Answer To Score Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Diunggah oleh
zhen1998Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Answer To Score Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Diunggah oleh
zhen1998Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
FORM 4 CHAPTER 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM &
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATION
ANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FROM 2003 2008
Year
Paper
No.
Type of
question
Question
No
2003
P2
S
1
2004
P3
P2
2005
P3
1a
2006
P2
S
P3
10a
10b
P2
2007
P3
P2
2008
P3
3,5
P2
S
P3
STRUCTURED QUESTION
1
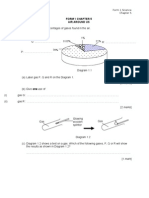
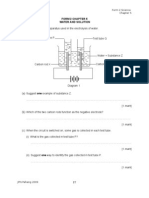
SPM 2003 /P2/ Q1
Figure 1 shows the set-up of apparatus for an experiment to determine the empirical
formula of magnesium oxide.
Figure 1
Result :
Mass of crucible + lid
Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium ribbon
Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium oxide
(a)
= 24.0 g
= 26.4 g
= 28.0 g
What is meant by empirical formula?
[1 mark]
(b)
(i)
Based on the above results,
Calculate the mass of magnesium and the mass of oxygen that have reacted.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Calculate the mole ratio of magnesium atoms to oxygen atoms
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
[Relative Atomic Mass: O = 16, Mg = 24]
[1 mark]
(iii)
Determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide.
[1 mark]
(iv)
Write the chemical equation for the reaction in this experiment.
[1 mark]
(c)
Why was the crucible lid opened once in a while during the experiment?
[1 mark]
(d)
Metal X is placed below hydrogen in the reactivity series. You are required to carry
out an experiment to determine the empirical formula of the oxide of metal X. The
apparatus provided are combustion tube, glass tube, cork, Bunsen burner, and
porcelain dish.
(i)
Draw a labeled diagram of the set-up of the apparatus for the experiment.
[2 marks]
(ii)
Describe the steps that should be taken to ensure that all the air in the combustion
tube has been expelled.
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
..
[3 marks]
SPM 2004/ P2/ Q1
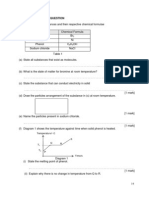
(a)
Table 2 shows four substances and their respective formulae
Substance
Chemical formula
Iodine
I2
Copper
Cu
Naphthalene
C10H8
Copper (II) sulphate
CuSO4
Table 2
Use information from Table 2 to answer the following equations
(i)
State one substance from Table 2 which exists as a molecule.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Which substance has the highest melting point, iodine, copper or naphthalene?
[1 mark]
(iii)
What is the state of matter of copper (II) sulphate at room temperature?
[1 mark]
(iv)
State the substance in Table 2 which can conduct electricity in the solid state.
[1 mark]
(v)
Draw the arrangement of particles in the substance in (a)(iv)
[1 mark]
(vi)
Write the ionic formula for the substance in (a)(iv).
[1 mark]
(b)
Graph 2.1 shows the temperature against time when solid naphthalene is heated
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Graph 2.1
(i)
State the melting point of naphthalene.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Explain why there is no change in temperature from Q to R
[2 marks]
(iii)
State how the movement of naphthalene particles changes between R and S during the
heating.
[1 mark
SPM 2006/ P2/ Q2
(i)
What is the chemical symbol used to represent one water molecule?
[1 mark]
(ii)
What is the name of the isotope of an element used as a standard in determining
relative atomic mass?
[1 mark]
b(i)
What is the mass of 6.0dm3 of carbon dioxide gas, CO2 at standard temperature and
pressure?
[1 mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 at standard temperature and pressure;
Relative atomic mass for CO2 = 44]
[2 marks]
Answer To Score Chemistry
(ii)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
How many molecules are there in 6.0 dm3 of carbon dioxide gas?
[Avogadro number = 6.02 x 1023]
[1 mark]
(iii)
Explain briefly the relationship between the volume, mass and the number of
molecules of carbon dioxide in 3b(i) and 3b(ii) at stansard temperature and
pressure.
