Installation Guide PM200
Diunggah oleh
Carlos AguiarHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Installation Guide PM200
Diunggah oleh
Carlos AguiarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PowerLogic Power Meter 200 and 200P
English
Installation Guide
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
INSTALLATION
12/2008
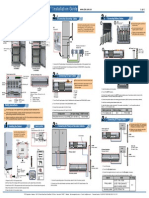
Dimensions
Figure 2: PM200 and 200P Dimensions
Box Contents
63230-510-209A1
DANGER
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION, OR ARC FLASH
Apply appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow safe electrical work
practices. In the USA, see NFPA 70E.
Only qualified electrical workers should install this equipment. Such work should be
performed only after reading this entire set of instructions.
NEVER work alone.
Before performing visual inspections, tests, or maintenance on this equipment, disconnect
all sources of electric power. Assume that all circuits are live until they have been completely
de-energized, tested, and tagged. Pay particular attention to the design of the power system.
Consider all sources of power, including the possibility of backfeeding.
Turn off all power supplying the power meter and the equipment in which it is installed before
working on it.
Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm that all power is off.
Before closing all covers and doors, carefully inspect the work area for tools and objects that
may have been left inside the equipment.
Use caution while removing or installing panels so that they do not extend into the energized
bus; avoid handling the panels, which could cause personal injury.
The successful operation of this equipment depends upon proper handling, installation, and
operation. Neglecting fundamental installation requirements may lead to personal injury as
well as damage to electrical equipment or other property.
NEVER bypass external fusing.
NEVER short the secondary of a PT.
NEVER open circuit a CT; use the shorting block to short circuit the leads of the CT before
removing the connection from the power meter.
Before performing Dielectric (Hi-Pot) or Megger testing on any equipment in which the power
meter is installed, disconnect all input and output wires to the power meter. High voltage
testing may damage electronic components contained in the power meter.
The power meter should be installed in a suitable electrical enclosure.
Failure to follow this instruction will result in death or serious injury
One (1) power meter
Two (2) retainer clips
One (1) installation sheet
+0.8
92 0.0
(3.62)
Parts of the PM200 and 200P
Figure 1: PM200 and 200P
Control Power.
Voltage Inputs.
Current Inputs.
Two Pulse Outputs (PM200P).
Not in use (PM200).
LED.
Regular flashing =
functioning system.
Irregular flashing =
communications indicator.
Steady OFF/ON = meter not
functioning.
+0.8
92 0.0
(3.62)
B
96
(3.78)
50
Mounting
(1.97)
1. Insert the power meter
through the 92 mm x 92 mm
(3.62 in. x 3.62 in.) cut-out
(see Figure 2).
2. Attach the two retainer clips to
the power meter using the
retainer slots at position A or
position B (shown in drawing
on right).
There are two sets of retainer
slots on the left, right, top and
bottom of the power meter. The
first set is for installation
locations thinner than 3 mm
(1/8 in.). The second set is for
installation locations 3 to 6 mm
(1/8 in. to 1/4 in.).
19
(0.75)
mm (in.)
96
(3.78)
WIRING
Voltage inputs and control power for distribution systems up to 277 V L-N and 480 V L-L complies with
metering category III. Also, terminal wiring should have a minimum temperature rating of 80 C.
Polarity marks must be followed as shown for CTs and PTs (). See Tables 1 and 4 for connector
specifications and wiring symbols.
Table 1:
Connector Specifications for PM200 and 200P
NOTE: For use on a flat surface of a
protective enclosure (for example, in the
USA: NEMA 1 rated enclosure or
better).
Connection
Number
Wire Dimensions
1 and 2
12 to 24 AWG
2.5 to 0.2 mm2
Voltage Inputs
(PTs)
3, 4, 5, and 6
12 to 24 AWG
2.5 to 0.2 mm2
.
4 in.lb
Two Pulse
7, 8, 9, and 10
Outputs (PM200P)*
12 to 24 AWG
2.5 to 0.2
mm2
4 in. lb
Current Input
(CTs)
12 to 24 AWG
2.5 to 0.2 mm2
14, 15, 16, 17,
18, and 19
Insulation
Strip Length
Torque
Power Supply
4 in lb
3.54 to
4.43 in lb
.
