Somatic Symptoms Disorder
Diunggah oleh
Krishia HidalgoDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Somatic Symptoms Disorder
Diunggah oleh
Krishia HidalgoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
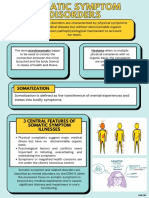
Somatic Symptoms
Disorder
Somatization is
defined as the
transference of
mental
experiences and
states into bodily
symptoms.
Somatoform
disorders can be
characterized as
the presence of
physical
symptoms that
suggest a medical
condition without
a demonstrable
organic basis to
account fully for
them. It is used
to convey the
connection
between the mind
(psyche) and the
body (soma) in
states of health
and illness. The
mind can cause
the body to create
physical
symptoms or to
worsen physical
Disorder
Dynamics
Somatization disorder is
characterized by multiple physical
symptoms. It begins by 30 years of
age, extends over several years,
and includes a combination of pain
and gastrointestinal, sexual, and
pseudoneurologic symptoms.
Conversion disorder involves
unexplained, usually sudden
deficits in sensory or motor
function (e.g., blindness, paralysis).
These deficits suggest a neurologic
disorder but are associated with
psychologic factors. An attitude of
la belle indifference, a seeming lack
of concern
Pain disorder has the primary
physical symptom of pain, which is
unrelieved by analgesics
Hypochondriasis is preoccupation
with the fear that one has a serious
disease (disease conviction) or will
get a serious disease (disease
phobia). It is thought that clients
with this disorder misinterpret
bodily sensations or functions.
Body dysmorphic disorder is
preoccupation with an imagined or
exaggerated defect in physical
appearance such as thinking ones
Needs
Interventions
The worsening of physical
Health teaching
symptoms helps them to meet
Establish a daily routine.
psychological needs for
Promote adequate nutrition
security, attention, and
and sleep.
affection through primary and
Expression of emotional
secondary gain. Primary gains
feelings
are the direct external benefits
Recognize relationship
that being sick provides, such
between stress/coping and
as relief of anxiety, conflict, or
physical symptoms.
distress. Secondary gains are
Keep a journal.
the internal or personal
Limit time spent on
benefits received from others
physical complaints.
because one is sick, such as
Limit primary and
attention from family
secondary gains.
members and comfort
measures
Coping strategies
Since treatment focuses on
Emotion-focused coping
managing symptoms and
strategies such as
improving quality of life, they
relaxation techniques,
need a trusting relationship
deep breathing, guided
with their health care provider.
imagery, and distraction
The health care provider must
Problem-focused coping
show empathy and sensitivity
strategies such as
to the clients physical
problem- solving strategies
complaints. A trusting
and role-playing
relationship with the health
Encourage family to
care provider helps to ensure
provide attention and
that clients stay with and
encouragement when
receive care from one provider
client has fewer
instead of doctor shopping.
complaints.
illnesses.
nose is too large or teeth are
crooked and unattractive.
