Asme Section V 2010 Visual
Diunggah oleh
mvrengarajan100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
740 tayangan3 halamanASME Section V 2010 Visual
Judul Asli
Asme Section v 2010 Visual
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniASME Section V 2010 Visual
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
740 tayangan3 halamanAsme Section V 2010 Visual
Diunggah oleh
mvrengarajanASME Section V 2010 Visual
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
2010 SECTION V
ARTICLE 9
VISUAL EXAMINATION
1-910 SCOPE
(a) This Article contains methods and requirements for
visual examination applicable when specified by areferene-
ing Code Section. Specific visual examination procedures
required for every type of examination are not included in
this Anicle, because there are many applications where
visual examinations are required. Some examples of these
applications include nondestructive examinations, leak
testing, in-service examinations and fabrication proce-
dures.
(b) The requirements of Amticle 1, General Require-
‘ments, apply when visual examination, in accordance with
Anticle 9, is required by a referencing Code Section.
(c) Definitions of terms for visual examination appear
in Anticle 1, Appendix I — Glossary of Terms in Nonde-
structive Examination, and Article 9, Appendix 1
1920 GENERAL
7-921 Written Procedure Requirements
‘T-921.1 Requirements. Visual examinations shall be
performed in accordance with a written procedure, which
shall, as a minimum, contain the requirements listed in
‘Table T-921, The written procedure shall establish a single
value, or range of values, for each requirement.
21.2 Procedure Qualification. When procedure
qualification is specified by the referencing Code Section,
‘a change of a requirement in Table T-921 identified as an
essential variable shal require requalification ofthe written
procedure by demonstration. A change of a requirement
‘identified as a nonessential variable does not require requal-
ification of the written procedure. All changes of essential
‘or nonessential variables from those specified within the
written procedure shall require revision of, or an addendum
to, the written procedure.
7-921.3 Demonstration. The procedure shall contain
or reference a report of what was used to demonstrate that
the examination procedure was adequate. In general,
fine line 2 in. (0.8 mm) or less in width, an artificial
imperfection or a simulated condition, located on the sur-
face or a similar surface to that to be examined, may be
considered as a method for procedure demonstration. The
167
ARTICLE 9
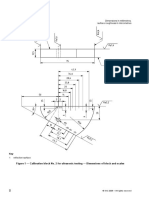
TABLE T-921
REQUIREMENTS OF A VISUAL EXAMINATION
PROCEDURE
Nore
Essential Essential
Requirement (As plicable) Variable __Variable
(Change in tectnlgue sed
Direct too frm translucent x
Direct ta remote x
Remote visual aids x
Personne! performance requirement, x
when eeauled
Lighting intensity (decrease ony) x
Configurations to be examined and base x
material product forme (pp, plat,
forgings, et.)
Lighting eguipment x
Methods or too used for surface x
preparation
Equipment or devices used for a deect x
technique
Sequence of examination x
Personnel qulieations x
condition or artificial imperfection should be in the least
discemable location on the area surface to be examined to
validate the procedure.
7-922 Personnel Requirements
‘The user ofthis Article shall be responsible for assigning
qualified personnel to perform visual examinations to the
requirements of this Article. At the option of the manufac-
turer, he may maintain one certification for each product,
fr several separate signed records based on the area or
type of work, or both combined. Where impractical to use
specialized visual examination personnel, knowledgeable
and trained personnel, having limited qualifications, may
be used to perform specific examinations, and to sign the
report forms. Personnel performing examinations shall be
{qualified in accordance with requirements of the referenc-
ing Code Section
1923
Personnel shall have an annual vision test to assure
natural or corrected near distance acuity such that they are
Physical Requirements
ARTICLE 9
capable of reading standard J-1 letters on standard Jaeger
test type charts for near vision, Equivalent near vision tests
‘are acceptable.
7-930 EQUIPMENT.
Equipment used for visual examination techniques, for
example, direct, remote, or translucent, shall have the capa-
bilities as specified in the procedure. Capabilities include,
but are not limited to viewing, magnifying, identifying,
measuring, and/or recording observations in accordance
With requirements of the referencing Code Section,
7-950
1-981
TECHNIQUE
Applications
Visual examination is generally used to determine such
things as the surface condition of the part, alignment of
mating surfaces, shape, or evidence of leaking. In addition,
visual examination is used to determine a composite materi-
al’s (translucent laminate) subsurface conditions.
