Chapter 09 - Input Data Editing
Diunggah oleh
bella_dsHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 09 - Input Data Editing
Diunggah oleh
bella_dsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
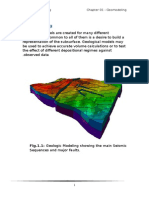
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Input Data Editing
There are few editing steps that must be completed before a
3D geological model is created. The steps include:
1. Creating 3D Surfaces:
a. From Interpretations (3D Seismic Lines).
b. From Fault Polygons (if the data available).
c. From Fault Sticks (if the data available).
d. From your own Fault Polygons.
2. Editing the Created Surfaces - Removing Surface Peaks.
3. Projecting Fault Polygons on their Surfaces.
a. From Fault Polygons (from data available).
b. From your own Fault Polygons.
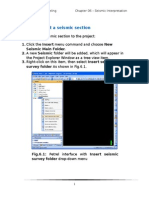
How to Create 3D Surfaces from
Interpretations
1. The first process in editing the input data is creating 3D
surfaces out of the 3D seismic lines. This process is
summarized by the following steps: Expand the Utilities
item in the Process Pane, and then double click on the
Make/Edit Surface. The Make/Edit Surface dialog box
appears.
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
2.In the Input Pane window, select the 3D seismic lines
whose surface is to be created; in this case select Top
Tarbert. Then go to the Geometry tab, and select the
Automatic.
Fig. 9.1: The Make/edit surface form
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
3. Press Apply. A surface will be created in Result surface
as shown in Fig. 9.2.
Fig.9.2: The Make/edit surface after
adding the Top Tarbet for both Main
input
4. Repeat the same process for the Sea Bed, Base
Cretaceous, Top Ness and Top Etive. But before you
create the other surfaces you have to remove the
previous surface by right clicking and choose Remove
icon from drop site and click No.
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig. 9.3: The Make/edit surface after
removing the previous surface.
5. Click the Insert menu command and choose New Folder.
Rename the folder to Gullfaks Input. And right click on
this folder then choose Insert folder. Rename it to
Surfaces (time). Move all the surfaces into the
Surfaces (Time).
Fi
g.9.4: 3D Surfaces displayed in 3D window
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
The settings of the 3D Surfaces may be
changed by:
1. For example, Right-click on Top Tarbert Surface then
selects Settings and hidden Contour Lines.
Fig.9.5: The Settings for Top Tarbert Surafce
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig.9.6: The Top Tarbert Surafce without contour lines
2. Go to the Insert pull down menu and select New
Annotations.
3. Move the Annotations into the Surfaces (Time) folder.
4. Right-clicking on the Annotations and selecting
Settings
5. On the Settings tab, click on Append item in the table
icon.
6. The Row form appears as shown in Fig.9.7
7. Select the Sea Bed surface, and click on the input icon.
8. On the Text tab, change the name.
5
7
Fig.9.7: Settings for Annotations
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
9. Repeat the same process if you want to add more
Append item.
Fig.9.8: Settings for Annotations after adding all the
surfaces.
Notice: Only one annotation object is allowed per project.
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig.9.9: Surfaces with their Annotations dipaleyed in 3D
window
10. Right click on the Top Tarbert surface then choose
Insert new attribute and click Ok.
Fig.9.10: Insert new attribute for Top Tarbert
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
11. Right click on the Continues, from Info tab, rename it
to ST8511r92. And change the template to Seismic
(default).
Fig.9.11: Settings for Continuous
10
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
How to Create 3D Surfaces from Fault Polygons
(Data Available)
1. Expand the Utilities item in the Process Pane, and then
double click on the Make/Edit Surface. The Make/Edit
Surface dialog box appears.
2. In the Input Pane window, select the Fault Polygons
whose surface is to be created; in this case select
Truncating fault. Then go to the Geometry tab, and
select the Automatic.
Fig.9.12: The Make/edit surface form
11
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
3. Press Apply. A fault sticks surface will be created in
Result surface as shown in Fig. 9.13.
Fig.7.13: The Make/edit surface after
adding the Truncating fault polygon
for both Main input
12
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
4. Repeat the same process for remain Fault Polygons.
But before you create the other Fault Polygon Surfaces
you have to remove the previous Fault Polygon
Surface by right clicking and choose Remove icon
from drop site and click No.