Encourage family to
decrease special attention
when client is in sick
role.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 07 Aromatherapy Questionnaire PDFDokumen1 halaman07 Aromatherapy Questionnaire PDFAgnesBelum ada peringkat
- Sensory Grant ProposalDokumen9 halamanSensory Grant Proposalapi-307141452100% (2)
- Money-Kyrle Counter-TransferenceDokumen9 halamanMoney-Kyrle Counter-TransferenceAna Tello100% (1)
- Hakomi: Probes: Notice What Happens For You When I Say It Could Be A Feeling or Thought, A Memory, Tension inDokumen2 halamanHakomi: Probes: Notice What Happens For You When I Say It Could Be A Feeling or Thought, A Memory, Tension inPaul Hubbard100% (1)
- PDET - Session2 - Identifying Long Term GoalsDokumen36 halamanPDET - Session2 - Identifying Long Term GoalsEmma DucanteBelum ada peringkat
- Somatic DisordersDokumen14 halamanSomatic DisordersNitya JaggiBelum ada peringkat
- Somatization DisorderDokumen1 halamanSomatization DisorderPauline Arrah LopezBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Somatic and DissociativeDokumen7 halaman3 Somatic and DissociativeMarian AlinoodBelum ada peringkat
- PSPA3714 Chapter 6 2021Dokumen59 halamanPSPA3714 Chapter 6 2021Kamogelo Makhura100% (1)
- Somatic Conditons Dolline and TarahDokumen10 halamanSomatic Conditons Dolline and TarahDolline BusoloBelum ada peringkat
- Somatic Symptom DisorderDokumen4 halamanSomatic Symptom DisorderHenz Castillo ZafraBelum ada peringkat
- Living Well Newsletters - An Integrated Approach To Treating Chronic Pain - July 2012 IssueDokumen5 halamanLiving Well Newsletters - An Integrated Approach To Treating Chronic Pain - July 2012 IssuePaula TropianoBelum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisorderDokumen5 halamanSomatoform Disorderrmconvidhya sri2015Belum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisordersDokumen6 halamanSomatoform Disordersgeorgeloto12Belum ada peringkat
- Somatic Symptom DisorderDokumen55 halamanSomatic Symptom DisorderZubair Mahmood KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisordersDokumen11 halamanSomatoform DisordersDr. Nivas SaminathanBelum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisordersDokumen10 halamanSomatoform Disorderssuresh patilBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Somatoform DisordersDokumen34 halamanOverview of Somatoform DisordersmebibegBelum ada peringkat
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)Dokumen6 halamanGeneralized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)Lovely SarangiBelum ada peringkat
- Pain and Pain ManagementDokumen7 halamanPain and Pain ManagementNatukunda DianahBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Health:: Anxiety DisorderDokumen7 halamanMental Health:: Anxiety Disordergulshang786Belum ada peringkat
- Icn Psychosomatic DisordersDokumen2 halamanIcn Psychosomatic Disordersaishatui733Belum ada peringkat
- Health Psych NotesDokumen7 halamanHealth Psych NotesVidhi DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- 5 HealthDokumen5 halaman5 HealthMarian AlinoodBelum ada peringkat
- Psychopathology Notes 3Dokumen8 halamanPsychopathology Notes 3chelsea hbBelum ada peringkat
- Psychosomatic 1Dokumen15 halamanPsychosomatic 1Jaiprakash AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- HEALTHDokumen1 halamanHEALTHRose Ann AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Health and Care Excellence in Depression Management RRRRDokumen10 halamanHealth and Care Excellence in Depression Management RRRR01941768509mueenBelum ada peringkat
- Somatic Symptoms and Related Disorder: Muh. Irsan HidayatDokumen16 halamanSomatic Symptoms and Related Disorder: Muh. Irsan HidayatMuhammad Irsan HidayatBelum ada peringkat
