Calculating Transforme
Diunggah oleh
krit_kasemDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Calculating Transforme
Diunggah oleh
krit_kasemHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
An example of calculating transformer size and voltage drop due to starting of large m...
Page 1 of 5
Home Technical Articles Article Categories Contact us Subscribe to articles Subscribe to
downloads El. Enginering Guides
EE General guides
Power Substations
Schneider Electric CTs
Siemens Basics of EE
ABB Drives Guides
Industry Automation
Relay control/protection
Alternative Energy
Electrical Software MS Excel Spreadsheets Electrical Design Docs Engineering Resources
Video Lectures Electrical Engineering
PLC Programming Training
Electric Testing and Maintenance (VIDEO)
Network Theorems and Laws
-
An example of calculating transformer
size and voltage drop due to starting of
large motor
Medium-voltage motor starting transformer (man. J. Schneider Elektrotechnik; photo credit:
DirectIndustry)
Example
Lets calculate voltage drop in transformer 1000KVA, 11/0.480 kV, impedance 5.75% due to
starting of 300 kW, 460V, 0.8 power factor, motor code D (kva/hp). Motor starts 2 times
per hour and the allowable voltage drop at transformer secondary terminal is 10%.
Calculation can be checked by using this MS Excel Spreadsheet dedicated especially to this kind
of problem.
Ok, lets get into the calculations
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/calculating-transformer-size-voltage-drop-due-to... 5/1/2558
An example of calculating transformer size and voltage drop due to starting of large m... Page 2 of 5
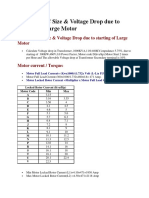
Motor current / Torque
Motor full load current = (Kw x 1000) / (1.732 x Volt (L-L) x P.F
Motor full load current = 300 1000 / 1.732 x 460 x 0.8 = 471 Amp.
Motor locked rotor current = Multiplier x Motor full load current
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/calculating-transformer-size-voltage-drop-due-to... 5/1/2558
An example of calculating transformer size and voltage drop due to starting of large m... Page 3 of 5
Locked rotor current (Kva/Hp)
Motor Code
Min
Max
3.15
3.16
3.55
3.56
4.1
4.5
4.6
5.1
5.6
5.7
6.3
6.4
7.1
7.2
8.1
9.1
10
10.1
11.2
11.3
12.5
12.6
14
14.1
16
16.1
18
18.1
20
20.1
22.4
22.5
Min. motor locked rotor current (L1) = 4.10 471 = 1930 Amp
Max. motor locked rotor current (L2) = 4.50 471 = 2118 Amp
Motor inrush Kva at Starting (Irsm) = Volt x locked rotor current x Full load
current x 1.732 / 1000
Motor inrush Kva at Starting (Irsm) = 460 x 2118 x 471 x 1.732 / 1000 = 1688 kVA
Transformer
Transformer full load current = kVA / (1.732 x Volt)
Transformer full load current = 1000 / (1.73 2 480) = 1203 Amp.
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/calculating-transformer-size-voltage-drop-due-to... 5/1/2558
An example of calculating transformer size and voltage drop due to starting of large m... Page 4 of 5
Short circuit current at TC secondary (Isc) = Transformer full load current /
Impedance
Short circuit current at TC secondary = 1203 / 5.75 = 20919 Amp
Maximum kVA of TC at rated Short circuit current (Q1) = (Volt x Isc x 1.732) /
1000
Maximum kVA of TC at rated Short circuit current (Q1) = 480 x 20919 x 1.732 / 1000 =
17391 kVA
Voltage drop at transformer secondary due to Motor Inrush (Vd) = (Irsm) / Q1
Voltage drop at transformer secondary due to Motor inrush (Vd) = 1688 / 17391 = 10%
Voltage drop at Transformer secondary is 10% which is within permissible limit.
Motor full load current 65% of Transformer full load current
471 Amp 65% x 1203 Amp = 471 Amp 781 Amp
Here voltage drop is within limit and Motor full load current TC full load current.
Size of Transformer is Adequate.