Fig.9.14: The Make/edit surface after
removing the previous fault polygon
surface.
13
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
5. Right click on the Gullfaks Input folder then choose
Insert folder. Rename it to Fault Polygons Surfaces.
And move all Fault Polygons Surfaces to this folder.
Fig.9.
15: 3D Fault Polygons Surfaces displayed in 3D window
14
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
How to Create 3D Surfaces from Fault Sticks
(Data Available)
1. Expand the Utilities item in the Process Pane, and then
double click on the Make/Edit Surface. The Make/Edit
Surface dialog box appears.
2. In the Input Pane window, select the Fault Sticks whose
surface is to be created; in this case select Truncating
fault. Then go to the Geometry tab, and select the
Automatic.
15
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig. 9.16: The Make/edit surface form
3. Press Apply. A fault sticks surface will be created in Result
surface as shown in Fig. 9.17.
Fig.9.17: The Make/edit surface after
adding the Truncating fault sticks for
both Main input
16
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
4. Repeat the same process for remain Fault Sticks. But
before you create the other Fault Sticks Surfaces you have
to remove the previous Fault Sticks Surface by right
clicking and choose Remove icon from drop site and
click No.
Fig. 9.18: The Make/edit surface after removing
the previous fault sticks surface.
17
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
6. Right click on the Faults (Time) folder then choose
Insert folder. Rename it to Fault Surfaces. And move
all Fault Sticks Surfaces to this folder.
Fig.
9.19: 3D Fault Sticks Surfaces displayed in 3D window
18
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
How to create 3D Surface from your own Fault
Polygon
To create fault polygons on a certain surface, follow the
steps:
1. Open a new 2D window and display the surface whose
fault polygons are to be created. In this case display the
Top Tarbert surface.
Fig.9.20: Top Tarbert surface displyed in 2D window
19
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
2. Activate the Make/Edit Polygons under Utilities in the
Processes Pane.
3. The Polygons Actions toolbar displays. Click on the
Start New Set of Polygons to start tracing a new set of
fault polygons for the TopTarbert surface. Every time you
start a new fault, you must click the Start New Set of
Polygon icon as shown in Fig. 9.21.
Fig.9.21: Creating fault polygons of the Top Tarbert
surface with Tool bar
20
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
4. For completeness, create a new folder, rename it Top
Tarbert Polygon, and place all fault polygons under this
folder.
Fig.9.22: Top Tarbert fault surface
21
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
5. Repeat the same process for Top Ness and Top Etive
surfaces. And make sure that you will create two folders
and rename them, Top Ness Polygons and Top Etive
Polygons. And place all fault polygons under each folder.
As shown in Fig.9.23. and Fig.9.24.
Fig.9.23: Top Ness fault surface
22
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig.9.24: Top Etive fault surface
23
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Editing Created Surfaces - Removing Surface
Peak
Peaks or spikes depend on the data if it is shown or not.
Notice: The data that we are working on it, it not showing
the Surface Peak. For that, we brought another data to show
you how we can remove the Surface Peak.
Peak on the 3D surfaces can be removed with a simple click
as follows;
1. Display the surface that contains the peak to be removed.
Activate the Make/Edit Surface under Utilities in the
Process Pane window. The Surface Actions toolbar
displays as shown in Fig. 9.25.
2. Choose the Peak Remover button on the Edit Surface
Tools toolbar
24
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig.9.25: 3D surfaces displayed with peak and tool bar
25
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
3. Click on the peak to be removed. The peak disappears as
shown in Fig. 9.26.
Fig.9.26: The 3D Surfaces after removing the peak
26
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Projecting Fault Polygons on their Surfaces
Fault polygons are often interpreted in the XY plane only;
hence their Z-values will be set to 0 as shown in Fig. 7.19. It
is an easy process, however, to get all fault polygons down
to their respective surfaces. This will give them their Zvalues at the correct position. This process is summarized by
the following steps:
1.From Fault Polygons (from data available)
Dr.Hassan, we didnt know how we project the fault polygons
on their surfaces.
If you lock at the demodata. For example (Boundary Fault
West):
The single fault projected on all 3D surfaces.