- Horizon Degree and Commerce College Chakwal: Psychopathology Assignment No. 1 Somatic Symptom and Related DisordersDokumen18 halamanHorizon Degree and Commerce College Chakwal: Psychopathology Assignment No. 1 Somatic Symptom and Related DisordersMuhammad Waseem AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Bab II SomatoformDokumen12 halamanBab II SomatoformDewiRekmawatiPradaswariBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 - Mental Health IssuesDokumen6 halamanUnit 3 - Mental Health Issuesdhanalakshmis0310Belum ada peringkat
- UTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalDokumen28 halamanUTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalBernard PadillaBelum ada peringkat
- Somatic Symptom IllnessesDokumen6 halamanSomatic Symptom IllnessesAngelica PabelloBelum ada peringkat
- E Notes Dimension of Health 2Dokumen4 halamanE Notes Dimension of Health 2Jenesha MuraliBelum ada peringkat
- 9-Somatoform Dissociative DisordersDokumen27 halaman9-Somatoform Dissociative DisordersSara Mohammed AliBelum ada peringkat
- Psycho - Group AssignmentDokumen20 halamanPsycho - Group AssignmentJonah the mixerBelum ada peringkat
- Life Is Full of Ups and Down.Dokumen5 halamanLife Is Full of Ups and Down.SELVAM PERUMALBelum ada peringkat
- Class 1Dokumen36 halamanClass 1Insta viralBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 117-Somatic DisordersDokumen5 halamanNCM 117-Somatic DisordersJa DimasBelum ada peringkat
- Abpsy 3rd Exam ReviewerDokumen7 halamanAbpsy 3rd Exam ReviewerJusa Aldrea PratoBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Mental HealthDokumen1 halamanThe Importance of Mental HealthRayden AlphaBelum ada peringkat
- Fragmente Anxietate Si Somatica Din DSM 5Dokumen8 halamanFragmente Anxietate Si Somatica Din DSM 51222Belum ada peringkat
- Symptoms of PsychoneurosisDokumen7 halamanSymptoms of PsychoneurosisirishjoymartinBelum ada peringkat
- QUARTER 3 HEALTH 7 Mental and Emotional HealthDokumen33 halamanQUARTER 3 HEALTH 7 Mental and Emotional HealthjobelleBelum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisordersDokumen41 halamanSomatoform DisordersTulika SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Psychosomatic Disorders 2023Dokumen9 halamanPsychosomatic Disorders 2023hnasdbsywnyBelum ada peringkat
- Depression Case AbstractDokumen19 halamanDepression Case AbstractLord Allen B. GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Somatoform DisordersDokumen15 halamanSomatoform DisordersSimranjeet KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensions of HealthDokumen4 halamanDimensions of HealthJasper Pangilayan OrañolaBelum ada peringkat
- Taking Care of Mental HealthDokumen19 halamanTaking Care of Mental HealthsainilBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensions of HealthDokumen3 halamanDimensions of HealthPinky Juntilla RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Aspects of Somatic Disorder in Child andDokumen61 halamanPsychiatric Aspects of Somatic Disorder in Child andZubair Mahmood KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Health Psychology: What Is Health Psychology? Health Psychology Focuses On How Our Biology, Social Context andDokumen2 halamanHealth Psychology: What Is Health Psychology? Health Psychology Focuses On How Our Biology, Social Context andsenadBelum ada peringkat
- How Emotional Pain Affects Your BodyDokumen6 halamanHow Emotional Pain Affects Your BodyNadeem IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Somatisation Definitions, Symptoms and CausesDokumen5 halamanSomatisation Definitions, Symptoms and CausesNaifa Claresta SalsabyllaBelum ada peringkat
- Nature of Health and IllnessDokumen28 halamanNature of Health and IllnessAgochi CollinsBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical PsychologyDokumen9 halamanClinical PsychologyLaavanyya JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Depression and Anxiety Concept MapDokumen4 halamanDepression and Anxiety Concept Mapsammillepointer86Belum ada peringkat
- Somatization DisordersDokumen26 halamanSomatization DisordersAljohn GalangBelum ada peringkat
- Psychosomatic Pain: Ertuğrul AllahverdiDokumen20 halamanPsychosomatic Pain: Ertuğrul AllahverdidiasBelum ada peringkat