0.45 N.m
0.45 N.m
0.45 N m
0.4 to 0.5 N m
1/4 in
6.0 mm
1/4 in
6.0 mm
1/4 in
6.0 mm
1/4 in
6.0 mm
* Connections 11, 12, and 13 are not present on the power meter. This connector is not in use for the PM200.
NOTE: Order PM7AND2HWKIT for connectors replacement.
Supported System Types
Table 2:
Number of
Wires
Table 3:
CTs
Qty.
Voltage Connections
ID
Qty.
ID
Meter Configuration
Type
System
Type
PT Primary
Scale
Figure Number
Number of
Wires
Single-Phase Wiring
2
3
I1
V1, Vn
L-N
10
No PT
I1
V1, V2
L-L
11
No PT
I1, I2
V1, V2, Vn
L-L with N
12*
No PT
I1, I3
V1, V2, V3
Delta
30
No PT
I1, I2, I3
V1, V2, V3
Delta
31
No PT
CTs
Voltage Connections
I1
V1, V2, V3
Delta
(Balanced)
32
No PT
I1, I2, I3
V1, V2, V3, Vn
4-wire
Delta
40
No PT
I1, I2, I3
V1, V2, V3, Vn
Wye
40
No PT
I1
V1, V2, V3, Vn
Wye
(Balanced)
44
No PT
Figure
Number
ID
Qty.
ID
Type
System
Type
PT Primary
Scale
I1, I2, I3
V1, V2, V3, (Vn
to Ground)
Grounded
Wye
40
Based on
voltage
13
I1, I2, I3
V1, V3 (Vn to
Ground)
Wye
42
Based on
voltage
14
V1, V2, V3 (Vn
to Ground)
Grounded
Wye
40
Based on
voltage
15
V1, V2, V3 (Vn
to Ground)
Grounded
Wye
(Balanced)
44
Based on
voltage
16
I1, I2
I1
Figure 3: 1-Phase Line-to-Neutral 2-Wire
System 1 CT
Table 4:
Wiring Diagram Symbols
20
Symbol
Voltage Connections
Meter Configuration
ID
Qty.
ID
Type
System
Type
PT Primary
Scale
I1, I3
V1, V3 (V2 to
Ground)
Delta
30
Based on
voltage
V1, V3 (V2 to
Ground)
Delta
31
Based on
voltage
10
V1, V3 (V2 to
Ground
Delta
(Balanced)
18
3
1
I1, I2, I3
I1
32
Based on
voltage
Fuse
11
I1, I2, I3
40
Based on
voltage
I1, I3
V1, V2, V3, (Vn
Wye
to Ground)
(Unbalanced)
40
Based on
voltage
12
I1
V1, V2, V3, (Vn
Wye
to Ground)
(Unbalanced)
44
Based on
voltage
17
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
VL-L <= 480V
Figure 5: 1-Phase Direct Voltage
Connection 2 CT
Figure 8: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye Direct
Voltage Input Connection 3 CT
L3
L1 L2
L3
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 11.
To avoid distortion, use parallel wires for control
power and voltage inputs. Keep the fuse close
to the power source.
Use with 120/240 V systems.
Use System type 31.
Figure 9: 3-Phase 3-Wire Delta Connection
2 CT 2 PT
Use System type 40.
Use with 480Y/277 V and 208Y/120 V systems.
Figure 10: 3-Phase 3-Wire Delta
Connection 3CT 2PT
Figure 6: 3-Phase 3-Wire 2 CT no PT
L1 L2
L1 L2
L3
L3
Earth ground
N
L1
L1 L2
L2
L3
Current transformer.
Polarity marks: = S1.
Shorting block
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
Potential transformer.
Polarity marks: = X1.
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Protection containing a voltage disconnect switch with a fuse or
disconnect circuit breaker (the protection device must be rated for
the available short-circuit current at the connection point).
L1
V1, V2, V3, (Vn
Wye
to Ground)
(Unbalanced)
14
15
16
17
18
19
L1 L2
1
2
3
N
Figure
Number
Qty.