27
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
2.From your own Fault Polygons.
1. Display Top Tarbert surface with Top Tarbert Polygons.
28
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig
.9.27: Fault polygons with 0 Z-values
29
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
2. Open the settings for the first fault polygon in Top
Tarbert polygons folder, we will take (Polygon 72) as
an example. and go to the Calculations tab as shown in
Fig. 9.28.
Fig. 9.28: Settings for Tarbert fault polygons dialog box
30
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
3. Select the Top Tarbert surface in the Input Pane, then
click on the blue arrow beside the A= in the Settings
dialog box.
Fig.9.29: Settings for Top Tarbert fault
polygons (inserting surface)
4. Press the Assign: Z=A button then press Apply and OK
buttons.
Fig.9.30: Settings for Top Tarbert fault polygons (Z=A)
31
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
5. Complete all the remain fault polygons for Top Tarbert
surface. And all the fault polygons moves down to the
surface as shown in
Fig. 9.31.
Fi
g. 9.31: Top Tarbert fault polygons projected on their
surface
32
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
6. Repeat the same process for the Top Ness and Top
Etive But remember you have to delete the previous
surface and insert the new surface by click on Delete
button.
Fig. 9.32: Top Ness fault polygons projected on their
surface
33
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 09 Input Data Editing
Fig. 9.33: Top Etive fault polygons projected on their
surface
34
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Seismic Inversion WorkflowDokumen12 halamanSeismic Inversion WorkflowNurlia AduBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Geology and Personal ComputersDari EverandStructural Geology and Personal ComputersPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Chapter 02 - Petrel InterfaceDokumen12 halamanChapter 02 - Petrel Interfacebella_ds100% (1)
- Attribute Matrix 2010Dokumen1 halamanAttribute Matrix 2010iakk100% (1)
- Petrophysical Modeling GuideDokumen8 halamanPetrophysical Modeling GuideAnonymous gTVJBHBelum ada peringkat
- An Interpreters Guide To Understanding and Working With Seismic-Derived Acoustic Impedance DataDokumen8 halamanAn Interpreters Guide To Understanding and Working With Seismic-Derived Acoustic Impedance Databella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 01 - GeomodelingDokumen10 halamanChapter 01 - Geomodelingbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- AP Biology 1st Semester Final Exam Review-2011.2012Dokumen13 halamanAP Biology 1st Semester Final Exam Review-2011.2012Jessica ShinBelum ada peringkat
- Shore Activities and Detachments Under The Command of Secretary of Navy and Chief of Naval OperationsDokumen53 halamanShore Activities and Detachments Under The Command of Secretary of Navy and Chief of Naval OperationskarakogluBelum ada peringkat
- Editing of Input Data: Important Icons Used in The Process StepsDokumen9 halamanEditing of Input Data: Important Icons Used in The Process StepsAnonymous qaI31H100% (1)
- Create horizons and zones in 3D geological modelingDokumen30 halamanCreate horizons and zones in 3D geological modelingbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Tips for Working in PetrelDokumen3 halamanTop 10 Tips for Working in PetrelHcene HcenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 06 - Seismic InterpretationDokumen11 halamanChapter 06 - Seismic Interpretationbella_ds0% (1)
- Chapter 05 - 3D Seismic DataDokumen8 halamanChapter 05 - 3D Seismic Databella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Velocity Sources Depth Conversion MethodsDokumen32 halamanSeismic Velocity Sources Depth Conversion MethodsDavid John MarcusBelum ada peringkat
- Petrel 2013Dokumen4 halamanPetrel 2013Milloshy RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- M7 - 3DGridBasedSeismicVelocities (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen30 halamanM7 - 3DGridBasedSeismicVelocities (Compatibility Mode)Ba TinaBelum ada peringkat