[3 marks]
SPM 2007 / P2/ Q3
(a) What is the meaning of empirical formula?
[1 mark]
(b)
Diagram 3.1 shows an incomplete equation which is one of the steps involved in
determining the empirical formula.
Complete this equation.
Mass
=
Relative atomic mass ..
Diagram 3.1
[1 mark]
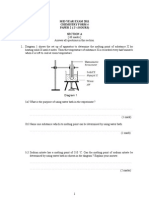
(c)
Diagram 3.2 shows the apparatus set-up for two methods used to determine the
empirical formula of two compounds.
Diagram 3.2
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Based on Diagram 3.2, determine the values of the following:
[Relative atomic mass : O=16, Pb = 207 ]
(i)
Mass of lead
= ..g
[1 mark]
(ii)
Number of moles of lead
= ..g
[1 mark]
(iii)
Mass of oxygen
= ..g
[1 mark]
(iv)
Number of moles of oxygen
= ..g
[1 mark]
(v)
Empirical formula of lead oxide
= .
[1 mark]
SPM 2007 / P2/ Q5
Diagram 5 shows the symbols of the atoms of element X and element Y.
The letter used are not the actual symbols of the elements.
Diagram 5
(a)
State the proton number of the atom of element X.
[1 mark]
b(i)
F4 Topic 4 : Periodic Table
Identify the position of element X in the Preiodic Table of Elements
[1 mark]
b(ii)
Explain why element X is placed at the position identified in 5(b)(i).
[1 mark]
Answer To Score Chemistry
c(i)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
F4 Topic 4 : Periodic Table
The reaction between element X and oxygen is less reactive than the reaction
between element Y and oxygen.
Explain this using ideas about valence electron.
[2 marks]
(ii)
Draw a labeled diagram to show the apparatus set-up that can be used to determine
the reactivity of the reaction between element X or element Y and oxygen gas.
[ 2marks]
(d)
2.3g of element X reacted completely with oxygen.
The following equation represents the reaction.
4X(s) + O2(g) 2X2O(s)
[Relative atomic mass : X = 23, O = 16]
(i)
Calculate the number of moles of element X.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Calculate the maximum mass of X2O formed.
[3 marks]
Answer To Score Chemistry
6
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
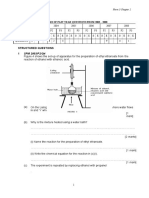
SPM 2008 / P2/ Q3
(a) Diagram 3.1 shows the results of an experiment to investigate the movement of
bromine particles in air.
Air
Gas jar
cover
Bromine vapour
Bromine vapour
spreads
throughout both
gas jars within
10 minutes
Cover removed
Diagram 3.1
(i)
(ii)
State the name of the process involved in this experiment.
[1 mark]
State the type of particle present in bromine gas, Br2.
[1 mark]
(iii)
Explain the observation in this experiment based on the kinetic theory of matter.
[3 marks]
(iv)
This experiment is repeated at a higher temperature.
Predict the time taken for the bromine vapour to spread throughout the space in both
gas jars.
[1 mark]
Answer To Score Chemistry
(b)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Diagram 3.2 shows two balloons containing oxygen gas and carbon dioxide gas
respectively.
0.5 mol
oxygen
gas, O2
0.5 mol
Carbon dioxide
gas, CO2
Balloon A
(i)
Balloon B
Diagram 3.2
Based on the given information:
Calculate the mass of oxygen gas in balloon A
[Relative atomic mass : O = 16]
[1 mark]
(ii)
Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide gas in balloon B.
[Molar volume of gas = 24 dm3 mol-1 at room temperature and pressure]
[1 mark]
(iii)
Compare the number of gas molecules in balloon A and in balloon B.
Explain your answer.
[2 marks]
Answer To Score Chemistry
7
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
SPM 2004/ P3/ Q1
A student carried out an experiment to determine the empirical formula of
magnesium oxide. The steps and set-up of apparatus of the experiment are shown in
Figure 1.
(a)
Complete the following table by stating the observation and related inferences in the
experiment.
Observation
Inferences
(i) ..
(i) .
(ii) .
(ii)
10
.