V
V
V
V
Use System type 10.
To avoid distortion, use parallel wires for control
power and voltage inputs. Keep the fuse close
to the power source.
Description
Voltages Greater Than 277 Vac L-N/480 Vac L-L
CTs
3
4
5
6
Voltage disconnect switch
Three-Phase Wiring
Number of
Wires
L1 L2
The following symbols are used in the wiring diagrams:
Figure 7: 3-Phase 3-Wire 3 CT no PT
Figure 4: 1-Phase Line-to-Line 2-Wire
System 1 CT
N L1
19
* System type 12 supports single phase circuits distributed from a 208/120 Vac 1-phase 3-wire service with
no PTs. System 12 also supports single phase circuits distributed from a 480/277 Vac or 208/120 Vac 3phase 4-wire service with no PTs. Any two of the three current channels can be used. Ensure that each
phase is wired to the proper phase input. For example: Circuits from A-Bwire phase A voltage and
current to V1 and I1 and wire phase B voltage and current to V2 and I2. Circuits from C-Awire phase C
voltage and current to V3 and I3 and wire phase A voltage and current to V1 and I1. Circuits from BCwire phase B voltage and current to V2 and I2 and wire phase C voltage and current to V3 and I3.
Note (Phases B-C): Voltage input V1 must be connected to phase A voltage to obtain frequency lock.
Table 3:
Meter Configuration
Qty.
Three-Phase Wiring
Wiring Diagrams
Voltages Greater Than 277 Vac L-N/480 Vac L-L
Three-Phase Wiring
Voltages Less Than or Equal to 277 Vac L-N/480 Vac L-L, Direct Connect No PTs
V1
L1
V2
L2
L3
V3
L2
L3
In 2 PT systems, these connections are equivalent.
Note: Pay attention to the polarity marks
V1
V2
V3
Use System type 12.
To avoid distortion, use parallel wires for control
power and voltage inputs. Keep the fuse close
to the power source.
Use System type 30.
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
For an open delta PT connection with 120 V L-L
secondaries, use System type 30.
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 31.
For an open delta PT connection with 120 V L-L
secondaries, use System type 31.
Figure 11: 3-Phase 3-Wire Wye Connection
3 CT 3 PT (unbalanced)
L1 L2
L3
L1 L2
Figure 12: 3-Phase 3-Wire Wye Connection
2CT 3PT (unbalanced)
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 40.
Figure 19: 3-Phase 3-Wire Direct Voltage
Input Connection 1 CT
(balanced)
L1 L2
L3
L1 L2
L3
L1 L2
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 40.
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 40.
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
Figure 13: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye Connection
3 CT 3 PT
Figure 14: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye 3CT 2PT
(balanced)
L3
L1 L2
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 40.
Figure 17: 3-Phase 3-Wire Wye 1CT 3PT
(unbalanced)
L3
L1 L2
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 42.
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
L1 L2
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Solid-state Pulse Output
There are two solid-state KY outputs. One is dedicated to kWH and the other is dedicated to kVARH.
Figure 25: Solid-state Outputs
Overcurrent Protective
100 mA
Digital Output / Pulse Output
KY is a solid state pulse output
rated for 240 Vac/dc max.
~=
Type of measurement
Screen title
Maintenance icon
Bar Chart (%)
Units
Display more menu items
Menu item
Selected menu indicator
Button
Return to previous menu
Values
Phase
3
4
5
6
V1
V2
V3
VN
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
14
15
16
17
18
19
I1+
I1
I2+
I2
I3+
I3
Use System type 32.
Use System type 44.
Figure 22: Direct Connect Control Power
(Phase to Neutral)
N L1 L2 L3
1 2
1 2
- +
-+
Phase to Phase only when voltage
< 415 + 10% Vac max.
See Table 5.
Phase to Neutral only when voltage
< 300 + 10% Vac max.
See Table 5.