- Geometrical AttributesDokumen129 halamanGeometrical AttributesMirza Ali100% (1)
- SCM Tipstricks Well Sections Petrel 3Dokumen8 halamanSCM Tipstricks Well Sections Petrel 3Nilesh SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- SCM Algorithm Comparison Petrel 2010Dokumen5 halamanSCM Algorithm Comparison Petrel 2010Paulo IvoBelum ada peringkat
- PetroMod2013 Manual CompletoDokumen23 halamanPetroMod2013 Manual CompletoDaniel PreciadoBelum ada peringkat
- Facies Classification-ML PDFDokumen4 halamanFacies Classification-ML PDFkmilo04Belum ada peringkat
- Field QC With VISTA (Houston)Dokumen9 halamanField QC With VISTA (Houston)LiliBelum ada peringkat
- 3D Structural Geology in "X" Area PDFDokumen55 halaman3D Structural Geology in "X" Area PDFzamridBelum ada peringkat
- Petroleum Geology & Geophysics: Prediction Model SeismicDokumen19 halamanPetroleum Geology & Geophysics: Prediction Model SeismicMirza Muhammad YudhistiraBelum ada peringkat
- Velocity ModelDokumen9 halamanVelocity ModelHumbang PurbaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Seismic StratigraphyDokumen48 halaman10 Seismic Stratigraphyzemabder100% (2)
- Basic Exploration SeismologyDokumen20 halamanBasic Exploration SeismologyHumbang PurbaBelum ada peringkat
- Well-Tie Workflow: Matt Hall 7 CommentsDokumen3 halamanWell-Tie Workflow: Matt Hall 7 CommentsMark MaoBelum ada peringkat
- Amplitude Contrast and Edge Enhancement For Fault Delineation in Seismic DataDokumen1 halamanAmplitude Contrast and Edge Enhancement For Fault Delineation in Seismic DataAnonymous VWxmb93BlK100% (1)
- Fault Seal AnalysisDokumen9 halamanFault Seal AnalysisBobby SiswantoBelum ada peringkat
- Blueback Rock Physics v4.0.2 - RelNotesDokumen19 halamanBlueback Rock Physics v4.0.2 - RelNoteskrackku k100% (1)
- Basin ModellingDokumen2 halamanBasin ModellingbmcconacBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - Processing of Seismic Reflection Data 1 01Dokumen70 halamanChapter 5 - Processing of Seismic Reflection Data 1 01Ricky ChiuBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Data Processing StepsDokumen39 halamanSeismic Data Processing StepsMordekhaiBelum ada peringkat
- HowTo Workflow Isatis PetrelDokumen7 halamanHowTo Workflow Isatis Petrelbidyut_iitkgpBelum ada peringkat
- Build A 3d Velocity Model From Checkshots Schlumberger Petrel PDFDokumen1 halamanBuild A 3d Velocity Model From Checkshots Schlumberger Petrel PDFzztannguyenzzBelum ada peringkat
- Ex06 PillarGriddingDokumen13 halamanEx06 PillarGriddingogunbiyi temitayoBelum ada peringkat
- Petrel 2015 Whats New Ps PDFDokumen4 halamanPetrel 2015 Whats New Ps PDFTroy ModiBelum ada peringkat
- Ex - Gravity - HT09 - Exercises Gravity SurveyingDokumen4 halamanEx - Gravity - HT09 - Exercises Gravity SurveyingShadi GarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Lithology from seismic inversionDokumen5 halamanLithology from seismic inversionHcene Hcen100% (1)
- Petrel TutoriorDokumen177 halamanPetrel TutoriorAlfian AminBelum ada peringkat
- Checkshot PDFDokumen16 halamanCheckshot PDFVidho TomodachiBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Attribute Genetic InversionDokumen1 halamanSeismic Attribute Genetic Inversionanima1982Belum ada peringkat
- Petrel TIPS&TRICKS From SCM: Importing Well Completion DataDokumen22 halamanPetrel TIPS&TRICKS From SCM: Importing Well Completion DataAngy Carolina Taborda VelasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Time DepthDokumen4 halamanTime DepthHcene HcenBelum ada peringkat
- Depth Conversion of Post Stack Seismic Migrated Horizon Map MigrationDokumen11 halamanDepth Conversion of Post Stack Seismic Migrated Horizon Map MigrationhimanshugstBelum ada peringkat
- Petrel Volume AttributeDokumen1 halamanPetrel Volume AttributeM Fauzan Murtadho100% (1)
- LC-2 - Intro. To Seismic InterpretationDokumen56 halamanLC-2 - Intro. To Seismic InterpretationWan SyahrulBelum ada peringkat
- Polarity of Seismic DataDokumen9 halamanPolarity of Seismic Databt2014Belum ada peringkat
- 04 - Initial Data Analysis - 2010Dokumen9 halaman04 - Initial Data Analysis - 2010Marcelo Saez100% (1)