7-952 Direet Visual Examination
Direct visual examination may usually be made when
access is sufficient to place the eye within 24 in. (600 mm)
of the surface to be examined and at an angle not less than
30 deg to the surface to be examined, Mirrors may be
used fo improve the angle of vision, and aids such as
‘a magnifying lens may be used to assist examinations.
lumination (natural or supplemental white light) for the
specific part, component, vessel, or section thereof being
examined is required. The minimum light intensity at the
examination surface/site shall be 100 footcandles
(1000 lux). The light source, technique used, and light
level verification is required to be demonstrated one time,
documented, and maintained on file
7-953 Remote Visual Examination
In some cases, remote visual examination may have
to be substituted for direct examination, Remote visual
examination may use visual aids such as mirrors, tele-
scopes, borescopes, fiber optics, cameras, or other suitable
instruments, Such systems shall have a resolution capabil-
ity at least equivalent to that obtainable by direct visual
‘observation.
7-954 Translucent Visual Examination
‘Translucent visual examination is a supplement of direct
visual examination. The method of translucent visual
2010 SECTION v
examination uses the aid of artificial lighting, which can
be contained in an illuminator that produces directional
lighting. The illuminator shall provide light of an intensity
that will illuminate and diffuse the light evenly through
the area or region under examination, The ambient lighting
‘must be so arranged that there are no surface glares or
reflections from the surface under examination and shall
bee less than the light applied through the area or region
under examination. The artificial light source shall have
sufficient intensity to permit “candling” any translucent
laminate thickness variations.
1980 EVALUATION
‘T-980.1 All examinations shall be evaluated in terms of |
the acceptance standards of the referencing Code Section.
T-980.2. An examination checklist shall be used to plan
visual examination and to verify that the requited visual
observations were performed. This checklist establishes
‘minimum examination requirements and does not indicate
the maximum examination which the Manufacturer may
perform in process
7-990 DOCUMENTATION
7-991 Report of Examination
‘T-991.1 A written report of the examination shall con-
tain the following information:
(a) the date of the examination
(b) procedure identification and revision used
(6) technique used
(d) results of the examination
(e) examination personnel identity, and, when required
by the referencing Code Section, qualification level
(P identification of the part or component examined,
T-991.2 Even though dimensions, ete, were recorded
inthe process of visual examination to aid inthe evaluation,
there need not be documentation of each viewing or each
dimensional check. Documentation shal include all obser-
vation and dimensional checks specified by the referencing
Code Section,
7-993 Record Maintenance
Records shall be maintained as required by the referene-
ing Code Section,
2010 SECTION V
ARTICLE 9
ARTICLE 9
MANDATORY APPENDIX
APPENDIX I — GLOSSARY OF
TERMS FOR VISUAL EXAMINATION
1910 SCOPE
‘This Mandatory Appendix is used for the purpose of
establishing standard terms and definitions of terms related
to Visual Examination which appear in Article 9.
1920 GENERAL
(a) Article 30, SE-1316, Section 9, provides the defini-
tion of footcandle (fe).
(b) Definitions of ems for visual examination and other
‘methods appear in Amicle I, Mandatory Appendix I, Glos-
sary of Terms for Nondestructive Examination,
(c) The following Code terms are used in conjunction
with Article 9:
‘artificial flaw: an intentional imperfection placed on the
surface of a material to depict a representative flaw con-
dition.
‘auxiliary lighting: an attifcial light source used as a
visual aid to improve viewing conditions and visual per-
ception.
‘candling: see translucent visual examination.
direct visual examination: a visual examination tech-
nique performed by eye and without any visual aids
169
(excluding light source, mirrors, and /or corrective lenses)
enhanced visual examination: a visual examination tech-
nique using visual aids to improve the viewing capability,
eg., magnifying aids, borescopes, video probes, fiber
optics, ete.