[6marks]
Answer To Score Chemistry
(b)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Record the reading to two decimal places for:
The mass of crucible and lid: g
The mass of crucible, lid and magnesium ribbon : g
ci)
The mass of crucible, lid and magnesium oxide when cooled : .g
[3marks]
What is the mass of magnesium that has been used?
(ii)
What is the mass of oxygen which reacted with magnesium?
(iii
Determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide
Use the information that the relative atomic mass, Mg = 24 and O = 16.
[3marks]
[3marks]
(d)
[3marks]
Based on your answer in (c)(iii), how many moles of magnesium and oxygen atoms
have reacted?
[3marks]
SPM 2005 /P3/ Q1
An experiment is carried out to determine the freezing point of naphthalene. Solid
naphthalene is heated in a water bath until it melts completely.
The initial temperature is recorded.
Then molten naphthalene is left to cool.
The reading of the temperature is recorded every 30 seconds.
Figure 1 shows the recorded thermometer readings at 30 seconds intervals.
11
Answer To Score Chemistry
a)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
Record the temperatures in the space provided in Figure 1.
[3marks]
b)
On the graph paper below, draw the graph of temperature against time for the
cooling of naphthalene.
12
Answer To Score Chemistry
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
[3marks]
ci)
Use the graph in (b), to determine the freezing point of naphthalene.
Show on the graph how you determine this freezing point.
(ii)
How does the graph in (b) show the freezing point of naphthalene?
[3marks]
[3marks]
13
Answer To Score Chemistry
(d)
Form 4 Chapter 2 The Structure of The Atom
Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equation
The temperature of naphthalene did not change from the 90th second until the 50th
second during the cooling process.
Explain why.
.
(e)
.
[3marks]
On the graph paper below sketch the curve you would expect if the molten
naphthalene is cooled quickly.
[3marks]
(f)
Naphthalene is an example of a covalent compound and sodium chloride is an
example of an ionic compound.
Classify the following into covalent or ionic compounds.
Glucose, potassium iodide, copper(II) sulphate,
Aluminium oxide, tetrachloromethane, ethanol
[3marks]
14
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Dokumen27 halamanStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinBelum ada peringkat
- Unusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryDari EverandUnusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryBelum ada peringkat
- Modul KimiaDokumen57 halamanModul KimiaAZIE207Belum ada peringkat
- spm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Dokumen14 halamanspm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Suriati Bt A RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDokumen12 halamanChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiEmily VinciBelum ada peringkat
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Dokumen16 halamanSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Trial 2012Dokumen14 halamanChem Trial 2012Han LingBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Catalysed Carbon-Carbon Bond-Forming ReactionsDari EverandMetal Catalysed Carbon-Carbon Bond-Forming ReactionsBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Dokumen9 halamanSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangBelum ada peringkat
- The Decomposition of Global Conformal Invariants (AM-182)Dari EverandThe Decomposition of Global Conformal Invariants (AM-182)Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Dokumen22 halamanChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1siti zalikhaBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia - Revision Final ExamDokumen37 halamanKimia - Revision Final ExamYu LyzaBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Section A: Temperatur E/ C S Q RDokumen5 halamanPaper 2 Section A: Temperatur E/ C S Q RNor Azrul IkwanBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Dokumen14 halamanFinal Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Norzilah MazaharBelum ada peringkat
- Chem F2Dokumen8 halamanChem F2Festus NanokBelum ada peringkat
- Revision - Chem - F4 Chapter 1-4Dokumen8 halamanRevision - Chem - F4 Chapter 1-4HaziraAzlyBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDokumen49 halamanSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziBelum ada peringkat
- Sns Paper 2 KimiaDokumen16 halamanSns Paper 2 KimiaDuong Han CalebBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsDokumen9 halamanExercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- Form 3 Worksheets Workbook 2020Dokumen45 halamanForm 3 Worksheets Workbook 2020livingstonechinyowaBelum ada peringkat
- SCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetDokumen11 halamanSCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetHarshil PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Paper 2 f4 Akhir SBP 06Dokumen35 halamanKimia Paper 2 f4 Akhir SBP 06Arisa YamatoBelum ada peringkat
- CI 9 Co Science Paper 4 Paper 6Dokumen21 halamanCI 9 Co Science Paper 4 Paper 6Jyoti SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Module Heat (QUESTION BASED)Dokumen21 halamanModule Heat (QUESTION BASED)Cart Kartika75% (4)
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDokumen12 halamanChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiSakinah Saad100% (3)
- 5th Form Exam ET 2014Dokumen20 halaman5th Form Exam ET 2014NIRVAN RAMESHBelum ada peringkat
- KIMIA SET 1 Perfect ScoreDokumen26 halamanKIMIA SET 1 Perfect Scorezariqz@cBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsDokumen16 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsLouis Lim0% (1)
- Example PTE Structured QuestionsDokumen5 halamanExample PTE Structured Questions301 Dhia JaharahBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Aras RendahDokumen35 halamanModul Aras RendahNurul Hasmah HarunBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Test 2Dokumen2 halamanChemistry Test 2Daniel Ngenokesho WandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 1 BK2-Intervensi Aras 1: RendahDokumen36 halamanModul 1 BK2-Intervensi Aras 1: RendahijaBelum ada peringkat
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerDokumen36 halamanUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- SOALANnnDokumen13 halamanSOALANnnKeertanaBelum ada peringkat
- Sda 3 Form 4Dokumen13 halamanSda 3 Form 4Crystal MachipisaBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Dokumen12 halaman1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Kertas 2 Pengesanan 2 t4 2015Dokumen15 halamanKimia Kertas 2 Pengesanan 2 t4 2015Hasbullah Md SukurBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Dokumen12 halamanCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42taimurmalik5562100% (1)
- GRADE 8 SCIENCE EXAM PAPER2 3rd TERMDokumen18 halamanGRADE 8 SCIENCE EXAM PAPER2 3rd TERMTijani Basit AbiodunBelum ada peringkat
- Ulangkaji Soalan Midyear f5 - ActualDokumen20 halamanUlangkaji Soalan Midyear f5 - ActualnurulizzahBelum ada peringkat
- Section A: SPM Chemistry Set 5 Paper 2Dokumen18 halamanSection A: SPM Chemistry Set 5 Paper 2Jaaizah JaafarBelum ada peringkat
- Projek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Dokumen9 halamanProjek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Zul BaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Structured Questions 1: SPM 2003/P2/Q4Dokumen16 halamanStructured Questions 1: SPM 2003/P2/Q4VinnySha SelvarajahBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry P1Dokumen13 halamanChemistry P1zachaeusBelum ada peringkat
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) JUJ 2010 Chemistry PDFDokumen197 halaman(Edu - Joshuatly.com) JUJ 2010 Chemistry PDFKak Ngah FienaBelum ada peringkat
- Form 2 Chapter 5Dokumen10 halamanForm 2 Chapter 5naza977587% (15)
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionDokumen32 halamanElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- 2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Dokumen15 halaman2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Nicholson NicholsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 3 2024 - Question PaperDokumen8 halamanChemistry Form 3 2024 - Question Paperwinfredmwende44Belum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Fa 2 Sem 2 F4Dokumen10 halamanPaper 2 Fa 2 Sem 2 F4Puteri FikriBelum ada peringkat
- 7 ChildhoodDokumen1 halaman7 Childhoodzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- 2 ArtDokumen1 halaman2 Artzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- 4 BuildingsDokumen1 halaman4 Buildingszhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- 6 ChangeDokumen1 halaman6 Changezhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- IELTS Writing Task 2 Sample Answer Essay Child DevelopmentDokumen7 halamanIELTS Writing Task 2 Sample Answer Essay Child Developmentzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- f5 Chapter 1 Essay QDokumen4 halamanf5 Chapter 1 Essay Qzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- Narrative Essay For SPMDokumen2 halamanNarrative Essay For SPMzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- Narrative Essay For SPMDokumen2 halamanNarrative Essay For SPMzhen1998Belum ada peringkat
- Tugas 3Dokumen20 halamanTugas 3dellaayuBelum ada peringkat
- MOA Agri BaseDokumen6 halamanMOA Agri BaseRodj Eli Mikael Viernes-IncognitoBelum ada peringkat
- Ancestral Healing PrayersDokumen4 halamanAncestral Healing Prayerssuperhumannz100% (13)
- HIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayDokumen9 halamanHIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayOscar Panez LizargaBelum ada peringkat
- Life&WorksofrizalDokumen5 halamanLife&WorksofrizalPatriciaBelum ada peringkat
- E 05-03-2022 Power Interruption Schedule FullDokumen22 halamanE 05-03-2022 Power Interruption Schedule FullAda Derana100% (2)
- Short-Term Load Forecasting by Artificial Intelligent Technologies PDFDokumen446 halamanShort-Term Load Forecasting by Artificial Intelligent Technologies PDFnssnitBelum ada peringkat
- Calcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Dokumen552 halamanCalcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Débora BretasBelum ada peringkat
- Jake Atlas Extract 2Dokumen25 halamanJake Atlas Extract 2Walker BooksBelum ada peringkat
- WHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Dokumen23 halamanWHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Sarthika Singhal Sarthika SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- The Final Bible of Christian SatanismDokumen309 halamanThe Final Bible of Christian SatanismLucifer White100% (1)
- Stockholm KammarbrassDokumen20 halamanStockholm KammarbrassManuel CoitoBelum ada peringkat
- Update UI Components With NavigationUIDokumen21 halamanUpdate UI Components With NavigationUISanjay PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Cruz-Arevalo v. Layosa DigestDokumen2 halamanCruz-Arevalo v. Layosa DigestPatricia Ann RueloBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge English Key Sample Paper 1 Reading and Writing v2Dokumen9 halamanCambridge English Key Sample Paper 1 Reading and Writing v2kalinguer100% (1)
- Saber Toothed CatDokumen4 halamanSaber Toothed CatMarie WilkersonBelum ada peringkat
- Supporting References in Release 12 SLA PDFDokumen8 halamanSupporting References in Release 12 SLA PDFsoireeBelum ada peringkat
- Some Problems in Determining The Origin of The Philippine Word Mutya' or Mutia'Dokumen34 halamanSome Problems in Determining The Origin of The Philippine Word Mutya' or Mutia'Irma ramosBelum ada peringkat
- Operations Management (Scheduling) PDFDokumen4 halamanOperations Management (Scheduling) PDFVijay Singh ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Promising Anti Convulsant Effect of A Herbal Drug in Wistar Albino RatsDokumen6 halamanPromising Anti Convulsant Effect of A Herbal Drug in Wistar Albino RatsIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Memoire On Edgar Allan PoeDokumen16 halamanMemoire On Edgar Allan PoeFarhaa AbdiBelum ada peringkat
- Deed of Power of Attorney To Sell SharesDokumen8 halamanDeed of Power of Attorney To Sell SharesridhofauzisBelum ada peringkat
- Reported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsDokumen4 halamanReported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsDaniela TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Ottley Sandra 2009Dokumen285 halamanOttley Sandra 2009Lucas Fariña AlheirosBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateDokumen18 halamanAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DatecuongBelum ada peringkat
- Desire of Ages Chapter-33Dokumen3 halamanDesire of Ages Chapter-33Iekzkad Realvilla100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 5 Quarter 2: Answer KeyDokumen4 halamanMathematics Grade 5 Quarter 2: Answer KeyApril Jean Cahoy100% (2)
- Spelling Master 1Dokumen1 halamanSpelling Master 1CristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Communication and Globalization Lesson 2Dokumen13 halamanCommunication and Globalization Lesson 2Zetrick Orate0% (1)
- Music 20 Century: What You Need To Know?Dokumen8 halamanMusic 20 Century: What You Need To Know?Reinrick MejicoBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDari EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDari EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (20)
- Oxygen: The molecule that made the worldDari EverandOxygen: The molecule that made the worldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (108)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDari EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugDari EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDari EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsBelum ada peringkat
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDari EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDari EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDari EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDari EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDari EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleBelum ada peringkat
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDari EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionDari EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)