblezaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen10 halamanCell CycleFatima Tul zahraBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Key Events and PhasesDokumen12 halamanCell Cycle and Cell Division: Key Events and PhasesTarun Sharma100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - BST Notes FinalDokumen6 halamanCell Cycle and Cell Division - BST Notes FinalSanjeevi RamasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Module in EnglishDokumen28 halamanModule in EnglishIannBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen19 halamanCell CycleAnahita SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle ExplainedDokumen35 halamanCell Cycle ExplainedHimanshi ShrresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseDokumen17 halamanChapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseIrish GatpoBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01Dokumen35 halamanBio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDokumen4 halamanModule 4-The Cell's Life Cycle10. Briol AlvinBelum ada peringkat
- GENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisDokumen12 halamanGENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisPercival RiegoBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology I Long Test ReviewerDokumen18 halamanGeneral Biology I Long Test ReviewerJillian GarcilanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division Explained: Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen22 halamanCell Division Explained: Mitosis and Meiosisevergarden33Belum ada peringkat
- Gen Bio - Lesson 05Dokumen46 halamanGen Bio - Lesson 05imageauto989Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle PDFDokumen12 halamanCell Cycle PDFAtiya FalakBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionDokumen23 halamanBiology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionKate Ashly Mae AteradoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle To MeiosisDokumen13 halamanCell Cycle To MeiosisSOPHIA ALESNABelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle Lecture ReviewerDokumen2 halamanCell Cycle Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Belum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen46 halamanCell Cycleatnasiya2026Belum ada peringkat
- CELL CYCLE - MitosisDokumen31 halamanCELL CYCLE - Mitosisandrew gauranaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokumen13 halamanCell Cycle and Cell DivisionHeerak SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis ExplainedDokumen12 halamanCell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis ExplainedJean Carmelette BalalloBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen23 halamanCell DivisionInsatiable CleeBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 4 Sec2Dokumen13 halamanMODULE 4 Sec2Tanalgo JPBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokumen12 halamanChapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShivani Shree SundaramoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Goal 8 20131105 195711 1Dokumen20 halamanGoal 8 20131105 195711 1api-278654596Belum ada peringkat
- THE CELL II: Nucleus, Cell Cycle, Cell Division, ApoptosisDokumen23 halamanTHE CELL II: Nucleus, Cell Cycle, Cell Division, ApoptosisDebby14Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Division and the Cell CycleDokumen48 halamanCell Division and the Cell CycleAisha A RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division and MitosisDokumen48 halamanCell Division and MitosisJesslyn VaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDokumen5 halamanModule 4-The Cell's Life CycleGoogle BackupBelum ada peringkat
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadDokumen11 halamanBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadJamie Hayes100% (26)
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Chaper12Dokumen24 halamanCell Cycle, Mitosis, Chaper12prehealthhelp43% (7)
- Week 2 - Cellular ReproductionDokumen25 halamanWeek 2 - Cellular Reproductionansammohame2007Belum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen2 halamanCell DivisionSohom PalBelum ada peringkat
- GENBIO1MOD3Dokumen11 halamanGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen8 halamanCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiBelum ada peringkat
- PBL-3: Effects of Smoking and Gutka on HealthDokumen8 halamanPBL-3: Effects of Smoking and Gutka on HealthRomi RajaBelum ada peringkat
- MITOSISDokumen39 halamanMITOSISEmmalyn VillosoBelum ada peringkat
- Children's Congress ProposalDokumen5 halamanChildren's Congress ProposalMA. CRISTINA SERVANDOBelum ada peringkat
- Team Performance ModelDokumen17 halamanTeam Performance ModelAdewumi Samson Segun100% (1)
- GINA 2021 Guidelines for Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentDokumen24 halamanGINA 2021 Guidelines for Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentBianca Watanabe - RatillaBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Fyi Report DocumentDokumen110 halaman2011 Fyi Report DocumentSmart Horizons Lifetime Training SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Carrillo & Associates, Inc: Rosa Antonia Carrillo, MSODDokumen3 halamanCarrillo & Associates, Inc: Rosa Antonia Carrillo, MSODalberto1954Belum ada peringkat
- Family Context of Mental Health Risk in Tsunami-Exposed AdolescentsDokumen11 halamanFamily Context of Mental Health Risk in Tsunami-Exposed AdolescentsVirgílio BaltasarBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Development FactorsDokumen9 halamanIndividual Development Factorshanani_leeBelum ada peringkat
- Mita Das (Universityof CalcuttaDokumen52 halamanMita Das (Universityof CalcuttaBishal Roy100% (1)
- Planning Design and Analysis of G+1 Hospital Building For Iiit Srikakulam CampusDokumen1 halamanPlanning Design and Analysis of G+1 Hospital Building For Iiit Srikakulam CampusSaritha TejavathBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Servicio Ventilador Bear Cub 750psvDokumen64 halamanManual de Servicio Ventilador Bear Cub 750psvVladimir BorjaBelum ada peringkat
- FM 999-3 Counter-Zombie Operations at The Fireteam Level v1.1Dokumen16 halamanFM 999-3 Counter-Zombie Operations at The Fireteam Level v1.1Arthur BarieBelum ada peringkat
- C& R 2010Dokumen29 halamanC& R 2010Dhananjaya MnBelum ada peringkat
- Effective Communication for InterpretersDokumen5 halamanEffective Communication for InterpretersRaimundo SousaBelum ada peringkat
- Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Form For Cohort Studies: SelectionDokumen2 halamanNewcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Form For Cohort Studies: SelectionKlinik KalitanjungBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Disease: Overview of The LiverDokumen6 halamanLiver Disease: Overview of The LiverMustafa AlmasoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Peace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsDokumen26 halamanPeace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsBelum ada peringkat
- Situation 1: One Day, Dika Hangs Out Alone To Get Some Fresh Air. When She PassesDokumen2 halamanSituation 1: One Day, Dika Hangs Out Alone To Get Some Fresh Air. When She PassesDika Pratiwi BudiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex Questions For Fundamentals of NursDokumen32 halamanNclex Questions For Fundamentals of NursJrBong SemaneroBelum ada peringkat
- Full Download Test Bank For Pharmacology 9th Edition by Mccuistion PDF Full ChapterDokumen36 halamanFull Download Test Bank For Pharmacology 9th Edition by Mccuistion PDF Full Chapterpotshardmonied5cuc100% (19)
- ACADEMIC CALENDAR MEDICAL PROGRAMME 2019/2020Dokumen1 halamanACADEMIC CALENDAR MEDICAL PROGRAMME 2019/2020AnNourBelum ada peringkat
- Asbmt: BK Virus Disease After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Cohort AnalysisDokumen7 halamanAsbmt: BK Virus Disease After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Cohort Analysiscalixto hernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Among The Laws Affecting The Practice of NursingDokumen3 halamanAmong The Laws Affecting The Practice of Nursingmarie100% (35)
- Gamble J Sped854 m8 Philosophy2Dokumen5 halamanGamble J Sped854 m8 Philosophy2api-295546890Belum ada peringkat