EXata
Diunggah oleh
Praveen SinghJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EXata
Diunggah oleh
Praveen SinghHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EXata specifications
Sl. No
Features
EXata allows users to set up, develop, and run custom network models. It provides feature rich visual
development environment, thereby allowing users to set up models quickly, efficiently code
protocols, and then run models that present real-time statistics and help packet-level debugging
insight.
Special extensions to connect with real systems
Emulation quality protocols
Internet Gateway
Connection Manager
Packet sniffer & SNMP support
Universal Protocol Adaptor (UPA) is embedded in EXata which enable users to run multiple real
applications on a single computer and assign each to run on a different emulated node in EXata.
EXata provides Hardware in Loop, Software in Loop and Human in Loop operations.
EXata supports variety of applications such as Internet Browsers, Tactical Communications, Situational
Awareness Information, Sensor Data, Instant Messengers, VOIP, Streaming Videos and Multi Player
Games.
EXata provides support for modeling a large variety of networks, including WANs, LANs, PANs and
abstract satellite networks.
10
EXata supports scalability in terms of accurate representation of network with ultra-fidelity of nodes
from 50 to 50,000.
EXata is able to seamlessly interface with Semi-Automated Forces (SAF) or Computer Generated
Forces (CGF) via HLA or DIS. SAFs provide a rich environment to represent a full range of operations,
systems and control processes from entity up to brigade level. Using a standard interface like HLS/DIS,
further it also serve as the communication effects server for SAF providing realistic communications.
EXata facilitates to conduct training and operations with next generation tactical networks and
devices that are being designed.
EXata helps to connect to multiple real applications and devices with a large, realistic virtual network.
11
EXata supports all IPv4 devices to interface.
12
EXata supports wireless models including SNR interference, path loss, terrain, modulation, mobility
and antennas allow modeling of highly detailed phenomena such as the banking of the airplane and
how it affects on-board routers.
EXata is platform independent. It runs on Windows, Linux, Unix and Mac OS X
13
www.ncs-in.com
Sl. No
Libraries in EXata
Specifications / Features
Base Libraries
Developer Library
Wireless Library
MAC layer models 802.3 , Abstract Link MAC, Abstract
Satellite Model, ARP, LLC
2. Network Layer Models ICMP, ICMPv6, IGMP, DualIP, IPSec,
IPv4, IPv6, Neighbor Discovery Protocol
3. Unicast Routing Protocol Models Bellman- Ford, RIPng, RIPv2,
Static and Default Routes
4. Multicast Routing Protocols Static and Default routes
5. Transport Layer Models Abstract TCP, TCP, UDP
6. Application Layer Models CBR, FTP, FTP/Generic, HTTP, MCBR,
TELNET, Traffic-Gen, Traffic-Trace, VBR
7. Multi Layer Models ATM
1. Propagation Models
1. Shadowing Model
1. Constant
2. Lognormal
2. Fading Models
1. Fast Rayleigh
2. Rayleigh
3. Ricean
3. Path-loss Models
1. Free Space
2. ITM
3. Two-Ray
4. Path-loss Matrix Model
2. Microwave Links
3. Antenna Models Omni directional, Patterned, Steerable and
switched beam
4. Physical Layer Models IEEE 802.11 a/g, IEEE 802.11b, Abstract
PHY, BER and SNR Reception Model, Radio Energy and Battery
Models
5. MAC Layer Models IEEE 802.11, 802.11e, 802.11s, Aloha MAC,
CSMA, Generic MAC, MACA, TDMA
6. Network Layer Models Mobile IPv4
7. Unicast Routing Protocols AODV, BRP, DYMO, DSR, Fish-eye,
IARP, IERP, LANMAR, LAR, OLSR-INRIA, OLSRv2, STAR, ZRP
8. Multicast Routing Protocol ODMRP
9. Mobility Models Random Waypoint, File based, Pedestrian
10. Terrain Models Cartesian terrain, DEM terrain format, DTED
terrain format, ESRI Shape-file terrain format, Urban terrain data
format
11. Weather Pattern Model
1.
www.ncs-in.com
Multi Media and Enterprise
1.
Mac Layer Model Detailed Switch Model, Switched Ethernet,
Virtual LAN (VLAN)
2.
Uni-Cast Routing Protocol Models Border Gateway Protocol
version 4 (BGPv4), Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
(EIGRP), Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), Open Shortest
Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) Routing Protocol, Open Shortest
Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) Routing Protocol
3.