Figure 27: Abbreviated IEC Menu Hierarchy*
D
E
U-V
PHASE
DMD
KWH
PQS
PQS
DMD
--->
3
4
Table 6:
~=
Power Source
*
3 - 240 Vdc
Ph
Qh
Sh
PF
5
6 PM200P
NOTE: The overcurrent protective
device must be rated for the short
circuit current at the connection point.
Control Power Transformer
120 or 240 Vac Secondary 50 Va max.
See Table 5.
Fuse Recommendation
Control Power Source
Source Voltage (Vs)
Fuse
Fuse Amperage
CPT
Vs 125 V
FNM or MDL
250 mA
CPT
125 < Vs 240 V
240 < Vs 305 V
FNQ or FNQ-R
250 mA
CPT
FNQ or FNQ-R
250 mA
Line Voltage
Vs 240 V
FNQ-R
250 mA
Line Voltage
Vs > 240 V
Vs 300 V
FNQ-R
250 mA
LP-CC
500 mA
See Figure 21 to Figure 24.
Over current protection should be located as close to the device as possible.
For selecting fuses and circuit breakers other than those listed above, use the following criteria:
Over current protection should be rated as listed above.
Current interrupt capacity should be selected based on the installation category and fault current capability.
Over current protection should be selected with a time delay.
The voltage rating should be based on the input voltage applied.
If a 0.25 A fuse is not available with the required fault current capability, use a fuse rated at a maximum of
0.5 A.
CT RATIO
800
5
C T
C T
1;
<-
PRIM
SECON.
OK
Getting Technical Support
Navigation
Load
See the online PM200 and 200P Reference Manual at www.powerlogic.com for more information on
setting up the power meter.
Button Symbols
--->
How the Buttons Work
100 mA
KVARH
DC Control Power 100 Vdc < V < 300 Vdc
See Table 5.
1. Press ###: until you see DIAGN.
2. Press SETUP.
3. Enter your password. The default password
is 00000.
4. Press OK.
5. Press METER.
6. Press CT.
7. Enter the PRIM CT (primary CT) number: 1
to 32762.
8. Press OK.
9. Enter the SEC. CT (secondary CT) number:
1 or 5.
10. Press OK.
11. Press 1; to return to the SETUP MODE
screen.
PEAK
Setup Example: This example shows how to set up CTs. Use the same method to set up PTs and
Communication.
- +
1 2
- +
NOTES:
Power Source
*
3 - 240 Vdc
V1
V2
V3
VN
DC
Use System type 32.
3
4
5
6
Load
7 8 9 10
Figure 24: Control Power Transformer
(CPT) Connection
L3
V1
V2
V3
VN
L1 L2 L3
Figure 26: Parts of PM200 and 200P Display
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
H.
I.
J.
K.
L.
L1 L2
3
4
5
6
Figure 21: Direct Connect Control Power
(Phase to Phase)
L3
Table 5:
Use System type 44.
L3
Use System type 44.
Figure 18: 3-Phase 3-Wire 1 CT 2 PT
(balanced)
L3
PM200P Pulse Output Capabilities
Maximum load current is 100 mA
at 25C. Derate 0.56 mA per C
above 25C.
Figure 23: Direct Connect Control Power
(DC Control Power)
1 2
L1 L2
Figure 20: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye Direct
Voltage Input Connection 1 CT
(balanced)
N L1 L2 L3
3
4
5
6
Figure 16: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye 1 CT 3PT
(balanced)
L3
Figure 15: 3-Phase 4-Wire Wye 2 CT 3 PT
(for balanced 3-wire loads)
Please refer to the Technical Support Contacts provided in the power meter shipping carton or go to
www.powerlogic.com.
View more menu items on the current level.
1;
Return to the previous menu level.
Indicates the menu item is selected and there are no menu levels below the current level.
DIAGN
INFO
(1)
RESET
(2)
SETUP
(2)
Change Values
*The power source should not be a safety extra low voltage (SELV) circuit. Pulse outputs are not
SELV rated.
METER
Change values or scroll through the available options. When the end of a range is reached,
pressing + again returns to the first value or option.
<-
Select the next number of a series.
OK
Move to the next editable field or exits the screen if the last editable field is selected.