‘ux (Lx): a unit of illumination equal to the direct illumi
nation on a surface that is everywhere one meter from a
uniform point source of one candle intensity or equal 10
‘one lumen per square meter.
remote visual examination: a visual examination tech-
nique used with visual aids for conditions where the area to
bbe examined is inaccessible for direct visual examination.
surface glare: reflections of artificial light that interfere
with visual examination.
translucent laminate: a series of glass reinforced layers,
bonded together, and having capabilites of transmitting
light.
translucent visual examination: a technique using artfi-
cial lighting intensity to permit viewing of translucent lami-
nate thickness variations (also called candling).
visual examination: a nondestructive examination
‘method used to evaluate an item by observation, such as:
the correct assembly, surface conditions, or cleanliness of
‘materials, parts, and components used in the fabrication
and construction of ASME Code vessels and hardware
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ASTM E433 71 (Reapproved 2018)Dokumen5 halamanASTM E433 71 (Reapproved 2018)VICTOR SEGOVIABelum ada peringkat
- VT General QuestionsDokumen6 halamanVT General Questionsgopakumar72100% (1)
- Astm Se 165 PDFDokumen17 halamanAstm Se 165 PDFJorge Luis ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Section V - Asme 2015 Article 1Dokumen26 halamanSection V - Asme 2015 Article 1HassanSoboh50% (4)
- ASME V Art 4 UT PDFDokumen44 halamanASME V Art 4 UT PDFNavanitheeshwaran SivasubramaniyamBelum ada peringkat
- 15.welding Engineering PDFDokumen15 halaman15.welding Engineering PDFEmad A.Ahmad100% (2)
- 15.welding Engineering PDFDokumen15 halaman15.welding Engineering PDFEmad A.Ahmad100% (2)
- MSS SP-112-2010Dokumen9 halamanMSS SP-112-2010Денис ПекшуевBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing, Pipe Fitting, and SewerageDokumen275 halamanPlumbing, Pipe Fitting, and SewerageRob GillespieBelum ada peringkat
- Engineer Manual - Engineer and Design Liquid Process Piping - ReviewDokumen245 halamanEngineer Manual - Engineer and Design Liquid Process Piping - ReviewSyedFAkharAbbas100% (5)
- Welding Handbook ESABDokumen529 halamanWelding Handbook ESABErdinc_Bal_1026100% (8)
- Astm A435 2012 PDFDokumen2 halamanAstm A435 2012 PDFJavier Ricardo Romero Bohorquez33% (3)
- Astm E1065Dokumen21 halamanAstm E1065Jiten KarmakarBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM E 1025-05 Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI)Dokumen7 halamanASTM E 1025-05 Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI)raza.slietBelum ada peringkat
- ASME V Article 7 Magnetic Particle ExaminationDokumen1 halamanASME V Article 7 Magnetic Particle ExaminationAmanda Ariesta Aprilia100% (4)
- ASME V Art 5 UTDokumen24 halamanASME V Art 5 UTMarcelino Navarrete EvaristoBelum ada peringkat
- Asme Sec V Article 9 Visual ExaminationDokumen11 halamanAsme Sec V Article 9 Visual ExaminationRamesh R100% (1)
- Welding SafetyDokumen43 halamanWelding Safetyjefmohd100% (3)
- Welding TechnologyDokumen218 halamanWelding Technologywbl_200789% (9)
- GE Hardness-testing-FAQ MIC 10Dokumen19 halamanGE Hardness-testing-FAQ MIC 10Harshit MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Asme - bpvc.v.2010 - Art 9Dokumen3 halamanAsme - bpvc.v.2010 - Art 9felipefistBelum ada peringkat
- Erection Manual-Pc PipingDokumen219 halamanErection Manual-Pc Pipingalinor_tn100% (2)
- A - Piping Joint HandbookDokumen161 halamanA - Piping Joint HandbookCharles Tauk100% (30)
- A - Piping Joint HandbookDokumen161 halamanA - Piping Joint HandbookCharles Tauk100% (30)
- Welding Science and Technology by MD Ibrahim KhanDokumen289 halamanWelding Science and Technology by MD Ibrahim Khanabidaliabid1Belum ada peringkat