Multicast Routing Protocol Models Distance Vector Multicast
Routing Protocol (DVMRP), Multicast Extensions to OSPF
(MOSPF), Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Protocol: Dense
and Sparse Modes
4.
Router Configuration Models Hot Standby Router Protocol
(HSRP), Policy-Based Routing (PBR), Route Maps, Route
Redistribution, Router Access Lists, Router Model
5.
QoS (Quality of Service) Models Differentiated Services
(DiffServ), Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS), Quality of
Service Extensions to OSPF (QOSPF)
6.
Multimedia Applications H323 and H225 Protocols, Real-time
Transport Protocol (RTP), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Voice
over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Add-on Libraries
1.
Satellite Library
Specifications:
PHY Layer : Satellite RSV Model and SATTSM PHY Model
MAC Layer : ANESAT Model
Features:
Different beam signatures from a cellular-style reuse (spot-beam)
to global multicast (potato or CONUS beam).
Advanced MAC simulation of multiple uplinks (return channels)
per downlink (forward channel).
Advanced modulation techniques and forward error correction
simulation.
Adaptive modulation techniques on the forward and reverse
directions of the satellite to adapt to dynamic transmission
conditions.
Quality of service and traffic conditioning to ensure fairness to all
users.
Satellite count limited only by available memory.
Support for advanced media access and resource allocation
algorithms for packet scheduling.
2.
Advanced Wireless Library
Models
1. MAC Layer Model->802.16 MAC and 802.16e MAC
2.PHY Layer Model->802.16 PHY
MAC Layer Features1. Point to Multi-Point (PMP) mode
2. Time Division Duplex (TDD) mode
3. Network entry and initialization
4. Dynamic flow management including service flow addition,
deletion and change
5. Bandwidth management
6. Scheduling service at the base station
7. MAC frame construction
8. Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC)
9. Convergence Sub layer
www.ncs-in.com
10. IEEE 802.16e Mobility Support
11. Interface other networks such as ATM, 802.3, 802.11 at network
layer.
12. Support 802.16 OFDMA PHY.
13. Simple admission control.
14. ARQ.
PHY Layer Features1. OFDMA physical model.
2. Variety channel bandwidth support.
3. Multiple FFT size support.
4. Multiple cyclic prefix time support.
5. Multiple data rates support.
6. BER-based reception quality estimation.
7. Sub channel SINR representation.
3.
4.
Sensor Network Model Library
Network Security Model Library
8. Data rate and transmission range estimation.
Models
1. MAC Layer Model-> ZigBee MAC Model
2. PHY Layer Model-> ZigBee PHY Model
MAC Layer Features1.
Generating network beacons if the device is a coordinator
2.
Synchronizing to network beacons
3.
Supporting PAN association and disassociation
4.
Employing the CSMA-CA mechanism for channel access
5.
Direct and indirect data transmission
6.
Providing a reliable link between two peer MAC entities
7. SSCS features, i.e., starting/stopping devices
PHY Layer Features1. 800, 900, and 2400 MHz multiple frequency bands support.
2. Multiple combinations of modulation schemes and spread
spectrum support.
3. BER based reception quality estimation.
4. Energy detection.
5. Link quality indication.
6. Clear channel assessment
Models :
1. MAC Layer Model WEP and CCMP Model
2. Network Layer Models Secure Neighbor Model, ISAKMP
Model, Certificate Model.
3. Routing Protocol Model ANODR Model
4. Multi Layer Model Adversary Model
MAC Layer Features :
1. Generic WEP and CCMP encryption/decryption
2. Crypto Latency
Routing Protocol Features-
1. On-demand routing
2. Network layer identity-free control flow and data flow
3. Anonymous virtual circuit establishment and maintenance (in
routing table)
Multi-Layer Protocol Features1.
Wormhole network protocols including wormhole tunneling
MAC as a contending bus, wormhole replaying MAC in an
aggressive CSMA, queuing delays, transmission delays,
propagation delays, prevention of infinite tunneling (i.e., do not
tunnel wormhole-replayed packets, which have already been
www.ncs-in.com
tunneled for at least once)
2.
Eavesdropping records (output as file contents
5.
Urban Propagation Model Library
Propagation Models1. Automatic Model Selection
2. COST 231-Hata Propagation Model
3. COST 231-Walfish-Ikegami (COST-WI) Propagation Mode
4. Okumura-Hata Propagation Model
5. Street Microcell Propagation Model
6. Street Mobile-to-mobile Propagation Model
7. Suburban Propagation Model
6.