METER
DMD PASSW PULSE
DMD
(3)
BARGR
MODE
NOTE: The PM200 does not include pulse outputs.
Set Up the Power Meter
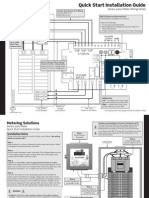
OPERATING THE DISPLAY
The power meter is equipped with a large, back-lit LCD display. It can display up to five lines of information
plus a sixth row of menu options. Figure 26 shows the different parts of the power meter display.
Figure 27 shows abbreviated hierarchical relationships of the menu screens for the PM200 and 200P.
Using the Setup Example below in conjunction with the menu hierarchy (Figure 27), complete a minimum
setup of the power meter. A minimum setup includes:
Set up CTs.
Set up PTs.
Set up Communication.
U = Voltage, L-L
V = Voltage, L-N
* The power meter can be configured to display either IEC or IEEE nomenclature. Figure 27 shows IEC
nomenclature.
(1) The INFO command includes model, firmware version, and serial number information.
(2) Reset and Setup menu items require a password to navigate to the second level menu.
(3) PULSE menu is included with PM200P. The PM200 does not include a PULSE menu.
Schneider Electric
Power Monitoring and Control
295 Tech Park Drive, Suite 100
This product must be installed, connected, and used in compliance with prevailing
standards and/or installation regulations. As standards, specifications, and designs
change from time to time, please ask for confirmation of the information given in
this publication.
LaVergne, TN 37086
Tel: +1 (615) 287-3400
63230-510-209A1
www.powerlogic.com
2008 Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved.
12/2008
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Belum ada peringkat
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsDari EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Penilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (3)
- LG Refridge ServiceManualDokumen79 halamanLG Refridge ServiceManualMichael Dianics100% (1)
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsDari EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsBelum ada peringkat
- PCC1 2 PDFDokumen10 halamanPCC1 2 PDFdheerajdb9950% (2)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDari Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Mayo College: Dining Hall at AjmerDokumen79 halamanMayo College: Dining Hall at AjmerFaquruddinBelum ada peringkat
- Beginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsDari EverandBeginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Marine Generator Set 3304B DINADokumen8 halamanMarine Generator Set 3304B DINACarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Water Standard Specification Index As On Dec 2015Dokumen10 halamanWater Standard Specification Index As On Dec 2015afp15060% (1)
- OmniMeter Universal Smart Meter User Manual EKM MeteringDokumen2 halamanOmniMeter Universal Smart Meter User Manual EKM MeteringChris CalderónBelum ada peringkat
- Inspection AND Test Procedures 7.6.4 Circuit Breakers, SFDokumen7 halamanInspection AND Test Procedures 7.6.4 Circuit Breakers, SFCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature Controller: User'S ManualDokumen32 halamanTemperature Controller: User'S ManualkmpoulosBelum ada peringkat
- Harsen ChargerDokumen1 halamanHarsen ChargerCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageDari EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageBelum ada peringkat
- CT Install TransformadorDokumen4 halamanCT Install TransformadorNishant SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Safety LOPADokumen28 halamanSafety LOPAnandorg1113100% (1)
- GH G ConversionDokumen146 halamanGH G ConversionjorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Philips TV 21PT5420/01 L01.2E AA Chassis - CL 16532008 - 041.eps (160501)Dokumen64 halamanPhilips TV 21PT5420/01 L01.2E AA Chassis - CL 16532008 - 041.eps (160501)r_marecekBelum ada peringkat