- PCN ISO 9712 NDT Training and Certification Level 1 2 and 3 Course Brochure 2021 BIT Chennai IndiaDokumen17 halamanPCN ISO 9712 NDT Training and Certification Level 1 2 and 3 Course Brochure 2021 BIT Chennai IndiaAMITBelum ada peringkat
- Astm E3024-2019Dokumen19 halamanAstm E3024-2019RICARDO REY100% (2)
- Industrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDari EverandIndustrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- IGS Piping GuideDokumen61 halamanIGS Piping GuidemvrengarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Astm A802Dokumen3 halamanAstm A802Julio Luyo100% (2)
- E 273 - 15Dokumen5 halamanE 273 - 15juan f100% (1)
- AWS A4.2M 2006 Standard Procedures For Calibrating Magnetic Instruments To Measure The Delta Ferrite Content of Austenitic and Duplex Ferritic-Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metal PDFDokumen58 halamanAWS A4.2M 2006 Standard Procedures For Calibrating Magnetic Instruments To Measure The Delta Ferrite Content of Austenitic and Duplex Ferritic-Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metal PDFErik Jhonattan Jara YpanaqueBelum ada peringkat
- EN ISO 7963 - Calibration Block No.2 PDFDokumen1 halamanEN ISO 7963 - Calibration Block No.2 PDFbhavin178Belum ada peringkat
- International StandardDokumen34 halamanInternational StandardHussein Blanco Calvete100% (1)
- ASME SB-444 (2013) - В-444-06 (R11) - eng.Dokumen4 halamanASME SB-444 (2013) - В-444-06 (R11) - eng.TetianaBelum ada peringkat
- BS en 10228 4 2016 Non Destructive Testi PDFDokumen30 halamanBS en 10228 4 2016 Non Destructive Testi PDFDaryna KupriianovaBelum ada peringkat
- Chiller Piping SystemDokumen12 halamanChiller Piping Systemsundarhvac67% (3)
- Chiller Piping SystemDokumen12 halamanChiller Piping Systemsundarhvac67% (3)
- Liquid Penetrant Testing NDT Level2 GulfndeDokumen19 halamanLiquid Penetrant Testing NDT Level2 GulfndeGulfnde IndiaBelum ada peringkat
- NDT Procedure BS EN 10306:2002 (Full Version Available From N-D-T.com)Dokumen6 halamanNDT Procedure BS EN 10306:2002 (Full Version Available From N-D-T.com)Mark BrailsfordBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 9712Dokumen38 halamanIso 9712Igor SeidlBelum ada peringkat
- Exc1 Exc2: BS EN 1090-2:2018Dokumen1 halamanExc1 Exc2: BS EN 1090-2:2018Luka DrascicBelum ada peringkat
- For Calibrating Magnetic Instruments Measure Ferrite Content Austenitic Duplex Ferritic-Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld MetalDokumen31 halamanFor Calibrating Magnetic Instruments Measure Ferrite Content Austenitic Duplex Ferritic-Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metalvricardol100% (1)
- ASME Section VDokumen2 halamanASME Section Vjhoiny55% (11)
- Belgian Standard ISO 10863 2020 EN ISO 10863 2020 NBN EN ISO 10863 2020Dokumen12 halamanBelgian Standard ISO 10863 2020 EN ISO 10863 2020 NBN EN ISO 10863 2020Luong Ho Vu100% (1)
- Welding and Inspection of PipingDokumen20 halamanWelding and Inspection of PipingMohammed Najim89% (9)
- Iqi Wire Type BSEN 462-1 PDFDokumen13 halamanIqi Wire Type BSEN 462-1 PDFThe Normal HeartBelum ada peringkat
- Astm E1220Dokumen6 halamanAstm E1220Gerardo Mediavilla100% (1)
- ISO 3452-2 Non Destructive Testing PenetrantDokumen34 halamanISO 3452-2 Non Destructive Testing PenetrantDemetrioBelum ada peringkat
- Pipe LineDokumen62 halamanPipe LineBahtiar Anak LaNang100% (1)
- Udlp-Tacom Welding Code, Almn (Ansi-Aws d1.2)Dokumen120 halamanUdlp-Tacom Welding Code, Almn (Ansi-Aws d1.2)mtcengineering100% (2)
- EN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshDokumen36 halamanEN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshNiranjan Rajavel TigerBelum ada peringkat
- Astm Se-273Dokumen5 halamanAstm Se-273Deyci Yamile Peña SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Astm e 165 (Liquidos Penetrantes) PDFDokumen20 halamanAstm e 165 (Liquidos Penetrantes) PDFAnonymous eB2AZT3Belum ada peringkat