TIREM Advanced Propagation
Model Library
UMTS Library
Propagation Models1. TIREM
Models1. Application Layer Model-> Packet Service Application
2. Multi-Layer Model->UMTS
Application Layer Features
1. Phone Call Traffic Generator
2. CBR and VBR models can be used to simulate conversational and
streaming applications
Multi-Layer Features1. General Features1. UMTS FDD (Frequency Division Duplex)
2. UE, Node B, RNC, SGSN, GGSN, and HLR node types
3. Support for four QoS classes: Background, Interactive, Streaming,
and Conversational
4. Open source admission control
2. Supported Physical Layer Features1. WCDMA PHY
2. Cell search
3. Radio link monitoring and measurement
4. Closed-loop power control
3. Supported Layer 2 Features-
7.
MAC Sub layer of Layer 2
1.
Mapping between logical channels and transport channels
2.
Selection of appropriate transport format for each transport
channel depending on traffic rate
3.
Identification of UEs on common transport channels
4.
Multiplexing/demultiplexing of upper layer PDUs into/from
transport blocks delivered to/from the physical layer on common
transport channels
5.
Multiplexing/demultiplexing of upper layer PDUs into/from
transport blocks delivered to/from the physical layer on dedicated
transport channels
6.
Access service class selection for RACH transmission
RLC Sub layer of Layer 2
1. TM transmission
1.No discard configuration for SDU discard
Function
2.Segmentation and reassembly
2. UM transmission
1. No discard configuration for SDU discard
Function
2. Segmentation, padding, and reassembly
5
www.ncs-in.com
3. Add/remove RLC header (sequence
Number and length indicator)
3. AM transmission
1. Segmentation, padding, and reassembly
2. Add/remove RLC header (sequence
number, length indicator, D/T bit, P bit,
PDU type, SUFI)
3. LAST_PDU triggered polling function
4. STATUS PDU transmission function
4.
Implemented Layer 3 Features-
Connection Management (CM)
1. Call Control (CC)
1. Call establishment for normal calls
2. Call maintenance
3. Call termination
2. Session Management (SM)
1. PDP context activation
2. PDP context deactivation
Mobility Management (MM) and GPRS Mobility Management (GMM)
1.
VLR and HLR
2.
GPRS attach
3.
IMSI attach
4.
MM connection management
5.
GMM connection management
6.
Combined routing area update and location update
Radio Resource Control (RRC)
1.
Initial cell selection and cell reselection
2.
Broadcast of system information blocks (complete combination
type only)
3.
Establishment, maintenance, and release of the RRC connection
4.
Establishment and release of radio bearers
5.
Assignment and release of radio resources
6.
RRC connection mobility functions
7.
UE measurement reporting and control of reporting
8.
Paging
Handovers
1.
Soft handover (break after handover)
2.
Intra-SGSN handover
3.
Inter-SGSN handover
GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) Features
1.
GTP header format
2.
GTP tunnel establishment
3.
GTP-U control and data service
High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) Features
1.
HS-DSCH channel with the following characteristics: 2 ms TTI, SF
=16, QPSK/QAM 16 modulation, transport block size derivation
www.ncs-in.com
8.
Cellular Model Library
2.
HS-SCCH with transport format information transmission
3.
HS-DPCCH with transmission of CQI
4.
Queue distribution in UTRAN MAC-hs
5.
Scheduling/priority handling in UTRAN MAC-hs
6.
Reordering function
7. Disassembly function
Models1. Abstract Cellular
2. GSM
3. User Behavior
Features For Abstract Model1. Support 900 MHz or 1800 MHz band at MSs and BSs
2.
Support various types of traffic
3.
Different fidelity for control and traffic channel
4.
Dynamic channel assignment and release
1. Channel Request on demand
2. Channel allocation/release
5.
Call admission control
6.
Handover
1.
2.
3.
4.
7.
Intra-cell HO
Inter-cell intra SC HO
Inter-cell Inter SC HO
Attach/cell selection and reselection
Location update
1. Periodic type
2. Attach type
8.
Location updating
9.
Call setup and tear down
1. Voice call setup
2. Voice call tear down
3. PDP context activation
10. PDP context deactivation
11. Threshold based Call admission control
12. VLR/HLR operations
1. Insert, delete, update Records
2. Look up records
3. VLR and HLR interaction
13. Update/Cancel Location - Normal type Supported Features For GSM
Model1. The configuration allowed is: one MSC, multiple Base Stations and
multiple Mobile Stations.
