Caf-8 Cma
Diunggah oleh
askermanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Caf-8 Cma
Diunggah oleh
askermanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Certificate in Accounting and Finance Stage Examinations
The Institute of
Chartered Accountants
of Pakistan
4 March 2015
3 hours 100 marks
Additional reading time 15 minutes
Cost and Management Accounting
Q.1
KPK Dairies Limited (KDL) is planning to introduce three energy flavored milk from 1 July
2015. In this respect, following projections have been made:
Planned production
(No. of packets)
Sales
(No. of packets)
Production cost per packet:
Direct material
Direct labour
Variable overheads
Fixed overheads
Selling and distribution cost per packet:
Variable overheads
Fixed overheads
Total cost per packet
C-Plus
I-Plus
V-Plus
540,000
275,000
185,000
425,000
255,000
170,000
----------- Rupees ----------100
98
97
15
13
12
23
19
16
25
22
20
12
5
180
8
5
165
10
5
160
KDL will sell its products through a distributor at a commission of 5% of sale price and
expects to earn a contribution margin of 40% of net sales i.e. sales minus distributor's
commission.
Required:
Compute break even sales in packets and rupees, assuming that ratio of quantities sold
would be as per projections.
Q.2
(17)
Diamond Investment Limited (DIL) is considering to set-up a plant for the production of a
single product X-49. The details relating to the investment are as under:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
The cost of plant amounting to Rs. 160 million would be payable in advance. It
includes installation and commissioning of the plant.
Working capital of Rs. 20 million would be required at the commencement of the
commercial operations.
DIL intends to sell X-49 at cost plus 25% (cost does not include depreciation on
plant). Sales for the first year are estimated at Rs. 300 million. The sales quantity
would increase at 6% per annum.
The plant would be depreciated at the rate of 20% under the reducing balance
method. Tax depreciation is to be calculated on the same basis. Estimated residual
value of the plant at the end of its useful life of four years would be equal to its
carrying value.
Tax rate is 34% and tax is payable in the year the liability arises.
DILs cost of capital is 18%. All costs and prices are expected to increase at the rate
of 5% per annum.
Required:
Compute the following:
(a)
Net present value of the project
(b)
Internal rate of return of the project
Assume that unless otherwise specified, all cash flows would arise at the end of the year.
(12)
(05)
Cost and Management Accounting
Q.3
Page 2 of 4
Sigma Limited (SL) is a manufacturer of Product A. SL operates at a normal capacity of
90% against its available annual capacity of 50,000 machine hours and uses absorption
costing. The following summarised profit statements were extracted from SL's budget for
the year ending 31 December 2015.
Sales
Opening inventory
Cost of production
Closing inventory
Under absorbed production overheads
Selling and administration cost (30% fixed)
Net profit
Actual - 2014
Units Rs. in '000
4,125
49,500
400
(3,400)
4,325
(38,925)
600
5,400
(100)
(3,000)
9,475
Budget - 2015
Units Rs. in '000
4,600
56,580
600
(5,400)
4,500
(44,325)
500
4,925
(5,250)
6,530
Other relevant information is as under:
2014
Budget - 2015
Standard machine hours per unit
10 hours
10 hours
Standard production overhead rate per unit
Rs.
2,000 Rs.
2,250
Estimated fixed production overheads at normal capacity
Rs. 3,600,000 Rs. 4,050,000
Actual production overheads (Actual machine hours 44,000) Rs. 8,750,000
-
Required:
(a) What do you understand by under/over absorbed production overheads?
(b) Analyse the under absorbed production overheads of SL for the year ended
31 December 2014, into spending and volume variances. Give two probable reasons
for each variance.
(c) Prepare budgeted Profit and Loss Statement for the year ending 31 December 2015,
using marginal costing.
(d) Analyse the difference between budgeted profit determined under absorption and
marginal costing, for the year ending 31 December 2015.
Q.4
(02)
(06)
(07)
(02)
KS Limited operates two production departments A and B to produce a product XP-29.
Following information pertains to Department A for the month of December 2014.
Opening work in process (Material 100%, conversion 80%)
Material
Direct labour and overheads
Actual cost for the month:
Material
Direct labour
Overheads
Expected losses
Closing work in process (Material 100%, conversion 80%)
Units transferred to Department B
Litres
15,000
-
Rs. in '000
120,000
5%
17,000
110,000
36,240
14,224
11,500
-
5,000
2,125
KS uses FIFO method for inventory valuation. Direct materials are added at the beginning
of the process. Expected losses are identified at the time of inspection which takes place at
the end of the process. Overheads are applied at the rate of 80% of direct labour cost.