- API 6A RadiographyDokumen4 halamanAPI 6A RadiographyminakshissawantBelum ada peringkat
- Astm A-833-17Dokumen5 halamanAstm A-833-17Mos Peerapat100% (2)
- En 571-1 - Penetrent TestingDokumen18 halamanEn 571-1 - Penetrent TestingVasilica Barbarasa100% (1)
- DIN en 462-1 Image Quality of Radiographs (Wire Type)Dokumen10 halamanDIN en 462-1 Image Quality of Radiographs (Wire Type)QA QC100% (2)
- JIS Z 2320-1-2007 Non-Destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle Testing - Part 1 General Principles-6 PDFDokumen31 halamanJIS Z 2320-1-2007 Non-Destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle Testing - Part 1 General Principles-6 PDFNguyễn Hữu BằngBelum ada peringkat
- Article 5 Ultrasonic Examination Methods For MaterialsDokumen10 halamanArticle 5 Ultrasonic Examination Methods For Materialsr_ramiresBelum ada peringkat
- Astm E747Dokumen3 halamanAstm E747AmithBelum ada peringkat
- E9018 G Welding ElectrodeDokumen1 halamanE9018 G Welding ElectrodeSai PrasathBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM E746-07 (2014) Standard Practice For Determining Relative Image Quality Response of Industrial Radiographic Imaging SystemsDokumen7 halamanASTM E746-07 (2014) Standard Practice For Determining Relative Image Quality Response of Industrial Radiographic Imaging SystemsnationalfoxBelum ada peringkat
- E125-97 MT Ref PhotosDokumen2 halamanE125-97 MT Ref PhotosveluBelum ada peringkat
- En 462 1 PDFDokumen12 halamanEn 462 1 PDFGabriele67% (3)
- Tc-1a 1975Dokumen11 halamanTc-1a 1975Waron100% (1)
- Table 6.7Dokumen2 halamanTable 6.7AngelTinocoBelum ada peringkat
- Sep 1922 enDokumen7 halamanSep 1922 enIngo Becker100% (2)
- Api 578 Positive Material Identification Pmi PDFDokumen24 halamanApi 578 Positive Material Identification Pmi PDFSANKARAN.KBelum ada peringkat
- Se 273Dokumen4 halamanSe 273solrac4371Belum ada peringkat
- Art 23 AsmeDokumen10 halamanArt 23 AsmeKirvi16Belum ada peringkat
- Codigo ASME (Arrastrado)Dokumen3 halamanCodigo ASME (Arrastrado)Mou RmzBelum ada peringkat
- V+ 5.visual Examination & Leak TestingDokumen4 halamanV+ 5.visual Examination & Leak TestingAMAL VISHNUBelum ada peringkat
- Article 9 Visual Examination: (A) This Article Contains Methods and RequirementsDokumen3 halamanArticle 9 Visual Examination: (A) This Article Contains Methods and RequirementsLorena Grijalba LeónBelum ada peringkat
- Article 9 Visual Examination: Laminate LaminateDokumen3 halamanArticle 9 Visual Examination: Laminate LaminateUMAYRBelum ada peringkat
- Article 9 Visual ExaminationDokumen3 halamanArticle 9 Visual Examinationpriesblack12Belum ada peringkat
- Welding of Ductile Iron: Welding Metallurgy Equipment and Filler MaterialsDokumen2 halamanWelding of Ductile Iron: Welding Metallurgy Equipment and Filler Materialshrk100Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen8 halamanChapter 1Carlos VegaBelum ada peringkat
- Cooling TowersDokumen6 halamanCooling TowersmvrengarajanBelum ada peringkat
- 2009 Welding DefectsDokumen1 halaman2009 Welding DefectsmvrengarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation in Supercritical Boiler Technology - The 750 Mwe Longview Power ProjectDokumen18 halamanInnovation in Supercritical Boiler Technology - The 750 Mwe Longview Power ProjectPradeep SrikanthBelum ada peringkat
- Columns BookDokumen12 halamanColumns BookmvrengarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Pickling of Steel PipesDokumen134 halamanAcid Pickling of Steel PipesMKAMRANBHATTIBelum ada peringkat
- Pipeline InstallationDokumen4 halamanPipeline Installationmego2micBelum ada peringkat
- Bohler Welding GuideDokumen515 halamanBohler Welding GuideGail HoltBelum ada peringkat
- Ut BooksDokumen96 halamanUt BooksmvrengarajanBelum ada peringkat