2.
Primary (900 MHz) band MSs and BSs, i.e. standard band is only
supported.
3.
Cell selection and reselection.
4.
Dynamic channel assignment and release.
5.
Location update.
6. Call setup and tear down (TCH/F).
7. Handover (Intra-MSC and inter-cell/BS).
14. Supported Features For User Behavior Model1. User attributes referenced by various models: sex, age, and
7
www.ncs-in.com
9.
Standard Interface Library
2.
3.
position
Configuring user attributes using profiles
User attributes for specifying traffic patterns
4.
Random assignment of traffic destination
5.
User calling, re-call and termination patterns
6.
7.
Distinction of area-of-interest and out-of-area users
Calculation of network service perception
Models:
1. High Level Architecture (HLA) Interface
2. Distributed Interactive Simulation (DIS) Interface
www.ncs-in.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyDari EverandMobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- eDXC RTB v4 MDokumen115 halamaneDXC RTB v4 Mamhtet100% (1)
- Ieee 802.11ac Wlan Simulation in MatlabDokumen6 halamanIeee 802.11ac Wlan Simulation in MatlabYAAKOV SOLOMONBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Aironet 1850 Series Access Points Data SheetDokumen28 halamanCisco Aironet 1850 Series Access Points Data SheetJoannaBelum ada peringkat
- OMNeTpp User ManualDokumen283 halamanOMNeTpp User ManualAnto PadaunanBelum ada peringkat
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsDari EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Sip PPT - (Topic SSL) .Dokumen21 halamanSip PPT - (Topic SSL) .Aayush JainBelum ada peringkat
- Sipxecs Enterprise Communications SystemDokumen7 halamanSipxecs Enterprise Communications SystemKurosaki AmirBelum ada peringkat
- VPN RSVPDokumen24 halamanVPN RSVPletiendung_dtvt7119Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Wireless Module 1 AnswersDokumen4 halamanFundamentals of Wireless Module 1 AnswersAsh_38100% (1)
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeDari EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 3 - Nse 2 v3 OkDokumen2 halamanQuiz 3 - Nse 2 v3 OkJohn Angelo Recalde MonarBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA (200-301) Certification Practice Exam Answers (ENSA v7.0)Dokumen54 halamanCCNA (200-301) Certification Practice Exam Answers (ENSA v7.0)samiBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On 802.11acDokumen88 halamanPresentation On 802.11acokhtayBelum ada peringkat
- Aastra 400 Communication ServersDokumen4 halamanAastra 400 Communication ServersNguyen Phu LocBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise OFDM 1 PDFDokumen33 halamanExercise OFDM 1 PDFAbdelhakim KhlifiBelum ada peringkat
- TP CCNP Sisas 8021xDokumen3 halamanTP CCNP Sisas 8021xATTIVIBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen21 halamanModule 1Shamna100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Lab - Preparing The Switch: TopologyDokumen9 halamanChapter 1 Lab - Preparing The Switch: TopologyHollman JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- KPI Parameters NotesDokumen3 halamanKPI Parameters Notesqudratullah ehsanBelum ada peringkat
- SS-7 System - TelephonyDokumen25 halamanSS-7 System - TelephonyvarunBelum ada peringkat
- Voice Over Ip (Voip) : by Kiran Kumar Devaram Varsha Mahadevan Shashidhar RampallyDokumen37 halamanVoice Over Ip (Voip) : by Kiran Kumar Devaram Varsha Mahadevan Shashidhar RampallysourabhchoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- D-Link DWL-3200AP Manual GuideDokumen83 halamanD-Link DWL-3200AP Manual GuideblogadderBelum ada peringkat
- Senior Report LTE MDokumen38 halamanSenior Report LTE MPhương Linh TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Network PresentationDokumen27 halamanGSM Network Presentationpolrb52Belum ada peringkat
- Dielectric Constant and Loss TangentDokumen3 halamanDielectric Constant and Loss TangentYaz AbueitaBelum ada peringkat
- 00 OverviewDokumen79 halaman00 OverviewMallesh C. BalamattiBelum ada peringkat
- ClearwaterDokumen187 halamanClearwaterAmadou Tidiane DialloBelum ada peringkat
- Asterisk Development Guide PDFDokumen1.055 halamanAsterisk Development Guide PDFJe RelBelum ada peringkat
- CMS v8.2 DS 1-0-0Dokumen2 halamanCMS v8.2 DS 1-0-0CarlosAlbertoBianchiPeredoBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Concept of Wireless Telecommunication:: 1.1.1 Mobile Communication ObjectivesDokumen77 halaman1.1 Concept of Wireless Telecommunication:: 1.1.1 Mobile Communication ObjectivesmgitecetechBelum ada peringkat
