A
Diunggah oleh
-Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A
Diunggah oleh
-Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
October 2009
Methods to Determine Diesel Cetane Number
By Ara Barsamian
ASTM recently published an updated ASTM D7170 test method for Derived Cetane Number
(DCN) measurement using the ignition delay principle, which provides for an economical and
reliable way to determine the diesel fuel cetane number.
The cetane number is a very important property of diesel oils indicating the quality of ignition of the
diesel fuel (the higher, the better), somewhat analogous to octanes for gasoline.
Methods for Determining Cetane Number of Diesel Fuels
There are basically four different methods in use:
1. Use of a Cetane Engine
2. Use of an Ignition Quality Tester
3. Use of a Near Infra-Red (NIR) Analyzer
4. Use of Cetane Indices
1. Use of a Cetane Engine
This is the "Gold" standard used as a referee method (ASTM D613); measurement is
straightforward once the engine is set up and calibrated.
The disadvantages are:
the high purchase cost ($500,000 plus), ongoing maintenance, and operating cost
requirement for trained staff and expertise for operation and maintenance
poor reliability and accuracy of results
Work Highlights
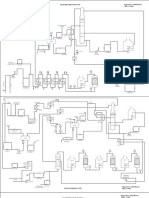
Fired Equipment
Reviewed the
Design Basis
Memorandum
(DBM)
prepared by a
process
licensor for a new hydrogen
plant to be installed at a
refinery in Europe. The
objective was to help ensure
that the DBM had sufficient
details to permit developing a
detailed design specification
that would meet the owners
requirements. Several areas
for improvement were
identified which were
discussed during the project
kickoff meeting, which are
expected to result in some
changes to the DBM.
Process, Operations, &
Safety
Completed a
Cold Eyes
Review of an
international
pharmaceutical companys
global engineering standards,
involving Incineration Systems,
Bulk Storage of Liquefied
Compressed Gases, and
Distillation & Solvent Recovery
Systems. Also participated in
their global standards
workshop to resolve issues
and improve/streamline
content.
Carmagen Engineering, Inc. Industry Leading Engineering Consulting and Training
4 West Main Street, Rockaway, NJ 07866 973-627-4455 www.carmagen.com
2. Use of an Ignition Quality Tester (IQT)
This is a method that measures the time delay between the start of fuel injection and the start of significant combustion
through auto-ignition of a pre-measured amount of diesel in a constant volume chamber. The time delay is used with a
formula to calculate the Derived Cetane Number (DCN) which correlates to the D613 cetane engine. This is a relatively
lower cost (less than one third of an engine), very reliable, high accuracy, faster, easily operated, and maintainable device.
There are two ASTM test methods using IQT: D6890 and D7170. The difference between them is the number of cycles
run for the test (32 cycles for D6890 vs. 25 cycles for D7170) and the averaging of results.
3. Use of a Near Infra-Red (NIR) Analyzer
This method uses a Near InfraRed (NIR) analyzer to obtain the absorption spectrum of diesel which then is fed to a
chemometric model to estimate cetane. Its reproducibility is an order of magnitude better than an engine; the reproducibility
is the same (because we use the engine as the referee). It is very reliable and low maintenance if the chemometric property
prediction model is set-up in accordance with ASTM E1655 practice and run as per ASTM D6122. The cost is the same as a
cetane engine, but it measures 10 to 15 diesel properties simultaneously every 1 to 2 minutes.
4. Use of Cetane Indices
This is an estimation of measured cetane number based on formulas in ASTM D976 or ASTM D4737. The calculations rely
on diesel fuels T10, T50, T90 distillation points, and gravity/density to estimate the cetane number. The sample population
used to regress the formulas for D976 and D4737 are different, and the accuracy (r, R) is different.
They are, however, accepted by pipelines and marine terminals in lieu of D613 measurements.
Cetane Number (CN) Measurement Method Precision Comparison is summarized in the following table (varies with CN).