Recommended EE articles
About Author //
Jignesh Parmar
jiguparmar - Jignesh Parmar has completed his B.E(Electrical) from
Gujarat University. He is member of Institution of Engineers
(MIE),India. Membership No:M-1473586.He has more than 12 years
experience in Transmission -Distribution-Electrical Energy theft
detection-Electrical Maintenance-Electrical Projects (Planning-DesigningTechnical Review-coordination -Execution). He is Presently associate
with one of the leading business group as a Assistant Manager at
Ahmedabad,India. He has published numbers of Technical Articles in "Electrical Mirror",
"Electrical India", "Lighting India", "Industrial Electrix"(Australian Power Publications)
Magazines. He is Freelancer Programmer of Advance Excel and design useful Excel base
Electrical Programs as per IS, NEC, IEC,IEEE codes. He is Technical Blogger and Familiar with
English, Hindi, Gujarati, French languages. He wants to Share his experience & Knowledge and
help technical enthusiasts to find suitable solutions and updating themselves on various
Engineering Topics.
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/calculating-transformer-size-voltage-drop-due-to... 5/1/2558
An example of calculating transformer size and voltage drop due to starting of large m... Page 5 of 5
2014 EEP - Electrical Engineering Portal. All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy | 32 queries in
0.198 seconds.
Powered by CsanyiGroup
SHARE
TOP
Get
PDF
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/calculating-transformer-size-voltage-drop-due-to... 5/1/2558
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Speed Signal ListDokumen42 halamanSpeed Signal ListGoran Mann0% (1)
- T60 741x AE1Dokumen694 halamanT60 741x AE1kumarinelBelum ada peringkat
- Guide to Installing Solar PV Systems in SingaporeDokumen64 halamanGuide to Installing Solar PV Systems in SingaporeFrancisco José Murias Dominguez100% (2)
- Guide to Installing Solar PV Systems in SingaporeDokumen64 halamanGuide to Installing Solar PV Systems in SingaporeFrancisco José Murias Dominguez100% (2)
- CERT-In Empanel OrgDokumen141 halamanCERT-In Empanel OrgavinashrajsumanBelum ada peringkat
- Cause & EffectDokumen5 halamanCause & EffectKit Champ50% (2)
- Sizing DOL motor starter parts for 415V 5HP induction motorDokumen7 halamanSizing DOL motor starter parts for 415V 5HP induction motorMALOY BANDYOPADHYAY100% (1)
- Start Sequence of MotorsDokumen4 halamanStart Sequence of MotorsSamuel AdamuBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate Transformer Size and MotorDokumen2 halamanCalculate Transformer Size and MotorThirumalBelum ada peringkat
- Single and three phase circuit power factor calculationsDokumen4 halamanSingle and three phase circuit power factor calculationsgsatyasrikanth100% (2)
- Effect of Load Shedding Strategy On Interconnected Power Systems Stability When A Blackout OccursDokumen6 halamanEffect of Load Shedding Strategy On Interconnected Power Systems Stability When A Blackout OccursMoon3pellBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate The Size of Capacitor Bank - One by Zero ElectronicsDokumen13 halamanHow To Calculate The Size of Capacitor Bank - One by Zero ElectronicsHemant Kumar100% (1)
- Fuse and Types of Fuses - Electrical Technology-OkDokumen7 halamanFuse and Types of Fuses - Electrical Technology-Okdrastir_777100% (1)
- Ug Zs1 Iom Man Rev.h 2012 06Dokumen110 halamanUg Zs1 Iom Man Rev.h 2012 06yulizard100% (1)
- Fault Calculation Duhail Annex 1Dokumen13 halamanFault Calculation Duhail Annex 1S Naved MasoodBelum ada peringkat
- MCC & ContactorsDokumen9 halamanMCC & ContactorsbimboawotikuBelum ada peringkat
- S.C Current Calculation at Various Point of Distribution System (14.1.14) UnlockDokumen20 halamanS.C Current Calculation at Various Point of Distribution System (14.1.14) UnlockVíctor RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Tee604 Transformer DesignDokumen14 halamanNotes Tee604 Transformer DesignAnonymous sAmJfcV100% (2)
- 3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation GuideDokumen5 halaman3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation Guidesiddiq shahBelum ada peringkat