- Learning WebRTC - Sample ChapterDokumen34 halamanLearning WebRTC - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- Omnet TutorialDokumen63 halamanOmnet TutorialaditiBelum ada peringkat
- 13 International RoamingDokumen10 halaman13 International RoamingMahesh Kumar NigamBelum ada peringkat
- Zenoss Core PresentationDokumen11 halamanZenoss Core PresentationSanthosh Salem100% (1)
- RL532A DatasheetDokumen2 halamanRL532A DatasheetMOHSIN RAZABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter6-SNMP-V3 - V2 - V1 Network ManagementDokumen21 halamanChapter6-SNMP-V3 - V2 - V1 Network Management94akuBelum ada peringkat
- Border Gateway ProtocolDokumen2 halamanBorder Gateway ProtocolBiswajit MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Viewer - Module 2 Exam - CCNA 1 French (Version 3.1)Dokumen9 halamanExam Viewer - Module 2 Exam - CCNA 1 French (Version 3.1)SAGALOGBelum ada peringkat
- IPv6 Foundations v2016Dokumen285 halamanIPv6 Foundations v2016ananthluckyBelum ada peringkat
- Atoll 332 Administrator ManualDokumen266 halamanAtoll 332 Administrator Manualben fradj hajerBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages of FirewallDokumen16 halamanAdvantages of FirewallBridget Smith69% (13)
- Wireless Simulation Vanet TCLDokumen5 halamanWireless Simulation Vanet TCLalione100% (1)
- Bts3900 GSM HuaweiDokumen5 halamanBts3900 GSM HuaweiTouta MedBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 SRI - Reseaux - CorrigéDokumen7 halaman2014 SRI - Reseaux - CorrigéMohammed HamdaouiBelum ada peringkat
- IPVoIPconfigDokumen4 halamanIPVoIPconfigCarlos BosmedianoBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual Networking ConceptsDokumen12 halamanVirtual Networking ConceptsShahid Mahmud100% (4)
- CCNA Discovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final ExamDokumen17 halamanCCNA Discovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final ExamJesusforgivemeBelum ada peringkat
- NS2Dokumen8 halamanNS2Nipurba KonarBelum ada peringkat
- DTMF Using FPGADokumen16 halamanDTMF Using FPGATejas DharaniBelum ada peringkat
- Codan Envoy HF Smart Radio EN2Dokumen3 halamanCodan Envoy HF Smart Radio EN2dot16eBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-5-Self Configuration and AutoconfigurationDokumen17 halamanUnit-5-Self Configuration and AutoconfigurationSwati0% (1)
- Stand Alone AP Flash File System FailDokumen3 halamanStand Alone AP Flash File System FailSriram BhupathirajuBelum ada peringkat
- Routeurs Cisco, Mise en Œuvre de BGP: 1) Introduction Au Protocole BGPDokumen2 halamanRouteurs Cisco, Mise en Œuvre de BGP: 1) Introduction Au Protocole BGPAnonymous k2SY4zdI3Belum ada peringkat
- Torrent Downloaded FromDokumen1 halamanTorrent Downloaded FromPraveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
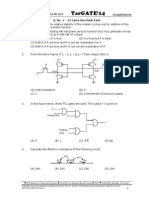
- Targate'14: Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark EachDokumen15 halamanTargate'14: Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark EachPraveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Form of Authority No DuesDokumen1 halamanForm of Authority No DuesPraveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokumen15 halaman6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- L5 2dtransDokumen21 halamanL5 2dtransMidhun ChakravarthyBelum ada peringkat
- First Year B.Tech Course Book (2013-14Dokumen21 halamanFirst Year B.Tech Course Book (2013-14Praveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Noise FigureDokumen22 halamanUnderstanding Noise FigureNameBelum ada peringkat
- Aumtomatic Number Plate RecognitionDokumen15 halamanAumtomatic Number Plate RecognitionSoujanya ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- DWTDokumen2 halamanDWTPraveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CH 19Dokumen68 halamanCH 19Praveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Mock Cat QuestionsDokumen13 halamanMock Cat QuestionsKavindra Singh UmathBelum ada peringkat
- PDE Assingment 2 (2013)Dokumen1 halamanPDE Assingment 2 (2013)Praveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Satellite CommunicationsDokumen14 halamanSatellite CommunicationsNicole ButlerBelum ada peringkat