Test Method
Repeatability r
Reproducibility R
Basis
613
0.8
2.8
39.5 CN fuel, referee
6890
0.85
2.56
39.5 CN fuel
7170
0.71
1.5 - 3.0 model specific
39.5 CN fuel
NIR analyzer
0.08
Same as referee method
39.5 CN fuel
Ara Barsamian has over 30 years of experience in blending (crude, mogas, distillate, fuel oil, lubes), oil movements, & storage (OM&S), crude handling
logistics, refinery tank farm sizing studies, refinery supply chain management, NIR analyzers, and master plan/automation benefits studies for major
process plants and hydrocarbon storage facilities. Please contact Jerry Lacatena (jlacatena@carmagen.com) if youd like more information on
Carmagens expertise in this area.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Ford CarbDokumen27 halamanFord Carbsmcdonald2536100% (1)
- Work Permit System: Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)Dokumen7 halamanWork Permit System: Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)Danilo de JurasBelum ada peringkat
- Omd Graviner Mk6 ManualDokumen90 halamanOmd Graviner Mk6 ManualChristis SavvaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Motor Perkins PDFDokumen8 halamanManual Motor Perkins PDFRobertoSoares0% (1)
- Minicargador 226B Serie 3Dokumen2 halamanMinicargador 226B Serie 3Luis LCBelum ada peringkat
- Simba 1354Dokumen4 halamanSimba 1354Manuel Uturunco AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDokumen18 halamanRenewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesPavan SinghBelum ada peringkat
- TM-5 Lubricator Bijur DelimonDokumen3 halamanTM-5 Lubricator Bijur DelimonFaulhaber Adrian100% (1)
- 6CTA 450 New Engine Performance SheetDokumen2 halaman6CTA 450 New Engine Performance SheetAgus Yudi100% (1)
- 1306a-E87tag6 PN3049Dokumen2 halaman1306a-E87tag6 PN3049Md Sh100% (2)
- LANCER Workshop ManualDokumen21 halamanLANCER Workshop ManualHameed0% (1)
- Eddy Current DynamometerDokumen10 halamanEddy Current DynamometerbavinrajBelum ada peringkat
- Kawasaki Ninja 300 ABS Owners Manual AustraliaDokumen149 halamanKawasaki Ninja 300 ABS Owners Manual Australiastinger30au0% (1)
- Ydrocracking Hemistry Ydrotreating HemistryDokumen33 halamanYdrocracking Hemistry Ydrotreating HemistryMohamed Sayed Abdo100% (2)
- 102 Hydro Treating Unit Prepared By: Abdul Haseeb NRL #: 11692Dokumen10 halaman102 Hydro Treating Unit Prepared By: Abdul Haseeb NRL #: 11692Abdul Haseeb QadeerBelum ada peringkat
- Carbon Footprints: A Presentation OnDokumen49 halamanCarbon Footprints: A Presentation OnKalsoom RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Tank Venting Calculation Guides - CheresourcesDokumen4 halamanTank Venting Calculation Guides - CheresourcesSteve WanBelum ada peringkat
- Modernizing The Opposed-Piston Two-Stroke Diesel Engine For More Efficient Commercial Vehicle ApplicationsDokumen26 halamanModernizing The Opposed-Piston Two-Stroke Diesel Engine For More Efficient Commercial Vehicle ApplicationsChu TuấnBelum ada peringkat
- (SB0A001) Measurement Products and Systems For The Oil and Gas IndustryDokumen62 halaman(SB0A001) Measurement Products and Systems For The Oil and Gas IndustryRoberto Carlos Teixeira100% (1)
- Elements, Compounds and MixturesDokumen71 halamanElements, Compounds and MixturesAkshitSanghavi100% (1)
- Xciting250 300 500Dokumen92 halamanXciting250 300 500AndreaBelum ada peringkat
- Perodua KancilDokumen3 halamanPerodua KancilNashrul MuhaiminBelum ada peringkat
- Patents: Methanol Synthesis Method Using Synthesis Gas Generated by A Mixed Reforming of Natural Gas and Carbon DioxideDokumen14 halamanPatents: Methanol Synthesis Method Using Synthesis Gas Generated by A Mixed Reforming of Natural Gas and Carbon DioxideAditi SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Main Course BookDokumen34 halamanUnit 3 Main Course BookMohan0% (1)
- Js Insight Gas Form CDokumen64 halamanJs Insight Gas Form CSomayajula SuryaramBelum ada peringkat
- Synthetic Lubricants Formulation GuideDokumen39 halamanSynthetic Lubricants Formulation Guideghaos1100% (3)
- Thermodynamic Real-Life SamplesDokumen2 halamanThermodynamic Real-Life SamplesKaren SargentoBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal EngineeringDokumen6 halamanThermal Engineeringmore_sandeepBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages of V Belt Drive in Slurry Application PumpsDokumen3 halamanAdvantages of V Belt Drive in Slurry Application PumpsPooja TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- DHDT BaiscsDokumen2 halamanDHDT BaiscsAvik Bhai100% (1)