Required:
(a) Equivalent production units
(b) Cost of goods transferred to Department B
(c) Accounting entries in the cost accounting system.
(02)
(09)
(06)
Cost and Management Accounting
Q.5
Page 3 of 4
Zee Chemicals Limited (ZCL) produces two joint products, Alpha and Beta from a single
production process. Both products are processed upto split-off point and sold without any
further processing.
Presently, ZCL is considering the following proposals:
Expansion of the existing facility by installing a new plant
Installation of a refining plant to sell either Alpha or Beta after refining
To assess the above proposals, following data has been gathered:
(i)
Actual cost incurred in the month of December 2014:
Direct material
Variable conversion costs (Rs. 230 per hour)
Fixed overheads
(ii)
Rs. in '000
15,000
4,890
2,600
Actual production and selling price for the month of December 2014:
Litres
Alpha
Beta
11,300
14,700
Selling price per
litre (Rs.)
1,000
1,125
(iii) There is no process loss and joint costs are apportioned between Alpha and Beta
according to the weight of their output.
(iv) Details of the proposed plans are as follows:
Capacity in machine hours per month
Cost of plant and its installation
Estimated residual value at the end of life
Estimated additional fixed overheads per month
Estimated useful life of the plant
(v)
20 Years
20 Years
Estimated variable cost of refining and sales price of refined products:
Direct material
Conversion cost (Rs. 150 per hour)
Selling price
(vi)
Expansion of
Installation of
existing facility refining plant
5,000
5,000
------------ Rs. in '000 -----------20,000
25,000
1,400
2,800
250
500
Alpha
Beta
Rupees per liter
90
125
68
80
1,380
1,525
There would be no loss during the refining process. There is adequate demand for
Alpha and Beta at split-off point and after refining.
Required:
Evaluate each of the above proposals and give your recommendations.
(16)
Cost and Management Accounting
Q.6
Page 4 of 4
Hi-tech Limited (HL) assembles and sells various components of heavy construction
equipment. HL is working on a proposal of assembling a new component EXV-99. Based on
study of the product and market survey, the following information has been worked out:
Projected lifetime sale of the component EXV-99
Selling price per unit
Target gross profit percentage
Units
Rs.
500,000
11,000
40%
Information about cost of production of the new component is as follows:
(i)
One unit of EXV-99 would require:
Parts no.
XX
YY
ZZ
Net quantity
1 unit
1.5 kg
1 unit
Cost per unit/kg (Rs.)
2,350
1,400
1,200
The above parts would be imported in a lot, for production of 1,000 units of EXV-99.
Custom duty and other import charges would be 15% of cost price. HL is negotiating
with the vendor who has agreed to offer further discount.
(ii)
On average, assembling of one unit of EXV-99 would require 1.8 skilled labour hours
at Rs. 200 per hour. The production would be carried out in a single shift of 8 hours.
At the start of each shift, set-up of machines would require 30 minutes. 6% of the
input quantity of YY and ZZ would be lost during assembly process.
(iii)
HL works at a normal annual capacity of 4,000,000 skilled hours. Actual production
overheads and skilled labour hours for the last two quarters are as under:
Quarter
ended
30-Sep-2014
31-Dec-2014
(iv)
Total assembly
Production
hours
overheads (Rs.)
950,000
65,600,000
1,050,000
68,000,000
A special machine that would be used exclusively for the production of EXV-99
would be purchased at a cost of Rs. 1,500,000.
Required:
From the above information, determine the discount that HL should obtain in order to
achieve the target gross profit.