- Ch.2 PN Fundamentals Study OutlineDokumen3 halamanCh.2 PN Fundamentals Study OutlineNani ReedBelum ada peringkat
- CPH 2711 Written Assignment Unit 1Dokumen4 halamanCPH 2711 Written Assignment Unit 1unclet12Belum ada peringkat
- Mod 2 HEALTHDokumen36 halamanMod 2 HEALTHJan Leo EgamenBelum ada peringkat
- The Mind-Body Connection: A Holistic Approach to Achieving Optimal Health and WellnessDari EverandThe Mind-Body Connection: A Holistic Approach to Achieving Optimal Health and WellnessBelum ada peringkat
- Biobehavioral Utility of Mindfulness-Based Art Therapy: Neurobiological Underpinnings and Mental Health ImpactsDokumen9 halamanBiobehavioral Utility of Mindfulness-Based Art Therapy: Neurobiological Underpinnings and Mental Health Impactsотец хентайBelum ada peringkat
- Art Therapy For Students Academic StressDokumen4 halamanArt Therapy For Students Academic Stresstiyas studiesBelum ada peringkat
- Motivational Interviewing Strategies CertificateDokumen1 halamanMotivational Interviewing Strategies CertificateTeri WILSONBelum ada peringkat
- Milieu Management 2017Dokumen26 halamanMilieu Management 2017norwaygirlBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Protocol Lexi Mireles Posttraumatic Stress DisorderDokumen8 halamanDiagnostic Protocol Lexi Mireles Posttraumatic Stress Disorderapi-488704485Belum ada peringkat
- Child Maladaptive Daydreaming Checklist (CMDC) : NOW or Very Much True Fairly Often Not TrueDokumen2 halamanChild Maladaptive Daydreaming Checklist (CMDC) : NOW or Very Much True Fairly Often Not TrueHaris ABelum ada peringkat
- "Building Trust With Counselling Clients" Article AnalysisDokumen2 halaman"Building Trust With Counselling Clients" Article AnalysisGirlie Faith Morales BrozasBelum ada peringkat
- Law of ExerciseDokumen3 halamanLaw of Exerciseakesha_akikoh100% (1)
- DSM 5 Neurodevelopmental NOTESDokumen27 halamanDSM 5 Neurodevelopmental NOTESmicrobeateria100% (2)
- Basic Principles of Guidance and CounsellingDokumen26 halamanBasic Principles of Guidance and CounsellingNur Izzati Adam100% (4)
- 08 Cognitive Behavioral TreatmentDokumen10 halaman08 Cognitive Behavioral TreatmentAnderson GaldinoBelum ada peringkat
- Cultural Humility in Psychotherapy SupervisionDokumen19 halamanCultural Humility in Psychotherapy SupervisionMilo DueBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Health Triage Tool 2006Dokumen1 halamanMental Health Triage Tool 2006MelbourneFXBelum ada peringkat
- Hakomi - ContactDokumen2 halamanHakomi - ContactPaul Hubbard100% (1)
- NURSING PRACTICE TEST I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice General InstructionsDokumen9 halamanNURSING PRACTICE TEST I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice General InstructionsjcruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- AP Therapy ExamDokumen6 halamanAP Therapy ExamDghdk NfksdnfBelum ada peringkat
- Final Research Paper Draft - AllenDokumen18 halamanFinal Research Paper Draft - Allenapi-583318017Belum ada peringkat
- Bornstein (2007, JPA) Toward A Process-Based Framework For Classifying Personality TestsDokumen7 halamanBornstein (2007, JPA) Toward A Process-Based Framework For Classifying Personality TestsFranco AllovattiBelum ada peringkat
- CidoyDokumen2 halamanCidoyElaine Fiona VillafuerteBelum ada peringkat
- Eating Disoder PPT 3Dokumen22 halamanEating Disoder PPT 3Jordz PlaciBelum ada peringkat
- Gratitude JournalDokumen31 halamanGratitude Journalmanchiraju raj kumar100% (1)
- Ki Khanga Pre Made CharactersDokumen20 halamanKi Khanga Pre Made CharactersJorge dos Santos ValpaçosBelum ada peringkat
- Technology and Women With ADHDDokumen13 halamanTechnology and Women With ADHDskiptonBelum ada peringkat
- Cognitive Communication Disorders in Right Brain Hemisphere Damage PDFDokumen1 halamanCognitive Communication Disorders in Right Brain Hemisphere Damage PDFCarolina Andrea Ramos RivasBelum ada peringkat
- Skills Assessment II 1Dokumen5 halamanSkills Assessment II 1api-582911813Belum ada peringkat