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Dari EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Commissioning and Maintenance MiCOM P125 P126 & P127-P12yEN CMC22Dokumen26 halamanCommissioning and Maintenance MiCOM P125 P126 & P127-P12yEN CMC22dennyyusufBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Diesel Engines for Unrestricted Continuous OperationDokumen2 halamanDiesel Engines for Unrestricted Continuous OperationJorge Bellido100% (1)
- Wind Turbine Installation-ManualDokumen23 halamanWind Turbine Installation-Manualויליאם סן מרמיגיוסBelum ada peringkat
- PM710Dokumen2 halamanPM710A. IvanBelum ada peringkat
- Conzerv 6438Dokumen10 halamanConzerv 6438Pur WantoBelum ada peringkat
- Em6438 6436 Dual Quick Start GuideDokumen10 halamanEm6438 6436 Dual Quick Start GuideReji KurianBelum ada peringkat
- EKM OmniMeter UL User Manual Spec Sheet SubmeterDokumen3 halamanEKM OmniMeter UL User Manual Spec Sheet SubmeterAdam BrouwerBelum ada peringkat
- OmniMeter Universal Smart Meter User Manual EKM MeteringDokumen3 halamanOmniMeter Universal Smart Meter User Manual EKM MeteringAdam BrouwerBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Start Guide - Series 20001Dokumen2 halamanQuick Start Guide - Series 20001Gustavo FeisbukeroBelum ada peringkat
- EKM Omnimeter Pulse v.4 Spec SheetDokumen4 halamanEKM Omnimeter Pulse v.4 Spec SheetAdam BrouwerBelum ada peringkat
- L01 2aabDokumen72 halamanL01 2aab111sBelum ada peringkat
- EM6400 QSG V01.d18 (Web) PDFDokumen4 halamanEM6400 QSG V01.d18 (Web) PDFGillala RamakanthBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Manual: Models 7EF and 7HF ControllersDokumen48 halamanInstruction Manual: Models 7EF and 7HF ControllerskmpoulosBelum ada peringkat
- Panasonic TX-25lk1p TX-28lk1p Chassis z8Dokumen22 halamanPanasonic TX-25lk1p TX-28lk1p Chassis z8drrebyBelum ada peringkat
- Im PK 1603Dokumen32 halamanIm PK 1603James James MorrisonBelum ada peringkat
- 25pt4622Philips+L7 3A+AADokumen48 halaman25pt4622Philips+L7 3A+AAWall BrysonBelum ada peringkat
- Te1.1e AaDokumen57 halamanTe1.1e AaSicoe VasileBelum ada peringkat
- TX-32PM1 and TX-28PM1 Service ManualDokumen28 halamanTX-32PM1 and TX-28PM1 Service ManualSean GuyBelum ada peringkat
- Adi TV Philips 21pt5221 60 Chassis L01.2A ABDokumen70 halamanAdi TV Philips 21pt5221 60 Chassis L01.2A ABbioteky33% (3)
- Philips L7.3a Aa Chassis TV SMDokumen49 halamanPhilips L7.3a Aa Chassis TV SMRoger_74Belum ada peringkat
- TX-28CK1P TX-25CK1P TX-21CK1P: Colour TelevisionDokumen24 halamanTX-28CK1P TX-25CK1P TX-21CK1P: Colour TelevisionAdrian StancaBelum ada peringkat
- EKM Omnimeter Pulse UL v.4 Spec SheetDokumen4 halamanEKM Omnimeter Pulse UL v.4 Spec SheetAdam BrouwerBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Start Guide PC321 Z TY Single 3 Phase Power Clamp 220614Dokumen10 halamanQuick Start Guide PC321 Z TY Single 3 Phase Power Clamp 220614Rainer MartikainenBelum ada peringkat
- SERVICE MANUAL FOR COLOR TVDokumen9 halamanSERVICE MANUAL FOR COLOR TValopezcuervoBelum ada peringkat
- DIN Rail Mounting Controller Instruction ManualDokumen35 halamanDIN Rail Mounting Controller Instruction Manualmjayaprakash225230Belum ada peringkat
- Philips Chassis L03.1uaaDokumen66 halamanPhilips Chassis L03.1uaaJorch Ramirez EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- TP48200A-D12A1 Quick Installation Guide V300R001 01 PDFDokumen2 halamanTP48200A-D12A1 Quick Installation Guide V300R001 01 PDFPavelKuzovkinBelum ada peringkat
- Zxdupa-Wr01 (v4.0r02m02) &zxdupa-Wr01 (v4.0r02m03) DC Power System Installation GuideDokumen4 halamanZxdupa-Wr01 (v4.0r02m02) &zxdupa-Wr01 (v4.0r02m03) DC Power System Installation GuideMichael WongBelum ada peringkat