- Is 900-Code of Practice For Installation and Maintenance of Induction MotorDokumen37 halamanIs 900-Code of Practice For Installation and Maintenance of Induction MotormailbkraoBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Current Calculation (Base KVA Method) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen17 halamanShort Circuit Current Calculation (Base KVA Method) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesAnonymous mNQq7ojBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TDokumen4 halamanTransformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TFarooq KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Pump Protection RelaysDokumen6 halamanMotor Pump Protection RelaysSatyajit Patra100% (1)
- Differential and Transformer Relay SettingsDokumen18 halamanDifferential and Transformer Relay Settingsaalamz93_854917254Belum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Current Calculation (Base KVA Method) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen4 halamanShort Circuit Current Calculation (Base KVA Method) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesSrikanth BhattBelum ada peringkat
- ON LOAD TAP CHANGERSDokumen2 halamanON LOAD TAP CHANGERSashish_patel111Belum ada peringkat
- Short - Circuit Current Calculation: Uscin% 50 - 630 800-2500Dokumen74 halamanShort - Circuit Current Calculation: Uscin% 50 - 630 800-2500uddinnadeemBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes ArticlesDokumen5 halamanCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes ArticlesVelu SamyBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate Size of Contactor, Fuse, C.B, Over Load Relay of DOL StarterDokumen5 halamanCalculate Size of Contactor, Fuse, C.B, Over Load Relay of DOL Startererson1981Belum ada peringkat
- Calculation To Choose Capacitor For Detuned FilterDokumen3 halamanCalculation To Choose Capacitor For Detuned FilterRonald H SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Der - Short Circuit Calculating Using Mva MethodDokumen4 halamanDer - Short Circuit Calculating Using Mva MethoddedeerlandBelum ada peringkat
- Cable CapacityDokumen15 halamanCable Capacityvijay_raina3114Belum ada peringkat
- ABB Numerical Relay EchnologyDokumen44 halamanABB Numerical Relay EchnologyNishit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 7SJ61 As High Impedance RelayDokumen36 halaman7SJ61 As High Impedance Relayzarun1Belum ada peringkat
- Vacuum Breaker 15kvDokumen52 halamanVacuum Breaker 15kvMarilou Garal0% (1)
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes Articles PDFDokumen5 halamanCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes Articles PDFJalla Siddeswara Reddy100% (1)
- Motor Starting - Open ElectricalDokumen12 halamanMotor Starting - Open ElectricalHoangBelum ada peringkat
- Electricneutron-Star Delta Motor ConnectionDokumen7 halamanElectricneutron-Star Delta Motor ConnectionJoe ElectricneutronBelum ada peringkat
- 11KV VCB Panel BOMDokumen50 halaman11KV VCB Panel BOMhonghoaso1100% (1)
- Selective Coordination Breaker Application ChartDokumen5 halamanSelective Coordination Breaker Application Charthanner90Belum ada peringkat
- CONTRACT - JAP006-D73 132/11kV PALM, JUMEIRAH S/S (4 Nos) 11Kv Switchgear VT CalculationDokumen20 halamanCONTRACT - JAP006-D73 132/11kV PALM, JUMEIRAH S/S (4 Nos) 11Kv Switchgear VT CalculationSankara Rao Bonala100% (1)
- Symmetrical Fault Calculations ExplainedDokumen27 halamanSymmetrical Fault Calculations ExplainedAsanka SamaranayakeBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Protection ApplicationDokumen27 halamanMotor Protection ApplicationMoulod MouloudBelum ada peringkat
- Auto Reclose TestingDokumen2 halamanAuto Reclose TestingSanjin Čamur100% (1)
- Design and Assembly of an Automatic Power Factor Correction Electrical PanelDokumen4 halamanDesign and Assembly of an Automatic Power Factor Correction Electrical PanelqxzyBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen10 halamanCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop - Electrical Notes & ArticlesCastiel Arthur100% (1)
- Operating 60Hz and 50Hz Transformers on Different FrequenciesDokumen9 halamanOperating 60Hz and 50Hz Transformers on Different FrequenciesKrishna JashaBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Coordination Calculations and Time Current CurvesDokumen7 halamanRelay Coordination Calculations and Time Current CurvesFareh KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Vacuum Circuit BreakerDokumen6 halamanVacuum Circuit BreakerMd Rodi BidinBelum ada peringkat