(THE END)
(16)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Information Technology: T I C A PDokumen2 halamanInformation Technology: T I C A PaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology: Continued On Next Page...Dokumen2 halamanInformation Technology: Continued On Next Page...askermanBelum ada peringkat
- E 16 - BMGDokumen3 halamanE 16 - BMGaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- D10 CaDokumen4 halamanD10 CaaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- D10 CacDokumen4 halamanD10 CacaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology: T I C A PDokumen2 halamanInformation Technology: T I C A PaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- D11 AudDokumen2 halamanD11 AudaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf-9 AudDokumen3 halamanCaf-9 AudaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- T I C A P: HE Nstitute of Hartered Ccountants of AkistanDokumen2 halamanT I C A P: HE Nstitute of Hartered Ccountants of AkistanaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Company LawDokumen3 halamanCompany LawaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf-6 TaxDokumen4 halamanCaf-6 TaxaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Laws2008Dokumen3 halamanCorporate Laws2008askermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf-3 (1) BLWDokumen3 halamanCaf-3 (1) BLWaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf 7 Far2Dokumen4 halamanCaf 7 Far2askermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf 6 BMBDokumen2 halamanCaf 6 BMBaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf-2 IefDokumen4 halamanCaf-2 IefaskermanBelum ada peringkat
- Caf 3 Far1Dokumen4 halamanCaf 3 Far1askerman0% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- LN Foundation (v10.5) CYUAnswersDokumen13 halamanLN Foundation (v10.5) CYUAnswersDiana Catherine Avella DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Project ReportDokumen3 halamanProject ReportKBelum ada peringkat
- Market Research-HCL TouchDokumen3 halamanMarket Research-HCL TouchVivek AzadBelum ada peringkat
- Auditing Problem - Correl 2 Exercise 1: Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScoreDokumen17 halamanAuditing Problem - Correl 2 Exercise 1: Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScorePrincesBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Green Marketing Practices On Consumer Buying DecisionDokumen130 halamanThe Impact of Green Marketing Practices On Consumer Buying DecisionpsychonomyBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2 15DPM21F1033Dokumen19 halamanTutorial 2 15DPM21F1033Frdus hmdnBelum ada peringkat
- Indylogix Business PlanDokumen26 halamanIndylogix Business Planlovekesh1Belum ada peringkat
- Job Order Costing The Four Seasons FinalDokumen22 halamanJob Order Costing The Four Seasons FinalRio RegalaBelum ada peringkat
- Variable Costing Case Part A SolutionDokumen3 halamanVariable Costing Case Part A SolutionG, BBelum ada peringkat
- Project SelectionDokumen2 halamanProject SelectionRojan ChanBelum ada peringkat
- ABDT2143 P. Retail MGMT SampleDokumen7 halamanABDT2143 P. Retail MGMT Sampledanielwwcheong8981Belum ada peringkat
- Journal Entry Voucher JEV No.: 01-2022-05-01118: Appendix 36Dokumen74 halamanJournal Entry Voucher JEV No.: 01-2022-05-01118: Appendix 36Cheynee GayleBelum ada peringkat
- Business Plan F-WPS OfficeDokumen13 halamanBusiness Plan F-WPS OfficeKristalyn Mary AlcagnoBelum ada peringkat
- Amisha Dubey - O507 - Lab Assgmt. - 3 - SSSOMDokumen4 halamanAmisha Dubey - O507 - Lab Assgmt. - 3 - SSSOMAastha GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Freeport Case AnalysisDokumen2 halamanFreeport Case AnalysisMudit AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Goods & Service Tax (OFI) White Paper On AccountingDokumen9 halamanGoods & Service Tax (OFI) White Paper On AccountingRahul JainBelum ada peringkat
- Atkinson CH 1 LectureDokumen42 halamanAtkinson CH 1 LectureAsad Zaman0% (1)
- Case Analysis of Netflix in 2011Dokumen7 halamanCase Analysis of Netflix in 2011Anisa TasnimBelum ada peringkat
- Problems On EpsDokumen5 halamanProblems On EpsShripradha AcharyaBelum ada peringkat
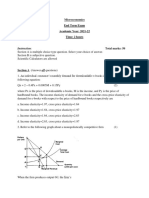
- Microeconomics End Term Exam Academic Year: 2021-22 Time: 2 HoursDokumen7 halamanMicroeconomics End Term Exam Academic Year: 2021-22 Time: 2 HoursKartik GurmuleBelum ada peringkat
- Disruptive Innovation in Healthcare 2009Dokumen25 halamanDisruptive Innovation in Healthcare 2009Patients Know BestBelum ada peringkat
- Book BuildingDokumen15 halamanBook BuildingPoojaDesaiBelum ada peringkat
- DM Course PDFDokumen3 halamanDM Course PDFSapna RajapurkarBelum ada peringkat
- Brand MaintenanceDokumen3 halamanBrand MaintenanceZara ImranBelum ada peringkat
- HHHDokumen25 halamanHHHElena RahmatikaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of OrganizationDokumen9 halamanIntroduction of Organizationthilini100% (1)
- Advanced Accounting Jeter Chapter 4Dokumen55 halamanAdvanced Accounting Jeter Chapter 4Hanna GabriellaBelum ada peringkat
- SCDL Project ReportDokumen75 halamanSCDL Project Reportvasu_suva100% (1)
- Financial Reporting M20: TutorialDokumen37 halamanFinancial Reporting M20: TutorialrandomBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 LalPir Power LTD ProspectusDokumen84 halaman2013 LalPir Power LTD ProspectusMuhammad Usman Saeed0% (1)