- Well Logs and Rock Physics in Seismic Reservoir CharacterizationDokumen7 halamanWell Logs and Rock Physics in Seismic Reservoir CharacterizationRaghav Kiran100% (1)
- Shortcut Keys in PetrelDokumen7 halamanShortcut Keys in PetrelTanaskumarKanesanBelum ada peringkat
- M8-2 - Train The Estimation ModelDokumen10 halamanM8-2 - Train The Estimation ModelJuan MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Detecting Faults and Fractures Using Spectral DecompositionDokumen2 halamanDetecting Faults and Fractures Using Spectral Decompositionanima1982Belum ada peringkat
- Seismic Reflection Data: What It Is, How It Can Be Used, & An Application at Elk Hills, CADokumen25 halamanSeismic Reflection Data: What It Is, How It Can Be Used, & An Application at Elk Hills, CAvishnurajBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Time 2 DepthDokumen11 halamanBasic Time 2 DepthAh Long100% (1)
- LAB BOOK (Seismic Imaging and Modelling) Paul Ssali 17390138 Submitted PDFDokumen328 halamanLAB BOOK (Seismic Imaging and Modelling) Paul Ssali 17390138 Submitted PDFJill DagreatBelum ada peringkat
- Deepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsDari EverandDeepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsJon R. RotzienBelum ada peringkat
- Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksDari EverandGeology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksBelum ada peringkat
- Advances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsDari EverandAdvances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsShuvajit BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993Dari EverandModeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993Belum ada peringkat
- Seismic Exploration of Hydrocarbons in Heterogeneous Reservoirs: New Theories, Methods and ApplicationsDari EverandSeismic Exploration of Hydrocarbons in Heterogeneous Reservoirs: New Theories, Methods and ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- ITB IFP Dual Master 2015 Application - Motivation FormDokumen6 halamanITB IFP Dual Master 2015 Application - Motivation Formbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- F029Dokumen5 halamanF029bella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- NDX ZuoDokumen28 halamanNDX Zuobella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Stratimagic 2015Dokumen6 halamanStratimagic 2015bella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation A.braathen Sinai Basement ReservoirsDokumen27 halamanPresentation A.braathen Sinai Basement Reservoirsbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Academic Transcript (In English)Dokumen2 halamanAcademic Transcript (In English)bella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Nautilus Full Course List: Nautilus Is Part of The RPS GroupDokumen23 halamanNautilus Full Course List: Nautilus Is Part of The RPS Groupbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Stratimagic 2015Dokumen6 halamanStratimagic 2015bella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Opendtect Seismic Lab IDokumen6 halamanOpendtect Seismic Lab IParth ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 - Geometrical Property ModelingDokumen5 halamanChapter 14 - Geometrical Property Modelingbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- MATLAB Curve FittingDokumen3 halamanMATLAB Curve FittingredpoptartBelum ada peringkat
- Shale Gas Reservoir Characterization WorkflowsDokumen5 halamanShale Gas Reservoir Characterization Workflowsbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- CGGV 0000007821Dokumen4 halamanCGGV 0000007821bella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Attributes - A Historical PerspectiveDokumen71 halamanSeismic Attributes - A Historical PerspectivePhạm Lê Huy KhánhBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 07 - Fault DataDokumen8 halamanChapter 07 - Fault Databella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - Fault ModelingDokumen52 halamanChapter 11 - Fault Modelingbella_ds100% (1)
- Chapter 08 - IsochoreDokumen3 halamanChapter 08 - Isochorebella_ds0% (1)