- 7-AZN-PDS-3501 - (20kV Switchgear (PDS) ) GA & SLD 24kV Switchgear SM6 - As BuiltDokumen40 halaman7-AZN-PDS-3501 - (20kV Switchgear (PDS) ) GA & SLD 24kV Switchgear SM6 - As BuiltRingoBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation TransformerDokumen6 halamanIsolation TransformerVaibhav AryaBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Bushing Tan Delta TestDokumen3 halamanTransformer Bushing Tan Delta Testp m yadavBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument Transformer.: Y. K. PandharipandeDokumen19 halamanInstrument Transformer.: Y. K. PandharipandePrem SagarBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument Transformer 190310Dokumen48 halamanInstrument Transformer 190310Joel GuiaoBelum ada peringkat
- Outdoor Instrument TransformersDokumen124 halamanOutdoor Instrument TransformersscribistBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Contractors and RelaysDokumen13 halaman2-Contractors and RelaysMais AlsharifBelum ada peringkat
- Generator GroundingDokumen3 halamanGenerator GroundingNoneya BidnessBelum ada peringkat
- BATTERY SIZING FOR OFF-GRID SYSTEMSDokumen41 halamanBATTERY SIZING FOR OFF-GRID SYSTEMSअंकित अरोड़ा100% (1)
- Short Circuit Calculations With Transformer and Source Impedance - Arc Flash & Electrical Power Training - BrainfillerDokumen5 halamanShort Circuit Calculations With Transformer and Source Impedance - Arc Flash & Electrical Power Training - BrainfillerJairo RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDari EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityBelum ada peringkat
- Trfo Voltage DropDokumen16 halamanTrfo Voltage Dropshivvaram100% (1)
- Trfo Voltage DropDokumen74 halamanTrfo Voltage DropshivvaramBelum ada peringkat
- Conceptual Design and Costing PDFDokumen20 halamanConceptual Design and Costing PDFkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- PV - Intro 2017Dokumen72 halamanPV - Intro 2017krit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- DSP Electrimacs2005 KhatounianDokumen6 halamanDSP Electrimacs2005 Khatouniankrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Bge Planning CriteriaDokumen50 halamanBge Planning Criteriakrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machines and DrivesDokumen123 halamanElectrical Machines and Drivesanon-427532100% (14)
- Practical Considerations For Siting Utility-Scale Battery ProjectsDokumen13 halamanPractical Considerations For Siting Utility-Scale Battery Projectskrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel Cell Handbook (2000)Dokumen352 halamanFuel Cell Handbook (2000)erhan ünal100% (4)
- PFC HandbookDokumen108 halamanPFC HandbookFelipeFalconiBelum ada peringkat
- Energetic Performance Analysis of A Solar Combisystem Applica 2014 Energy PDokumen8 halamanEnergetic Performance Analysis of A Solar Combisystem Applica 2014 Energy Pkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Greater Safety, Dependability, and Efficiency For Your AssetsDokumen2 halamanGreater Safety, Dependability, and Efficiency For Your Assetskrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature VariationDokumen7 halamanTemperature Variationkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- STATCOM and Capacitor Banks in A Fixed Speed Wind Farm 2014 Energy ProcediaDokumen11 halamanSTATCOM and Capacitor Banks in A Fixed Speed Wind Farm 2014 Energy Procediakrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Robust STATCOM Control Design Using P-Q Theory For Wind Driven Induction GeneratorDokumen6 halamanRobust STATCOM Control Design Using P-Q Theory For Wind Driven Induction Generatorkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Installation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPDokumen7 halamanInstallation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- AllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideDokumen310 halamanAllenBradley ScadaSystemGuideNguyen Chien100% (1)
- Cabling Best Practices GA BP 036 02Dokumen35 halamanCabling Best Practices GA BP 036 02Justin FisherBelum ada peringkat