- Technics Su c909sDokumen61 halamanTechnics Su c909sschaiBelum ada peringkat
- EKM Omnimeter Pulse UL v4 Spec SheetDokumen4 halamanEKM Omnimeter Pulse UL v4 Spec SheetAdam BrouwerBelum ada peringkat
- Eurotherm 3216 PDFDokumen6 halamanEurotherm 3216 PDFRoyalty GouldBelum ada peringkat
- Panasonic TX-21at1p Chassis Z-8tDokumen22 halamanPanasonic TX-21at1p Chassis Z-8taureliancoBelum ada peringkat
- Edc Manual RoseDokumen48 halamanEdc Manual RoseRagabindu GuruBelum ada peringkat
- Panasonic TX-36PF10 TX-32PF10 (Euro-5 Chassis)Dokumen49 halamanPanasonic TX-36PF10 TX-32PF10 (Euro-5 Chassis)manitou1997Belum ada peringkat
- LA 76931S 7N DatasheetDokumen20 halamanLA 76931S 7N DatasheetjulioescandonBelum ada peringkat
- DCL 33AInstructionManualDokumen20 halamanDCL 33AInstructionManualDobrin PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Varlogic NRC12Dokumen44 halamanManual Varlogic NRC12David LaurenteBelum ada peringkat
- KDE200 Series User Manual 20180412Dokumen88 halamanKDE200 Series User Manual 20180412Thanh Tuyền TrươngBelum ada peringkat
- TV LG 21fu1rDokumen16 halamanTV LG 21fu1rpurwants100% (1)
- TV Philips l03.1l Aa 21pt6446Dokumen53 halamanTV Philips l03.1l Aa 21pt6446José Mamani Oyardo100% (1)
- Em306a User ManualDokumen2 halamanEm306a User ManualNguyễnĐìnhDầnBelum ada peringkat
- Philips Chassis L01.2e AaDokumen64 halamanPhilips Chassis L01.2e AaliviucatalinBelum ada peringkat
- 5vdc Din ControllerDokumen11 halaman5vdc Din ControllerBals GaddaBelum ada peringkat
- SKE Evaporator Fan Ø 500 mmDokumen3 halamanSKE Evaporator Fan Ø 500 mmCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Classification According To-SizeDokumen4 halamanClassification According To-SizeCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Enset Ngine: PerformancesDokumen2 halamanEnset Ngine: PerformancesCarlos Aguiar0% (1)
- Log - 16 12 2019Dokumen1 halamanLog - 16 12 2019Dalton YamamotoBelum ada peringkat
- Yuasa Battery Care GuideDokumen1 halamanYuasa Battery Care GuideCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Square Straight Steel Pole Assembly: SportslightingDokumen1 halamanSquare Straight Steel Pole Assembly: SportslightingCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- PCC1 2Dokumen9 halamanPCC1 2Carlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Rainbow Usage Guide: Data Connection EstablishmentDokumen13 halamanRainbow Usage Guide: Data Connection EstablishmentPedroBelum ada peringkat
- Homelite Consumer Products, IncDokumen10 halamanHomelite Consumer Products, IncCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- NTC Icl P11Dokumen18 halamanNTC Icl P11Carlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- 10 K ThermistorDokumen61 halaman10 K ThermistorWuland WaisnawaBelum ada peringkat
- NTC Icl P11Dokumen18 halamanNTC Icl P11Carlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- I035 ElectricalTester JAN 2016Dokumen8 halamanI035 ElectricalTester JAN 2016blem_0075Belum ada peringkat
- Rainbow Usage Guide: Data Connection EstablishmentDokumen13 halamanRainbow Usage Guide: Data Connection EstablishmentPedroBelum ada peringkat
- NSX-S505 NSX-A508 CD Stereo Cassette Receiver Manual Parts ListDokumen22 halamanNSX-S505 NSX-A508 CD Stereo Cassette Receiver Manual Parts ListRicardoBelum ada peringkat