- Chapter 07 - Fault DataDokumen8 halamanChapter 07 - Fault Databella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Aapg08 Chimney PosterDokumen6 halamanAapg08 Chimney Posterbella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 - Well CorrelationDokumen33 halamanChapter 10 - Well Correlationbella_ds50% (2)
- Chapter 05 - 3D Seismic DataDokumen8 halamanChapter 05 - 3D Seismic Databella_dsBelum ada peringkat
- Petrel 2011 - Data ImportDokumen41 halamanPetrel 2011 - Data ImportBangsawan Arief100% (1)
- Chapter 03 - Data SetDokumen8 halamanChapter 03 - Data Setbella_ds100% (1)
- Chapter 1 PetrelDokumen5 halamanChapter 1 PetrelmydealiaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Front Desk Receptionist ResumeDokumen5 halamanSample Front Desk Receptionist ResumeReyvie FabroBelum ada peringkat
- SMAW Product DevelopmentDokumen9 halamanSMAW Product Developmenttibo bursioBelum ada peringkat
- Direct Shear TestDokumen10 halamanDirect Shear TestRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikBelum ada peringkat
- All Projects Should Be Typed On A4 SheetsDokumen3 halamanAll Projects Should Be Typed On A4 SheetsNikita AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Distribution: X e X FDokumen30 halamanNormal Distribution: X e X FNilesh DhakeBelum ada peringkat
- Dryer User ManualDokumen118 halamanDryer User ManualAyman Alhassny100% (1)
- Cronograma Ingles I v2Dokumen1 halamanCronograma Ingles I v2Ariana GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Determinants of Consumer BehaviourDokumen16 halamanDeterminants of Consumer BehaviouritistysondogBelum ada peringkat
- UTS - Comparative Literature - Indah Savitri - S1 Sastra Inggris - 101201001Dokumen6 halamanUTS - Comparative Literature - Indah Savitri - S1 Sastra Inggris - 101201001indahcantik1904Belum ada peringkat
- HandoverDokumen23 halamanHandoveryekoyesewBelum ada peringkat
- Sta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Dokumen1 halamanSta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Mira VeranoBelum ada peringkat
- Validated UHPLC-MS - MS Method For Quantification of Doxycycline in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm PatientsDokumen14 halamanValidated UHPLC-MS - MS Method For Quantification of Doxycycline in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm PatientsAkhmad ArdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Masala Kitchen Menus: Chowpatty ChatDokumen6 halamanMasala Kitchen Menus: Chowpatty ChatAlex ShparberBelum ada peringkat
- Assalamu'alaikum WR WB.: Emcee Script (1) Pre - AnnouncementDokumen3 halamanAssalamu'alaikum WR WB.: Emcee Script (1) Pre - AnnouncementGian AlfaBelum ada peringkat
- Reducing Healthcare Workers' InjuriesDokumen24 halamanReducing Healthcare Workers' InjuriesAnaBelum ada peringkat
- Compiler Design Lab ManualDokumen24 halamanCompiler Design Lab ManualAbhi Kamate29% (7)
- Us Aers Roadmap Noncontrolling Interest 2019 PDFDokumen194 halamanUs Aers Roadmap Noncontrolling Interest 2019 PDFUlii PntBelum ada peringkat
- Ocimum Species Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological ImportanceDokumen13 halamanOcimum Species Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological ImportanceManika ManikaBelum ada peringkat
- Hitachi Loader Lx70 Lx80 Service Manual KM 111 00yyy FTT HDokumen22 halamanHitachi Loader Lx70 Lx80 Service Manual KM 111 00yyy FTT Hmarymurphy140886wdi100% (103)
- Paige AMCA Silencer PaperDokumen8 halamanPaige AMCA Silencer Paperapop1971Belum ada peringkat
- English Vocabulary For MedicineDokumen5 halamanEnglish Vocabulary For MedicineDentistryuv 2020100% (1)
- Influence of Contours On ArchitectureDokumen68 halamanInfluence of Contours On Architecture蘇蘇Belum ada peringkat
- ML Performance Improvement CheatsheetDokumen11 halamanML Performance Improvement Cheatsheetrahulsukhija100% (1)
- Review Unit 10 Test CHP 17Dokumen13 halamanReview Unit 10 Test CHP 17TechnoKittyKittyBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6. TNCTDokumen32 halamanLesson 6. TNCTEsther EdaniolBelum ada peringkat
- Court Testimony-WpsDokumen3 halamanCourt Testimony-WpsCrisanto HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CV Jan 2015 SDokumen4 halamanCV Jan 2015 Sapi-276142935Belum ada peringkat