- Outdoor enclosure dimensions and pressure relief optionsDokumen1 halamanOutdoor enclosure dimensions and pressure relief optionskrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer ChecklistDokumen50 halamanTransformer ChecklistGaurav YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Dsed314001en (Web)Dokumen24 halamanDsed314001en (Web)krit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Installation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPDokumen7 halamanInstallation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Katarzyna SobotkaDokumen68 halamanKatarzyna Sobotkakrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel Cell Megawatt Power Plant PlatformDokumen2 halamanFuel Cell Megawatt Power Plant Platformkrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Testing & Commissioning Procedure (Electrical)Dokumen100 halamanTesting & Commissioning Procedure (Electrical)Roland Nicolas100% (1)
- 28786Dokumen44 halaman28786Enda TolonBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel Cell Handbook (2000)Dokumen352 halamanFuel Cell Handbook (2000)erhan ünal100% (4)
- Lightning Protection A GDokumen23 halamanLightning Protection A Gdaladar2008Belum ada peringkat
- 5 Serious Environmental Impacts of HVAC Over HVDC Overhead Transmission LinesDokumen8 halaman5 Serious Environmental Impacts of HVAC Over HVDC Overhead Transmission Lineskrit_kasemBelum ada peringkat
- Ethernet WPDokumen14 halamanEthernet WPdimaomarBelum ada peringkat
- SOA Suite 10g Developer GuideDokumen47 halamanSOA Suite 10g Developer GuideTusharBelum ada peringkat
- Dennis Resume 2009Dokumen7 halamanDennis Resume 2009440grafixBelum ada peringkat
- EpicorSLS10 MigrateGuide SQL 10.2.100.505100Dokumen219 halamanEpicorSLS10 MigrateGuide SQL 10.2.100.505100Marianne Hernandez MendietaBelum ada peringkat
- Vicat Apparatus Setting Time and Consistency of Cement: StandardsDokumen1 halamanVicat Apparatus Setting Time and Consistency of Cement: StandardsSciencetes PlusBelum ada peringkat
- 01JUN TardeDokumen259 halaman01JUN TardeDanBarberaBelum ada peringkat
- Tecnica 144-164Dokumen21 halamanTecnica 144-164TedyS1959Belum ada peringkat
- 2004 E60 530D Glowplug Controller ReplacedDokumen16 halaman2004 E60 530D Glowplug Controller ReplacedAlexandru Bogdan OvidenieBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure Al Osais International Holding CompanyDokumen4 halamanBrochure Al Osais International Holding CompanyhafezasadBelum ada peringkat
- Jha of PaintingDokumen3 halamanJha of PaintingAllan Camacho Regalado100% (1)
- Arch Required FlowchartDokumen1 halamanArch Required FlowchartgullipalliBelum ada peringkat
- Tube Cutter: MS-TC-308Dokumen1 halamanTube Cutter: MS-TC-308Claudio SavazziBelum ada peringkat
- EA - Maturity ModelDokumen12 halamanEA - Maturity ModelAntonius SonyBelum ada peringkat
- Crane Safety Program EssentialsDokumen11 halamanCrane Safety Program Essentialssekhargm100% (1)
- SCHLENKER Katalog 2022 EN - WEBDokumen136 halamanSCHLENKER Katalog 2022 EN - WEBhosseinBelum ada peringkat
- Written Lockout/Tagout Program University of South Carolina (Enter Department Name Here)Dokumen13 halamanWritten Lockout/Tagout Program University of South Carolina (Enter Department Name Here)SaidBelum ada peringkat
- RCS-Productdescription2 0 PDFDokumen25 halamanRCS-Productdescription2 0 PDFIgor SangulinBelum ada peringkat
- SKF SM 20 - CSTR SpecificationDokumen3 halamanSKF SM 20 - CSTR SpecificationPaweł HejmowskiBelum ada peringkat
- KrisEnergy LTD - Appendix D - Volume2Dokumen194 halamanKrisEnergy LTD - Appendix D - Volume2Invest StockBelum ada peringkat
- Bloomberg Businessweek USADokumen84 halamanBloomberg Businessweek USAalexe012Belum ada peringkat
- Conclusion and RecommendationDokumen2 halamanConclusion and RecommendationKholidi ChooBelum ada peringkat
- Assam & Nagaland 1Dokumen218 halamanAssam & Nagaland 1Ahmer KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Portable Machine MM2000iDokumen3 halamanPortable Machine MM2000ijromero_rpgBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PMBOK - 2014Dokumen49 halamanIntroduction To PMBOK - 2014'babi MulugetaBelum ada peringkat
- R/C Soaring Digest - Apr 2012Dokumen68 halamanR/C Soaring Digest - Apr 2012Aviation/Space History LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- A Burners PDFDokumen37 halamanA Burners PDFaldoking202028Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 8. English Daily Test For Grade 5Dokumen3 halamanUnit 8. English Daily Test For Grade 5NINGSIHBelum ada peringkat
- Store Layout & ArchitectureDokumen76 halamanStore Layout & ArchitectureGyan Singh100% (1)