- SC-AK22 Operating InstructionsDokumen32 halamanSC-AK22 Operating InstructionsCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Aiwa CX-500 SchematicDokumen2 halamanAiwa CX-500 SchematicCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- MN 66279 RSCDokumen97 halamanMN 66279 RSCCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Camsco TransferDokumen8 halamanCamsco TransferCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Miniature High Power Relay Provides 8A Switching CapabilitiesDokumen2 halamanMiniature High Power Relay Provides 8A Switching CapabilitiesCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Satir Data Sheetshotfind SDokumen2 halaman2017 Satir Data Sheetshotfind SCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- ESD5500E Series Speed Control Unit: SpecificationsDokumen5 halamanESD5500E Series Speed Control Unit: SpecificationsMurilo FigueiredoBelum ada peringkat
- Common Notes DC Geared MotorDokumen4 halamanCommon Notes DC Geared MotorCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- ESD5100 SeriesDokumen5 halamanESD5100 SeriesCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Kr230u Engine SpecificationsDokumen4 halamanKr230u Engine SpecificationsCarlos AguiarBelum ada peringkat
- Turbocharged Engines PDFDokumen72 halamanTurbocharged Engines PDFVeler VelericBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Unit 1 - Building With Nature SSDokumen28 halamanChapter 4 Unit 1 - Building With Nature SSJeffreyBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokumen2 halamanQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.tamilarasi87thulasiBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conservation Oppurtunities in Boiler SystemDokumen34 halamanEnergy Conservation Oppurtunities in Boiler SystemSiddharth Jain67% (3)
- Edited Economics AsDokumen476 halamanEdited Economics AsShakeela ShanmuganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Microcontroller-Based Power Monitoring for COE RoomsDokumen8 halamanMicrocontroller-Based Power Monitoring for COE Roomskenneth_molenilla1475Belum ada peringkat
- 3/27/2016 Portable AC On Rent Pune - Portable AC Rentals Pune - AC Rentals Pune On SulekhaDokumen3 halaman3/27/2016 Portable AC On Rent Pune - Portable AC Rentals Pune - AC Rentals Pune On SulekhadcoolsamBelum ada peringkat
- Acoustic Variables - Kasia's E-PortfolioDokumen2 halamanAcoustic Variables - Kasia's E-Portfoliomuhammad ShoaibBelum ada peringkat
- FMM Question Set 1Dokumen16 halamanFMM Question Set 1Abhijit KuchbhilikhtaBelum ada peringkat
- Design and implementation of a solar-powered electric smart benchDokumen7 halamanDesign and implementation of a solar-powered electric smart benchAmir KalčoBelum ada peringkat
- 3512TA - 1000kVA - LV - Spec Sheet PDFDokumen5 halaman3512TA - 1000kVA - LV - Spec Sheet PDFavinash_1229Belum ada peringkat
- PPTs ON BONTON CABLESDokumen10 halamanPPTs ON BONTON CABLESShaishav Anand100% (1)
- 947 SampleDokumen6 halaman947 SamplesarveshkdahiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Pepsin Enzyme Activity LabDokumen4 halamanPepsin Enzyme Activity LabDebrah DebbieBelum ada peringkat
- How Electric Cars Work: A Guide to EV TechnologyDokumen4 halamanHow Electric Cars Work: A Guide to EV TechnologyCarla LoiaconoBelum ada peringkat
- Xref 2010Dokumen1 halamanXref 2010Axel Mahya AvichenaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 (3) Collection, Transport, TransferDokumen32 halamanModule 4 (3) Collection, Transport, TransfervanilivaniliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Structure of AtomsDokumen16 halamanChapter 2 Structure of AtomsCherry T CYBelum ada peringkat
- Flux and Refining Agent InjectionDokumen1 halamanFlux and Refining Agent InjectionСтанислав ПодольскийBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsDokumen14 halamanAssessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsKarthik SRSBelum ada peringkat
- American Zettler AZ8 1CH 24DSEDokumen4 halamanAmerican Zettler AZ8 1CH 24DSEadiegooscarBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad de Potencia Hidraulica Hycon HPP13 FlexDokumen9 halamanUnidad de Potencia Hidraulica Hycon HPP13 FlexJorge Diaz Nestor MonsalveBelum ada peringkat