- Advertisement - Teaching Posts - 05-07-2011Dokumen24 halamanAdvertisement - Teaching Posts - 05-07-2011Praveen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Madagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerDokumen2 halamanMadagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerfranciscogarridoBelum ada peringkat
- SWSP6033 00 2022T3 V1.0-1Dokumen14 halamanSWSP6033 00 2022T3 V1.0-1ayman.abaidallah1990Belum ada peringkat
- Car Loan ProposalDokumen6 halamanCar Loan ProposalRolly Acuna100% (3)
- TIA Portal v11 - HMI ConnectionDokumen4 halamanTIA Portal v11 - HMI ConnectionasdasdasdasdasdasdasadaBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisDokumen21 halamanApplication of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisAdrian NavarraBelum ada peringkat
- Student Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan TemplateDokumen7 halamanStudent Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan Templateapi-3531253350% (1)
- Lecture 9-EVENT BUDGETDokumen19 halamanLecture 9-EVENT BUDGETAlbina AbilkairBelum ada peringkat
- Residential Water Piping Installation GuideDokumen28 halamanResidential Water Piping Installation GuideMunir RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- FeistGorman - 1998-Psychology of Science-Integration of A Nascent Discipline - 2Dokumen45 halamanFeistGorman - 1998-Psychology of Science-Integration of A Nascent Discipline - 2Josué SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Certificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Dokumen2 halamanCertificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Jojo Aboyme CorcillesBelum ada peringkat
- Flotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedDokumen1 halamanFlotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedLuis GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Kerala Dinesh Beedi - WikipediaDokumen12 halamanKerala Dinesh Beedi - Wikipediaaymanamna2016Belum ada peringkat
- Brinker Insider Trading SuitDokumen5 halamanBrinker Insider Trading SuitDallasObserverBelum ada peringkat
- Metatron AustraliaDokumen11 halamanMetatron AustraliaMetatron AustraliaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper 1 Eng Lang StudiesDokumen4 halamanResearch Paper 1 Eng Lang Studiessastra damarBelum ada peringkat
- Life Stories and Travel UnitDokumen3 halamanLife Stories and Travel UnitSamuel MatsinheBelum ada peringkat
- Restructuring ScenariosDokumen57 halamanRestructuring ScenariosEmir KarabegovićBelum ada peringkat
- The Experience of God Being Consciousness BlissDokumen376 halamanThe Experience of God Being Consciousness BlissVivian Hyppolito100% (6)
- 4 5895601813654079927 PDFDokumen249 halaman4 5895601813654079927 PDFqabsBelum ada peringkat
- Remnan TIIDokumen68 halamanRemnan TIIJOSE MIGUEL SARABIABelum ada peringkat
- Swot AnalysisDokumen6 halamanSwot AnalysisSneha SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Dokumen4 halamanUnit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Kinga WojtasBelum ada peringkat
- 5.2.1 1539323575 2163Dokumen30 halaman5.2.1 1539323575 2163Brinda TBelum ada peringkat
- Sagnik CVDokumen3 halamanSagnik CVSagnik GangulyBelum ada peringkat
- Preterite vs Imperfect in SpanishDokumen16 halamanPreterite vs Imperfect in SpanishOsa NilefunBelum ada peringkat
- Times Leader 04-10-2013Dokumen37 halamanTimes Leader 04-10-2013The Times LeaderBelum ada peringkat
- V-AMP3: User ManualDokumen19 halamanV-AMP3: User Manualnutmeg_kickerBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 8 - Managing Early Growth of The New VentureDokumen11 halamanTopic 8 - Managing Early Growth of The New VentureMohamad Amirul Azry Chow100% (3)
- StructDokumen2 halamanStructandriessebastianBelum ada peringkat
- Apexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDokumen12 halamanApexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDaniel VelciuBelum ada peringkat
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoDari EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Best Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptDari EverandBest Dives West Hemisphere ExcerptPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptDari EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensDari EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensBelum ada peringkat
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksDari EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksBelum ada peringkat
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptDari EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)